Understanding FASTA and FASTQ Files in DNA Sequencing
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is a FASTA file?
A file format that contains thoroughly analyzed DNA sequences with 'iffy' bases removed, ready for use.
What are the two sections of a FASTA file?
The first line is a header starting with '>', followed by the accession number and description; the second line contains the DNA or RNA sequence.
What is the purpose of FASTQ files?
FASTQ files serve as raw data generated from sequencing runs, used for genomics, metagenomics, and RNA-Seq.
How many lines are in a FASTQ file and what do they represent?
FASTQ files have 4 lines: Line 1 is the read ID and run information, Line 2 is the sequence data, Line 3 starts with '+', and Line 4 contains quality scores.
What is the PHRED score in the context of FASTQ files?
The PHRED score is a measure of the quality of a base call, calculated as quality score = -10 x log10(Pe), where Pe is the probability of an error.
What is the minimum acceptable PHRED score?
The minimum acceptable PHRED score is 30.
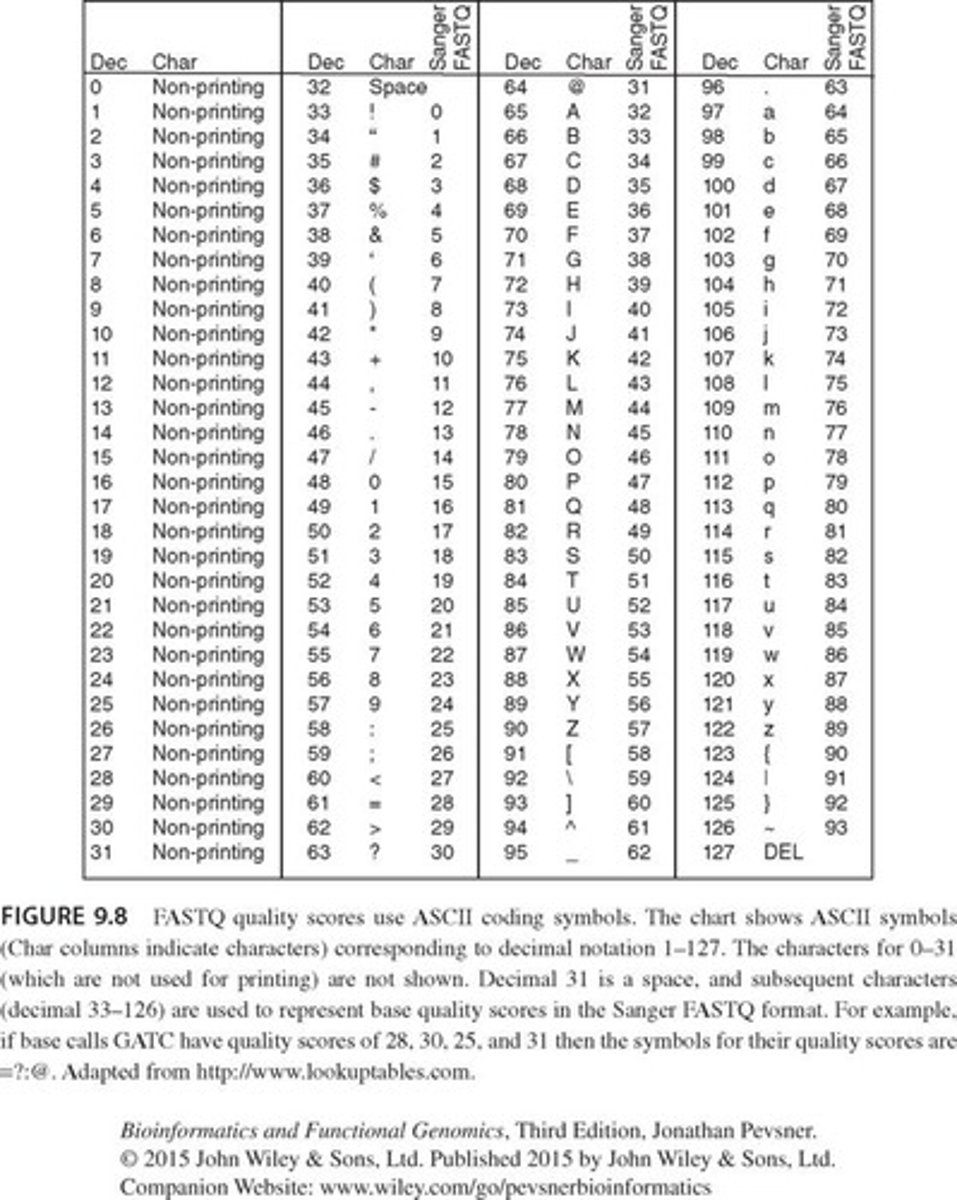
What is the purpose of using ASCII symbols in the Read Quality section of a FASTQ file?
ASCII symbols represent decimal numbers in a single space, allowing for compact representation of quality scores.
What is the first application of FASTQ files mentioned?
The assembly of a genome, where DNA fragments are put in order to reconstruct the original sequence.
What is the second application of FASTQ files?
Metagenomics of a bacterial population for microbiome analysis, involving DNA extraction and sequencing of 16S rRNA.
What is the third application of FASTQ files?
RNA-Seq, which involves RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and sequencing of mRNA populations.
What is multiplexing in DNA sequencing?
Multiplexing allows multiple samples to be sequenced in one run by assigning unique barcodes to each sample.
What is demultiplexing?
Demultiplexing is the process of sorting sequences after sequencing to assign them to the correct sample based on barcodes.
What is the significance of the header line in a FASTA file?
The header line provides the accession number and a brief description of the sequence.
What type of data does Line 2 of a FASTQ file contain?
Line 2 contains the actual sequence data represented by bases G, A, T, and C.
What does Line 3 of a FASTQ file signify?
Line 3 starts with a '+' symbol and may include additional information about the sequence.
What is the maximum PHRED score?
The maximum PHRED score is 93.
How does the computer handle FASTQ files after sequencing?
The computer sorts through the sequences and assigns each to the appropriate sample bin during demultiplexing.
What is the role of 16S rRNA primers in metagenomics?
16S rRNA primers are used to amplify DNA from bacterial populations for sequencing.
What is the purpose of data visualization in sequencing applications?
Data visualization helps make complex sequencing data more understandable and interpretable.
What is the significance of overlapping fragments in genome assembly?
Overlapping fragments allow for accurate reconstruction of the original genome sequence.
What is the output of a sequencing run using multiplexing?
The output is millions of FASTQ files that need to be sorted into their respective samples.
What is a common method for fragmenting genomes for sequencing?
Sonication is a common method used to randomly fragment genomes for sequencing.
What type of sequencing data is generated for RNA-Seq?
Millions of reads from single mRNA molecules are generated for RNA-Seq analysis.
What is the relationship between the number of samples and cost in NGS runs?
Submitting more samples in one run reduces the cost per sample significantly.
What does the term 'library of 16S rRNA gene reads' refer to?
It refers to a collection of sequenced 16S rRNA genes from a bacterial population used for analysis.