Bio 112 Exam 2
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Macroevolution
Evolutionary change above the species level.
Origin of first cells
-complex due to not having the same conditions as early earth
-earth was hot, mostly oceanarium, volcanoes, low O2.
What were the easiest fossils?
prokaryotes
what followed mass extinction?
Major radiation
evo-devo
evolutionary developmental biology
exaptation
the process in which existing structures take on new functions through descent with modification (ex: porcupine had hair and adapted to spikes)
regulatory genes
control gene expression
heterochrony
Evolutionary change in the timing or rate of an organism's development. (ex: chimp skull vs. human skull)
Paedomorphosis
a changing in timing produces a sexually mature adult with juvenile features (ex: axolotl is a baby salamander but can still reproduce)
Homeotic genes
Genes that determine basic features of where a body part is.
viruses-origin
there are no fossils so we do not know when they were created. Only proof we have is viral footprint.
Who discovered viruses?
Ivanovsky: worked with TMV (Tobacco mosaic virus), poured through a filter and something smaller than bacteria was still left behind, considered toxic.
Twort: (1935), isolated and described a virus
When was the electron microscope invented?
1930s
virus size/imaging
20-400 nm, too small for light microscope. They contain DNA, RNA, and protein.
Virus structure
acellular
no metabolism
no growth
must be inside host cell to replicate- obligate intercellular parasite
can infect all life forms
helical viruses
hollow, cylindrical capsid
Ebola- flexible
TB-non flexible
enveloped virus
A virus enclosed within a phospholipid membrane derived from its host cell.
(Herpes family)
Icosahedral viruses
Capsids forming 20 triangular faces and 12 corners. (adenovirus)
Complex virus
A virus with a complicated structure, such as a bacteriophage.
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
DNA viruses
enter the host cell's nucleus and are replicated and assembled there. Uses RNA polymerase for transcription of mRNA and our ribosomes.
RNA viruses
Single stranded, looks like mRNA so it can go directly to host ribosomes to make proteins.
Retroviruses
use reverse transcriptase to copy their RNA genome into DNA
entry inhibitors (fusion inhibitors)
bind to viral particles and prevents HIV entry into healthy cells.
reverse transcripts inhibitors
blocks ability to turn to DNA
intergrade inhibitors
Blocks proviral DNA from getting into your genome.
Protease inhibitors
inhibits the ability to cut long proteins into functional smaller proteins.
Prions
"protein gone bad" a protein that was folded wrong and cause other proteins to follow.
Capsules/ slime layers
carbs and proteins allow cells to stick to surfaces.
Qurum sensing
chemicals sent out in the slime layer to communicate with other cells.
Fimbria
A short, hairlike proteins of a prokaryotic cell that helps it adhere to the substrate or to other cells. Used to make biofilm
Biofilm
bacterial cells adhering to surfaces in a protective slime allowing the resistance to antibiotics and cleaners.
chemotaxis
Cell movement that occurs in response to chemical stimulus
phototaxis
movement in response to light
geotaxis
movement in response to gravity
structure of prokaryotic bacteria
no membrane bound organelles
no organelles
have ribosomes
no nucleus
no microtubules
invagination for aerobic cellular respiration
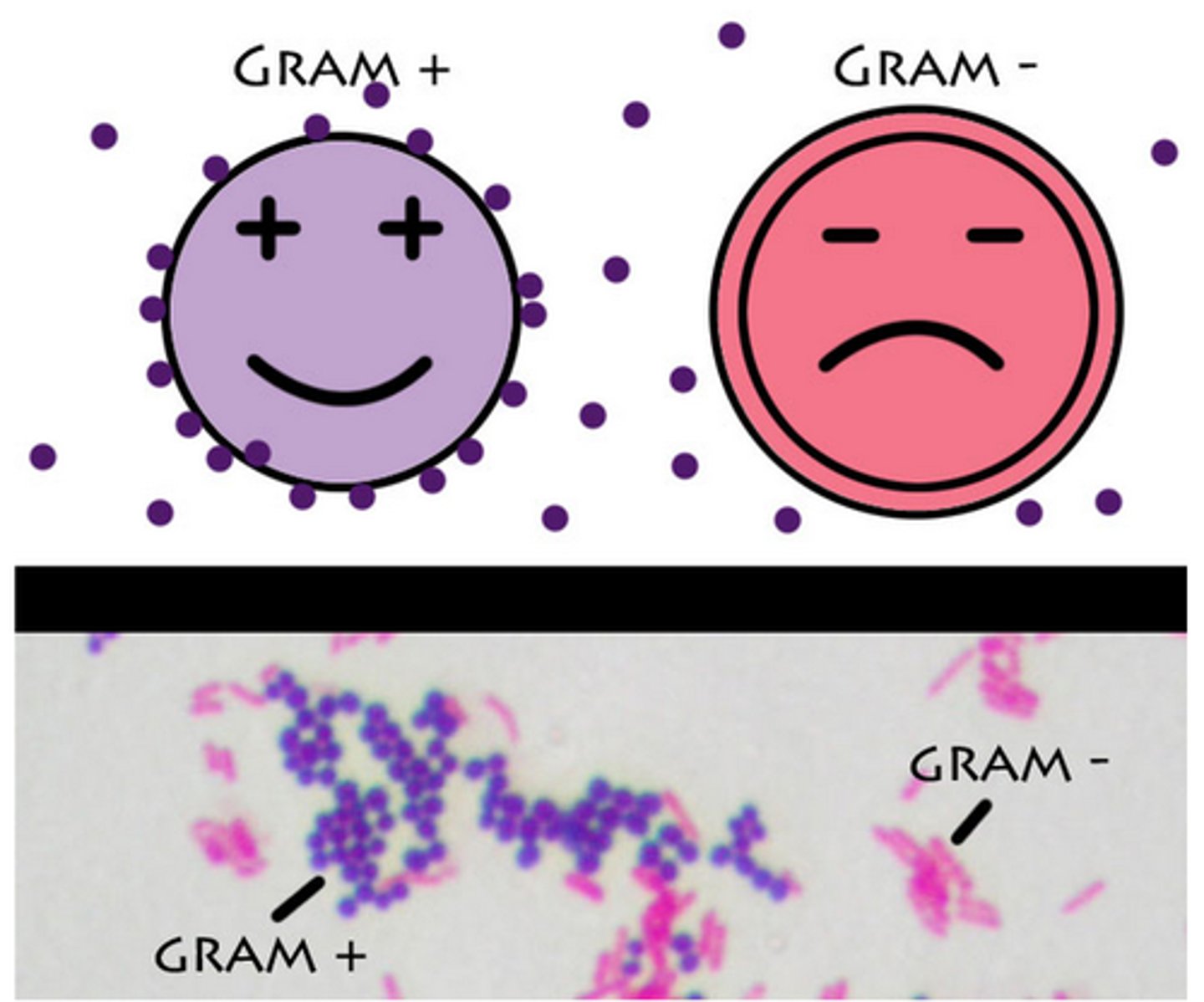
Gram staining
+ = dark purple (one cell plasma membrane, periplasmic space, and cell wall made of peptiodoglycon)
- = light pink (one cell plasma membrane, 2 periplasmic spaces, one cell wall, and one outermsmbrane made of lipoplyoacharides).
Which of these plastids do not contain pigment?
a. chloroplast: photosynthesis
b. chromoplast: pigment synthesis
c. luekoplast: storage of metabolic things
answer: C
how do bacteria gain genetic diversity if they can't have sex?
-mutation: one mutation can change phenotype
-tranformation: Griffith Experiment
-transduction: transfer of gene by a virus, DNA carried by bacteriophages
-conjunction: "sex" pills, no offspring are made
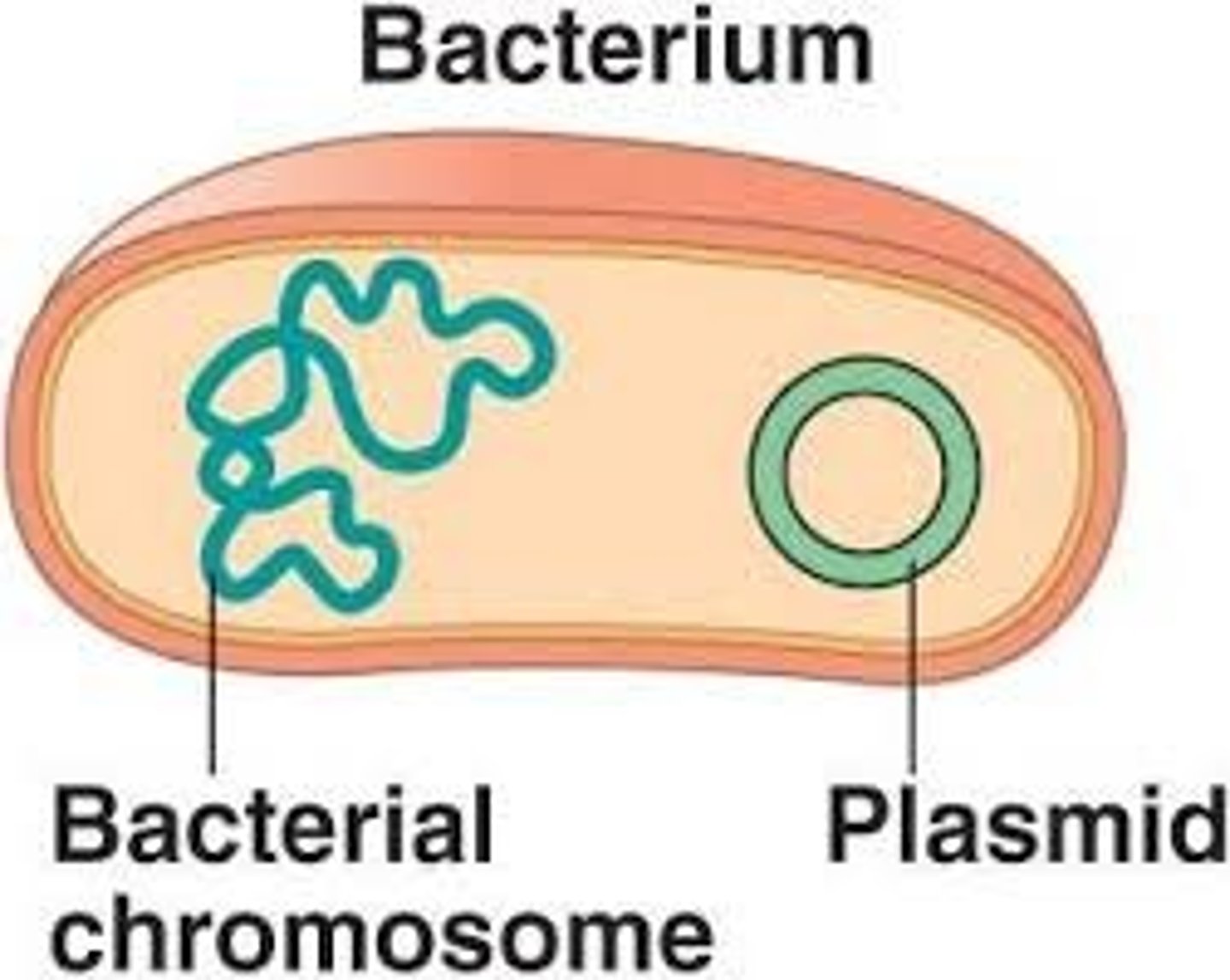
Plasmid
A small, circular section of extra DNA that confers one or more traits to a bacterium and can be reproduced separately from the main bacterial genetic code. Can add diversity.
Binary fission
bacteria cells splitting rapidly. Growth is limited by food, moisture, crowding.
endospores
A resistant, dormant structure formed inside of some bacteria that can withstand harsh conditions
Griffith's experiment
genetic material could be transferred between dead bacteria and living bacteria
Apicomplexans
A type of parasitic protozoan. Some apicomplexan cause serious human disease like malaria. Life cycle is mostly haploid.
Ciliates
A protozoans that move by waving tiny, hair-like organelles called cilia.
unicellular
aquatic
asexual
feed on bacteria in algae
no cell wall
oomycytes
contains 5 different groups of filamentous, multinucleac, absorptive cells.
Archeaplastida
Includes both Red Algae & Green Algae
This group gave rise to land plants!
This diverse group is also important as photosynthetic organisms in aquatic systems, including Volvox & "sea weeds"
paraphyletic group
green algae, no land plants.
red algae
marine algae in which the chlorophyll is masked by a red or purplish pigment (phycotheran), helps builds reefs.
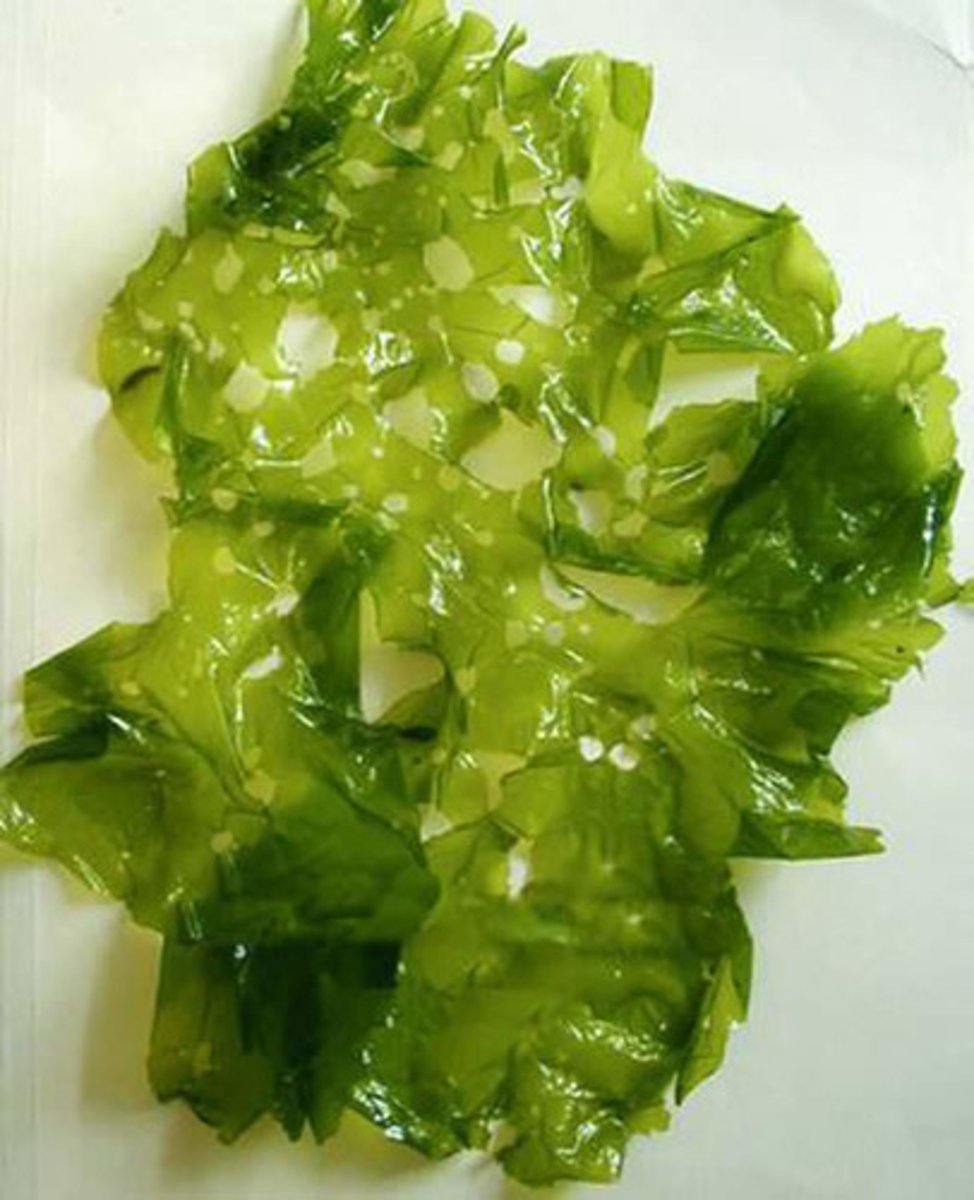
Chlorophytes
part of green algae; aquatic, creates oxygen, (phytoplankton-primary producers in food chain)

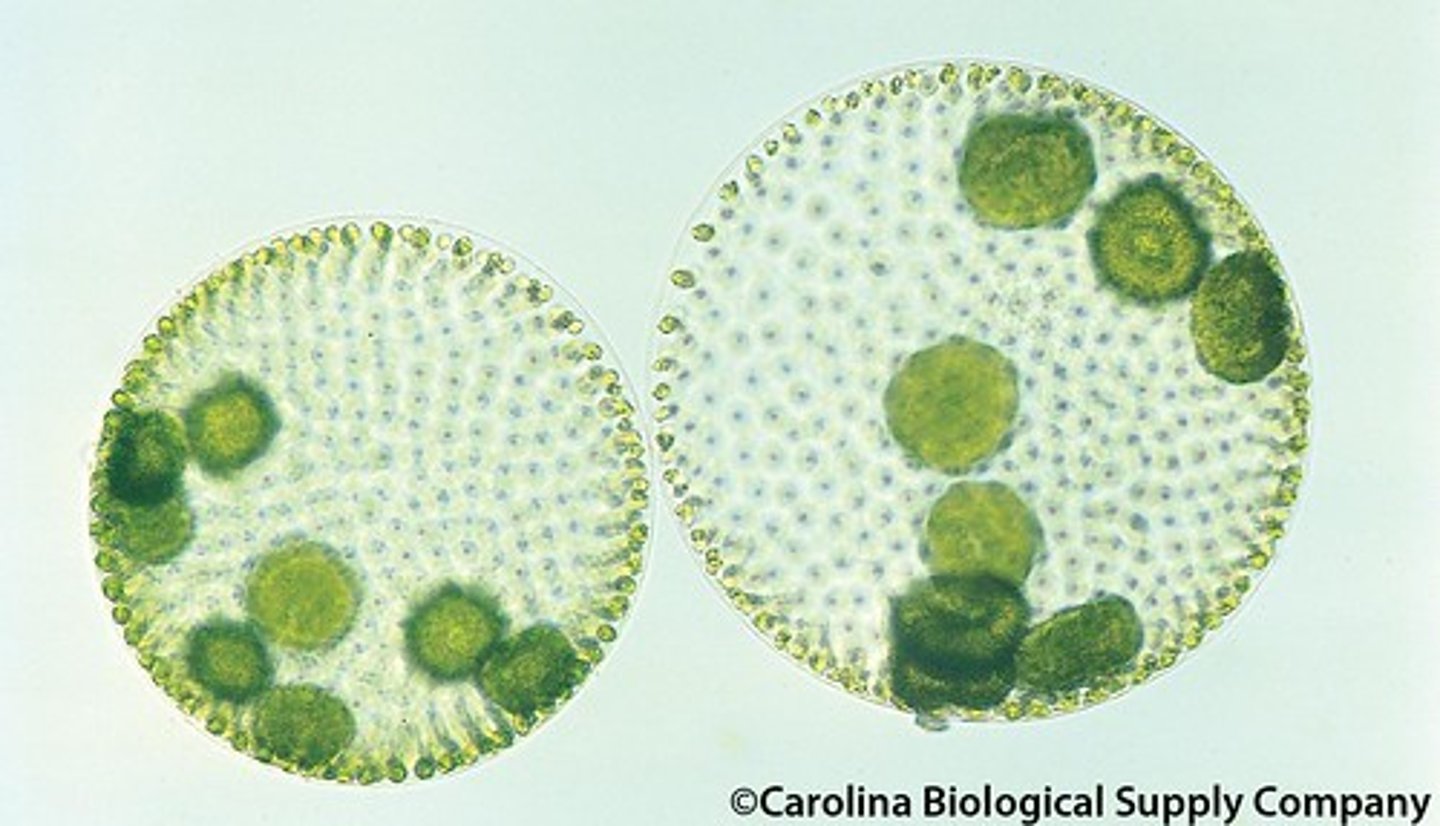
Volvox
colonial green algae
Ameobozoans
Slime molds, tubulinds, entameobas, move and feed by pseudopodia, no cell wall.
Tubulinds
Amoeba proteus, feeds on other bacteria
Entramoebas
parasite on animals, spreads by durable cyst (ex: Entamoeba histolytic- kill and digest lining of intestines).
Heterotrophic
An organism that cannot make its own food. (absorptive)
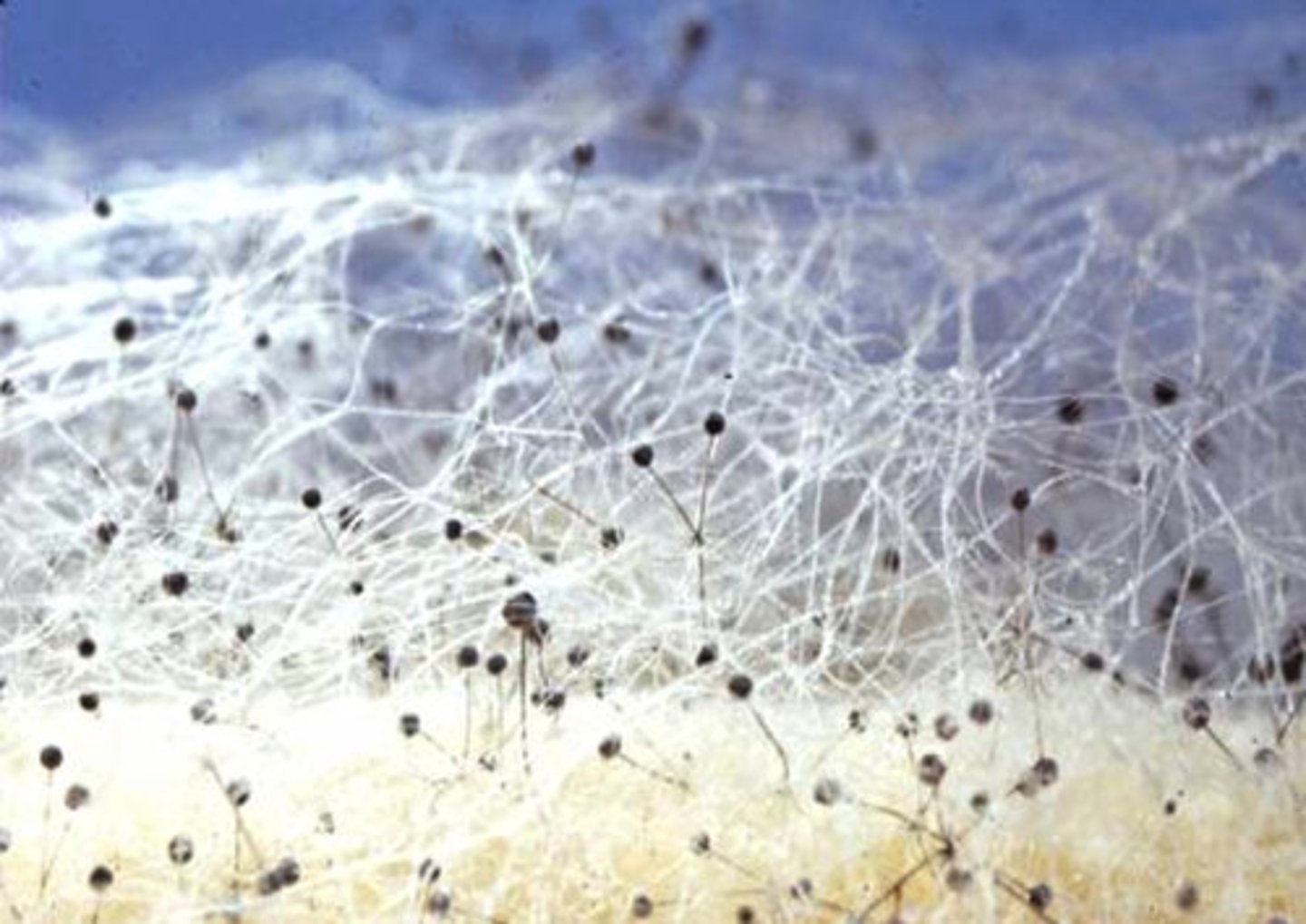
Chytrids
aquatic and produce flagellated spores; they were the first fungi, contain hyphae.
yeast
unicellular fungi
mycelium
main fungus body, made of hyphae, often underground or within host.
hyphae
tubular cells with rigid cell walls contains chitin. Absorptive heterotrophs and feed off organic materials.

chitin
polymer that is made of N-acetylgulcosamine.
septate in hyphae
the cross walls (coenocytic), allow for rapid cytoplasmic streaming.
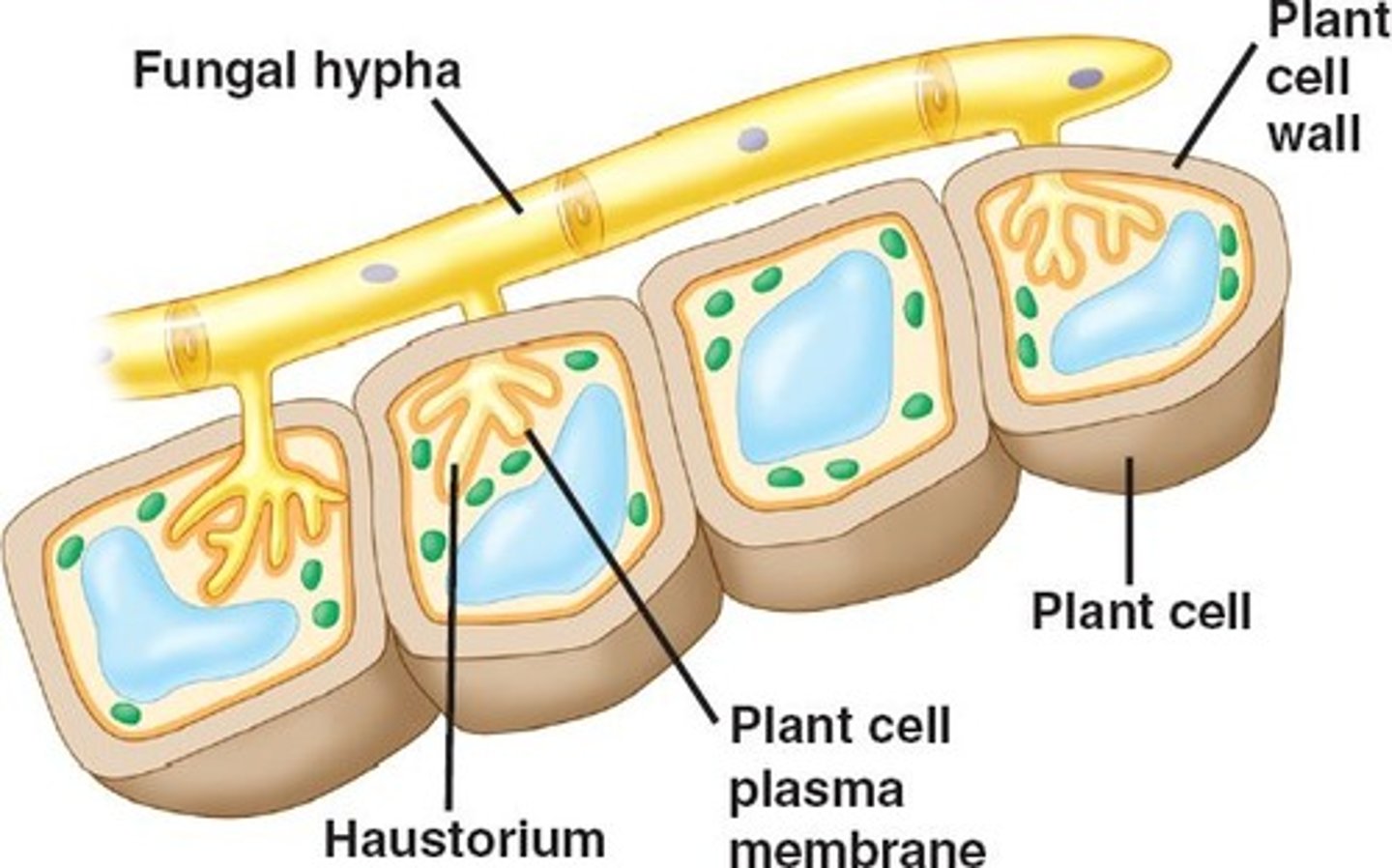
Haustorium
A hypha of a parasitic fungus that enters the host's cells, absorbing nutrition directly from the cytoplasm without disrupting the cell wall.
Which organelle that is an essential compound of all other eukaryotic cells is functionally absent in diplomonads and parabasalids and no longer works?
mitochondria
Euglenozoans, online the diplomats & parabasalids, have...?
a flagellum made of crystalline rod
which of the listed protists can produce red tide?
dinoflagellates
which of the listed protists makes a cell wall out of silica?
diatom
In fungi, the combined processes of plasomgamy and karyogamy are equivalent to what in a plant or animal?
fertilization
a colonial eukaryotic organism is composed of cells:
that are sharing resources
what is the function of Cumbria in bacteria?
adhere to surfaces
which of the following things are true about movement in bacteria?
can be active and directed toward or away from stimulus.
small rings if DNA in bacteria are called which of the following?
plasmids
which of the things below describes a heterotrophic organism?
consumes organic material for its carbon
a prokaryote that does both photosynthesis and oxygen-dependent cellular respiration is:
a photo autotroph and obligate aerobic
which of the following describes a class of antivirals called protease inhibitors?
drugs that inhibit an enzyme which would normally cut a long protein into smaller functional proteins.
which microscope must be used in order to see viral particles?
electron microscope
which of the following is not true about viruses
they fall into the classification of prokaryotes.
What is a sporangium?
Multicellular organ on the sporophyte that produces spores in order to begin the lifecycle of a gametophytes.
Gametophyte is how many N?
1N
Diploid
2N
archegoniophore
protects the sporophytes from the enviornment. (liverwort)
When are sperm and egg produced in the life cycle of bryophytes?
during antheridia, sperm is dispersed and fertilizes to archegonia-egg.
give 3 examples of bryophytes
mosses, liverworts, hornworts.
What 2 organisms make up lichen?
fungus and algae/cynobacteria.
True or false: Bryophytes and lichen are pioneer species?
true
Name 2 examples of vascular, seedless plants.
Lycophytes (club mosses), monilophytes (ferns)
Why is vascular tissue important?
allows plant to be taller, larger, and produce more sporophytes.
phloem?
located in the leaves, carries sugar and organic products
xylem?
located in truck and roots, carries water and minerals.
tracheids?
strengthens the walls combined with lignin. Only fungus can break this down.
what becomes the dominant structure that we see today?
2N
tropism?
A growth response of a plant toward or away from a stimulus
microphyll leaves?
1 vein (1 vascular bundle) - lycophytes
megaphyll leaves
multiple veins in leaves - ferns and seed plants.
Why are seedless vascular plants important?
during the Paleozoic era, they increased food supply, lowered CO2, increased O2. Allowing animals to thrive. (carbon-fixation)
all caterpillar moth larvae (but not adults) are able to produce silk. If a species of moth is able to produce silk as a winged adult, we could call this a case of...
paedomorphosis
the basic make up of a virus consists of which of the following things?
RNA or DNA and a protein coat
Describe the structure of streptococci
linear chain of cocci cells
Describe the structure of staphylococcus
clusters of cocci cells
Assuming a Gram is positive bacteria had a capsule layer, what layers would you encounter if you went from the outside of the bacteria towards the middle?
Capsule, cell wall, periplasmic space, cell membrane.
Assuming a Gram is negative bacteria had a capsule layer, what layers would you encounter if you went from the outside of the bacteria towards the middle?
capsule, outermsmbrane, periplasmic space, cell wall, periplasmic space, cell membrane.