exam 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following statements about Metabolic Syndrome is false?
It is also know as Syndrome X and Insulin Resistance Syndrome.
Excess visceral fat is a greater risk factor than excess subcutaneous fat for Metabolic Syndrome.
The onset of symptoms is typically very rapid.
It is a cluster of pathologies that increases the risk for cardiovascular disease.
It is also know as Syndrome X and Insulin Resistance Syndrome.
Excess visceral fat is a greater risk factor than excess subcutaneous fat for Metabolic Syndrome.
The onset of symptoms is typically very rapid.
It is a cluster of pathologies that increases the risk for cardiovascular disease.
The onset of symptoms is typically very rapid.
2
New cards
Which of the following is neither a core component nor an additional component of Metabolic Syndrome?
Hyperinsulinemia
Adipocyte dysfunction
Dyslipidemia
Microalbuminuria
Hyperkeratosis
Hyperinsulinemia
Adipocyte dysfunction
Dyslipidemia
Microalbuminuria
Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis
3
New cards
Of the following pairs of components, which are the earliest that arise with Metabolic Syndrome?
dyslipidemia and hyperinsulinemia.
insulin resistance and hypertension.
impaired glucose tolerance and dyslipidemia.
hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance
dyslipidemia and hyperinsulinemia.
insulin resistance and hypertension.
impaired glucose tolerance and dyslipidemia.
hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance
hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance
4
New cards
When it comes to essential hypertension in Metabolic Syndrome, it is suggested that __________ and __________ may be responsible for the development of this core component by increasing central sympathetic outflow, causing peripheral vasoconstriction, and more
insulin resistance; hyperinsulinemia
5
New cards
The tissue type primarily responsible for peripheral glucose disposal and for whole-body insulin resistance is:
skeletal muscle
6
New cards
Individuals with a 2-hour glucose level above 200 mg/dL during an OGTT can be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
True or False
True or False
True
7
New cards
Skeletal muscle is a major organ for both the removal of glucose from the bloodstream and the delivery of glucose into the bloodstream following glycogen breakdown.
True or False
True or False
False
8
New cards
Reactive oxygen species cause cellular dysfunction and do not play a role in normal growth and metabolism
True or False
True or False
False
9
New cards
Glucose that enters the bloodstream from the intestines is first processed and detected by the pancreas
True or False
True or False
False
10
New cards
Release of adiponectin from fat cells would promote the development of cardiovascular associated defects and impairments in Metabolic Syndrome.
True or False
True or False
False
11
New cards
Phosphorylation events become less common throughout the subsequent stages of cellular signal transduction
True or False
True or False
False
12
New cards
A chemical messenger secreted by one cell and acting on the same cell in the same tissue is an example of paracrine communication
True or False
True or False
False
13
New cards
Enzymes which remove phosphates from cellular proteins are called __________, whereas enzymes which add phosphates to cellular proteins are called __________.
phosphatases; kinases
14
New cards
Which of the following statements regarding signal transduction is **FALSE**?
Phosphorylation of proteins is a critical (and quite common) component of signal transduction in cells.
The use of second messengers allows for signal transduction events to be amplified in the cell.
Signal transduction relies exclusively on cell surface receptors in order to change cellular behavior.
Signal transduction is used by the body to change the function of cells
Phosphorylation of proteins is a critical (and quite common) component of signal transduction in cells.
The use of second messengers allows for signal transduction events to be amplified in the cell.
Signal transduction relies exclusively on cell surface receptors in order to change cellular behavior.
Signal transduction is used by the body to change the function of cells
Signal transduction relies exclusively on cell surface receptors in order to change cellular behavior.
15
New cards
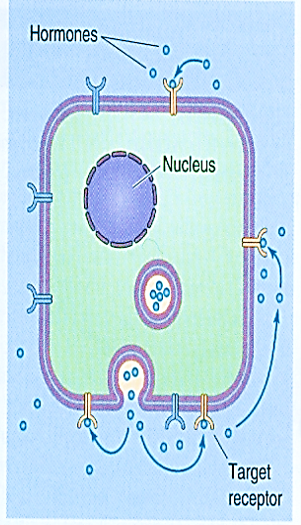
Which mechanism of cell-cell communication is illustrated by the figure below?
autocrine
16
New cards
ACh receptors are ligand-gated ion channels that permit the movement of what ion when ACh binds?
Na+
17
New cards
When a ligand binds to a GPCR, the activated GPCR becomes capable to doing what for G proteins?
It can now enable a new GTP molecule from the cytoplasm to replace the old GDP molecule bound to the α subunit of the G protein.
18
New cards
Adenylate cyclase uses the substrate _____ to form the second messenger chemical _____, and the increase in this second messenger chemical causes the activation of the enzyme named _____.
ATP; cAMP; PKA
19
New cards
The α subunits of the _____ subfamily of G proteins interact with (and stimulate) adenylate cyclase when activated.
Gs
20
New cards
The α subunits of the _____ subfamily of G proteins interact with phospholipase C (PLC) when activated.
Gq,11
21
New cards
The insulin receptor is an integral part of the insulin signaling cascade. Which of the following statements is true regarding the insulin receptor?
The insuline receptor is a monomer, consisting of 2 extracellular alpha-subunits that bind the hormone and two trasmembrane beta-subunits.
The insulin receptor can only phosphorylate itself to stimulate a signal downstream.
The insulin receptor is a tyrosine phosphatase.
The insulin receptor is a heterotetramer, consisting of 2 extracellular alpha-subunits that bind the hormone and 2 transmembrane beta-subunits.
Insulin binds to the cystein rich domains of the beta-subunits, thereby enhancing, via a specific conformation change, the tyrosine kinase activity of the alpha-subunits.
The insuline receptor is a monomer, consisting of 2 extracellular alpha-subunits that bind the hormone and two trasmembrane beta-subunits.
The insulin receptor can only phosphorylate itself to stimulate a signal downstream.
The insulin receptor is a tyrosine phosphatase.
The insulin receptor is a heterotetramer, consisting of 2 extracellular alpha-subunits that bind the hormone and 2 transmembrane beta-subunits.
Insulin binds to the cystein rich domains of the beta-subunits, thereby enhancing, via a specific conformation change, the tyrosine kinase activity of the alpha-subunits.
The insulin receptor is a heterotetramer, consisting of 2 extracellular alpha-subunits that bind the hormone and 2 transmembrane beta-subunits.
22
New cards
Which of the following statements about IRS proteins is **FALSE:**
Tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS acts as a docking protein to regulated downstream signaling factors.
IRS proteins are phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by the activated insulin receptor.
Tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS can propogate signaling to modulate numerous aspects of cell metabolism, such as glucose transport, glycogen synthesis, lipid synthesis, and protein synthesis.
Tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS increases the enzymatic activity of the IRS protein
Tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS acts as a docking protein to regulated downstream signaling factors.
IRS proteins are phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by the activated insulin receptor.
Tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS can propogate signaling to modulate numerous aspects of cell metabolism, such as glucose transport, glycogen synthesis, lipid synthesis, and protein synthesis.
Tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS increases the enzymatic activity of the IRS protein
Tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS increases the enzymatic activity of the IRS protein.
23
New cards
Insulin increases glucose transport into skeletal muscle cells by:
Increasing translocation of GLUT-4-containing vesicles to the plasma membrane.
24
New cards
Which of the following statements about the transport of glucose across the endothelium of capillaries in skeletal muscle is/are **FALSE**?
How much glucose is delivered across the endothelium to the skeletal muscle cells can influence the rate glucose transport by the muscle cells.
This transendothelial glucose transport is mediated by the GLUT-1 isoform.
This transendothelial glucose transport can be __directly__ increased by insulin.
Increased blood flow to the capillary can increase glucose transport to the extracellular space
How much glucose is delivered across the endothelium to the skeletal muscle cells can influence the rate glucose transport by the muscle cells.
This transendothelial glucose transport is mediated by the GLUT-1 isoform.
This transendothelial glucose transport can be __directly__ increased by insulin.
Increased blood flow to the capillary can increase glucose transport to the extracellular space
This transendothelial glucose transport can be __directly__ increased by insulin.
25
New cards
The Km of GLUT4 is lower than the Km of GLUT2, which means that glucose transport via GLUT4 will saturate...?
at a lower glucose concentration than GLUT2.
26
New cards
Which of the following is the main site of dysfunction in the myocyte insulin signaling cascade?
PIP2
PDK1
PKB/AKT
IRS-1
PIP2
PDK1
PKB/AKT
IRS-1
IRS-1
27
New cards
Glucose delivery to skeletal muscle tissue is reduced in the Metabolic Syndrome due to all of the following mechanisms **EXCEPT**:
Reduced NO-stimulated vasodilation of arterioles
Impaired insulin stimulation of eNOS in smooth muscle cells
Decreased transendothelial glucose transport via GLUT-1
Less blood flow to the capillaries perfusing the muscle
Reduced NO-stimulated vasodilation of arterioles
Impaired insulin stimulation of eNOS in smooth muscle cells
Decreased transendothelial glucose transport via GLUT-1
Less blood flow to the capillaries perfusing the muscle
Impaired insulin stimulation of eNOS in smooth muscle cells
28
New cards
Only IRS-1 is affected by the up-regulation of PKCtheta activity caused by free fatty acids (FFAs).
True or False
True or False
False
29
New cards
An inhibitor of the serine kinase GSK-3beta will have all of the following effects on insulin-resistant skeletal muscle ***except:***
Cause reduced serine kinase activity of GSK-3beta.
Cause decreased serine phosphorylation of IRS-1 in the presence of insulin.
Cause decreased insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation.
Cause increased insulin-stimulated glucose transport.
Cause reduced serine kinase activity of GSK-3beta.
Cause decreased serine phosphorylation of IRS-1 in the presence of insulin.
Cause decreased insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation.
Cause increased insulin-stimulated glucose transport.
Cause decreased insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation.
30
New cards
Serine phosphorylation is known to impair the functionality of insulin signaling. Which of the following kinases ***cannot*** initiate this effect?
JNK
p38 MAPK
GSK-3beta
PI3K
JNK
p38 MAPK
GSK-3beta
PI3K
PI3K
31
New cards
Which of the following is not a cell type expressed in the Islet of Langerhans?
Gamma
Delta
Alpha
F
Gamma
Delta
Alpha
F
Gamma
32
New cards
Which second messenger chemical is a major player in the signal transduction pathway through which glucose stimulates release of insulin by β cells of the endocrine pancreas?
Ca+2
33
New cards
When glucose levels in the blood rise, the resulting increase in ATP concentration within β cells __________ the **closing** of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the plasma membrane.
increases/promotes
34
New cards
High levels of glucose will have all of the following effects on the Alpha cell **EXCEPT**?
Activation of Na+ channels and membrane repolarization.
Increased glucose entry via transport using GLUT-1.
Lack of the opening of Ca2+ channels and no change in intracellular Ca2+ levels.
Inhibition of glucagon release
Activation of Na+ channels and membrane repolarization.
Increased glucose entry via transport using GLUT-1.
Lack of the opening of Ca2+ channels and no change in intracellular Ca2+ levels.
Inhibition of glucagon release
Activation of Na+ channels and membrane repolarization.
35
New cards
Exercise results in increased sympathetic nerve activity to the pancreas which is associated with decreased insulin secretion by the Beta cells. Which of the following is NOT involved in that process?
Gq
PKA
cAMP
Norepinephrine
G-protein coupled receptors
Gq
PKA
cAMP
Norepinephrine
G-protein coupled receptors
Gq
36
New cards
Which of the following is associated with the short-term (acute) effects of a rise in plasma FFA's?
\
β-cell apoptosis
More insulin release by the β cell
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Decreased mitochondrial production of ATP
\
β-cell apoptosis
More insulin release by the β cell
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Decreased mitochondrial production of ATP
More insulin release by the β cell
37
New cards
Sulfonylureas were developed to help overcome insulin resistance and prevent/control hyperglycemia. These drugs do the job of _____ by binding to and closing a ______.
ATP, K+channel
38
New cards
Based on our limited body of knowledge regarding the details of Alpha cell regulation during the development of type 2 diabetes, which the following is FALSE?
SNS overactivity will affect α-adrenergic receptors on the α-cell, increasing glucagon release.
Just like β-cells, under oxidative stress α-cells are targeted by the apoptotic activity of caspases\*\*.\*\*
Glucagon release by α-cells can increase as local insulin levels decrease due to a removal of inhibition.
Preserved function of α-cells in the absence of sufficient insulin secretion by β-cells can exacerbate hyperglycemia.
SNS overactivity will affect α-adrenergic receptors on the α-cell, increasing glucagon release.
Just like β-cells, under oxidative stress α-cells are targeted by the apoptotic activity of caspases\*\*.\*\*
Glucagon release by α-cells can increase as local insulin levels decrease due to a removal of inhibition.
Preserved function of α-cells in the absence of sufficient insulin secretion by β-cells can exacerbate hyperglycemia.
Just like β-cells, under oxidative stress α-cells are targeted by the apoptotic activity of caspases**.**
39
New cards
The onset of the phase of β cell failure coincides with the transition from a state of impaired glucose tolerance to overt type 2 diabetes.
True or False
True or False
True
40
New cards
For Metabolic Syndrome, the increase in insulin resistance happens simultaneously with both the increase in secretion of insulin and the elevation of fasting plasma glucose.
True or False
True or False
False
41
New cards
Glucagon stimulates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver.
True or False
True or False
True
42
New cards
GSK-3 and GS are inactive when phosphorylated.
True or False
True or False
True
43
New cards
Which of the following proteins is an enzyme which catalyzes one of the rate-limiting steps for gluconeogenesis in liver cells?
glycogen phosphorylase a
GSK-3β
hexokinase
PEPCK
glycogen phosphorylase a
GSK-3β
hexokinase
PEPCK
PEPCK
44
New cards
The movement of glucose into or out of the hepatocyte depends on the hormone-mediated availability of GLUT-2 transporters. Specifically, GLUT-2 is inserted into the plasma membrane, or removed from it, depending on the presence, or absence, of insulin.
True or False
True or False
False
45
New cards
When activated by the insulin signaling pathway, PP1G will increase the activity of ______ and decrease the activity of ______.
Glycogen synthase, glycogen phosphorylase a
46
New cards
The primary impact of insulin acting on hepatocytes is the ___________ of glycogen synthesis and the _____________ of both glycogen breakdown and gluconeogenesis. Thus overall, insulin leads to a(n) ___________ in hepatic glucose production (HGP).
stimulation; suppression; decrease
47
New cards
In the transition from a state of impaired glucose tolerance to overt Type 2 diabetes, the individual will experience _____________ insulin secretion and ______________ plasma glucose levels in response to a carbohydrate-containing meal.
decreased, increased
48
New cards
When does HGP normally become elevated in the course of the development of the Metabolic Syndrome and type 2 diabetes?
Elevated HGP begins to develop once Beta cell failure starts.
49
New cards
While the glucagon:insulin ratio is enhanced in the Metabolic Syndrome, it underestimates the elevation of HGP because it doesn’t take into account insulin resistance.
True or False
True or False
True
50
New cards
Excess SNS signaling to pancreatic α-cells will result in enhanced glucagon secretion. This simulatory effect requires which of the following cell signaling events?
It requires increased synthesis of glucagon and more dense packaging of glucagon into secretory vesicles.
It requires the binding of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine to α-adrenergic receptors coupled to Gs.
It requires an increase in intracellular Ca2+ levels, causing enhanced exocytosis of glucagon-containing vesicles\*\*.\*\*
It requires the production of the second messenger PIP3, which opens Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane.
It requires increased synthesis of glucagon and more dense packaging of glucagon into secretory vesicles.
It requires the binding of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine to α-adrenergic receptors coupled to Gs.
It requires an increase in intracellular Ca2+ levels, causing enhanced exocytosis of glucagon-containing vesicles\*\*.\*\*
It requires the production of the second messenger PIP3, which opens Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane.
It requires an increase in intracellular Ca2+ levels, causing enhanced exocytosis of glucagon-containing vesicles**.**
51
New cards
Which of the following is not considered to be an adipokine?
FFAs
PAI-1
Adiponectin
Resistin
Angiotensinogen
FFAs
PAI-1
Adiponectin
Resistin
Angiotensinogen
FFAs
52
New cards
As visceral adiposity begins to increase, there is a parallel increase in the secretion and action of adiponectin.
True or False
True or False
False
53
New cards
Which of the following statements about adiponectin is false?
The primary form of adiponectin in the plasma is the globular form.
Adiponectin can exist in the plasma as high molecular weight forms, low molecular weight forms, and globular forms.
The globular form of adiponectin has biological action.
Adiponectin is secreted primarily by white fat cells.
The primary form of adiponectin in the plasma is the globular form.
Adiponectin can exist in the plasma as high molecular weight forms, low molecular weight forms, and globular forms.
The globular form of adiponectin has biological action.
Adiponectin is secreted primarily by white fat cells.
The primary form of adiponectin in the plasma is the globular form.
54
New cards
APPL1 increases glucose transport in skeletal muscle cells by interacting directly with the insulin receptor.
True or False
True or False
False
55
New cards
Which of the following is an accurate statement about adiponectin and its relationship to insulin sensitivity?
Circulating adiponectin levels are positively correlated with fasting insulin levels.
Circulating adiponectin levels are positively correlated with % body fat.
Circulating adiponectin levels are positively correlated with whole-body insulin sensitivity.
Adiponectin levels are higher in insulin-resistant subjects compared to insulin-sensitive subjects.
Circulating adiponectin levels are positively correlated with fasting insulin levels.
Circulating adiponectin levels are positively correlated with % body fat.
Circulating adiponectin levels are positively correlated with whole-body insulin sensitivity.
Adiponectin levels are higher in insulin-resistant subjects compared to insulin-sensitive subjects.
Circulating adiponectin levels are positively correlated with whole-body insulin sensitivity.
56
New cards
Most of the individuals who have some degree of hypertension also have signs of impaired glucose tolerance and insulin resistance
True or False
True or False
True
57
New cards
Increased SNS activity in the Metabolic Syndrome is associated with enhanced renal release of the peptidase renin.
True or False
True or False
True
58
New cards
Renin acts to cleave __________ to form __________. This peptide is then cleaved by __________ to form the bioactive peptide __________.
angiotensinogen, ANG I, ACE, ANG II
59
New cards
The pharmacological inhibition of ACE would lead to an increase in blood pressure.
True or False
True or False
False
60
New cards
With increasing resting blood pressure, there are generally increases in fasting plasma insulin and in whole-body insulin sensitivity.
True or False
True or False
False
61
New cards
In Metabolic Syndrome, which of the following characteristics of cardiovascular disease (CVD) begins to develop before the deterioration of insulin secretory function (and thus before any transition to a diabetic state)?
microvascular complications such as retinopathy and nephropathy
elevated fasting blood glucose levels
elevated hepatic glucose production (HGP)
atherogenesis
microvascular complications such as retinopathy and nephropathy
elevated fasting blood glucose levels
elevated hepatic glucose production (HGP)
atherogenesis
atherogenesis
62
New cards
Which of statement about protein phosphorylation is true?
It can only increase the catalytic activity of enzymes.
It requires inorganic phosphate in addition to ATP for the enzymatic reaction.
It can be reversed by phosphodiesterases.
It occurs on serine, threonine and tyrosine amino acid residues
It can only increase the catalytic activity of enzymes.
It requires inorganic phosphate in addition to ATP for the enzymatic reaction.
It can be reversed by phosphodiesterases.
It occurs on serine, threonine and tyrosine amino acid residues
It occurs on serine, threonine and tyrosine amino acid residues.
63
New cards
From the list below, identify the adipokine which can positively affect insulin action in a variety of cell types, including myocytes.
resistin
adiponectin
TNF-α
angiotensinogen
resistin
adiponectin
TNF-α
angiotensinogen
adiponectin
64
New cards
Which organ/tissue is the major one responsible for peripheral disposal of glucose in response to the glucose level rise caused by consumption of a carbohydrate-containing meal?
\
\
skeletal muscle
65
New cards
Which of the following is a correct statement about the liver and glucose homeostasis?
It modulates gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in response to insulin and glucagon.
It breaks down stored glycogen to glucose in a process called gluconeogenesis.
It stores glucose carbons primarily as fat in its hepatocytes.
It is able to process nutrients from the intestines via the hepatic-portal circulation, but only after those nutrients are first sensed by endocrine pancreas
It modulates gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in response to insulin and glucagon.
It breaks down stored glycogen to glucose in a process called gluconeogenesis.
It stores glucose carbons primarily as fat in its hepatocytes.
It is able to process nutrients from the intestines via the hepatic-portal circulation, but only after those nutrients are first sensed by endocrine pancreas
It modulates gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in response to insulin and glucagon.
66
New cards
To modulate the function of target cells, successful cell-cell communication involves receptor-ligand binding, __________, and __________.
signal transduction via second messengers; modifications to existing proteins as well as modification to gene expression in order to change cell function
67
New cards
The synthesis and secretion of insulin and glucagon takes place in the exocrine pancreas.
False
68
New cards
For the signal transduction process, the “transmission and modulation” steps specifically involve
the amplification of intracellular signaling due to multiple steps, for example by the phosphorylation of effector proteins or enzymes.
69
New cards
Metabolic syndrome develops over the course of many years. An increase in __________ likely initiates the condition, with early subsequent defects being __________ and __________. Other core components develop thereafter, resulting in a progressively increasing risk of heart attack or stroke.
central adiposity; insulin resistance; compensatory hyperinsulinemia
70
New cards
Which component (core or additional) of Metabolic Syndrome can be defined as the inability to properly manage an increase in blood glucose levels?
impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)
71
New cards
Insulin can bind to receptors on the smooth muscle cells of arterioles which supply blood to the capillary beds of the skeletal muscle tissue. In doing so, insulin will activate nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in those smooth muscle cells, leading to nitric oxide production and vasodilation.
True or False
True or False
False
72
New cards
Phosphorylation of which amino acid results in negative modulation of insulin receptor signaling activity when insulin is bound?
serine
73
New cards
Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) by __________ during insulin signaling in skeletal muscle, prevents phosphorylation of glycogen synthase (GS) by GSK-3. This results in __________ of glycogen synthesis.
PKB/Akt; stimulation
74
New cards
Reducing the concentration of FFAs in the bloodstream will lead to less __________ phosphorylation of __________ by PKCθ.
serine; both IR and IRS
75
New cards
Which of the following enzymes involved in insulin signaling adds phosphates to phospholipids in order to create interaction partners for other proteins to bind to?
PI3K
76
New cards
Which of the following kinases is activated by an increase in plasma FFAs?
PKCθ
77
New cards
Which of the following events turns a G protein "off" in that it prevents the Gα subunit from interacting with effectors?
The α-subunit of the G-protein dissociates from the βγ-subunit.
GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP on the α-subunit.
The bound GDP molecule is exchanged for a new GTP molecule within the α-subunit.
The G-protein dissociates from the receptor.
The α-subunit of the G-protein dissociates from the βγ-subunit.
GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP on the α-subunit.
The bound GDP molecule is exchanged for a new GTP molecule within the α-subunit.
The G-protein dissociates from the receptor.
GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP on the α-subunit.
78
New cards
Which of the following influences is clearly ***not*** involved in the activation of stress kinases which increase insulin resistance in skeletal muscle?
hyperglycemia
decreased activity of eNOS in response to insulin binding in endothelial cells
increased concentration of free fatty acids in the blood
increased concentration of inflammatory factors in the blood
hyperglycemia
decreased activity of eNOS in response to insulin binding in endothelial cells
increased concentration of free fatty acids in the blood
increased concentration of inflammatory factors in the blood
decreased activity of eNOS in response to insulin binding in endothelial cells
79
New cards
The insulin receptor is which type of catalytic receptor?
a receptor tyrosine kinase
80
New cards
Which chemical second messenger is produced by activated phospholipase C (PLC)?
both DAG and IP3
81
New cards
Which phase of dysfunction in the secretory capacity of pancreatic β-cells in the Metabolic Syndrome is the direct result of acute exposure of these cells to high levels of FFAs and/or glucose in the bloodstream?
the compensatory hyperinsulinemia phase
82
New cards
In the face of long-term elevations in FFAs and/or glucose, the mitochondrial dysfunction evident in β-cells during the relative β-cell failure phase leads to __________ in ATP production and a corresponding __________ in the release of insulin.
a decrease; decrease
83
New cards
Which phase of dysfunction in the secretory capacity of pancreatic β-cells in the Metabolic Syndrome is the result of the loss of β-cell mass?
the relative β-cell failure phase
84
New cards
Low levels of glucose, as seen by the pancreas, will result in all of the following, EXCEPT
Glucagon release
Beta cell depolarization
Quiescent Beta cells
Sodium channel activation in the Alpha cell
Glucagon release
Beta cell depolarization
Quiescent Beta cells
Sodium channel activation in the Alpha cell
Beta cell depolarization
85
New cards
Pancreatic beta cells are able to sense elevations in blood glucose levels because of increased GLUT-4 translocation to the plasma membrane.
True or False
True or False
False
86
New cards
There is a genuine dysfunction in the glucagon secretory mechanism of α-cells of the pancreas in the Metabolic Syndrome.
True or False
True or False
False
87
New cards
Sympathetic signaling to α-cells involves the binding of NE to α1-adrenergic receptors. These receptors are GPCRs that are coupled to a subfamily of G proteins which causes downstream elevations of Ca2+ in the cytoplasm. Given this information, with which subfamily of G proteins must these GPCRs be coupling?
Gq
88
New cards
Hormones secreted from the respective cells in the pancreas are delivered to the hepatic-portal circulation by the pancreatic duct.
True or False
True or False
False
89
New cards
Parasympathetic signaling to β-cells involves the binding of ACh to muscarinic receptors. These receptors are GPCRs that are coupled to a subfamily of G proteins which causes downstream elevations of Ca2+ in the cytoplasm. Given this information, with which subfamily of G proteins must these GPCRs be coupling?
Gq
90
New cards
Sulfonylureas have beneficial effects on β-cells by binding to __________ and causing them to __________.
KATP channels ; close
91
New cards
Which of the following statements about HGP in the Metabolic Syndrome is true?
One adaptation contributing to elevated HGP is an increase in lipolysis
An increase in HGP is observed in all individuals with the Metabolic Syndrome.
An increase in HGP precedes the phase of compensatory hyperinsulinemia.
One adaptation contributing to elevated HGP is a greater parasympathetic activation of the α-cells.
One adaptation contributing to elevated HGP is an increase in lipolysis
An increase in HGP is observed in all individuals with the Metabolic Syndrome.
An increase in HGP precedes the phase of compensatory hyperinsulinemia.
One adaptation contributing to elevated HGP is a greater parasympathetic activation of the α-cells.
One adaptation contributing to elevated HGP is an increase in lipolysis
92
New cards
Excess serine phosphorylation of IR and IRS in hepatocytes will be associated with all of the the following EXCEPT:
Diminished suppression of glycogenolysis by insulin\*\*.\*\*
Increased insulin-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of IR and IRS\*\*.\*\*
Increased glycogen synthesis in response to insulin.
Diminished suppression of gluconeogensis by insulin.
Diminished suppression of glycogenolysis by insulin\*\*.\*\*
Increased insulin-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of IR and IRS\*\*.\*\*
Increased glycogen synthesis in response to insulin.
Diminished suppression of gluconeogensis by insulin.
Increased insulin-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of IR and IRS**.**
93
New cards
In hepatocytes, decreased tyrosine phosphorylation of the IR and IRS-1 will result in decreased HGP.
True or False
True or False
False
94
New cards
Control of the level of gene transcription for the enzymes PEPCK and G6Pase is the major mechanism for regulation of gluconeogenesis. Which of the following signaling proteins are NOT involved in the DOWN-regulation of gene expression for PEPCK and G6Pase?
PKB/Akt
p38 kinase
PLC
IRS-1
PKB/Akt
p38 kinase
PLC
IRS-1
PLC
95
New cards
Hormone-mediated effects on HGP occur most rapidly through cellular adjustments to gluconeogenesis, whereas the modulation of glycogenolysis and glycogenesis takes much longer.
True or False
True or False
False
96
New cards
A person with the Metabolic Syndrome will very likely end up with a reduced level of insulin secretion by beta-cells. This will almost certainly lead to:
less inhibition of glucagon secretion from alpha-cells in the pancreas
97
New cards
GSK-3 can disrupt insulin signaling in two ways. It can do so by phosphorylating serine residues on IRS-1, and it can also do so by phosphorylating and inhibiting glycogen synthase.
True or False
True or False
True
98
New cards
For hepatocytes, which of the following events ***will not occur*** in response to excessive serine phosphorylation of IR and IRS?
diminished suppression of glycogenolysis by insulin
diminished suppression of gluconeogensis by insulin
diminished HGP
decreased insulin-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of IR and IRS
diminished suppression of glycogenolysis by insulin
diminished suppression of gluconeogensis by insulin
diminished HGP
decreased insulin-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of IR and IRS
diminished HGP
99
New cards
When activated by the insulin signaling pathway, PP1 will increase the activity of ______ and decrease the activity of ______.
Glycogen synthase, glycogen phosphorylase
100
New cards
The transcription of the genes for the enzymes PEPCK and G6Pase is the major mechanism for the regulation of gluconeogenesis. Which of the following proteins is ***not*** involved in their downregulation (in the reduction of the expression of those genes)?
Ser-phosphorylated GSK-3
activated PKA
activated insulin receptor
Tyr-phosphorylated IRS-1
Ser-phosphorylated GSK-3
activated PKA
activated insulin receptor
Tyr-phosphorylated IRS-1
activated PKA