Organic Chemistry Chapter 4
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
WHat is a reaction mechanism?
shows step by step of how a reaction occurs
What are the steps of a free-radical chain reaction?
initiation
Propagation
Termination
What happens in the initiation step?
the radical intermediate forms
What happens in the proprogation step?
the intermediate reacts with a stable molecule to produce another reactive intermediate (and a product molecule)
What happens in the termination step?
side rxns destroy the reactive intermediate
WHat are free radicals?
reactive species with odd numbers of electrons
What is an exothermic reaction?
heat is released
What is an endothermic reaction?
heat is absorbed
What types of products do reactions favor?
products with the lowest enthalpy (strongest bonds).
What is a transition state indicated with?
‡
What are the highest energy points in an energy reaction diagram?
transition states
What is the slowest step of a reaction?
the step with the highest activation energy.
What happens to the rate of the reaction as Ea increases?
decreases
What happens to the rate as temperature increases?
rate increases
How do fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine react??
fluorine reacts explosively (low Ea)
chlorine reacts at a moderate rate (higher Ea)
bromine reacts at a low rate (must be heated) (high Ea)
iodine does not react (highest Ea)
How do you assign priority to hydrogens in a structure?
by seeing how many hydrogens are bonded to a carbon
What is a primary hydrogen?
all of the hydrogens in a structure with 3 bonded hydrogens
What is a secondary hydrogen?
all of the hydrogens in a structure with 2 bonded hydrogens
What is a tertiary hydrogen?
all of the hydrogens in a structure with 1 bonded hydrogen
What degree of hydrogens are more reactive?
3>2>1
What halogens are selective for higher degree hydrogens?
bromine is highly selective and will target the lowest Ea hydrogens (3 degree)). chlorine is moderately selective. Fluorine is not selective.
What is the Hammond Postulate?
related species similar in energy are also similar in structure, The structure of the transition state resembles the structure of closest stable species.
What does the transition state resemble in an endothermic reaction?
the product
What does the transition state resemble in an exothermic reaction?
the reactant
What are reactive intermediates?
short lived species that are never present in high concentrations
What are the types of carbon reactive intermediates?
carbocation, radial, carboanion, carbene
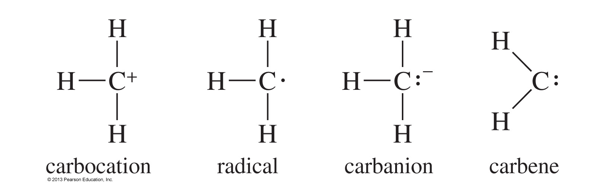
How does the stability of the carbocation work?
3>2>1>methyl
How does the stability of the radical work?
3>2>1>methyl
How does the stability of carboanions work?
methyl>1>2>3
How does the stability of carbenes work>
none
What are the properties of carbocations?
electrophilic, strong acids
What are the properties of radicals?
electron deficent
What are the properties of carbanion?
nucleophilic, strong bases
What are the properties of carbenes?
both nucleophilic and electrophilic.