Biology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/211
Last updated 4:51 PM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
1
New cards
Lock and key mechanism
active site on enzyme fits substrate exactly
2
New cards
Enzymes
proteins that act as biological catalysts; speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells
3
New cards
Stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf in the lower epidermis through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
4
New cards
spongy mesophyll
Loose tissue beneath the palisade layer of a leaf; has many air spaces between its cells
5
New cards
waxy cuticle
Forms a waterproof layer to stop water loss due to photosynthesis
6
New cards
palisade mesophyll
layer of cells under the upper epidermis of a leaf, contains most chlorophyll and is where photosynthesis takes place
7
New cards
guard cells
control the opening and closing of stomata
8
New cards
Lower epidermis
protective layer on the bottom of leaf which contains stomata & guard cells
9
New cards
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --\> light energy --\> C6H12O6 + 6O2
10
New cards
Xylem
vascular tissue strengthened with lignin that carries water and minerals upward from the roots to every part of a plant
11
New cards
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances bidirectionally throughout a plant (up & down)
12
New cards
magnesium (plant nutrition)
Needed to make chloroplasts without, photosynthesis stops and leaves turn yellow.
13
New cards
Nitrates (plant nutrition)
Needed for production of proteins + amino acids, nucleic acid and plant hormones. Without it, plants don't grow properly.
14
New cards
Potassium (plant nutrition)
Needed to produce enzymes that catalyze photosynthesis and respiration. Without it, fruits/flowers don't grow properly and leaves discolour.
15
New cards
Phosphates (plant nutrition)
Needed for making DNA and cell membranes. Needed for respiration and growth. Without it, they have poor growth and old leaves become purple.
16
New cards
Leaf adaptations for efficient photosynthesis
Transparent upper epidermis
Chloroplasts mostly in palisade layer, near the top
Leaves are broad for a large surface area to be exposed to light
Waxy cuticle reduces water loss from evaporation.
Chloroplasts mostly in palisade layer, near the top
Leaves are broad for a large surface area to be exposed to light
Waxy cuticle reduces water loss from evaporation.
17
New cards
Photosynthesis happens in...
Palisade mesophyll layer of the leaf, specifically in the chloroplast organelle
18
New cards
Chemical formula for glucose
C6 H12 O6
19
New cards
How do plants store glucose?
as starch or sucrose
20
New cards
What is a limiting factor?
the factor that stops photosynthesis going any faster
21
New cards
What is transpiration?
The loss of water vapor through the stomata of leaves.
22
New cards
Why does transpiration happen?
a plant needs to open its stomata to let in co2 so that it can produce glucose, this also lets water out. theres a higher concentration of water inside the leaf than in the air outside , so water moves out of the leaf by diffusion
23
New cards
Transpiration stream
Movement of water up through the xylem from the roots to the leaves
24
New cards
Why does humidity affect transpiration
If the air is humid, there is a lot of water in it already, so there's not much difference between the inside and the outside of the leaf, slowing the diffusion that allows transpiration.
25
New cards
How does extreme low or high temperature affect transpiration
Low: Less energy for evaporation and photosynthesis
High: Dry leaf, denatured enzymes thus photosynthesis stops, evaporation happens faster.
High: Dry leaf, denatured enzymes thus photosynthesis stops, evaporation happens faster.
26
New cards
How does light intensity effect transpiration
The brighter the light, the greater the transpiration rate because more light increases the rate of photosynthesis, causing the stomata to open to let carbon dioxide in. If it is dark, stomata begin to close
27
New cards
How does air movement affect the rate of transpiration
Circulates the air around the leaf replacing the water vapour that just left the stomata.
28
New cards
aerobic respiration
-Occurs in mitochondria
-Is a chemical reaction that releases energy
-Converts energy from glucose
-Needed for all living processes
-Aerobic just means "with oxygen"
-Produces a lot of ATP (32 molecules per molecule of glucose)
-Is a chemical reaction that releases energy
-Converts energy from glucose
-Needed for all living processes
-Aerobic just means "with oxygen"
-Produces a lot of ATP (32 molecules per molecule of glucose)
29
New cards
What is excess glucose stored as?
Stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles
30
New cards
Formula for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --\> 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy
31
New cards
Respiration
The process of transferring energy from glucose which happens constantly in every living cell.
32
New cards
anaerobic respiration in animals formula
glucose \---\> lactic acid (+ATP)
33
New cards
anaerobic respiration in plants + microorganisms formula
glucose \---\> ethanol + carbon dioxide (+energy)
34
New cards
Which type of respiration produces more ATP?
aerobic respiration
35
New cards
Why is lactic acid build up caused by anaerobic respiration a problem for muscles?
Lactic acid is poison for muscles and if it builds up it can lead to cramps
36
New cards
Difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
Aerobic:
-Oxygen is used
-CO2 produced
-All multicellular organisms
-A lot of ATP released in comparison to anaerobic
Anaerobic:
-Doesn't use oxygen
-Lactic acid produced
-Less ATP released
-Microorganisms, plants and muscles for short periods of time
-In yeast and plants produces alcohol.
-Oxygen is used
-CO2 produced
-All multicellular organisms
-A lot of ATP released in comparison to anaerobic
Anaerobic:
-Doesn't use oxygen
-Lactic acid produced
-Less ATP released
-Microorganisms, plants and muscles for short periods of time
-In yeast and plants produces alcohol.
37
New cards
What is oxygen debt?
The amount of extra oxygen the body needs after exercise to react with the accumulated lactic acid and remove it from the cells
38
New cards
What is the role of ATP?
Main source of chemical energy for cells
39
New cards
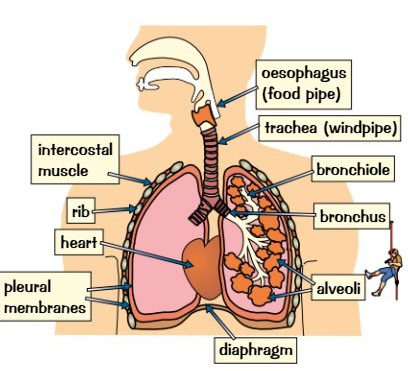
how are lungs adapted for gas exchange
The alveoli give the lungs a really big surface area. this helps gas exchange happen easily and efficiently. they have moist, thin walls (just one cell thick) they have a lot of tiny blood vessels called capillaries.
40
New cards
What is the role of the trachea?
The trachea is the tube which leads from the nose/ mouth to the bronchi
It allows air to follow in and out during breathing
It allows air to follow in and out during breathing
41
New cards
Role of intercostal muscles
Surround ribs and allow them to expand/contract when lungs do so.
42
New cards
Role of ribcage
To protect chest organs like heart and lungs.
43
New cards
Explain the function of diaphragm
Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges. This contraction creates a vacuum, which pulls air into the lungs. Upon exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its domelike shape, and air is forced out of the lungs.
44
New cards
How does oxygen get from our lungs to our blood?
Through gas exchange occurring in the alveoli.
45
New cards
How are alveoli adapted for gas exchange?
- large surface area due to high number of alveoli
- good blood supply, high concentration gradient to . . . allow diffusion
- thin, short diffusion pathway
- moist, dissolve gases
- good blood supply, high concentration gradient to . . . allow diffusion
- thin, short diffusion pathway
- moist, dissolve gases
46
New cards
How does exercise affect breathing rate?
Breathing rates increase during exercise because the body needs more energy, because it is moving faster and since breathing is what provides oxygen to the body, more oxygen is needed. Thus breathing rate increases. Oxygen is needed to release energy. Also, after exercise the body needs more oxygen to pay off "oxygen debt".
47
New cards
How is the heart adapted to its function?
-The left side of the heart has thicker muscle than the right side of the heart. This is because the left side of the heart pumps blood to the whole body whereas the right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs. Thicker muscle can contract more strongly to pump the blood out of the heart at a higher pressure, so it travels further.
-There are valves in between each chamber to prevent the blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
-The muscle cells in the heart respond to an electrical signal, enabling them to contract at the same time
-There are valves in between each chamber to prevent the blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
-The muscle cells in the heart respond to an electrical signal, enabling them to contract at the same time
48
New cards
How does blood flow through the heart?
Inferior and superior vena cava (1) dump blood into the right atrium (2)
blood passes through tricuspid valve to right ventricle (3)
then through semi-lunar valve to 2 pulmonary arteries (4) that lead to the lungs (5) where blood becomes oxygenated
Pulmonary veins (6) bring blood from the lungs back to the left atrium (7)
pass through bicuspid valve to left ventricle (8) is large and muscular to pump blood into the aorta (9) and to the rest of the body (10)
Eventually blood will be pumped back to each vena cava (1)
blood passes through tricuspid valve to right ventricle (3)
then through semi-lunar valve to 2 pulmonary arteries (4) that lead to the lungs (5) where blood becomes oxygenated
Pulmonary veins (6) bring blood from the lungs back to the left atrium (7)
pass through bicuspid valve to left ventricle (8) is large and muscular to pump blood into the aorta (9) and to the rest of the body (10)
Eventually blood will be pumped back to each vena cava (1)
49
New cards
Structure, function and example of veins
-Thinner walls due to the lower pressure of the blood
-To compensate for low blood pressure, lumen is large to assist blood flow
-Have valves to stop blood from flowing in wrong direction
-Carry blood to the heart
-Example: Vena Cava
-To compensate for low blood pressure, lumen is large to assist blood flow
-Have valves to stop blood from flowing in wrong direction
-Carry blood to the heart
-Example: Vena Cava
50
New cards
Structure, function and example of arteries
-Carries blood away from heart
-Thick walls due to high blood pressure
-Elastic fibers allow it to expand
-Example: Aorta
-Thick walls due to high blood pressure
-Elastic fibers allow it to expand
-Example: Aorta
51
New cards
Structure & function of capillary
- one cell thick to allow rapid diffusion
- pores in wall allow white blood cells to exit
-permeable wall
-Found close to cells
- pores in wall allow white blood cells to exit
-permeable wall
-Found close to cells
52
New cards
Function and structure of red blood cells
-Component of blood
-Transport oxygen around the body
-Contain haemoglobin, which combines with oxygen
-Have a bi-concave shape (dents on both sides)
-Lack nucleus to absorb oxygen
-Have a large surface area to absorb more oxygen
-Transport oxygen around the body
-Contain haemoglobin, which combines with oxygen
-Have a bi-concave shape (dents on both sides)
-Lack nucleus to absorb oxygen
-Have a large surface area to absorb more oxygen
53
New cards
Function and structure of white blood cells
-Component of blood
-Have nucleus
-Product antibodies and antitoxins
-Antibodies to kill pathogens
-Antitoxins to neutralise toxins produced by pathogens
-Have nucleus
-Product antibodies and antitoxins
-Antibodies to kill pathogens
-Antitoxins to neutralise toxins produced by pathogens
54
New cards
Purpose of plasma
-Component of blood
-Liquid that carries substances including: nutrients (eg. glucose), waste products and CO2 (waste from respiration) and carried the main components of blood (red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets)
-Liquid that carries substances including: nutrients (eg. glucose), waste products and CO2 (waste from respiration) and carried the main components of blood (red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets)
55
New cards
Purpose of platelets
Blood clotting
56
New cards
What problem occurs if a person doesn't have platelets?
Their cuts don't form scabs, thus they keep bleeding and bruise easily.
57
New cards
Why is smoking bad?
Causes emphysema (smoking causes damage by stimulating immune cells that then damage alveoli creating less surface area, thus less O2, thus making it harder to breathe) and chronic bronchitis (tiny particles of tar in cigarettes cause inflammation of bronchioles making it harder to breathe.) Contains tar (damage cilia, bad for oral health), nicotine (highly addictive/makes you want to smoke more, causes higher blood pressure and may lead to heart attack) and carbon monoxide (harmful chemical, makes fetus have lower birth weight and binds to haemoglobin, preventing O2 from binding to haemoglobin).
58
New cards
What are the 3 roles of the kidney?
1) removal of urea
2) adjustment of ion (salt) levels in the blood
3) adjustment of water content of blood
2) adjustment of ion (salt) levels in the blood
3) adjustment of water content of blood
59
New cards
What are the excretory products of the kidney?
Urea, ions (salt) and water
60
New cards
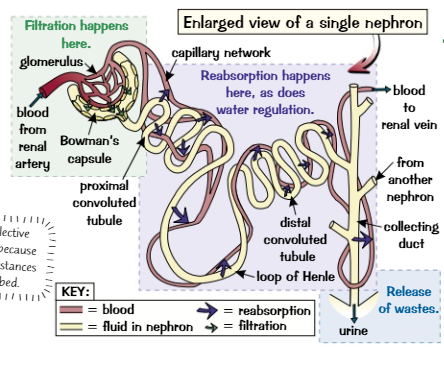
What are nephrons?
Filtration units in the kidneys
61
New cards
What happens when blood passes through the nephrons
1) Ultrafiltration: blood from renal artery flows through glomerulus, high pressure is then built up, squeezing water, urea, glucose and ions out of blood into Bowman's capsule. Membranes between blood vessels in glomerulus and Bowman's capsule act like filters, thus big molecules like proteins stay in blood.
2) Reabsorption: useful substances are then reabsorbed into blood. Glucose is reabsorbed in proximal convoluted tubule, sufficient water and sufficient ions are also reabsorbed.
3) Removal of wastes: remaining substances form urine. They continue out of the nephron, through the ureter into the bladder and exit the body via the urethra.
2) Reabsorption: useful substances are then reabsorbed into blood. Glucose is reabsorbed in proximal convoluted tubule, sufficient water and sufficient ions are also reabsorbed.
3) Removal of wastes: remaining substances form urine. They continue out of the nephron, through the ureter into the bladder and exit the body via the urethra.
62
New cards
What is glomerular filtrate?
The filtered liquid in the Bowman's capsule
63
New cards
What is osmoregulation?
The control of water balance.
64
New cards
What is ADH?
Anti-diuretic hormone - it controls the concentration of urine and is released into the bloodstream by the pituitary gland. ADH makes nephrons more permeable so more water is reabsorbed into the blood.
65
New cards
How does the body respond to water loss?
Brain detects water loss\----\>pituitary gland releases MORE ADH\---\>ADH makes kidney reabsorb more water\---\>body is now hydrated
66
New cards
How does the body respond to water gain?
Brain detects water gain\---\>pituitary gland releases LESS ADH\---\>Less ADH means kidneys reabsorb less water\---\>body is now hydrated.
67
New cards
What is coronary heart disease?
When the coronary arteries that supply the blood to the muscle of the heart get blocked by layers of fatty material building up. This causes arteries to become narrow, blood flow is restricted and there's a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle, leading to a heart attack.
68
New cards
What are the factors that can cause coronary heart disease?
-Diet high in saturated fat. Can lead to fatty deposits forming inside arteries, causing coronary heart disease.
-Smoking, since it increases blood pressure, which can damage the coronary arteries due to making the formation of blood clots more likely. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can also cause damage which can lead to fatty deposits forming.
-Being inactive can cause high blood pressure, damaging lining of arteries, making it more likely for fatty deposits to form.
-Stress can cause strain on heart due to high blood pressure
-Lots of salt can have osmotic effects and raise blood pressure, putting a strain on the heart
-Smoking, since it increases blood pressure, which can damage the coronary arteries due to making the formation of blood clots more likely. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can also cause damage which can lead to fatty deposits forming.
-Being inactive can cause high blood pressure, damaging lining of arteries, making it more likely for fatty deposits to form.
-Stress can cause strain on heart due to high blood pressure
-Lots of salt can have osmotic effects and raise blood pressure, putting a strain on the heart
69
New cards
How can heart disease be treated?
-Artificial heart/heart transplant
-Stents (placed in lumen to keep passage open)
-Medications (e.g. aspirin or statin)
-Stents (placed in lumen to keep passage open)
-Medications (e.g. aspirin or statin)
70
New cards
Strengths/limitations of stents
Strengths:
-Can be replaced
-Can be biodegradable or via a drug
Limitations
-May close after 2 years
-Can be made with metal
-Can be replaced
-Can be biodegradable or via a drug
Limitations
-May close after 2 years
-Can be made with metal
71
New cards
Strengths/limitations of medicine to treat heart disease
Strength:
-Reduces risk of heart attack/stroke
-Reduces risk of heart attack/stroke
72
New cards
Strengths/limitations of artificial hearts
Strengths:
-No tissue match or immunosuppressants
Limitations:
-Lots of machinery
-Operation
-Expensive
-Temporary
-No tissue match or immunosuppressants
Limitations:
-Lots of machinery
-Operation
-Expensive
-Temporary
73
New cards
Strengths/limitations of heart transplant
Strengths:
-Patients live longer
-High energy levels
Limitations:
-Operation
-Expensive
-Difficult to find tissue match
-Immunosuppressants
-High risk of death
-Patients live longer
-High energy levels
Limitations:
-Operation
-Expensive
-Difficult to find tissue match
-Immunosuppressants
-High risk of death
74
New cards
Where are pleural membranes located?
around the lungs
75
New cards
What are the 3 main components of the blood carried by plasma?
Red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets.
76
New cards
What are pathogens?
microorganisms that cause disease
77
New cards
specific vs nonspecific immunity
Nonspecific- general protection against all pathogens e.g. Cilia lining airways traps pathogens
Specific- intensified immune functions used to fight against classified disease e.g. antibodies are specific to their pathogen
Specific- intensified immune functions used to fight against classified disease e.g. antibodies are specific to their pathogen
78
New cards
What are phagocytes and what do they do?
White blood cells that are attracted to pathogens and surround them with their cell membranes to engulf them to let their enzymes destroy it. They are non specific (attack anything that's not meant to be there). This process is known as phagocytosis.
79
New cards
How can we demonstrate respiration?
You can use a hydrogen-carbonate indicator to show that living organisms product CO2 as they respire The hydrogen carbonate indicator will change from an orange colour to yellow in the presence of carbon dioxide.
80
New cards
What are antibodies and what do they do?
Certain white blood cells called lymphocytes detect antigen (unique molecule on surface of pathogen) and produce antibodies in response. Antibodies then lock onto the antigens, rendering them useless. Other white blood cells now destroy them. Antibodies are specific to a particular pathogen and can be produced very quickly should the same pathogen re-enter the body.
81
New cards
What type of white blood cells produce antibodies?
lymphocytes
82
New cards
What are antitoxins and what do they do?
Bacteria can produce toxins harmful to the body. White blood cells detect the toxin and produce antitoxins. Antitoxins then neutralise the effect of toxins.
83
New cards
How do vaccines protect from future infection?
When you're infected with a new pathogen, it can take lymphocytes a while to produce antibodies, and in that time you could get more sick or even die. Vaccines are the solution to this, they involve injecting dead or inactive pathogens into the body. These carry antigens, so even though they're harmless they still trigger an immune response (your lymphocytes produce antibodies to attack them). Memory cells will then be produced and will stay in the blood, thus if the same pathogen re-enters the body, antibodies will be produced much faster and in greater numbers.
84
New cards
8 life processes all living things must be able to do (MRS GRENC)
Require nutrition, respire, excrete, respond to stimuli, move, control internal conditions, reproduce and grow & develop
85
New cards
Cells
Basic unit of life
86
New cards
Eukaryotic cells
Found in plants, animals, fungi and protoctists, 10-100 micrometers, a eukaryote is made up of eukaryotic cells, contain nucleus
87
New cards
Protoctists
single-celled organisms with nucleus that don't fit into other categories other than eukaryotic.
88
New cards
prokaryotic cell
0.1-5 micrometers, prokaryote is made up of prokaryotic cells, bacteria are prokaryote, lack nucleus mitochondria and chloroplasts, have DNA loop/s in cytoplasm, DNA loop/ring (which it can have 1 or more of) are called plasmids
89
New cards
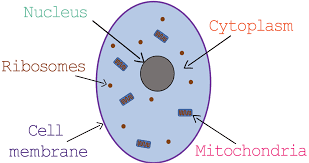
Animal cell organelles
Mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), golgi, lysosomes, nucleus
90
New cards
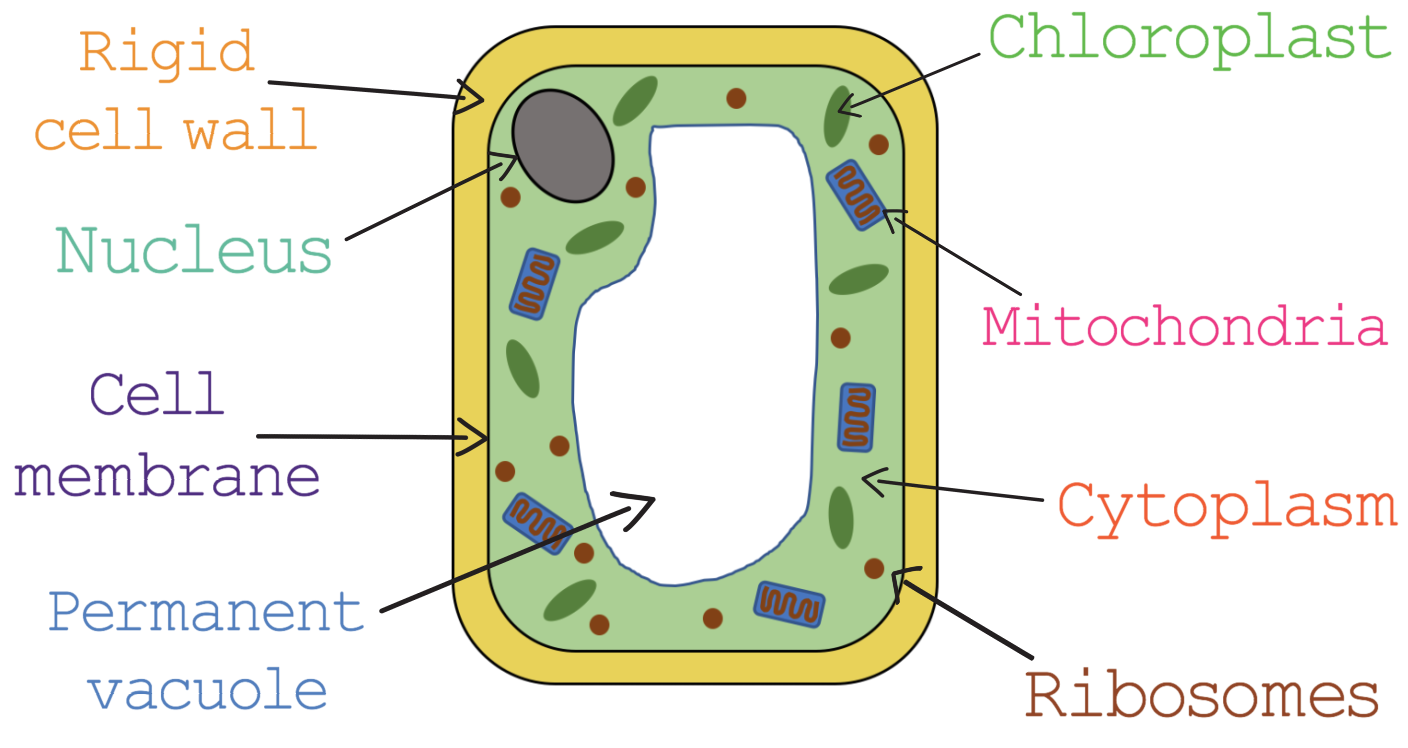
Plant cells
Include same organelles as animal cells but also possess vacuoles, chloroplasts and a cell wall (which is made of cellulose)
91
New cards
Algal cells organlles
same as plant cells
92
New cards
Fungal cells organelles
Similar to plant cells, except they lack chloroplasts and their cell walls are made of chitin instead of cellulose
93
New cards
cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
94
New cards
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended, also where most of cell's chemical reactions take place
95
New cards
DNA
molecule that stores genetic information in all organisms
96
New cards
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
97
New cards
Enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things
98
New cards
Tissues
Groups of cells with a common structure and function.
99
New cards
Mesophyll
found in plants, capable of photosynthesis
100
New cards
Epidermal tissue
Found in plants and animals, examples include human skin and waxy covering on some plants