Judaism
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
208 Terms
T/F: Judaism is an abrahamic tradition
True—they consider Abraham to be the of the Jews
around how old is Judaism
~3000 years
covenant + what does it mean
an agreement established between God and the Israelites —> Jews are God’s people
Torah
God’s revelation of the divine will to the chosen people
In what book and when was the Torah written
Recorded in the Hebrew Bible w/ the writings of rabbis from the first centuries after the romans destroyed the Second Temple in Jerusalem
What happened after the temple was destroyed?
a whole branch of Judaism was gone
when was the second temple destroyed
70 AD
Yahweh
another name for God b/c God’s name is too holy to be spoken
Shema
uniqueness of the Jews’ relationship with God + Judaism’s most basic theological statement
“Hear, O Israel! The Lord is our God, the Lord alone”
What does Torah translate to?
the law or “instruction”
Pentateuch — what is it and what does it mean
another name for the Torah proper — Greek term meaning “Five Books” for the first 5 books of the Bible
who did God give the Pentateuch to and where?
Moses on Mt. Sinai
Tanakh
Written Torah
How many parts is the Tanakh written in + what are those parts?
3 parts
Torah Proper —> first five books
The Prophets —> historical accounts and proclamations of God’s will
The Writings —> Poetry of the psalms, wisdom literature, short stories, historical accounts, etc (diverse)
How many specific laws is in the Torah?
613
what is the Torah a code for?
holiness
Where is the Torah kept?
in an ark
Mishnah
oral Torah / sacred text
was the Mishnah written down? If so, when?
yes in 200 AD but orally preached by rabbis
Rabbi
teacher of Torah and leader of Jewish Worship; hebrew for teacher; someone who has mastered the sacred writing of Judaism (mainly the bible and talmud)
Talmud
vast depository of the Mishnah + interpretation of God’s will with the written Torah (massive work)
Who are the people of the covenant?
Jews (people of Judea), Israelites
what type of religion is Judaism?
monotheistic
what does Shema translate to?
“hear”
How do Jews live out the covenant?
honoring God’s Divine Will and Laws in all aspects
How many books in the Tanakh/written torah?
24 books
Where does the name “Tanakh” come from?
T = the torah proper (first five books)
N = nevi’im (the book of the prophets)
K = ketuvim (writings)
Is the oral Torah the law?
NO — it’s the study and interpretation of the law by rabbis
What two books is the oral Torah written in?
Mishnah — bare bones of the laws
Talmud — explains the Mishnah
when was the Mishnah written
200ish AD
when was the Talmud written?
600 AD
Why was the Oral Torah written down?
b/c the Romans destroyed the Second Temple
Why was the temple so important?
it was a sacrificial place for Jews + animal sacrifices were very important
who are the Pharisees
took over the Levites / priests’ traditions
When was the Diaspora + why did it happen?
135 AD b/c Roman killed Jews out of the land
Jewish timline
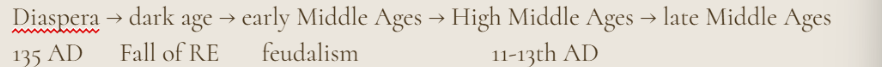
Deicide
Jews were falsely accused of this (killing Jesus)
Classical Judaism
descendants of Israelites — second temple destroyed + failed second revolt (diaspora)
Medieval Judaism (8th-mid 18th. C.) — major information
under European rule + Jews were successful moneylenders + black death + violent persecution
Why were Jews accused of starting the bubonic plague?
they were successful moneylenders which led to economic jealousy
where did most Jews escape persecution to
West (Poland had most)
What did Jews have to wear in Medieval Judaism and why?
identifying clothing b/c it was secular/church law
examples of identifying clothing
hat
yellow badge called Rotellaround badge
What were 2 causes of Anti-Judaism?
economic jealousy
religious fervor
what were 2 things Jews were accused of?
Blood libels — that they used Christian children for rituals
deicide — that they killed Jesus
What was the Catholic Churches’ 2 responses to Anti-Judaism
Official pronouncement
condemned violence
forbade forced conversion
Contributed to anti-Semitism by…
socially marginalizign Jews
Respecting supersessionism or replacement theology
Supersessionism + what did the Church say
to sit upon to preside over a theological claim — claimed that Christians have replaced the Jews as God’s people because the Jews rejected Jesus
What arose from the Enlightenment? (3)
New forms of modern Judaism
Hasidism
Zionism
Anti-Semitism
Hasidism
Kbbaith mysticism — God is known first w/ the heart then through personal relationships
Zionism (when did it come about + what was it)
arose in late 19th c. after Holocaust
support for Israel
When was Israel established as a state?
1948
Shoah
Jewish word for Holocaust
translation of Holocaust
“Burnt offering”
translation of Shoah
“catastrophe”
Anti-Semitism
hostility against Jews + belief that Jews were a separate race
Holocaust/Shoah
persecution of Jews by german nazis + death of 6 million Jews
Modern Judaism
Jewish Emancipation after Enlightenment — Jews gained equal political + civil rights
What specific rights did Jews gain?
access to education
right to own property
right to hold public office
right to participate fully in society and freely engage in a wide variety of occupations/professions
What points did Nostra Aetate make? (5)
stressed shared spiritual heritage (patrimony)
advocated for respect + dialogue
rejected charge of deicide
called for accuracy in Christian biblical interpretation + religious education
denounced all displays (past + current) of hatred, persecution, and anti-Semitism
How is life sancitified?
through day-to-day observance of the commandments
mitzvah
other name for commandment
What is the main form of prayer?
daily + consistent worship
Who is prayer obligatory for?
adult males over 13
examples of items used for prayer (4)
kipah
tefillin
tallit
mezuzah
kipah
head covering (also called yarmulke in Yiddish)
tefillin
small black leather box containing four biblical passages written on parchment
Tallit
garment worn during prayer
mezuzah
a thing you hang between entrances and doorways + shows a visible reminder of the Jewish people for both household and those who enter
orthopraxy
emphasizes the right practices + a direct statement to Torah
orthodoxy
emphasizes the right/generally accepted doctrine, practice, etc.
synagogue
center of Jewish prayer, study, and fellowship
what does the Synagogue contain?
Sefer Torah
Sefer Torah
scroll with the first five books of the Bible hand written in Hebrew and delicate paper
What is often the center of social life + worship?
the home
t/f: the home usually has a mezuzah
True
Kosher
proper — following strict dietary and food preparation rules/laws; designation for prepared foods meaning its ingredients and preparation have been certified as kosher by a proper rabbinic authority
Does Kosher mean the food was blessed by a rabbi?
NO
Is a land animal kosher?
if it has split hooves + chews its cud + has both kosher signs
Is fowl kosher?
The Torah lists 24 non-kosher bird species (basically all predatory/scavenger birds)
is fish/seafood kosher?
only if it has fins and scales — water mammals are NOT kosher
are reptiles, amphibians, worms, and insects kosher?
NO with the exception of four types of locust
What does meat include?
any food containing even a small quantity of meat or bones of mammals and fowl
What does dairy include?
milk of any kosher animal + any milk products made with it (even foods containing a small quantity)
What two types of food cannot be eaten together?
dairy and meat can NOT be eaten together
pareve
foods that are neither meat nor dairy
What are eggs, fruits, vegetables, and grains considered?
pareve
Can pareve foods be mixed with / eaten together w/ meat or dairy?
Yes — BUT fish (pareve) cannot be eaten with meat b/c of health concerns outlined in Talmud
Torah translation
“instruction”
YHWH
means Hebrew has no vowels
What is contained in the mishnah?
collected teachings of the rabbis of the preceding four centuries
what does Talmud translate to?
Study and knowledge
What is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism?
Talmud
what is the most important text of the oral torah?
Mishnah
What is the primary source of Jewish religious law and theology?
Talmud
When and where were the two versions of the Talmud written down?
450 AD in Palestine
600 AD in Babylon
what does Prophet translate to
“one who speaks for”
What does diaspora literally mean + what language
greek for dispersion
Diaspora definition
the situation of Jews living away from their ancestral homeland which has been a circumstance for most Jews since classical period
What did zionism seek to do + since when?
re establish a Jewish homeland since 1948