MCAT Behaviorial Science - Identity and Personality
1/127
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
self-concept
our awareness of ourselves as distinct from others and our own internal list of answers to the question Who am I?
self-schema
a self-given label that carries with it a set of qualities
ex. athlete = youth, physical fitness, specific dress and behaviour
identity
the individual components of our self-concept related to the groups to which we belong
ex. Religious affiliation, sexual orientation, personal relationships, and membership
Gender identity
describes people’s appraisals of themselves on scales of masculinity and femininity as two separate axes; usually established by age three, though subject to change; not necessarily tied to biological sex or sexual orientation; third genders
Androgyny
the state of being simultaneously very masculine and very feminine
undifferentiated (gender)
low scores on both masculine and feminine scales
gender schema
key components of gender identity are transmitted through cultural and societal means
transgender
gender identity does not match sex assigned at birth; heavily stigmatized; gender identity disorder → gender dysphoria
Ethnic identity
associated with membership in a particular racial/ethnic group, often with a common ancestry, cultural heritage, and language
nationality
based on political borders; result of shared history, media, cuisine, and national symbols such as a country’s flag; need not be tied to one’s ethnicity or even to legal citizenship

hierarchy of salience
let the situation dictate which identity holds the most importance for us at any given moment
Self-discrepancy theory
each of us has three selves (actual, ideal, ought) and that perceived differences between these selves lead to negative feelings
actual self
self-concept; the way we see ourselves as we currently are
ideal self
the person we would like to be
ought self
our representation of the way others think we should be
self-esteem
self-worth; how one feels about themself
self-efficacy
our belief in our ability to succeed
Overconfidence
self-efficacy is far too high to be realistic; to take on tasks for which we are not ready, leading to frustration, humiliation, or sometimes even personal injury
learned helplessness
low self-efficacy; a developed perceived lack of control over the outcome of a situation; strongly related to clinical depression
Locus of control
to the way we characterize the influences in our lives
internal locus of control
view themselves as controlling their own fate
external locus of control
the events in their lives are caused by luck or outside influences
libido
sex drive
Psychosexual Development (Freud)
In each stage, children are faced with a conflict between societal demands and the desire to reduce the libidinal tension associated with different erogenous zones of the body

Fixation
occurs when a child is overindulged or overly frustrated during a stage of development; forms a personality pattern based on that particular stage
neurosis
functional mental disorder stemming from fixation
oral stage
0 → 1 y/o
gratification is obtained primarily through putting objects into the mouth, biting, and sucking
fixation: excessive dependency (smoking, drinking)
anal stage
1 → 3 y/o
gratification is gained through the elimination and retention of waste materials; toilet training
fixation: excessive orderliness (anal-retentiveness) or sloppiness
phallic stage
3 → 5 y/o
resolution of the Oedipal conflict for male children or the analogous Electra conflict for female children; child experiences guilt over desire for opposite sex parent and learns to identify with same sex parent
fixation: queerness, authority issues
Oedipal conflict
the male child envies his father’s intimate relationship with his mother and fears castration at his father’s hands; wishes to eliminate his father and possess his mother; deals with his guilty feelings by identifying with his father, establishing his sexual identity, and internalizing moral values
castrastion anxiety
fear in male children of losing penis or masculinity; anatagonism with father
penis envy
desire in female children to possess a penis or masculinity; affection to father
Electra conflict
a girl's initial sexual attachment to her mother ends upon discovering that she — the daughter — has no penis, she then transfers her libidinal desire (sexual attachment) to her father and increases sexual competition with her mother
sublimation
socially unacceptable impulses or idealizations are transformed into socially acceptable actions or behavior, possibly resulting in a long-term conversion of the initial impulse
latency stage
5 → puberty
sublimated libido
fixation: social issues
genital stage
puberty → adulthood
if prior development has proceeded correctly, the person should enter into healthy heterosexual relationships
fixation: fetishism/paraphilia from failures at previous stages
theory of psychosocial development (Erikson)
personality development is driven by the successful resolution of a series of social and emotional conflicts
conflicts arise because an individual lacks some critical social or emotional skill → represents an opportunity to learn a new social or emotional skill
positive or negative resolution → development requires positive
an individual who fails to obtain a positive resolution at one stage can still advance to later stages → later in life, may even learn the skill that they failed to learn during the developmental conflict
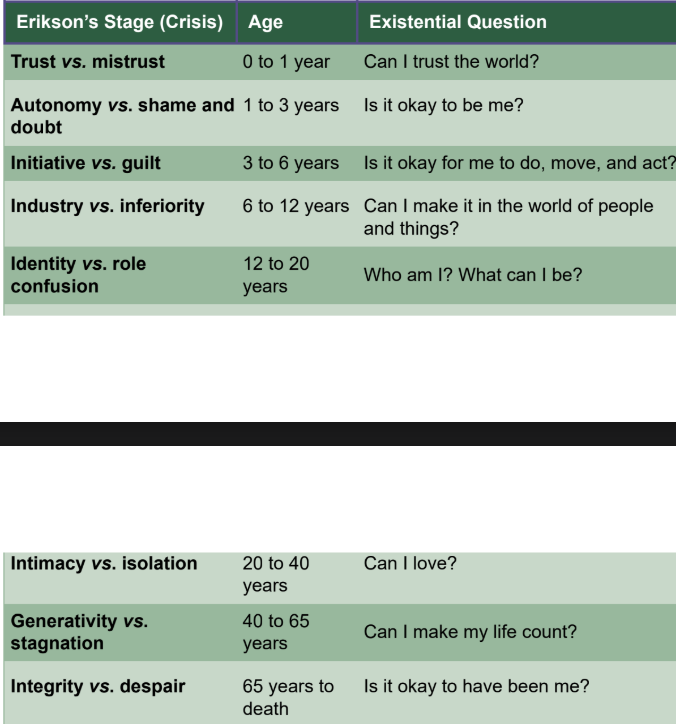
trust vs. mistrust
first year of life
newborn depends on their caregivers for support
positive: caregivers succeed in providing → learns to trust caregivers and others
autonomy vs. shame and doubt
1 to 3 years
children begin to explore their surroundings and develop their interests
positive: feeling able to exert control over the world → exercise choice as well as self-restraint
negative: overly controlled and criticized → sense of doubt and a persistent external locus of control
initiative vs. guilt
3 to 6 years
basic cause and effect principles in physics, and starting and finishing out tasks for a purpose
positive: sense of purpose, the ability to initiate activities, and the ability to enjoy accomplishment
negative: overcome by the fear of punishment → unduly restrict themselves or may overcompensate by showing off
industry vs. inferiority
6 to 12 years
becoming aware of themselves as individuals
positive: feel competent, be able to exercise their abilities and intelligence in the world, and be able to affect the world in the way that they desire
negative: sense of inadequacy, a sense of inability to act in a competent manner, and low self-esteem
identity vs. role confusion
12 to 20 years
explore their independence to determine who they are and what their purpose is in society
positive: fidelity, the ability to see oneself as a unique and integrated person with sustained loyalties
negative: confusion about one’s identity and an amorphous personality that shifts from day to day
intimacy vs. isolation
20 to 40 years
creating long-lasting bonds with others
positive: ability to have intimate relationships with others, and the ability to commit oneself to another person and to one’s own goals
negative: avoidance of commitment, alienation, and distancing of oneself from others and one’s ideals
generativity vs. stagnation
40 to 65 years
advancing present and future society
positive: individual capable of being a productive, caring, and contributing member of society
negative: self-indulgent, bored, and self-centered with little care for others
integrity vs. despair
above 65 years
reflective and contemplative
positive: wisdom, detached concern with life itself, with assurance in the meaning of life, dignity, and an acceptance of the fact that one’s life has been worthwhile, along with a readiness to face death
negative: bitterness about one’s life, a feeling that life has been worthless, fear over one’s own impending death
theory of moral reasoning (Kohlberg)
as our cognitive abilities grow, we are able to think about the world in more complex and nuanced ways, and this directly affects the ways in which we resolve moral dilemmas and perceive the notion of right and wrong
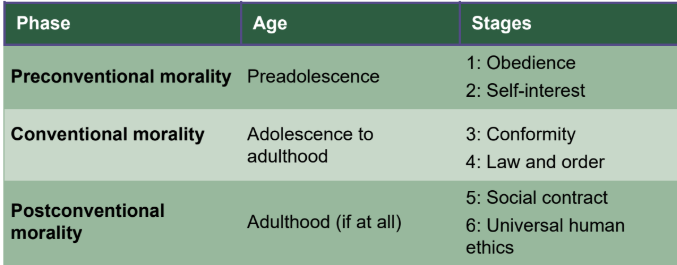
Preconventional morality
Preadolescence
obedience - avoiding punishment
self-interest - gaining rewards
Conventional morality
Adolescence to adulthood
Conformity - “nice person” orientation; approval from others
Law and Order - maintains social order
Postconventional morality
Adulthood (if at all) - based on social mores, which may conflict with laws
Social Contract - moral rules as convention for greater good/rights
Universal Human Ethics - decisions should be made in consideration of abstract principles
instrumental relativist stage
self-interest moral stage; based on the concepts of reciprocity and sharing: I’ll scratch your back, you scratch mine.
zone of proximal development
skills and abilities that have not yet fully developed but are in the process of development; requires the help of a “more knowledgeable other”
social learning theory (Bandura)
Young children observe and encode the behaviors they see in others, and may later imitate these behaviors, esp. from people like them
role-taking
experiment with other identities by taking on the roles of others, such as when children play house or school
theory of mind
ability to sense how another’s mind works
looking-glass self
Our understanding of how others see us, which relies on perceiving a reflection of ourselves based on the words and actions of others
reference group
the group that we use as a standard to evaluate ourselves
Personality
describes the set of thoughts, feelings, traits, and behaviors that are characteristic of an individual across time and location; describes how we act and react to the world around us
psychoanalytic/psychodynamic theories of personality
assumption of unconscious internal states that motivate the overt actions of individuals and determine personality
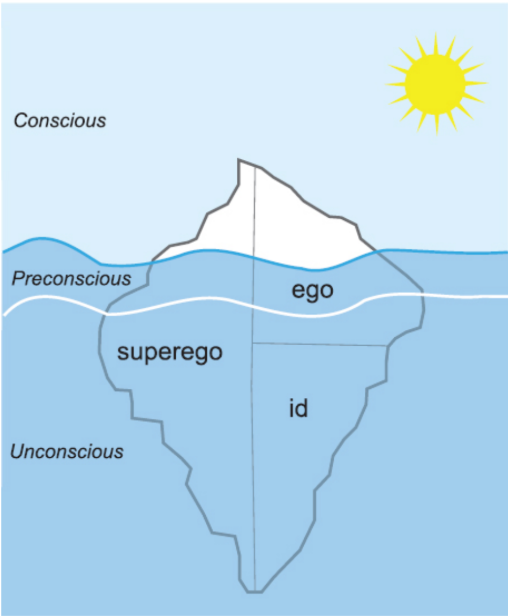
id
the basic, primal, inborn urges to survive and reproduce
pleasure principle
achieve immediate gratification to relieve any pent-up tension
primary process
id’s response to frustration based on the pleasure principle: obtain satisfaction now, not later
wish fulfillment
Mental imagery, such as daydreaming or fantasy, that fulfills need for immediate satisfaction
ego
the organizer of the mind; receives its power from—and can never be fully independent of—the id
reality principle
taking into account objective reality as it guides or inhibits the activity of the id and the id’s pleasure principle
secondary process
postpone the pleasure principle until satisfaction can actually be obtained; promotes the growth of perception, memory, problem solving, thinking, and reality testing
superego
perfectionist, judging our actions and responding with pride at our accomplishments and guilt at our failures;reflection of the morals taught to children by their caregivers; conscience and ego-ideal
conscience
collection of the improper actions for which a child is punished
ego-ideal
proper actions for which a child is rewarded
preconscious
thoughts that we aren’t currently aware of
unconscious
thoughts that have been repressed; not subconscious allegedly
instinct (Freud)
innate psychological representation of a biological need
Life instincts (Eros)
promote an individual’s quest for survival through thirst, hunger, and sexual needs
Death instincts (Thanatos)
represent an unconscious wish for death and destruction
defense mechanisms
ego’s recourse for relieving anxiety caused by the clash of the id and superego
deny, falsify, or distort reality and operate unconsciously
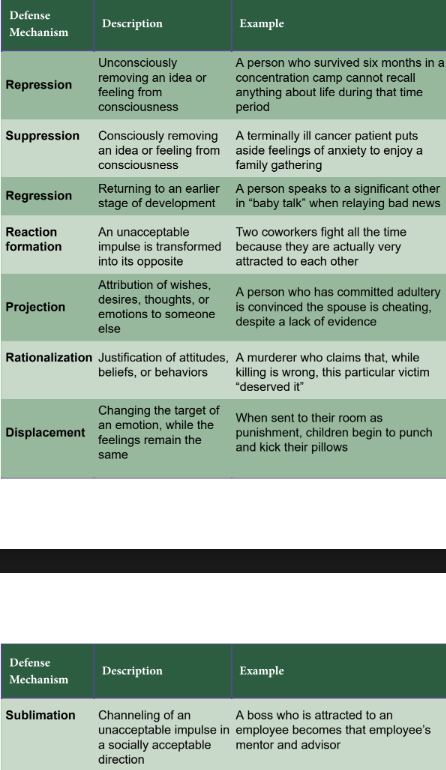
Repression
ego’s way of forcing undesired thoughts and urges to the unconscious and underlies many of the other defense mechanisms
suppression
more deliberate, conscious form of forgetting than repression
Regression
reversion to an earlier developmental state
Reaction formation
when an individual suppresses urges by unconsciously converting these urges into their exact opposites
Projection
individuals attribute their undesired feelings to others
Rorschach inkblot test
relies on the assumption that clients project their unconscious feelings onto the shape

thematic apperception test
a series of pictures that are presented to the client, who is asked to make up a story about each one; attempts to elucidate the client’s own unconscious thoughts and feelings
Rationalization
justification of behaviors in a manner that is acceptable to the self and society
Displacement
transference of an undesired urge from one person or object to another
sublimation
transformation of unacceptable urges into socially acceptable behaviors
personal unconscious
Freud’s notion of the unconscious
collective unconscious
powerful system that is shared among all humans and considered to be a residue of the experiences of our early ancestors; building blocks are images of common experiences
archetypes
common images with an emotional element in the collective unconscious
persona
a mask that we wear in public, and is the part of our personality that we present to the world; adaptive to our social interactions, emphasizing those qualities that improve our social standing and suppressing our other, less desirable qualities
anima (feminine) & animus (masculine)
gender- inappropriate qualities; feminine behaviors in males and masculine behaviors in females
shadow
responsible for the appearance of unpleasant and socially reprehensible thoughts, feelings, and actions experienced in the unconscious mind
self (Jung)
point of intersection between the collective unconscious, the personal unconscious, and the conscious mind; strives for unity
word association testing
assess how unconscious elements may be influencing the conscious mind and thus the self; patients respond to a single word with the first word that comes to mind
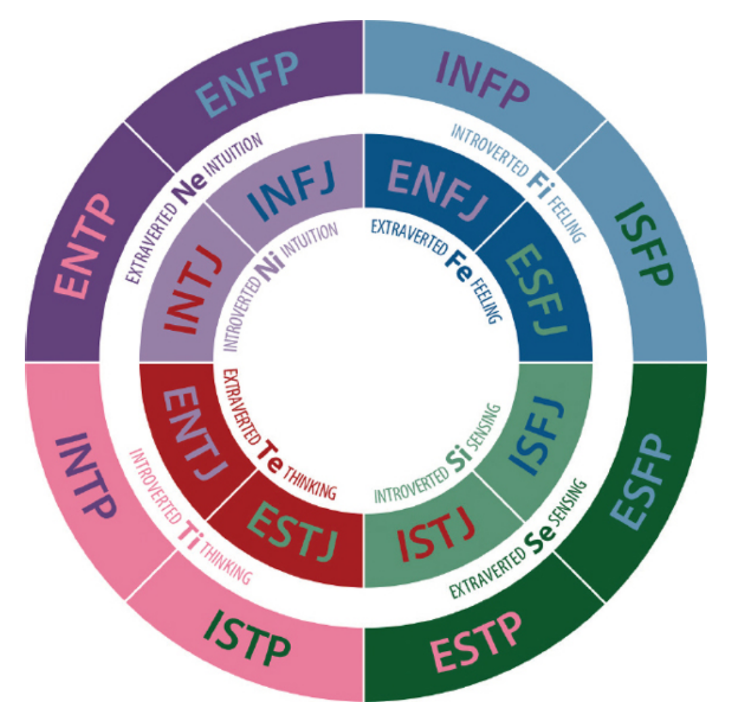
Myers–Briggs Type Inventory (MBTI)
personality test
Extraversion (E, orientation toward the external world) vs. introversion (I, orientation toward the inner, personal world)
Sensing (S, obtaining objective information about the world) vs. intuiting (N, working with information abstractly)
Thinking (T, using logic and reason) vs. feeling (F, using a value system or personal beliefs)
Judging (J, preferring orderliness) vs. perceiving (P, preferring spontaneity)
inferiority complex (Adler)
an individual’s sense of incompleteness, imperfection, and inferiority both physically and socially
creative self
the force by which individuals shape their uniqueness and establish their personality
Style of life
represents the manifestation of the creative self and describes a person’s unique way of achieving superiority
fictional finalism
individuals are motivated more by their expectations of the future than by past experiences
neurotic needs (Horney)
directed toward making life and interactions bearable; become problematic if they fit at least one of four criteria:
disproportionate in intensity
indiscriminate in application
partially disregard reality
tendency to provoke intense anxiety
ex. affection and approval, exploit others, self-sufficiency and independence
basic anxiety
Inadequate caregiving can cause vulnerability and helplessness
basic hostility
neglect and rejection cause anger