Planet Earth Climate Test
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
Terestrial Radiation
Radiation that is reemitted by earth.
2
New cards
Climate
The overall weather patterns of an area over a long period of time (30-100 years).
3
New cards
Biome
Large areas characterized by wildlife, vegetation, and soil that have formed in response to a shared physical climate.
4
New cards
Adaptation
Many plants and animals have developed specific features like white fur or shallow roots to survive in harsh conditions.
5
New cards
Climographs
Used to describe climate in locations (average temp is plotted as a line and rainfall by a bar).
6
New cards
Insolation
Incoming solar radiation
7
New cards
4 climate zones
Polar and subpolar, temperate, subtropical, tropical.
8
New cards
Ocean currents
Gain temperature from where they originated and will bring it to other places.
9
New cards
Carbon Cycle
Movement of carbon through different versions of resivours on earth (Atmosphere: Burning fossil fuels: Co2/Geosphere: Creation of fossil fuels: Limestone/Biosphere: Photosynthesis: Co2 to O2/Hydrosphere: Co2 dissolves into water)
10
New cards
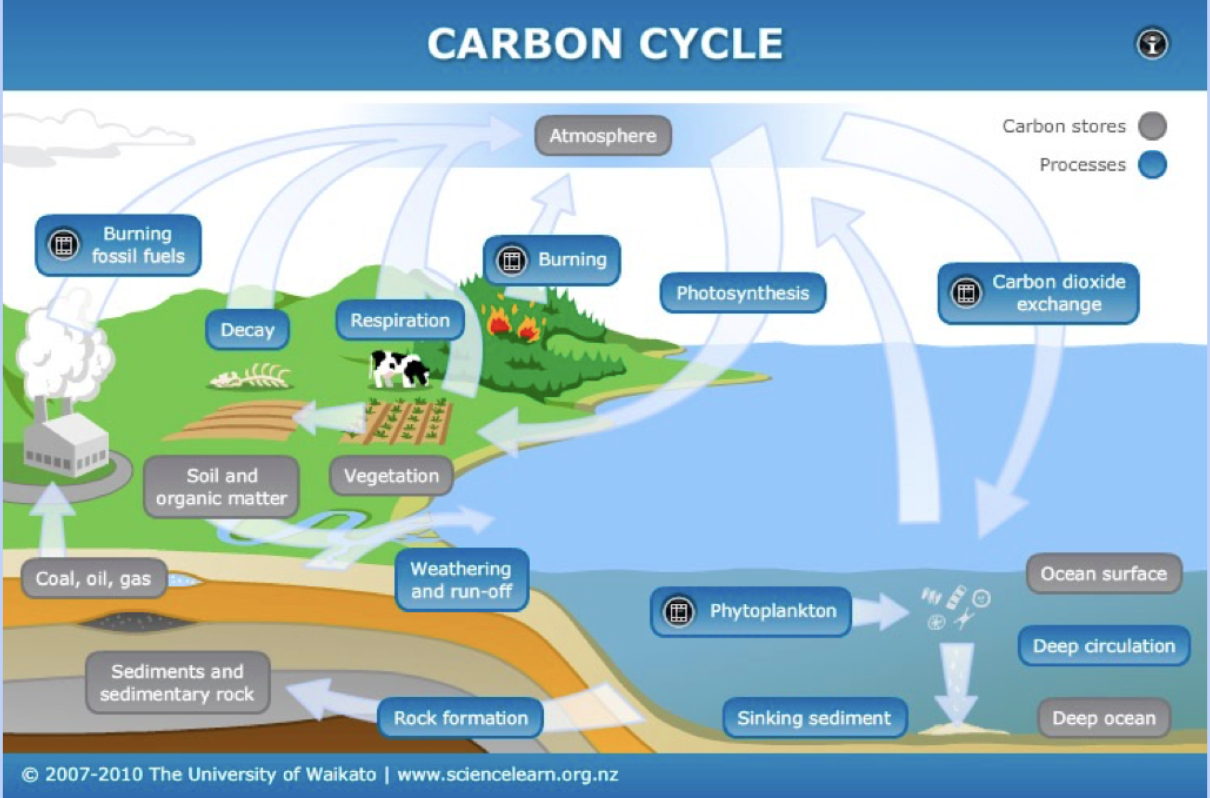
Carbon Cycle
11
New cards
Fossil Fuels
Layers of organic carbon that were compressed by heat and pressure faster than they could decay (Coal, oil , natural gas).
12
New cards
Anthropogenic Carbon
Refers to pollutants originally from human activities (Power plants burning fossil fuels for electricity/Transportation using fossil fuels/Deforestation taking away plants that photosynthesize)
13
New cards
Natural Cycles
Ocean currents, solar variations, volcanic eruptions, orbital variations (24.5%-22.5% tilt every 41,000 years/Orbit change: ecentricity every 100,000 years/Vega, north star precession every 26,000 years)
14
New cards
Ph Scale
1-14 (lower ph means higher acidification)
15
New cards
Ocean Water
absorbs 30% of Co2 and reacts with it to make carbonic acid.
16
New cards
Greenhouse Effect
Co2 and other gases trap heat keeping the earth warm (sunlight reflected back at earth.
17
New cards
Conduction
Transfer of heat from one molecule to the next through molecular collisions.
18
New cards
Convection
Transfer of heat by mass movement or circulation within a substance (therefore the hotter the less dense).
19
New cards
Radiation
Tranfer of heat by electromagnetic waves.
20
New cards
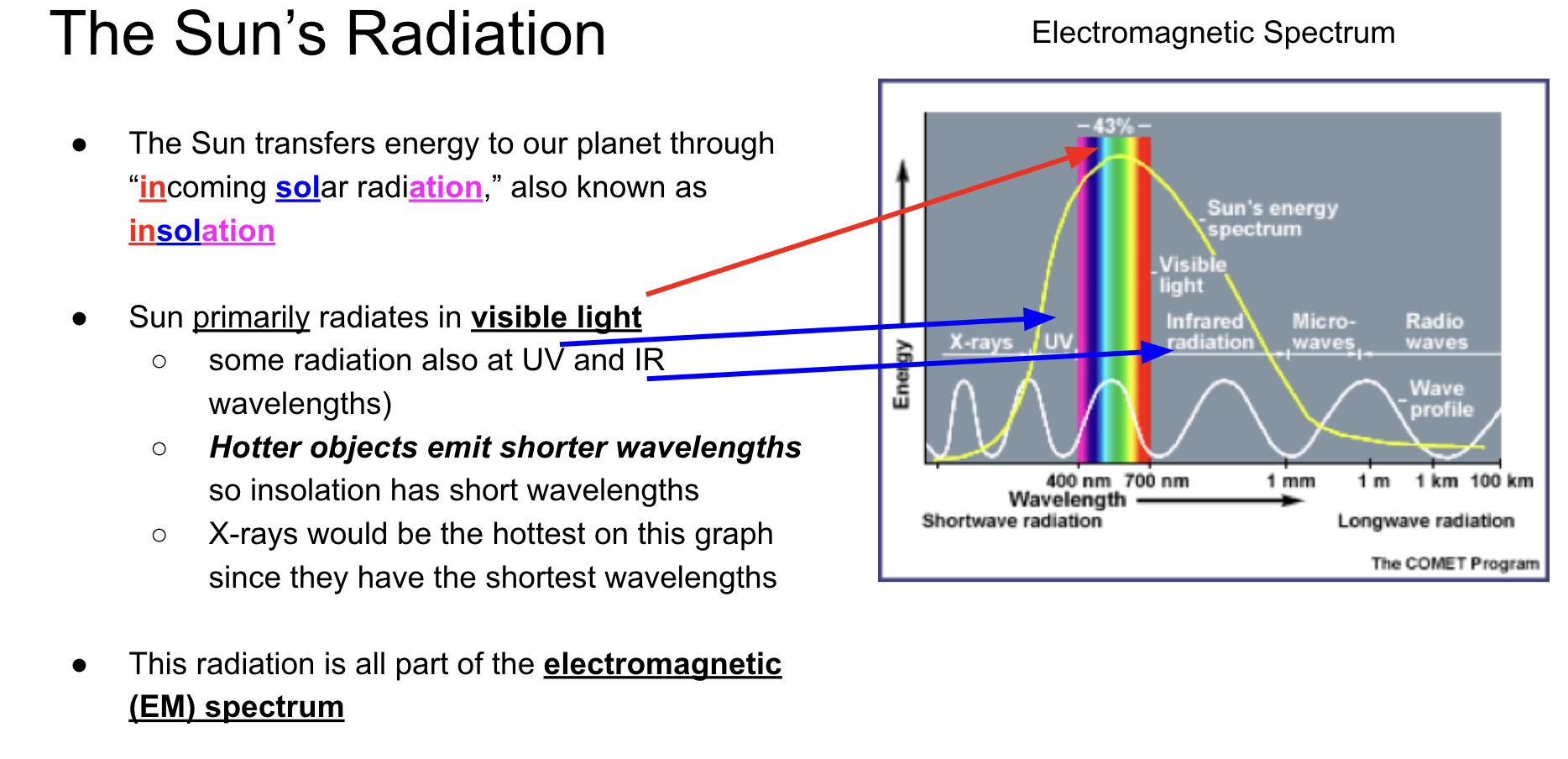
EM Waves
Vibration of particles (magnetic & electrical/dist between crests = wavelength/waves per second = Hz).
21
New cards
Insolation
50% absorbed by earth, 20% absorbed by atmosphere, and 30% reflected or scattered
22
New cards
Radiation vs. Reradiation
Radiation is shorter wavelengths, reradiation is infared longer wavelengths.
23
New cards
Selective absorbers
Gases that absorb only specific wavelengths of radiation (Visible light not absorbed by gases/Gases like carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane). Without natural greenhouse earth would be 60 degrees colder.
24
New cards
Climate change long term effects
Increased natural disasters, increase ocean acidification, increase ocean sea levels, increase melting sea ice, food crisis, flooding, economic and educational stress, and more.
25
New cards
COP 21 Paris Agreement Outcomes
Every 8 years countries strengthen climate actions, adaptation (help most vulnerable), long term goal (net 0 emissions), more transparency with climate actions, and climate financial support for developing countries.
26
New cards
Paris Agreement
Adopted by 196 countries, is a legally binding treaty on climate change action created by the UNFCC. Was put into effect on 11/4/16.
27
New cards
How to reduce anthropogenic carbon emissions
use less electricity, renewable/nuclear energy not fossil fuels, plant more trees, more efficient or energy efficient transportation, and more insulation in homes/businesses.