Hypothalamus and autonomic control
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What’s the relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland?
hypothalamus will make the hormones for or that stimulate the pituitary glands so control their activity + negative feedback
What are the different divisions of the ANS?
PSNS + SNS
How were key regions involved in autonomic control identified experimentally?
control of sympathetic preganglionic neurons were found by electrical excitation in different parts of the medulla of a cat (ventrolateral medulla)
How many major nuclei make up the hypothalamus?
11
Define a nuclei?
group of neuronal cell bodies working together towards a same function
What are 3 roles of the hypothalamus?
motivated behaviour
links body to mind via ANS and pituitary
regulates homeostasis
Which structures of the hypothalamus link body to mind?
medial, periventricular and pituitary
Where are the periventricular, medial and lateral parts of the hypothalamus found in relation to the third ventricle?
third ventricle then periventricular then medial finally lateral
Which structure in the hypothalamus is involved in motivated behaviour?
lateral part
Once a vital parameter has been disrupted, what mechanisms follow to indicate this change then to resolve it, by the hypothalamus?
sensory inputs integrated in the hypothalamus where it can use:
ANS
neuroendocrine system
behavioural changes
to restore vital parameters
What are contextual inputs that could affect the action of the hypothalamus in regulating homeostasis?
social eg like needing to go to the toilet modified by prefrontal or cerebral cortexes stop body from going to toilet
When hot, what is an example of ANS or behavioural action that could be coded by the hypothalamus to come back to the correct body temp.?
ANS = increase blood flow to release heat
behavioural = take coat off
What are 2 important nuclei of the hypothalamus called ?
paraventricular nucleus and supraoptic nucleus
How does the adenohypophysis release hormones into circulation? Which cells release these hormones and stimulates that release?
into portal vein (2 capillary networks directly connected)
troph cells, from parvocellular neurons
How does the neurohypophysis release hormones into circulation? Which cells release these hormones?
directly into system circulation
magnocellular neurons
Which pituitary gland secretes tropic hormones ? Name a couple
anterior, flat peg (FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH)
Which pituitary secretes hormones linked to lactation and growth? Name them
anterior, flat peg (PRL, endorphins, Growth Hormone )
Which pituitary secretes hormones linked to body fluid balance and parturition (+ lactation)?
posterior, ADH and Oxytocin
What are effectors of the ANS?
smooth + cardiac muscle and glands + brown adipose tissue
To what degree can the ANS function without the hypothalamus?
sensory and motor divisions still work fine, brainstem nuclei can still maintain cardiac, vasomotor and respiratory functions without the hypothalamus
What would require more input from the hypothalamus:
pupillary dilation; salivation; regulation of body temp.?
greatest cortical input ie the body temp., the other two are more reflexes - hypothalamus would be involved in salivation when thinking of food
What are examples of preganglionic neurons in the ANS?
brainstem and spinal cord
What are examples of postganglionic neurons in the ANS?
sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia
What are examples of effector cells in the ANS?
smooth muscle cell, gland cell, brown adipocytes
Where do para.sympathetic ganglia develop from?
neural crest
Where do the brainstem and the spinal cord develop from? What type of NT do they release and therefore what are they termed?
neural tube
ACh so cholinergic paraganglionic neurons
What are the most prevalent receptors within the ANS?
Nicotinic ACh receptors
Where do sympathetic preganglionic neurons sit in the nervous system? Where do they go out after passing through the other horns?
T1 to L3 so in the lateral horn (thoracic - lumbar region of it)
ventral horn
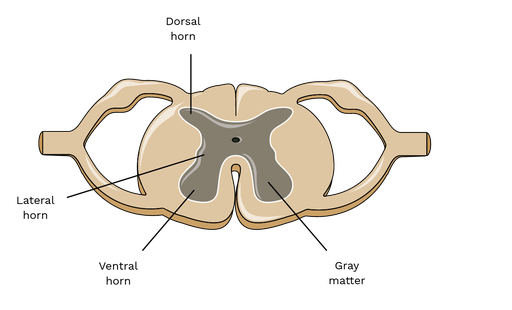
What is the sympathetic chain ganglia?
series of interconnected ganglia located bilaterally on either side of the spinal column, serving as relay stations
What controls sympathetic preganglionic neurons?
Nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS - dorsal sensory nucleus) + ventrolateral medulla (regulates nerve activity, BP, pain)
Where do parasympathetic preganglionic neurons sit?
sacral spinal cord (not in the lateral horn, more like lateral area)
What is the parasympathetic chain ganglia?
doesn’t exist
What types of receptors are expressed on sympathetic postganglionic neurons? What do these neurons produce?
AChRs
NE
What types of receptors are expressed on parasympathetic postganglionic neurons? What do these neurons produce?
AChRs
ACh
What’s the importance of the vagus nerve?
carries ~80% of total parasympathetic outflow (Vagus is Latin for wanderer) + lots of afferents
What are 2 essential structures of the cranial parasympathetic organisation? Name 3 nuclei in this organisation?
midbrain and medulla
edinger-westphal nucleus
dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
nucleus ambiguus
Which nerve carries parasympathetic info from the dorsal motor and ambiguus nuclei?
vagus nerve (CN X ie tenth cranial nerve)
Which nerve carries parasympathetic info from the edinger-westphal nucelus?
oculomotor nerve (CN III ie third cranial nerve)