Dental Anatomy and Occlusion
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Anterior tooth placement gives which sounds?
F and V sounds
TRUE or FALSE
A function of incisors is chewing
FALSE
Answer: Cutting and incising
Which sounds do the human dentition assist with?
- S sounds
- F sounds
- V sounds
Functions of the Human Dentition
1. Helps in _____
2. Aids in _____ and _____
3. Gives _____ and _____ to the face
4. Helps in giving facial _____
5. Like in animals, it may be used for _____ and _____
1. mastication
2. articulation, speech
3. shape, beauty
4. expressions
5. self-protection, attack
What are the type of dentitions?
Primary and Permanent
TRUE or FALSE
Premolar is found in Primary dentitions
FALSE
Answer: Found only in the Permanent dentition
Which process the longest root and are located at the corners of the dental arch?
Canines
What are important guides in occlusion due to their anchorage and position in the dental arches?
Canines
What is for seizing, piercing, tearing and cutting of food?
Canines
What tear and also grind?
Premolars
Premolars are _____ to canines, _____ to molars
distal, mesial
What dentition is first to contribute in maintaining Vertical Dimension to the face?
Premolars
Which completes the smile by eliminating dark corners?
Premolars
Which teeth contribute to vertical dimension?
Premolar and molars
What are large multicusped?
Molars
What function in crushing, grinding, and chewing?
Molars
What are V-shaped valleys between adjacent teeth?
Embrasures
Embrasures aids in?
Self-cleaning
What are the 4 types of Embrasures?
- facial or buccal
- lingual
- incisal or occlusal
- gingival
Class I Occlusion
Maxillary and Mandibular on same arch
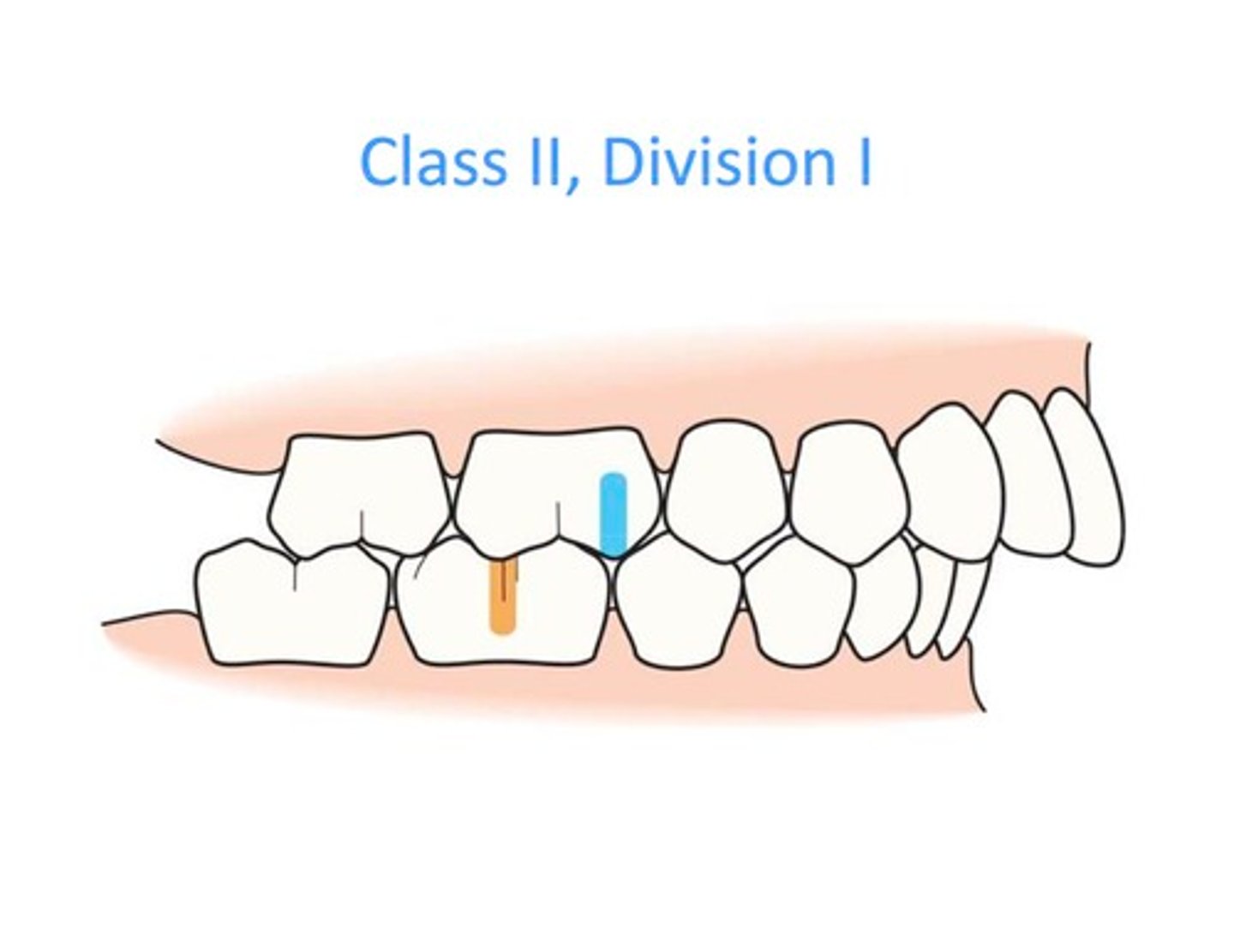
Class II Occlusion
Maxillary arch is forward
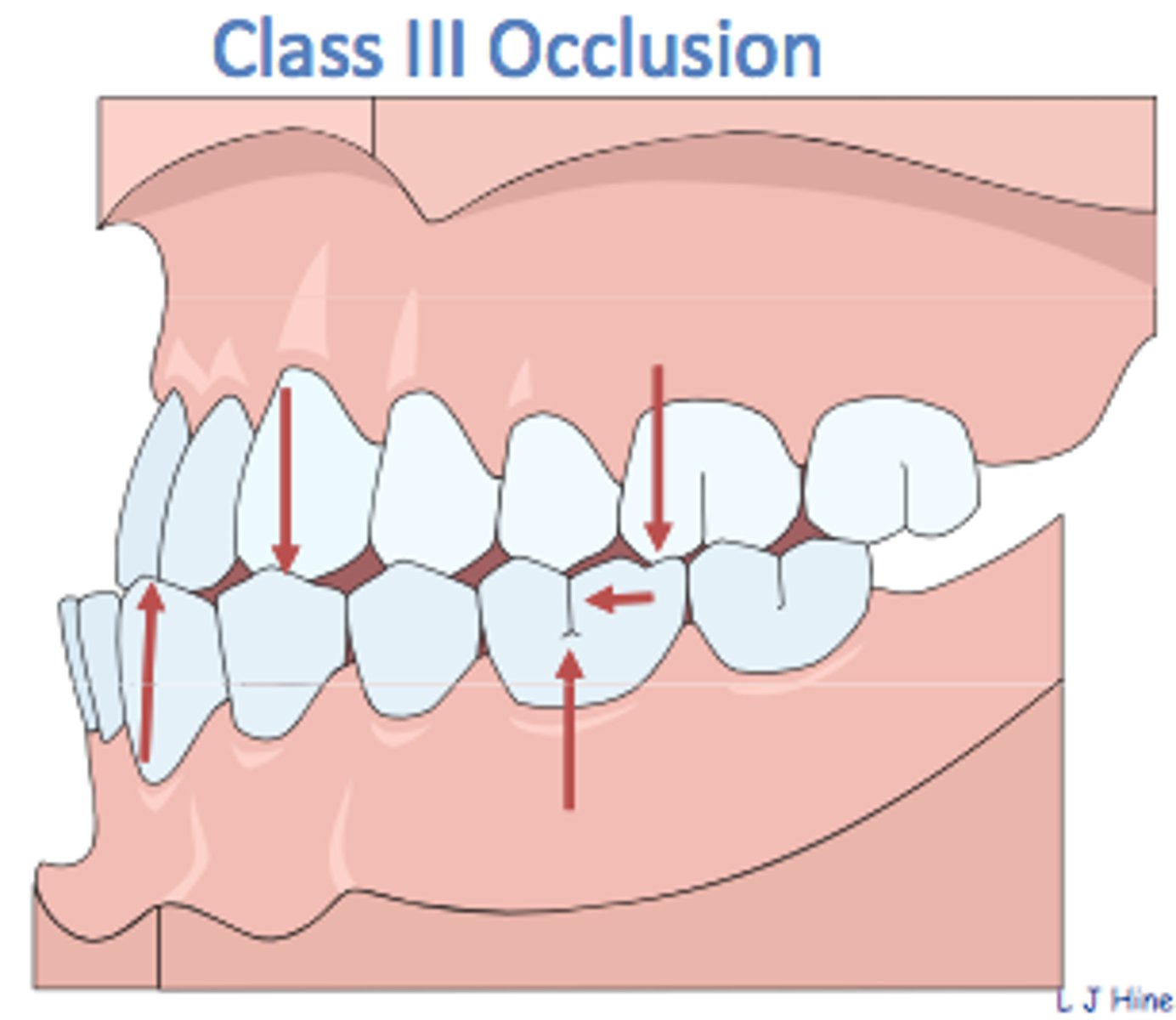
Class III Occlusion
Maxillary arch is backward
Human teeth are divided into classes on the basis of what two features?
Form and function
What are the classes of teeth found in primary dentitions?
Incisor, canine, and molar
What are the classes of teeth found in permanent dentitions?
Incisor, canine, premolar, molar
What are the two types of human teeth?
Primary and secondary
The teeth serve four main functions:
1. Mastication
2. Esthetics
3. Speech
4. Protection of supporting tissues
What is the vermilion border of the lips?
Transition from highly keratinized external skin to less keratinized internal skin.
How are F and V sounds produced?
The upper lip contacts the wet-dry line of the lower lip.
The protective form of tooth function applies to what two things?
1. Contiguous investing tissues
2. Pulp
Where are incisors located?
Entrance to the oral cavity
How many incisors are there per quadrant?
Two incisors
Human incisors are responsible for:
Cutting and incising
How many incisors are there per arch?
Four
What are facial features of the maxillary central incisor? Incisal edge, cervical line, mesial outline, distal outline.
1. Incisal edge: nearly straight
2. Cervical line: gracefully curved
3. Mesial outline: straight
4. Distal outline: Rounded
What are three features of the lingual aspect of the maxillary central incisor?
1. Mesial and distal marginal ridges
2. Incisal edge
3. Prominent cingulum
What shape do the mesial and distal aspect of the proximal view of maxillary central incisor have?
Distinctive triangular outline
The incisal ridge of the crown of the maxillary central incisor is aligned on the _____________ axis of the tooth.
Long
The incisal crown of the maxillary central incisor is what shape?
Triangular
Where is the mesial contact point for maxillary central incisors?
At the incisal
Where is the distal contact point for maxillary central incisors?
junction of the incisal third and the middle third
What are facial features of the mandibular central incisor? Incisal edge, cervical line, mesial outline, distal outline.
1. Incisal edge: straight
2. Mesial outline: It descends apically from a sharp mesial angle
3. Distal outline: It descends apically from a sharp distal angle
What is the difference between the lingual surface of the maxillary and mandibular central incisor in regards to marginal ridges and cingulum?
No definite marginal ridges and small cingulum in mandibular central incisors.
What shape do the mesial and distal aspect of the proximal view of mandibular central incisor have?
Triangular outline
The incisal edge of the mandibular central incisor is perpendicular to what line?
Line passing labiolingually through the tooth.
What are the three esthetic functions of the incisor?
1. Smile
2. Lip support
3. Facial harmony
What tooth has the longest root?
maxillary canine
What is the function of the canine?
Tearing food
From a proximal view, what is the shape of a canine's crown?
Triangular
Why are canines good candidates for abutment teeth?
They have a stocky crown and a long root.
What teeth acts as a guide during occlusion?
Canine
What are the lingual features of the maxillary canine? Ridges (mesial, distal, lingual) and cingulum
1. Distinct mesial and distal marginal ridges
2. Well-developed cingulum
3.Prominent lingual ridge that divides the lingual surface into mesial and distal fossae.
How do maxillary and mandibular canines differ in regards to lingual features?
Mandibular canines have less defined lingual features.
Where are canines located?
At the corners of the dental arch.
What are the two esthetic functions of the canine?
1. Lip support
2. Turn the corner
What are the two functions of the premolars?
1. Tearing and grinding food
2. Maintain vertical dimension
What features of the premolar permit their function?
1. Facial cusp resemble canines
2. Lingual cusps have a rounded anatomic form
Where are premolars located?
Distal to canines and mesial to molars.
What is the esthetic function of premolars?
complete smile by eliminating dark corners.
What are the functions of molars?
1. mastication
2. maintain proper vertical dimensions of face
What are embrasures?
The V-shaped valleys between adjacent teeth.
What is the function of embrasures?
Spillway for food to escape during chewing, facilitating the self cleansing process.
What are the four types of embrasures?
1. Facial
2. Lingual
3. Incisal
4. Gingival
What is a class I occlusion?
normal occlusion
What is a class II occlusion?
Mesial buccal cusp of maxillary first molar is mesial to the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar
What is a class III occlusion?
MB cusp of the max first molar occludes posteriorly to the buccal fissure of lower first molar, or even in the embrasure between first and second molars