Chapter 19: Image Quality Constancy (Simulator)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
portal verification systems, such as EPI, OBI, etc. must be calibrated___. Why?
regularly
Ensure quality images are produced= limit the need to repeat imaging
A simulation can take place in the treatment room using treatment equipment. Why do we bother with a dedicated simulator?
1. (Main reason) To reduce the burden on the tx machines.
2. To deliver a more accurate tx plan.
What is more widely used?
Conventional Simulators
Flouro Simulators
CT Simulators
CT Simulators
Why are CT simulators more widely used?
They give more detailed info on tissue:
(a) density, and
(b) geometry
What do the QA procedures for CT sim focus on?
The interpretation and transfer of:
data and
geometry
What CT items require Weekly QA?
Safety Switches
Alignment of Gantry Laser w. Center of Imaging Plane
Image Performance Checks:
List the Image Performance Checks:
CT # Accuracy for Water
Image Noise
In-Plane Spatial Integrity
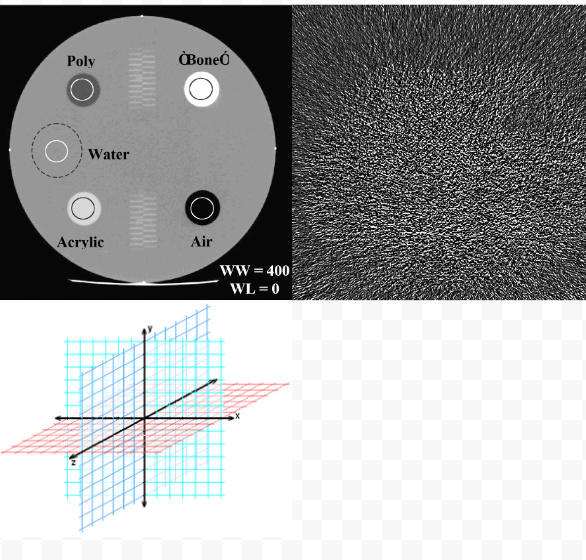
What should the CT # for water be?
0 HU

Tolerances for the following:
± 5HU
Manufacturer Specifications
± 1mm
± 2mm
CT items that require Monthly QA:
Orientation of gantry lasers
Spacing of lateral wall lasers in respect to lateral gantry lasers
Orientation of wall & ceiling lasers in respect to imaging plane
Mechanical Table Functions
Image Reconstruction
Exposure Quality
OSO’s MTF i(photoshop) exposed
CBCT stand fore
Cone Beam CT
What images does CBCT take?
verification films
CBCT provides imaging in __ dimensions.
1
2
3
4
3
CBCT uses __ beam.
MV
KV
either
either
CBCT shape of the beam:
cone-shaped
How does CBCT capture images?
Revolves around the patient, capturing a broader volume of data at each revolution around the patient.
What is the advantage of the Cone-Shaped beam?
easier for the image translator to reconstruct anatomic data = clearer more accurate images
Where is the KV CBCT mounted on a linac? Why is it on a linac?
On gantry at 90 degrees to tx head (KV arms)
Gives 3D image of a 2D detector for: target localization verification before tx deliver
OBI stand for
Onboard Imaging
True or False: CBCT is an OBI system
True
Purpose of OBIs:
Because the reproducibility of a setup can fluctuate or the patient’s external/internal anatomy can fluctuate during the course of the tx…
OBI helps therapists make adjustments to tx fields more readily.
Types of EPID/OBI Systems
Cone Beam CT (CBCT)
Fluoroscopic Portal Imaging Detector
Ionization Chamber Detector
Amorphous Silicon Flat Panel Detector
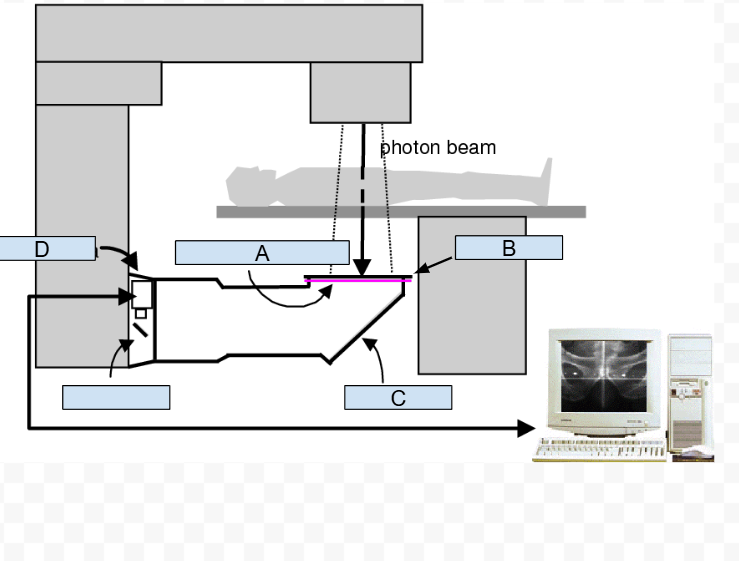
A. Fluoroscopy screen
B. metal plate
C. 45° high reflectance mirror
D. Camera
How does the Fluoroscopic Portal Imaging Detector work?
The digital processor in a Fluoroscopic Portal Imaging Detector enhances the poor contrast MV images by replacing them with a high x-ray energy digital fluoroscopy image system. Resulting in instant, better quality images.
How does the Fluoroscopic Portal Imaging Detector produce an image?
Image is formed on a fluoroscopy screen and transferred to the camera via a high reflectance mirror.
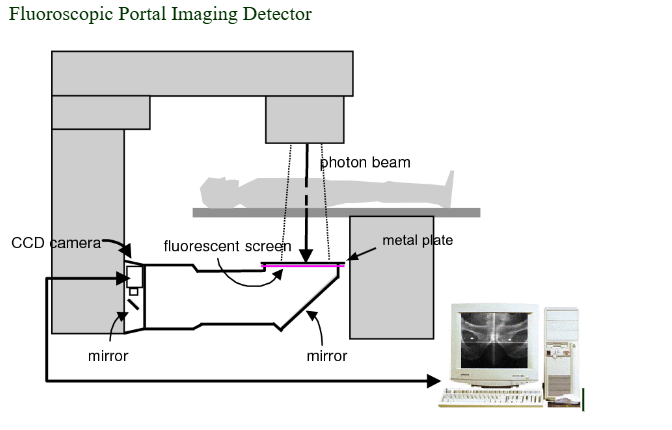
Where is the high reflectance mirror positioned?
45° under the fluoroscopic screen.
How often should you calibrate the (Fluoroscopic Portal Imaging Detector) camera?
Every few days
How often should you calibrate the Fluoroscopic Portal Imaging Detector?
Monthly
Whenever the FPID was bumped or moved
OBI systems need ___ calibration.
Regular
Some OBI systems send a ___ message indicating that the fluoroscopic screen needs to be exposed, so that adjustments can be made to the detector.
Weekly