A-level Biology (U1)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are monomers?
Monomers are the smallest single units from which larger molecules (such as polymers) are made.
What are polymers?
Polymers are long chains of molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together
What are monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are monomers (the smallest single units) that make up carbohydrates
What are examples of monomers?
Examples of monomers:
Monosaccharides
Amino Acids
Nucleotides
How are monomers seperated or joined?
Monomers are separated or joined by:
A condensation reactions joins 2 monomers together with the formation of a chemical bond - a water molecule is lost in the formation of the bond
A hydrolysis reaction separates 2 monomers by breaking the chemical bond between them, using a molecule of water to do so
What are common examples of monosaccharides?
Common examples are:
Glucose
Galactose
Fructose
What are carbohydrates made up of?
Carbohydrates are made up of the elements:
Carbon (C), Oxygen (O), and Hydrogen (H)
What are the common disaccharides?
Common disaccharides are:
Maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
How is maltose formed?
Maltose is formed from a condensation reaction between 2 alpha glucose molecules,
This releases a molecule of water and forms a (1,4) glycosidic bond between the monomers
How is sucrose formed?
Sucrose is formed from a condensation reaction between a glucose and fructose molecule,
This releases a molecule of water and forms a glycosidic bond between the monomers
How is lactose formed?
Lactose is formed from a condensation reaction between a glucose and galactose molecule
This releases a molecule of water and forms a glycosidic bond between the monomers
What is the molecular formula for maltose, sucrose and lactose
The molecular formula is:
C12H22O11
What is an isomer?
An isomer is a molecule which has the same molecular formula but a unique arrangement of atoms in space.
This means that they will have different chemical and physical properties
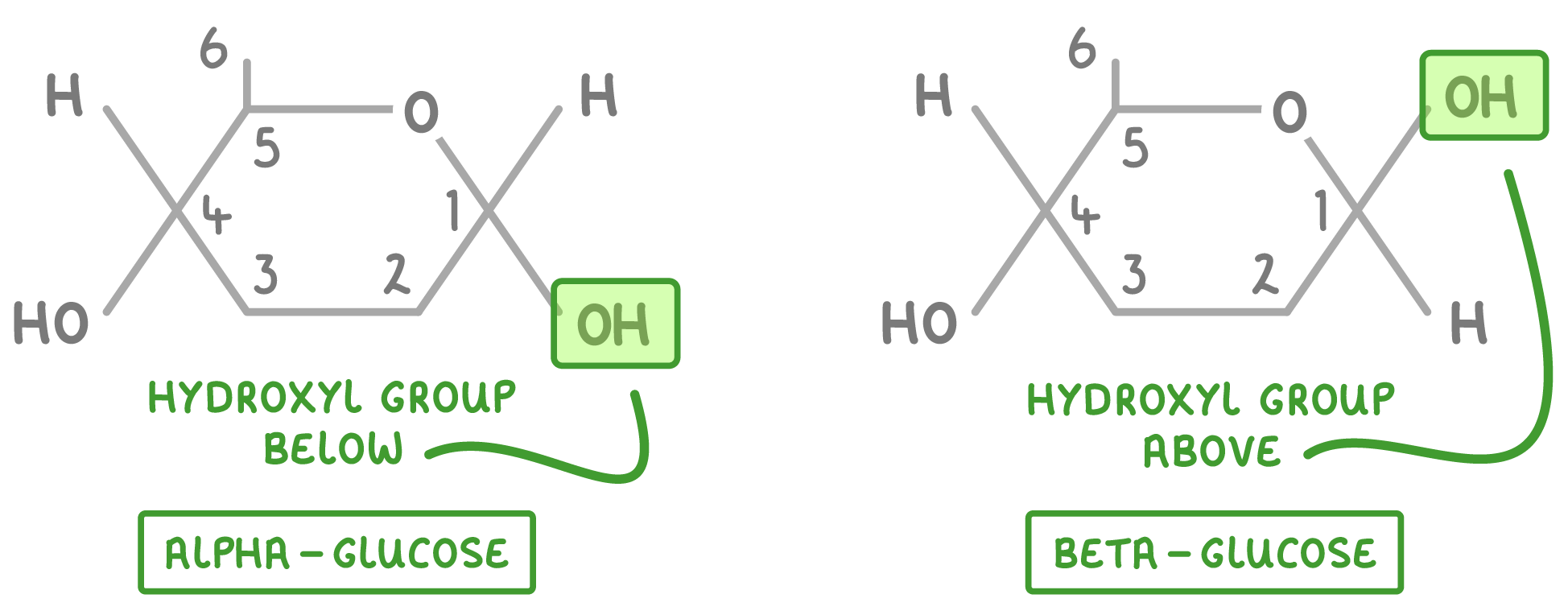
What are the 2 isomers of glucose?
In alpha glucose, the hydroxyl group is below
In beta glucose the hydroxyl group is above
How are polysaccharides formed?
Polysaccharides are formed by the condensation reaction of many monosaccharides with glycosidic bonds between them, to form a long chain carbohydrate
What are the examples of polysaccharides?
Examples are:
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
What are the 2 structures of starch?
The two structures of starch:
Amylose
Amylopectin
Describe the structure of amylose
Structure of Amylose:
Long and unbranched
Tightly coiled into a helical shape - stabilized by internal hydrogen bonds between the glucose units
Made up of chains of alpha glucose

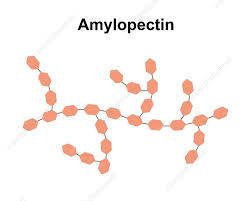
Describe the structure of amylopectin
Structure of Amylopectin:
Long and Branched
Contains many side branches
Made up of chains of alpha glucose
Describe the function of amylose
Function of Amylose:
Long and Unbranched — means it is a large molecule, hence is a good for storage as it cannot diffuse out of the cell membrane
Tightly coiled — means it is a good storage molecule as more of the molecule can be stored in a smaller space

Describe the function of amylopectin
Function of Amylopectin:
Many side branches - Means they are easily hydrolysed
— Allow enzymes to break down the molecule easier, to get access to the glycosidic bonds and break them down easier, allowing glucose to be released quickly
Properties of starch
Properties of starch:
Insoluble - Doesn’t affect the water potential of the cell (hence it is a good storage molecule)
Large molecules - Cannot pass across the cell membrane, so cannot diffuse out of the cell (good storage molecule)
Compact - more can be stored in a smaller space
Branched - easily hydrolysed to rapidly release glucose
How do you test if starch is present in a sample?
To test for starch:
Add test sample to a test tube
Add iodine dissolved in potassium iodide solution to test sample
If sample turns orange-brown to blue-black then starch is present
If no starch is present, then sample stays the same colour (no colour change)