AP Psych Unit 3- Dev 6-9
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
association
predicting an outcome based on certain stimuli/relations
ex —→ lighting expected after hearing thunder
classical conditioning
learning process discovered by Ivan Pavlov: an automatic response due to forming an association between natural stimuli and a previously neutral stimuli, leading to a learned response
unconditional stimuli (US)
stimuli that naturallly causes a response without prior learning
ex —→ dog food
unconditioned response
unlearned , natural response to the US
ex—→ salivation to food
neutral stimuli
no conditioned response
ex—→ tone
conditioned stimuli (CS)
a previously neutral stimuli (tone, after being paired with the natural stimuli of food, then taken away) that triggers a conditioned response (salivation)
conditioned response (CR)
a learned response to previously neutral stimuli
note —→ the response stays the same ex. salivation
acquisition
the initial stage of learning: when neutral stimulus + unconditioned stimuli are paired and introduced
note —→ the neutral stimuli is always before the US (food)
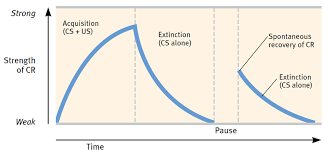
extinction
the second stage in learning: the diminishing of a conditioned response(salivation) due to natural stimulus no longer following the conditioned stimuli (tone)
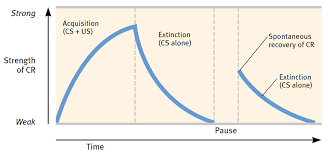
spontaneous recovery
the 3rd stage of learning: reappearence of extinguished conditioned response (salivation) after stopping conditioning
note —→ the strength of the CR is less than pre-extinction
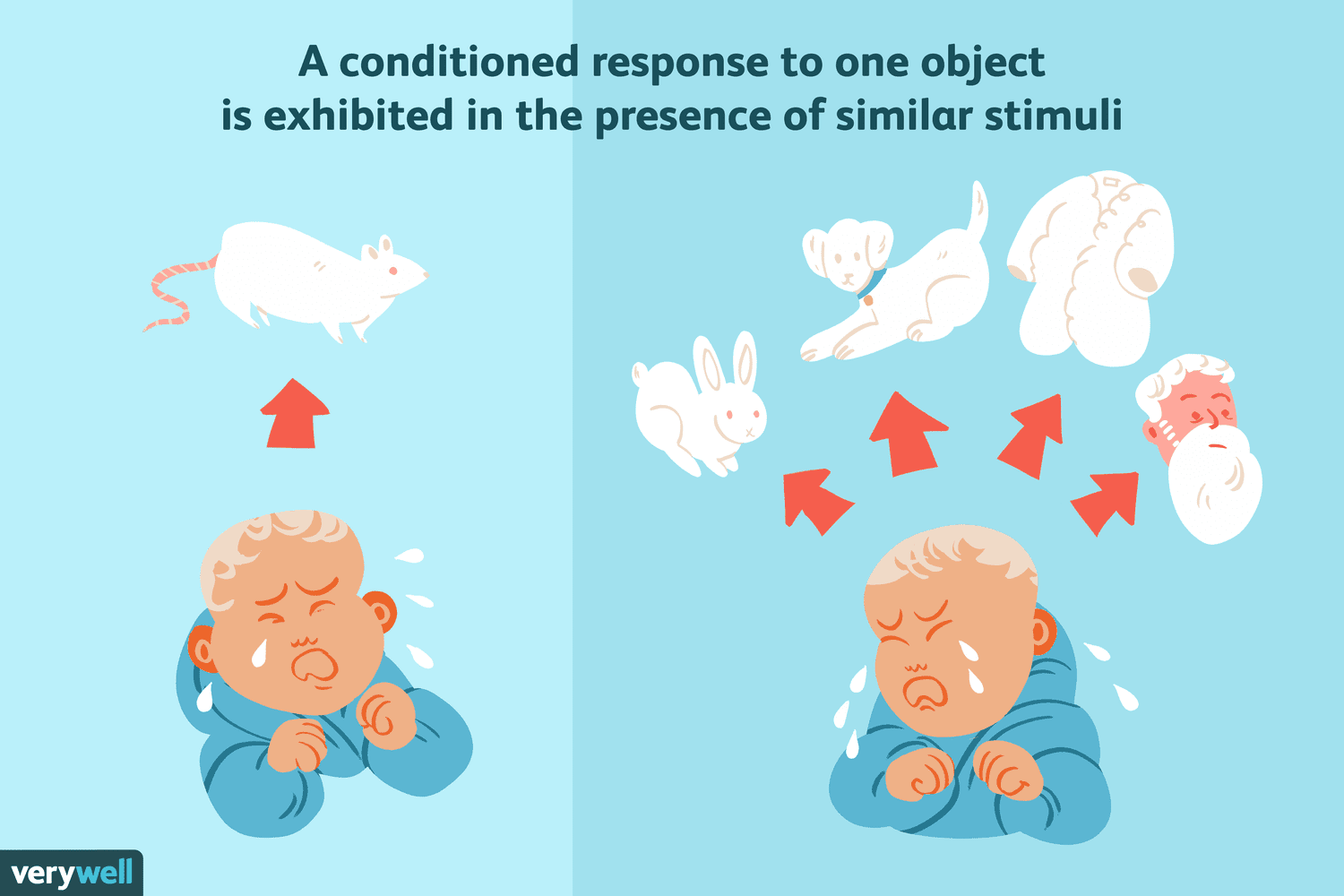
stimulus generalization
tendency to experience a conditioned response (Little Albert fear) to similar conditioned stimuli (white fuzzy thing/rat)

stimulus discrimination
learned ability to distinguish b/w a conditioned stimuli and similar stimulus (due to difference threshold)
higher order conditioning/second order
a neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimuli by associating it with the previous conditioned response (snapping fingers AND the tone, eventually removing the tone to make the finger snapping the main CS)
counter conditioning
replacing an unwanted conditioned response with a more desirable one by associating feared stimulus w/ positive events
ex —→ bring treat to dog when cat around
taste aversion
learned avoidance of a particular food that has been associated with illness/discomfort
biological preparedness
certain associations are more easily learned b/c of their perception
ex—→ snake more scary than bunny
habituation
decrease in response to stimuli after repeated presentations
ex—→ gunshots heard over and over