Principles of Aerobic and Anaerobic Exercise
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Adult ACSM physical activity recommendations
150-300 min/week of moderate intensity activity OR 75-150 min/week of vigorous intensity activity
resistance training at least 2 days/week with at least 1 set of 8 to 12 repetitions for all major muscle groups
Child Ages 3-5 ACSM physical activity recommendations
active throughout the day
Child Ages 6-17 ACSM physical activity recommendations
60 or more minutes/day of moderate to vigorous physical activity
activities that promote muscle strength 2-3 days/week
Energy Systems defined
Metabolic systems involving biochemical reactions resulting in the formation of metabolites used for cell function and activity
What are the three types of energy systems?
phospagen system (ATP-PC)
Anaerobic Glycolytic System
Aerobic System
Energy Systems curve
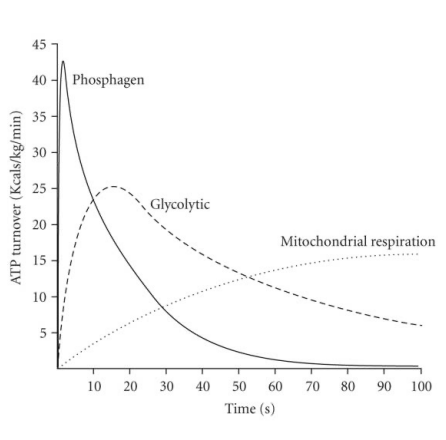
Phosphagen System (ATP-PC)
no oxygen required, uses ATP and PC
energy for short, quick bursts of activity
major energy source for first 30 seconds of exercise
Anaerobic Glycolytic System
no oxygen required, uses glucose through glycolysis (slow glycolysis)
energy for moderate intensity, short duration activities
major energy source for 30th-90th second of exercise
Aerobic System
oxygen required, uses glycogen, fats, and protein through Krebs cycle and electron transport chain
energy for low intensity, long duration activities
predominate energy source after 2nd minute of exercise
Aerobic Exercise
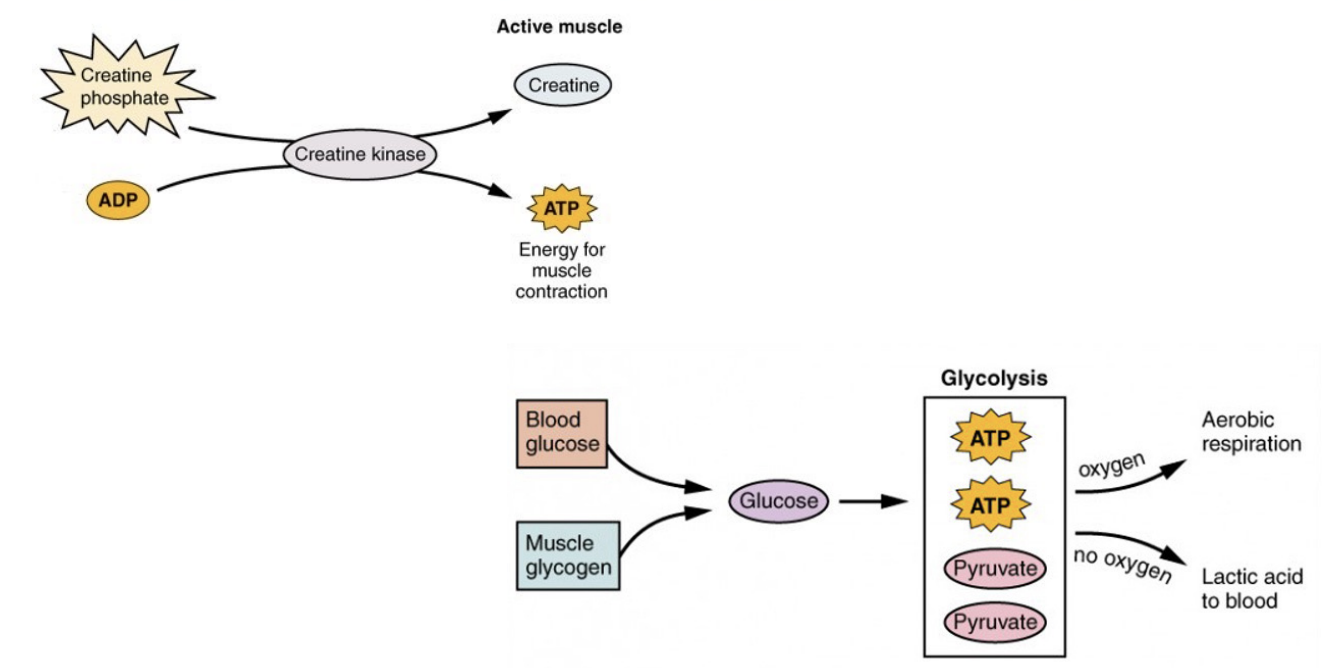
Aerobic exercise is defined as
continuous training consisting of large, rhythmic movements for asustained duration (running, walking, jogging)
what type of system(s) does aerobic exercise use?
aerobic energy system
anaerobic exercise is
shorter duration, high intensity exercise (weightlifting, resistance bands, exercise machines, etc)
anaerobic exercise utilize which system(s)
phosphagen and anaerobic glycolytic systems
What are the three principles of exercise?
overload principle
specific adaptation to imposed demands (SAID) principle
Reversibility principle
What is the overload principle
guides the use of resistive exercise in improving muscle performance
If muscle performance is to improve, resistance load must exceed metabolic capacity of the muscle (challenge the muscle)
what is the SAID principle?
To improve specific muscle performance elements, the resistance program should match those elements
create specific exercises to best meet goals of patient
Reversibility Principle
If training is stopped, the improvements are reversed and detraining begins 1-2 weeks after stopping resistance exercises (lost in average of 2-4 weeks)
What are the three muscle performance parameters?
strength
power
endurance
Strength
muscle’s ability to exert force during a single maximal effort
power
muscle’s ability to exert force over time
power formula
Power = (Force * Distance)/Time
Endurance
muscle’s ability to continue to perform repetitions or sustained activities while resisting fatigue
what two things increases linearly with increasing workload/exercise intensity?
heart rate (10bpm/MET)
systolic blood pressure (10 mmHg/MET)
what decreases slightly or remains undchanged with increased exercise intensity?
diastolic blood pressure (vasodilation)
what remains unchanged during increased exercise intensity?
SpO2
what increases up to 4x during increased exercise intensity
respiratory rate (from 12 to 48 breaths/min)
cardiac output (from 5L to 25-30L/min with max activity)
what increases 8x with increased exercise intensity
tidal volume ( from 0.5L/breath to 4.0L/breath)
what increases 30x with max activity
minute ventilation
what is an abnormal response/red flag?
resting SBP greater than 180 mmHg or DBP greater than 105 mmHg, exercise contraindicated
what blood pressure should you stop exercise?
220/105 mmHg
at what amount of SBP decrease should you stop exercise?
more than 10 mmHg
what other reasons should you stop exercise
unexplained dyspnea, abnormal heart rate response, chest pain, arm pain, dizziness, confusion, lightheadedness, pallor
at what abnormal heart rate response should you stop exercise?
10 beats/min
what does FITT-VP stand for?
F- frequency
I- intensity
T- type
T- time
V-volume
P- progression
Frequency
number of exercise sessions per day or per weekly
initially low/high intensity and low/high rep exercises can be performed multiple times a day (great for post op)
initially low intensity and low rep exercises can be performed multiple times a day (great for post op)
Intensity
load or level of resistance
how to measure aerobic intensity?
% of VO2max, HR max, or HR reserve and/or Perceived Exertion (RPE)
How to measure anaerobic intensity?
% of 1 or 10 repetition max (1RM or 10RM), perceived repetitions in reserve (RIR), and/or RPE
is a 1 RM or a 10 RM preferable?
10 RM (sub max)
what tests can help get a baseline for aerobic intensity?
Bruce protocol, 6 min walk test
what test can help get a baseline for anaerobic intensity?
handheld dynamometer
Heart max (tanaka formula)
208 - (0.7 x age)
what do you take as a percentage of for intensity prescription?
a percentage of heart rate max
heart rate reserve
Max HR - Resting HR
How do you get the targeted HR intensity?
percentage of heart rate reserve + resting heart rate
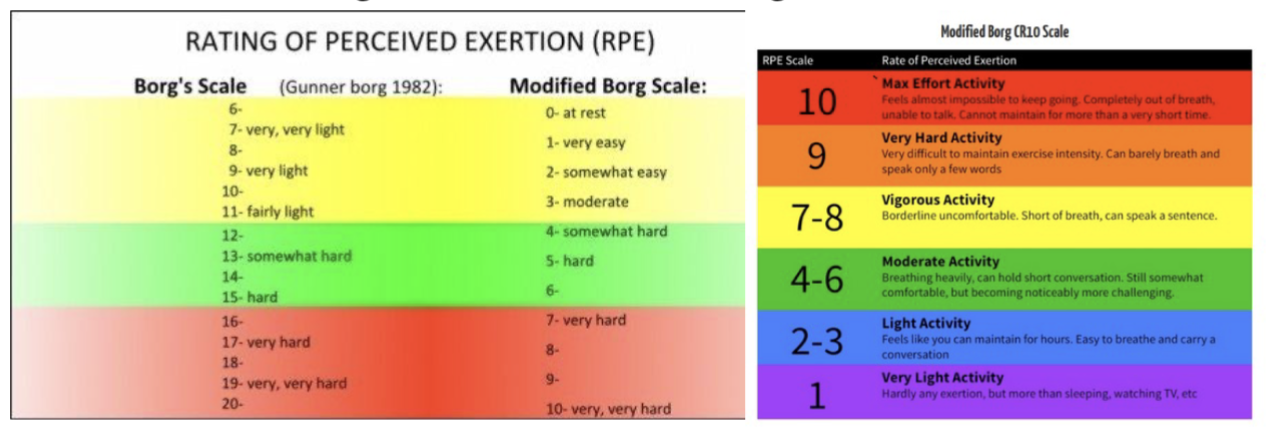
what does the Borg Scale measure?
a subjective rating of how difficult a task is
repetition max definition
the greatest amount of weight or load that can be moved with control through the full, available range of motion a specific number of times before fatiguing (eg. 1 rep max, 10 rep max, % of rep max)
repetitions in reserve definition
number of repetitions that the individual feels they are from failure
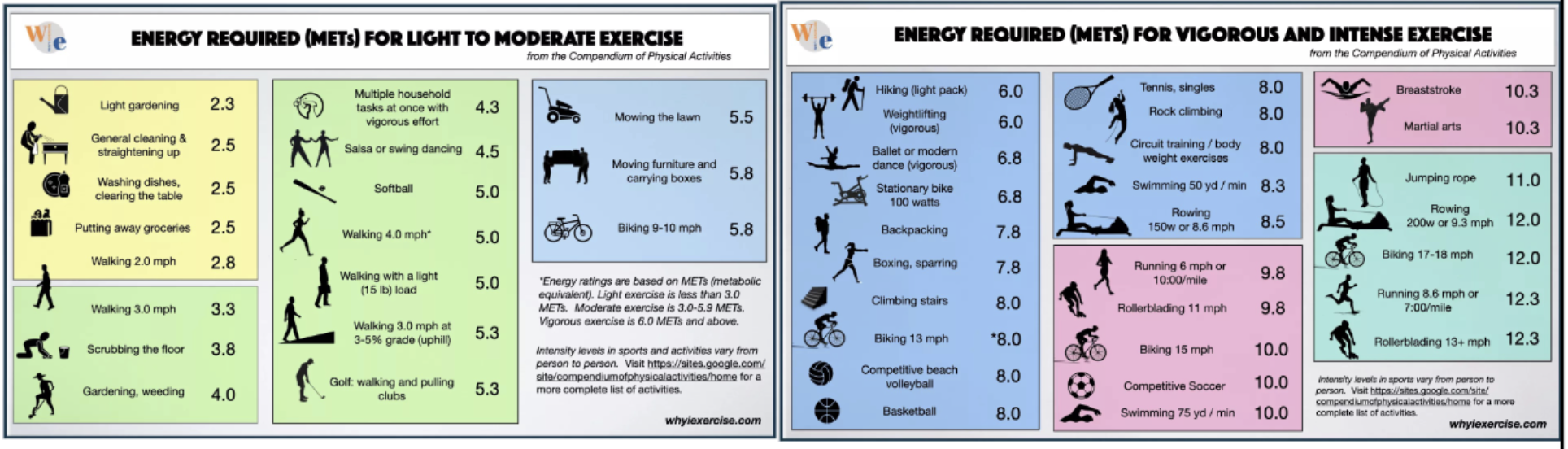
metabolic equivalents (MET) definition
ratio of rate of energy expenditure during an activity to the rate of energy expended at rest
Type definition
mode of exercise (e.g. running, weightlifting)
concentric
e.g. weight lifting = shortening the muscle
eccentric exercise
lengthening the muscle = e.g. resistance bands
Time definition
duration of the exercise (time, rest minutes, number of sets)
volume definition
total amount of exercise
aerobic volume equation
frequency x time x intensity (MET-min/wk, kcal/wk)
anaerobic volume equation
total repetitions x intensity (per session or per week)
progression definition
how you make the exercise harder
what are some examples of progression?
increase aerobic exercise by time
increase weight by 5 pounds
increase reps
change body position
add in a cognitive task
change surface
if the person is weak what type of exercise should you choose?
strengthen and load
if the person has capacity to do something, what type of exercise should you choose?
consider alternatives such as fear avoidance or graded exposure
what exercise considerations improve strength?
60-80% of 1 RM, 8-12 reps, 2-3 sets; 40-60% of max effort
what exercise considerations improve power?
load exercise specific and may ranges from 0-95% 1RM, focusing on speed
what exercise considerations improve endurance?
light load with high repetitions (at or below 67% of 1RM)
for those who are untrained, how do you improve form and technique?
lighter loads with ligher repetitions
General Exercise Order
large muscle multi-joint —> small muscle multi-joint —> large muscle single joint —> small muscle single joint —> trunk stability
higher before lower intensity