6A Arenes
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Benzene molecular formula
What do aliphatic, aromatic, alicyclic, saturated and unsaturated mean

Benzene molecular formula
C6H6
What does the structure of delocalised benzene and kekule benzene look like
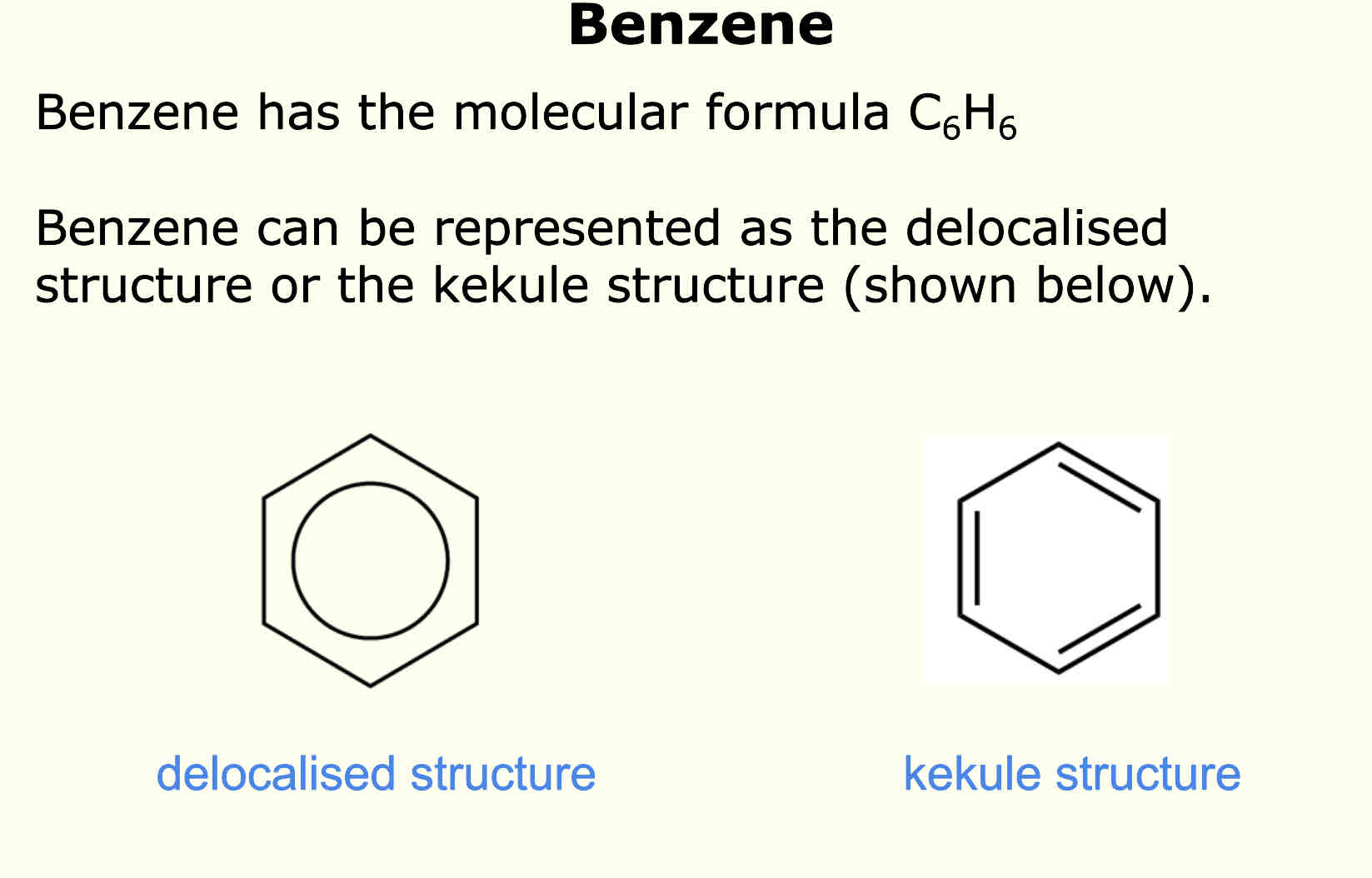
Evidence for the delocalised structure of benzene
Each C-C bond length is the same
Benzene reactivity is different to an alkene, benzene cannot do electrophillic addition like alkenes
Less exothermic enthalpy change of hydrogenation than expected, this means more energy was needed to break C=C bonds in benzene than expected (more ends than it should be)
How to form structure of benzene
Adjacent p orbitals overlap sideways to form pi bonds, the pi bonds spread over above and below the plane, the electrons are therefore delocalised.
What are similarities and differences between kekule and delocalised structure of benzene
Similarities:
Both models involve overlap of p orbitals
Both models suggest there is n - electron density above and below the plane of the ring
Differences:
Kekule model suggests alternating pi bonds but delocalised model suggests delocalised pi ring system.
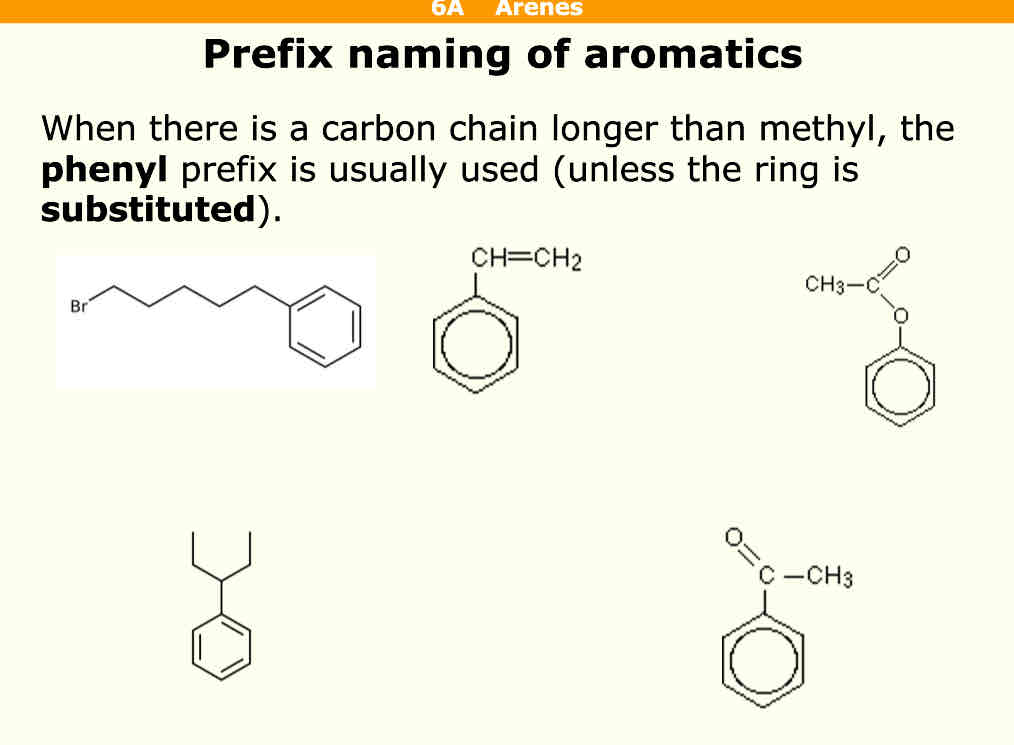
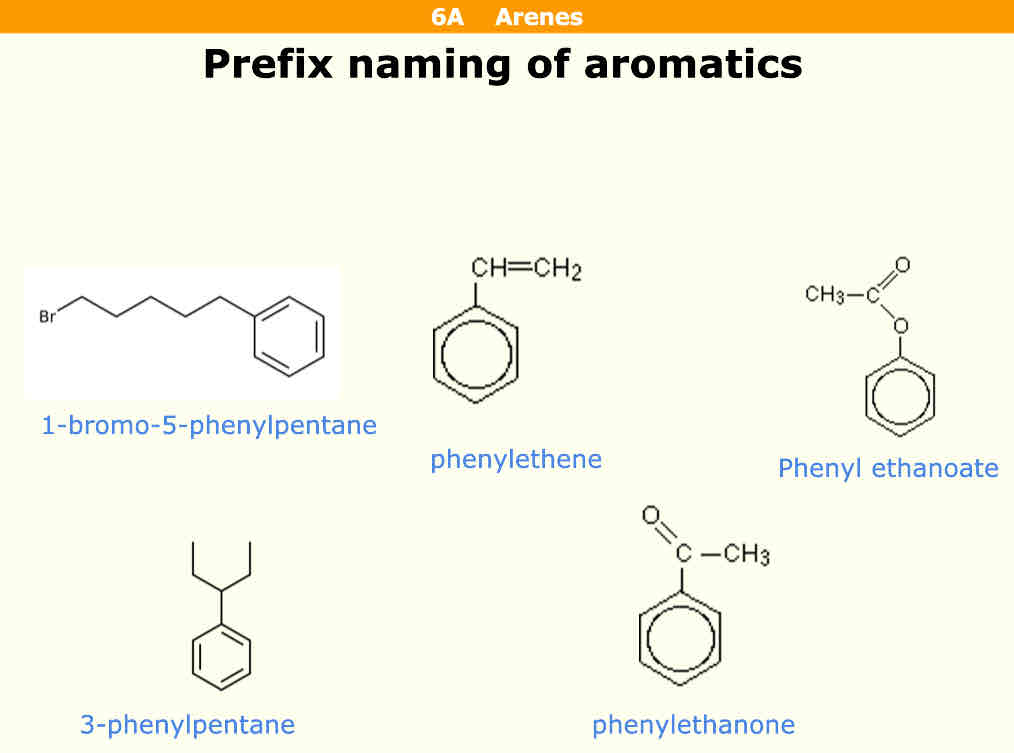
How do you name aromatics using prefixes
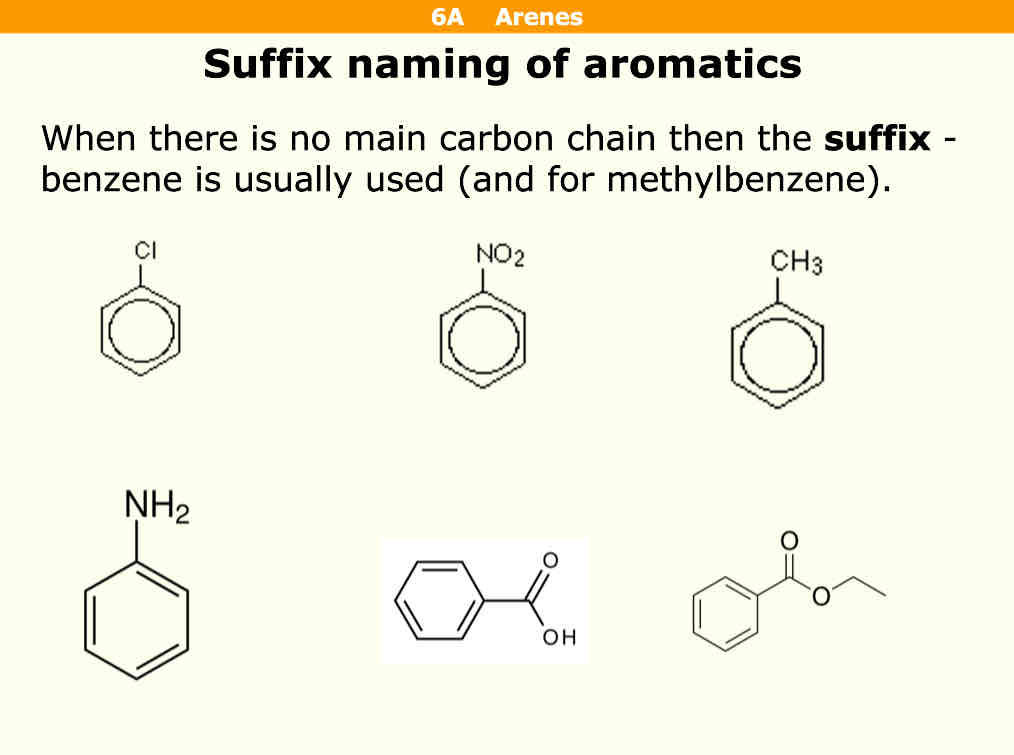
How do you name aromatics with suffix naming
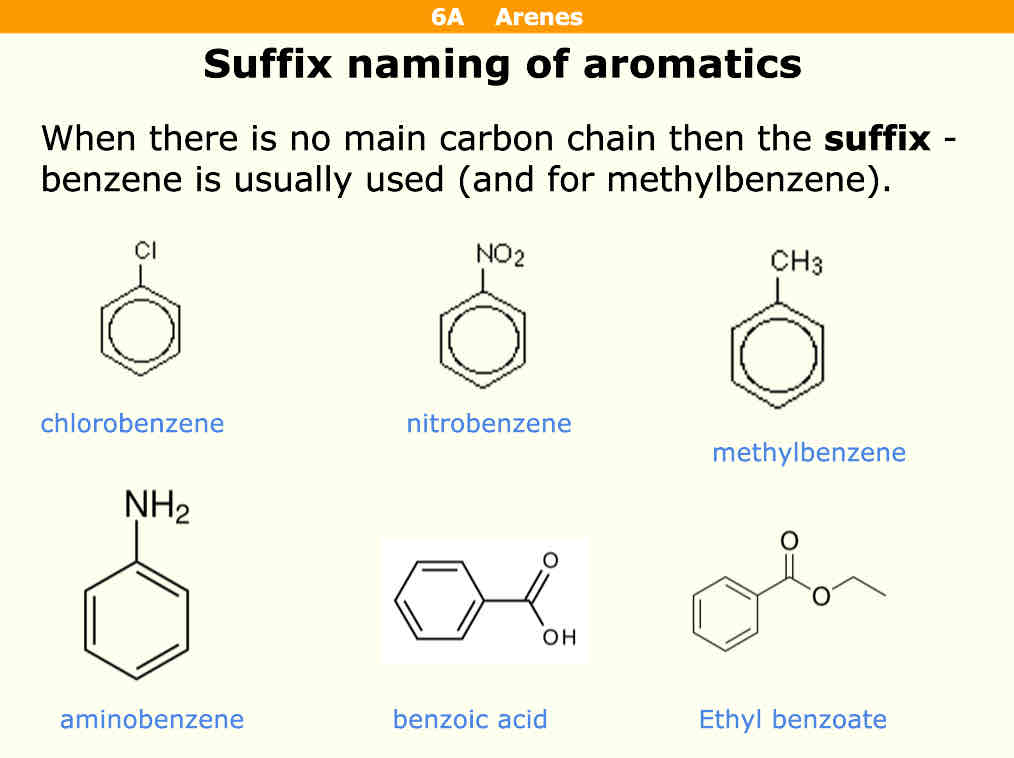
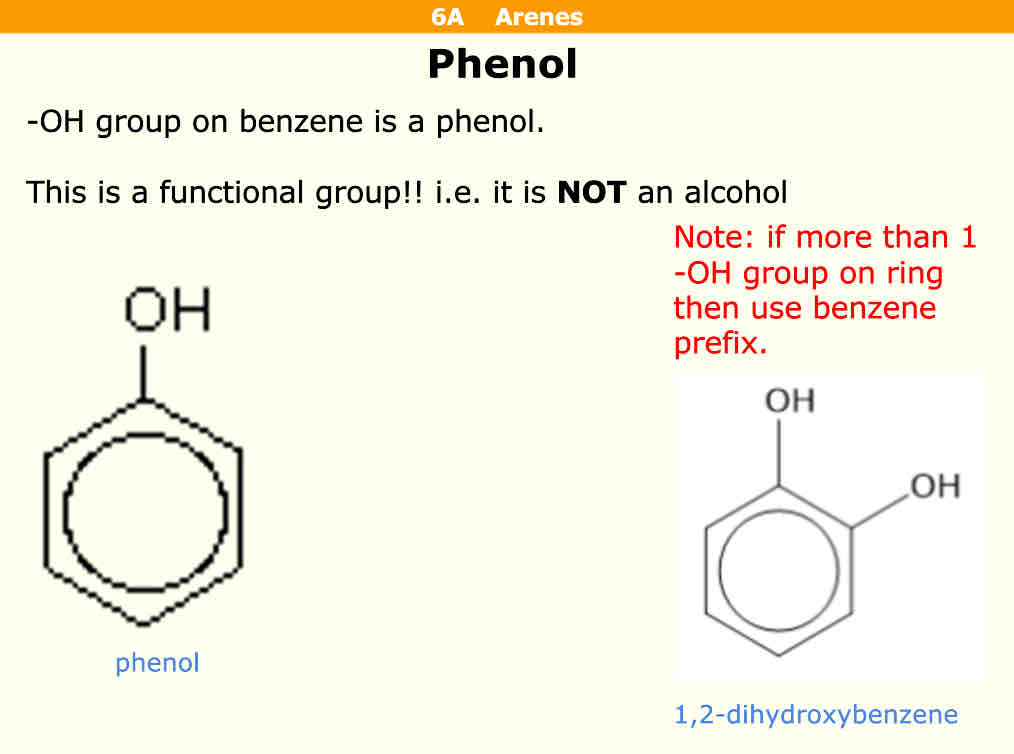
What is a phenol
An OH group on a benzene
What endings are these molecules
NO2
NH2
NO2 = nitro
NH2 = amino
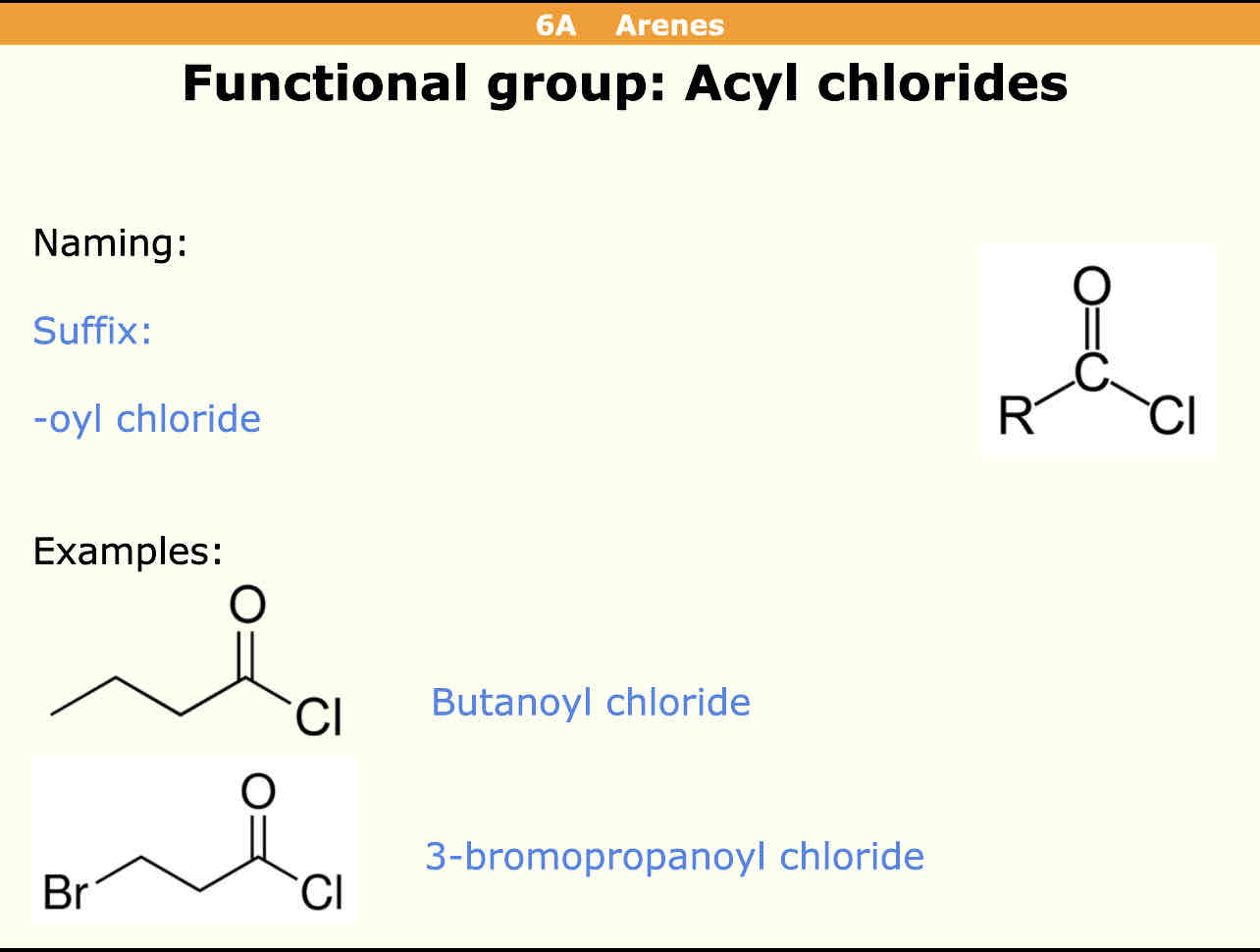
What is the suffix for RCOCl groups (Acyl chlorides)
- oyl chloride eg: butanoyl chloride
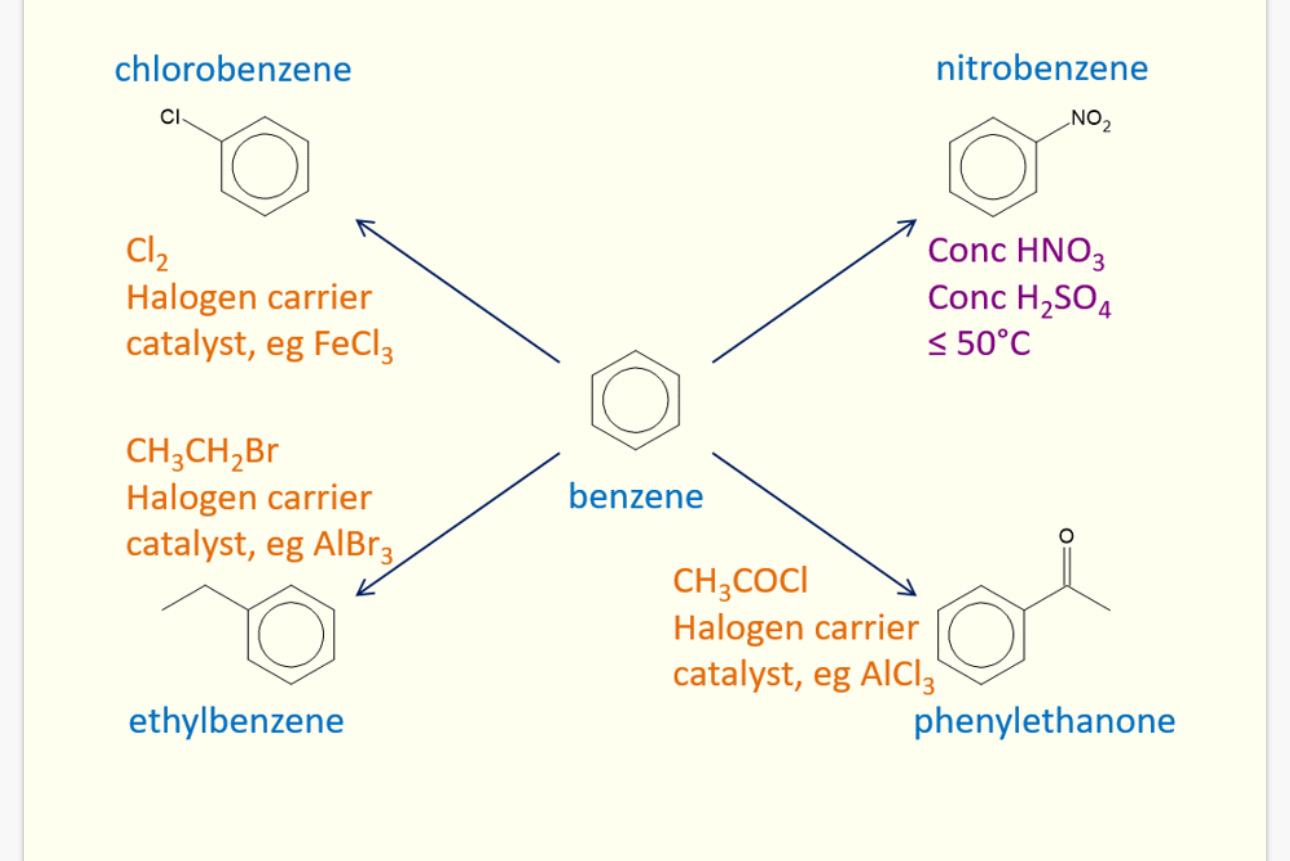
What are the 5 reactions of benzene
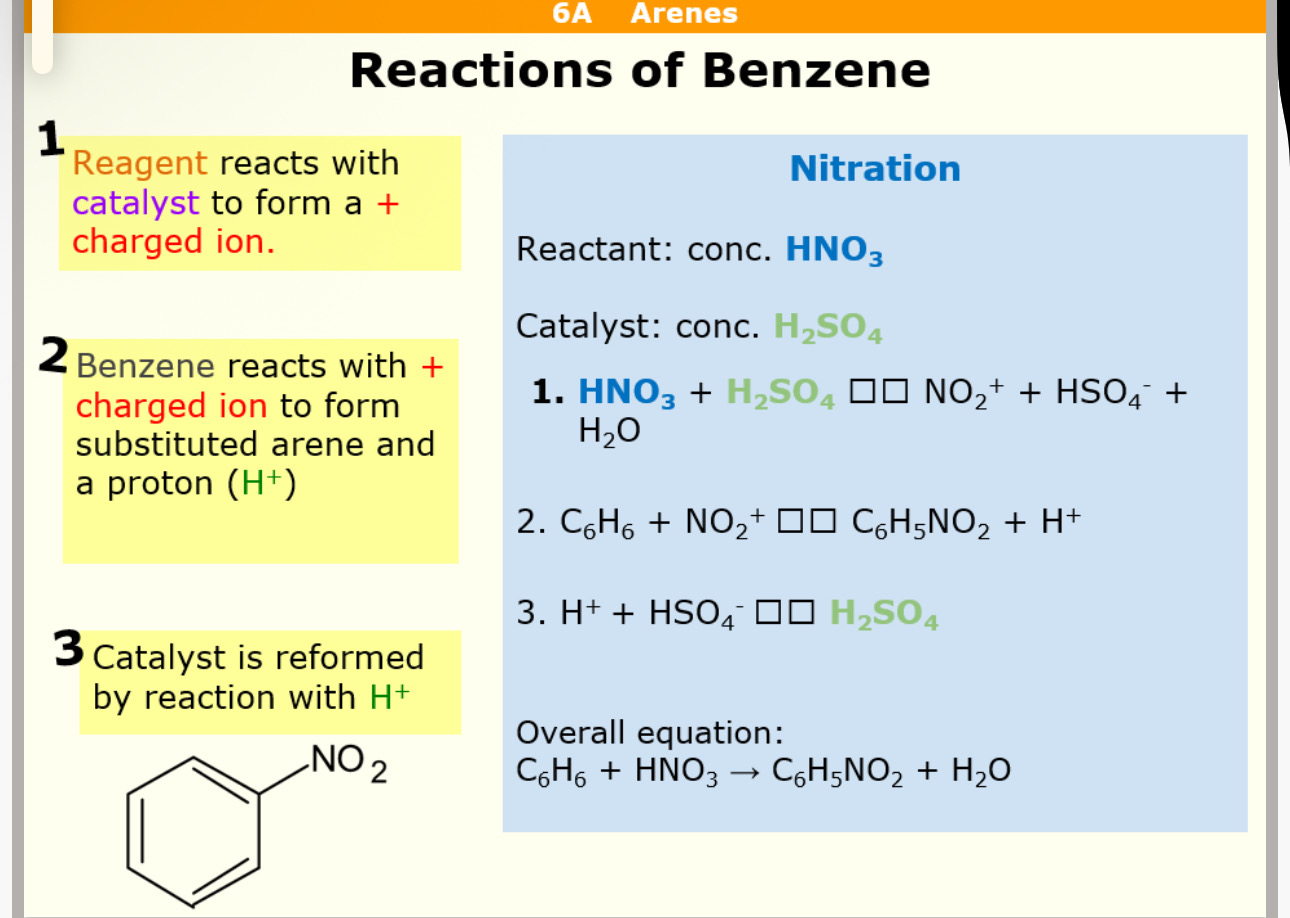
Nitration= reagent = HNO3 Catalyst = H2SO4
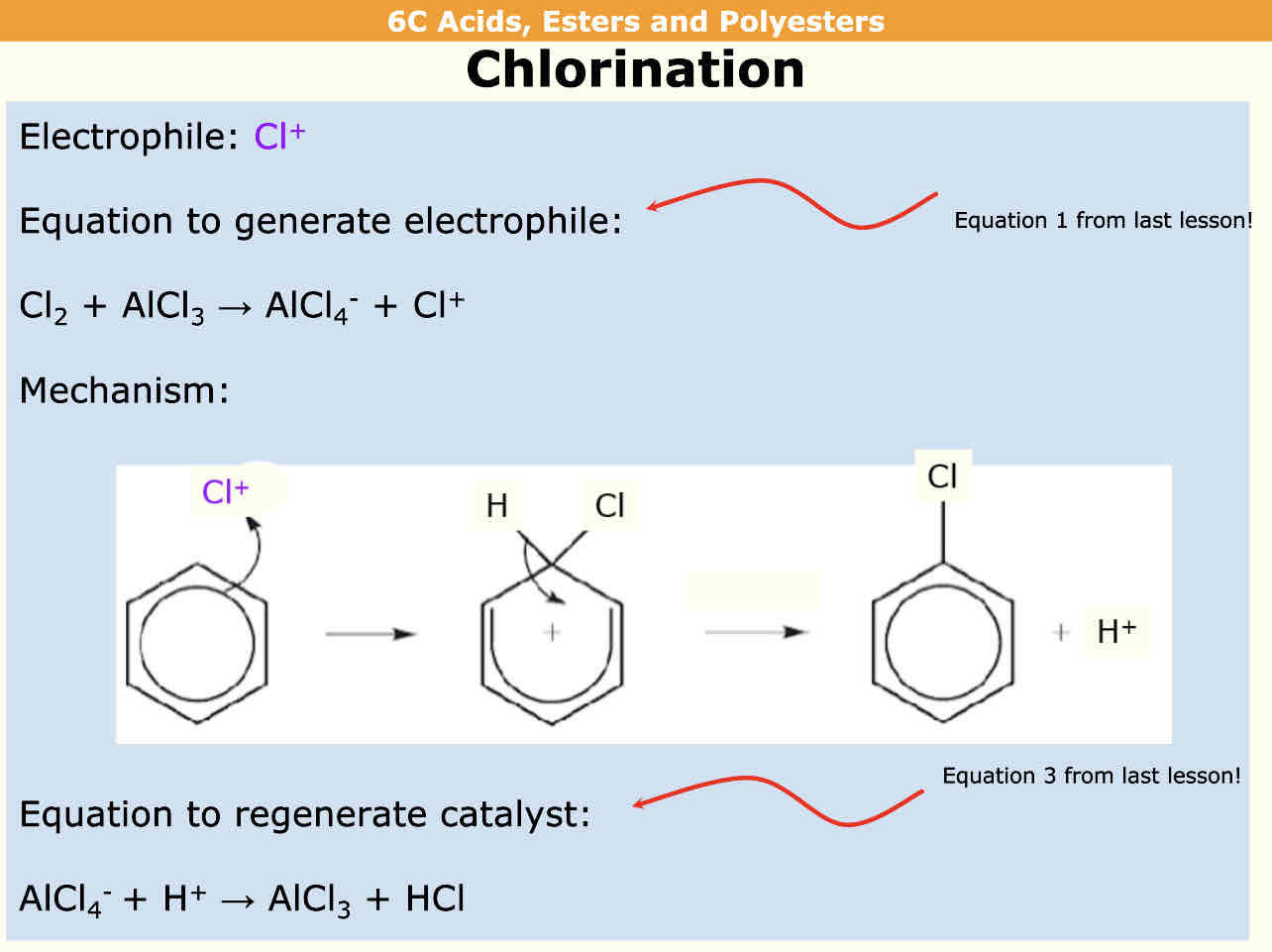
Chlorination reagent = Cl2 Catalyst = AlCl3
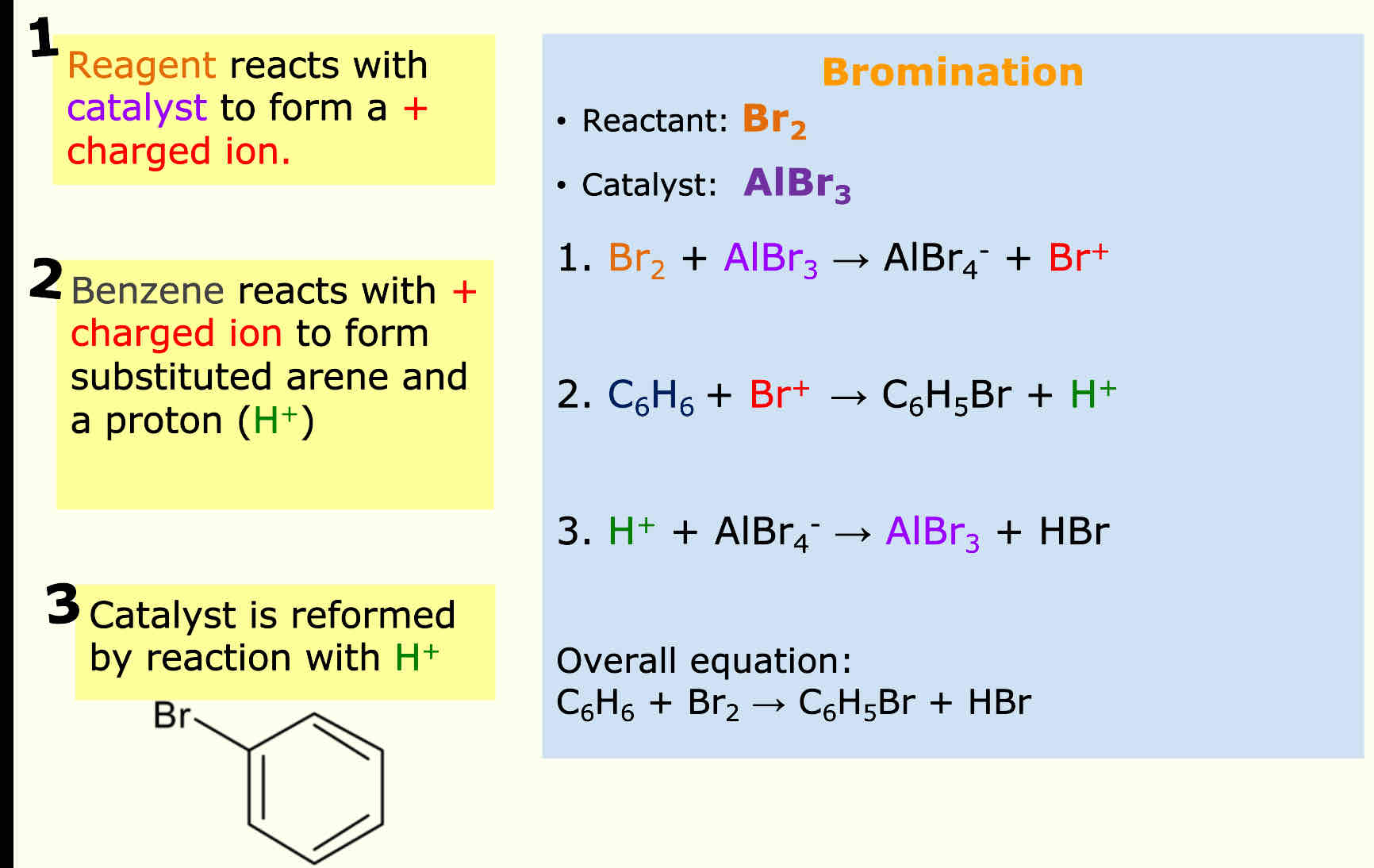
Bromination reagent = Br2 Catalyst = AlBr3
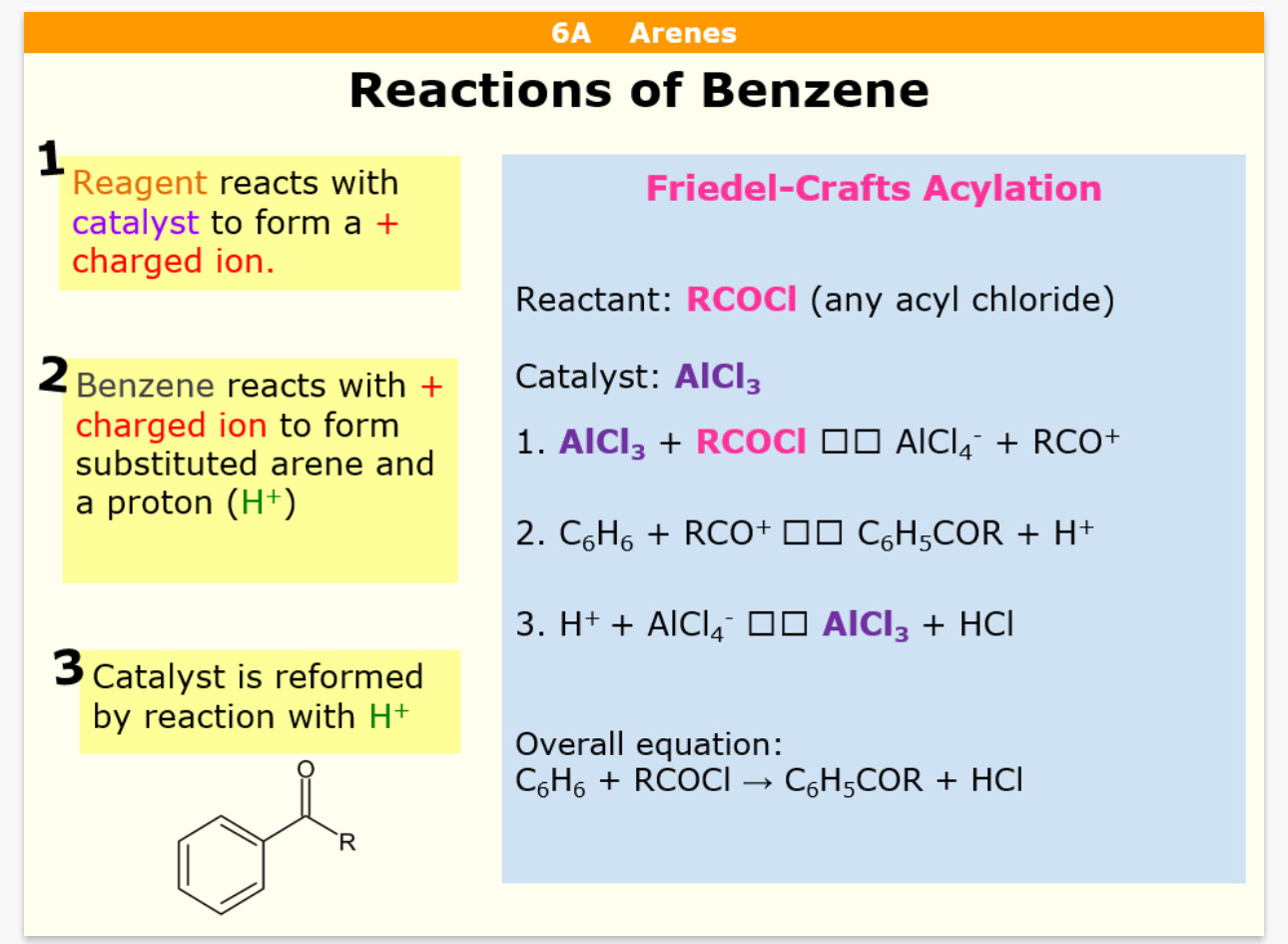
Acylation reagent = RCOCl (R = anything) Catalyst = AlCl3
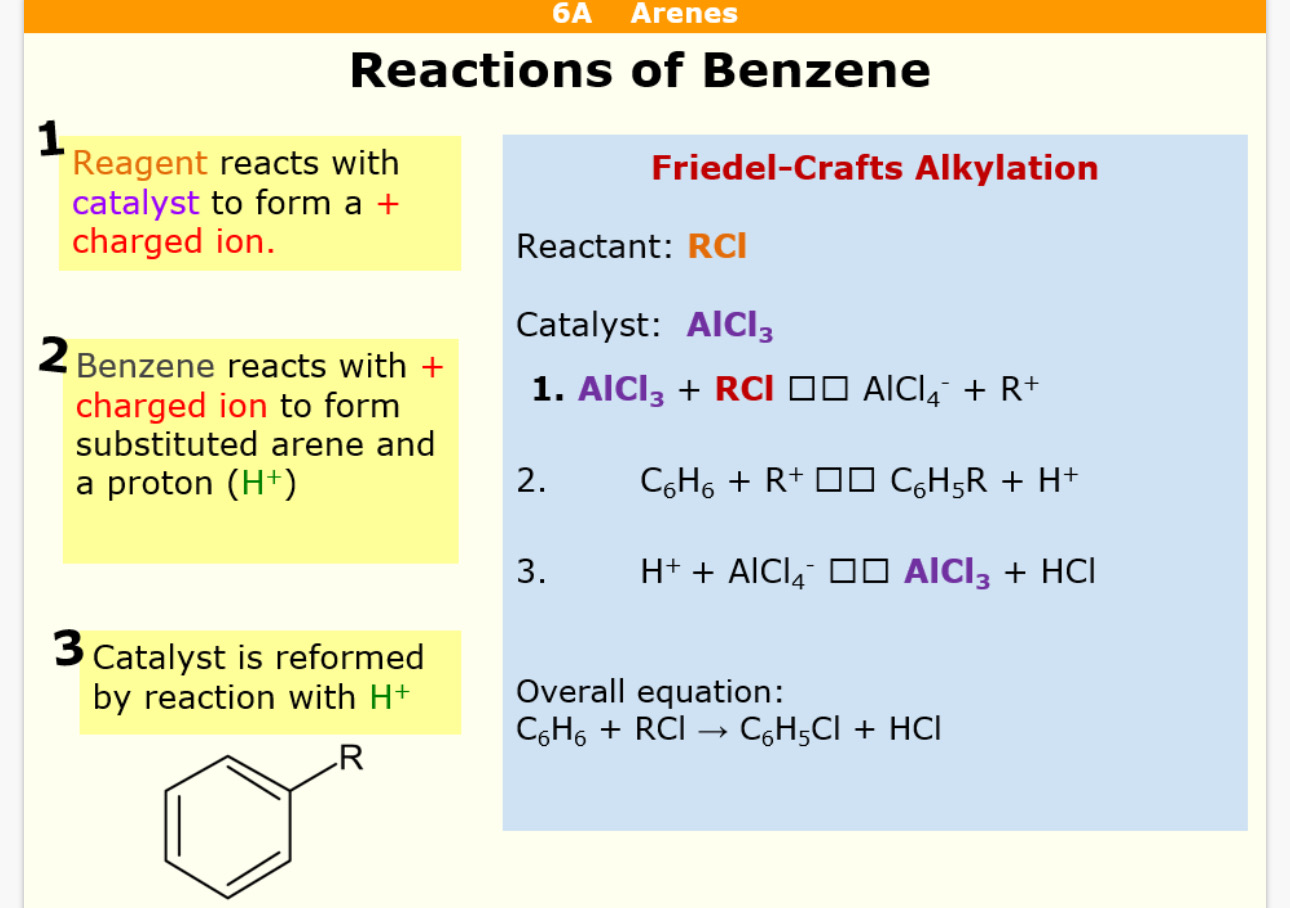
Akylation reagent = RCl (R = anything) Catalyst = AlCl3
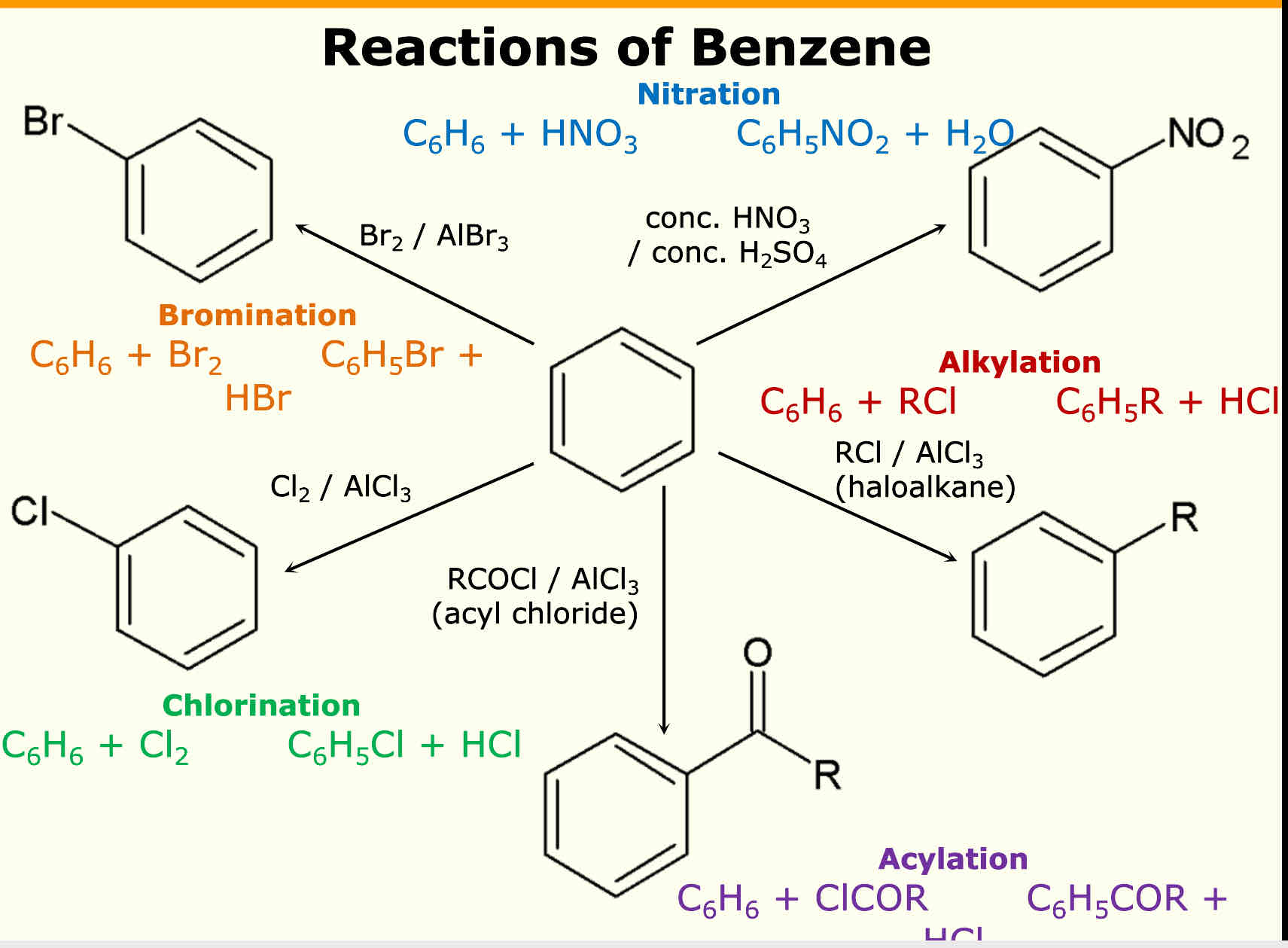
What product does chlorination produce
Methyl benzene
What product does Acylation produce
Phenyl ketone
What product does nitration form
What are the steps for the reactions of Benzene
Eg: bromination in this case but
The reactant reacts with the catalyst to form a charged ion and negative product
Benzene reacts with the charged ion to form arene and h+ ion
Catalyst is reformed from H+ reacting with negative product
Cancel things that come up on both sides of equation to get overall equation
Nitration reaction with benzene
What is the Acylation reaction with benzene
What is the alkylation reaction with benzene
In benzene reactions a halogen carrier is required
Halogen is removed on end product
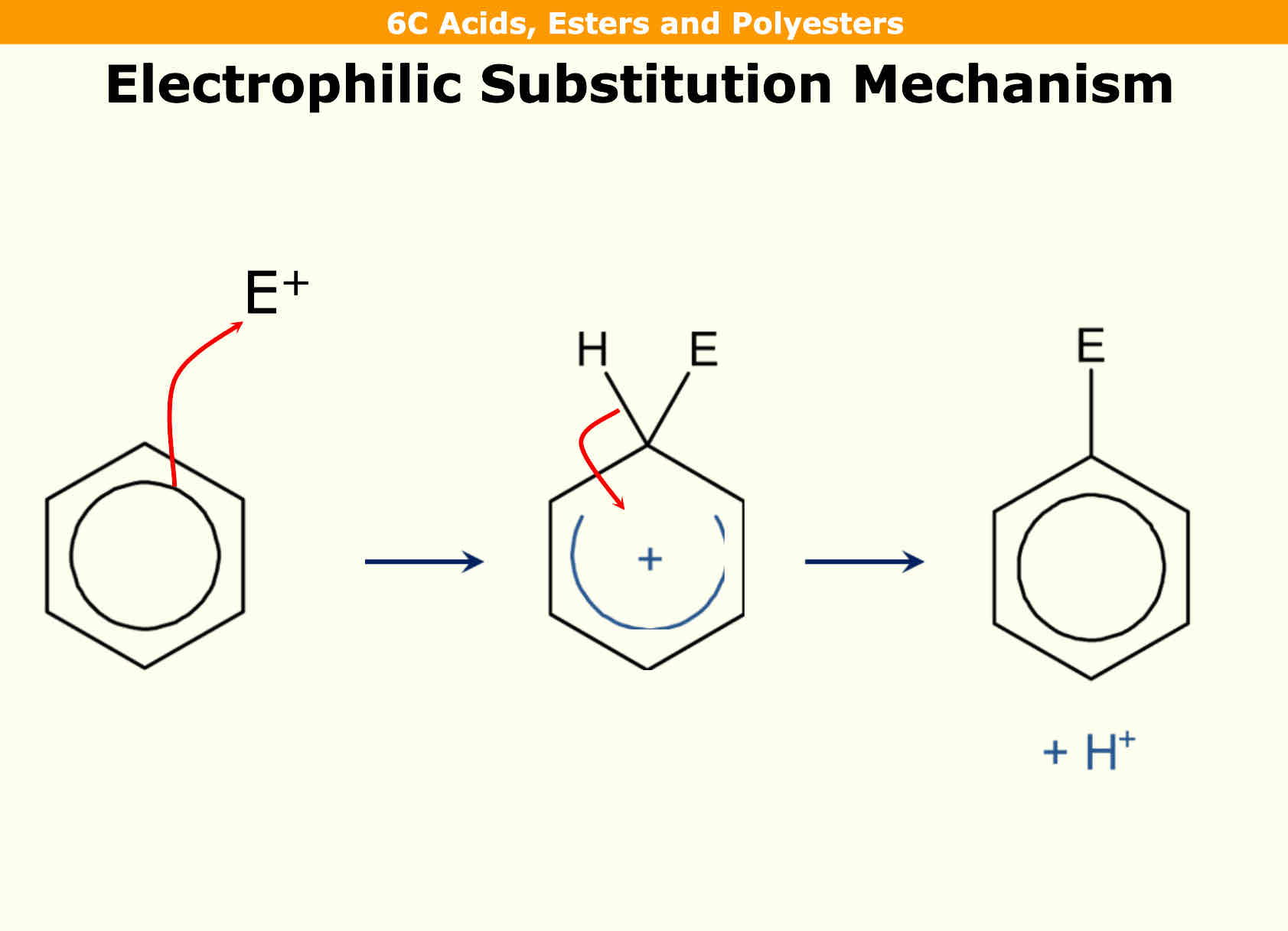
Electrophillic substitution of benzene
First you have an electrophile with a curly arrow coming from circumference of the circle
A bond is then formed with electrophile and carbon with hydrogen originally being there
A horseshoe with cation is in the middle with a curly arrow being drawn from hydrogen to the centre. This adds 2 electrons on it so benzene can be re - established
H becomes H+ as it has lost an electron and E (electrophile) replaces the H as a substitution reaction
Electrophillic substitution with an actual electrophile
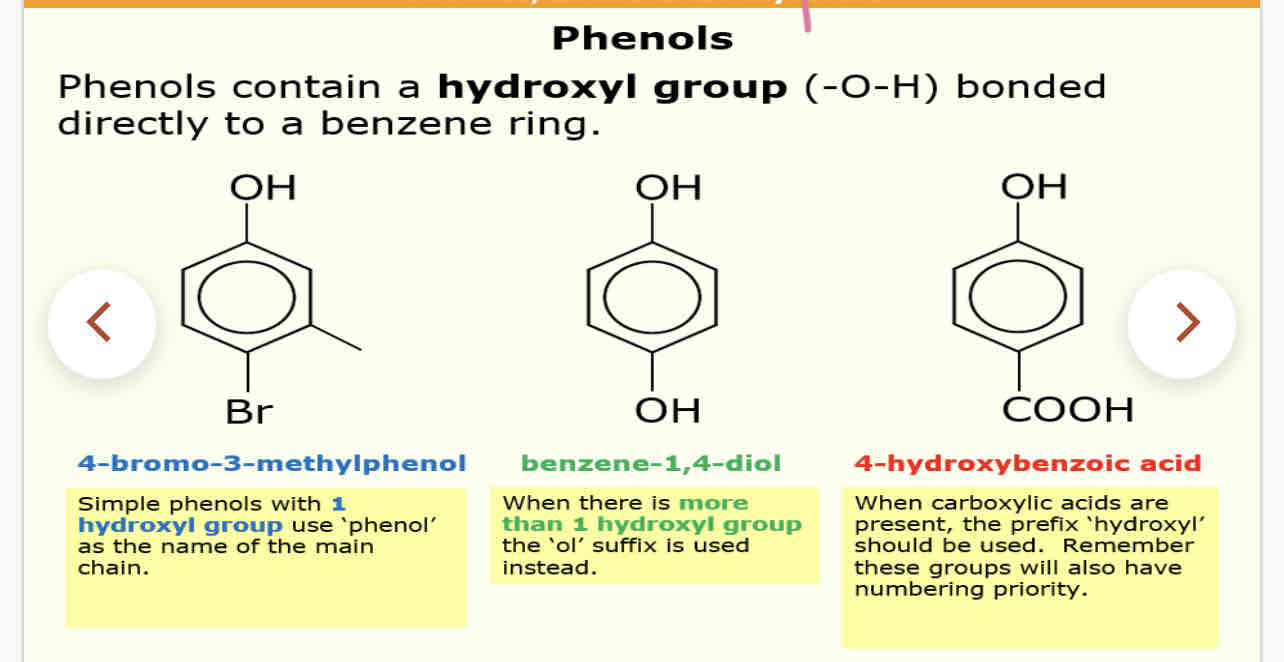
What are phenols
Contain a hydroxyl group (-o-h) bonded directly onto benzene ring
1 OH group is phenol
More than 1 use the suffix ol
Use of phenol
It is an antiseptic
What is the appearance of phenol?
What is the solubility of phenol?
A pink solid
It can dissolve because of the hydrogen bonds. However, it is sparingly soluble as most of the molecule is non polar
What type of acid is phenol
Weak acid, they react with metals and strong bases
They don’t react with carbonates as they are weak bases in excess they do, they form ONA if sodium carbonate
Explain the reactivity of phenol compared to benzene/ Why is phenol much more reactive than benzene
Benzene has pi rings above and below plane of rings
Phenol has pi rings above and below with an OH
lone pair on O of OH is delocalised into the ring
This makes ring more electron rich
Therefore the ring is able to induced dipoles into electrophile
What can phenols react without
A catalyst and at room temperature and pressure
Describe the acidity of phenols
Electrons in OH bond are delocalised into benzene ring
This makes OH bond weaker
This means H+ is formed more easily
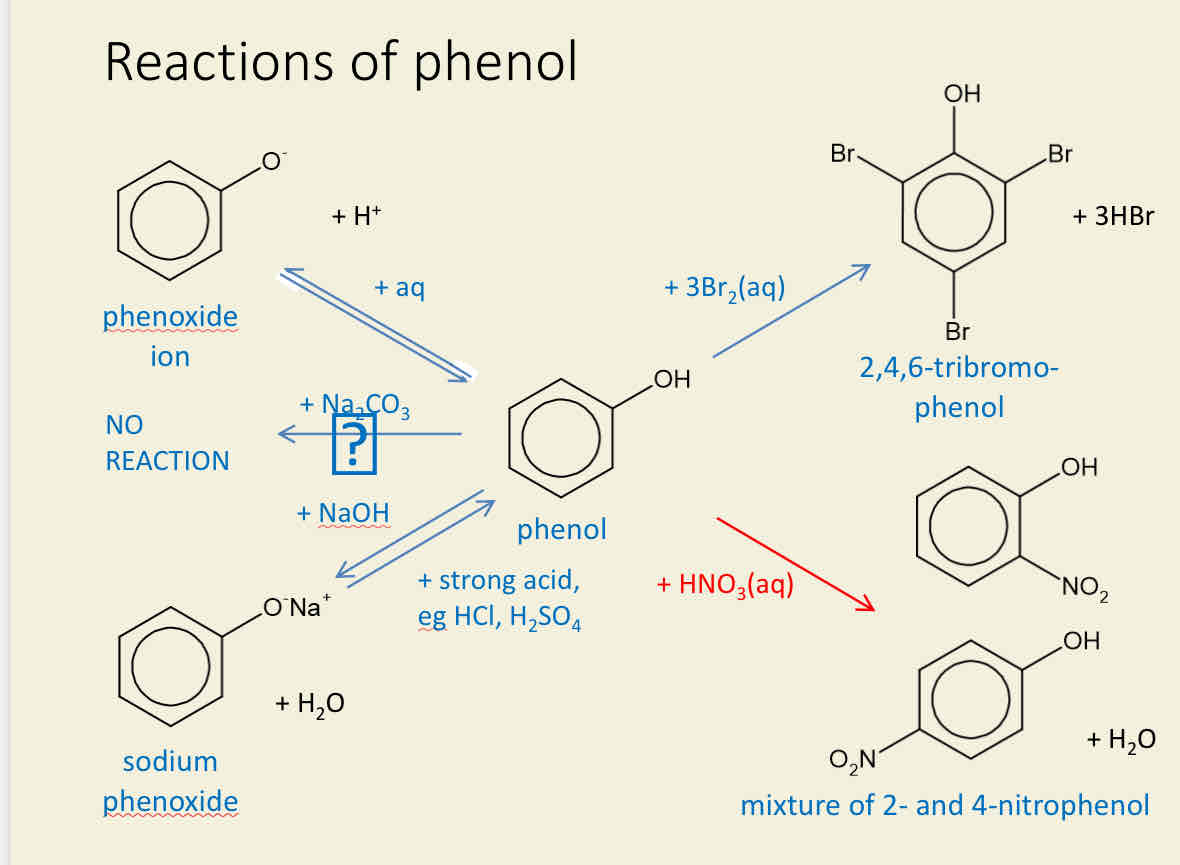
What are the Reactions of phenols
•Phenol reacts with water (aq) to form phenoxide ion and H+ ion
•No reaction occurs between phenol and carbonate
•Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide (NAOH) to form sodium phenoxide and water.
To turn sodium phenoxide back to phenol needs to be a strong acid eg: HCl or H2SO4
•phenol reacts with 3 molecules of bromine water (3Br2 aq) to form 2,4,6 tribromophenol and 3 molecules of hydrogen bromide.
•Phenol can react with nitric acid (HNO3 (aq) to form
a mixture of 2 nitrophenol and 4 nitrophenol with water and a product too.
When phenol reacts with the 3 molecules of bromine (3Br2) (aq) what observations are found
Bromine is decolourised
A white precipitate of 2,4,6 tribromophenol is formed
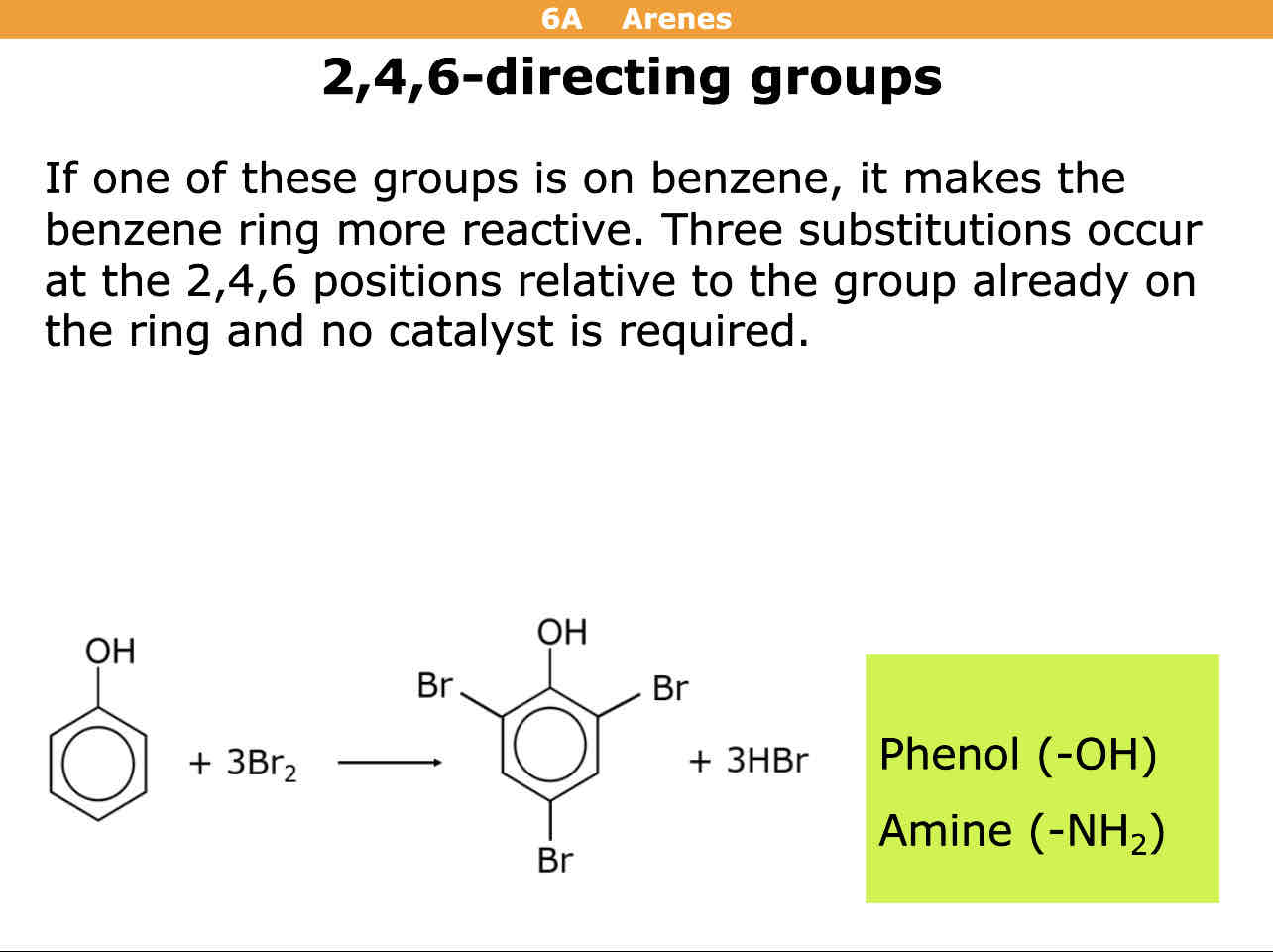
In directing effects if the molecule is a phenol or amine group on it, what director is it
2,4,6
Meaning the molecule it reacts with binds to the 2nd,4th, and 6th position
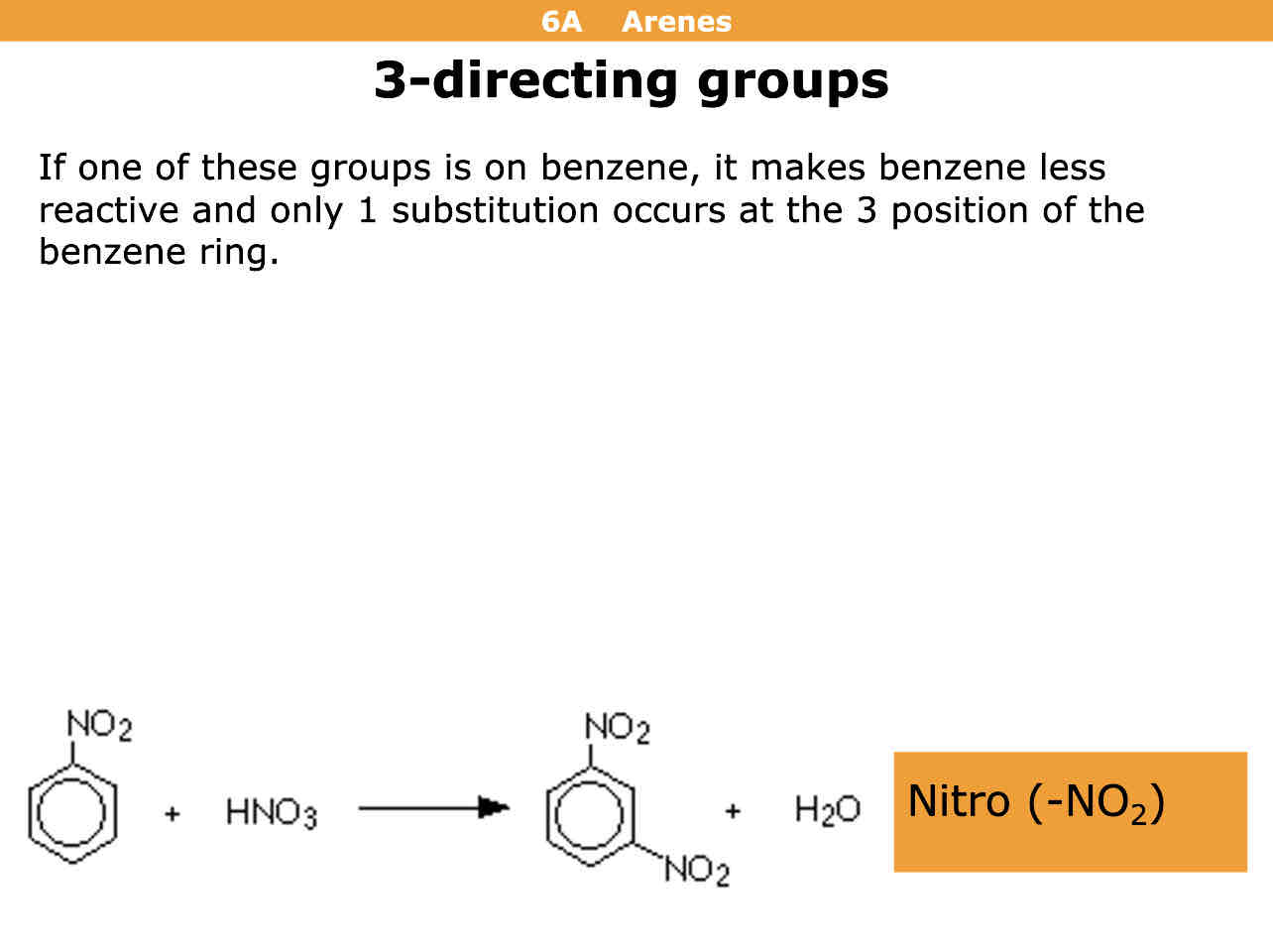
I’m directing effects if the molecule is a nitro what director is it
3 director
Meaning the molecule it reacts with bonds on to the third position
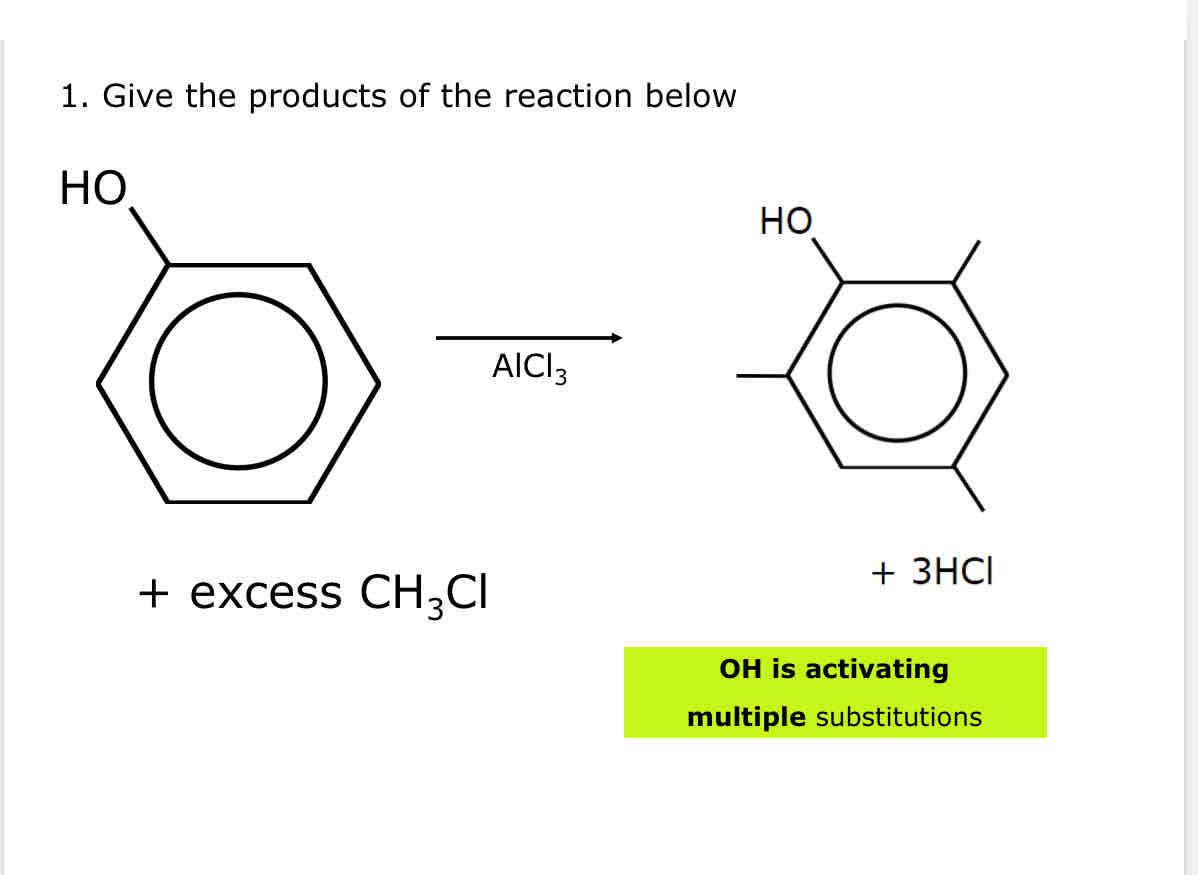
Example of directing
Out of alkenes, arenes and alkanes which is the most to least reactive with electrophiles and why?
Alkene is most = can polarise electrophiles without a catalyst
Arenes 2nd most = a catalyst is needed to ionise elcetrophiles, activated Arenes don’t need a catalyst
alkane least reactive = do not undergo Electrophillic attack so no electron density
However, benzene is less reactive than cyclohexane
How to work out theoretical mass or actual mass in percentage yield question when given percentage yield
If trying to find actual mass it’s 100/ percentage yield
If trying to find theoretical yield it’s percentage yield /100
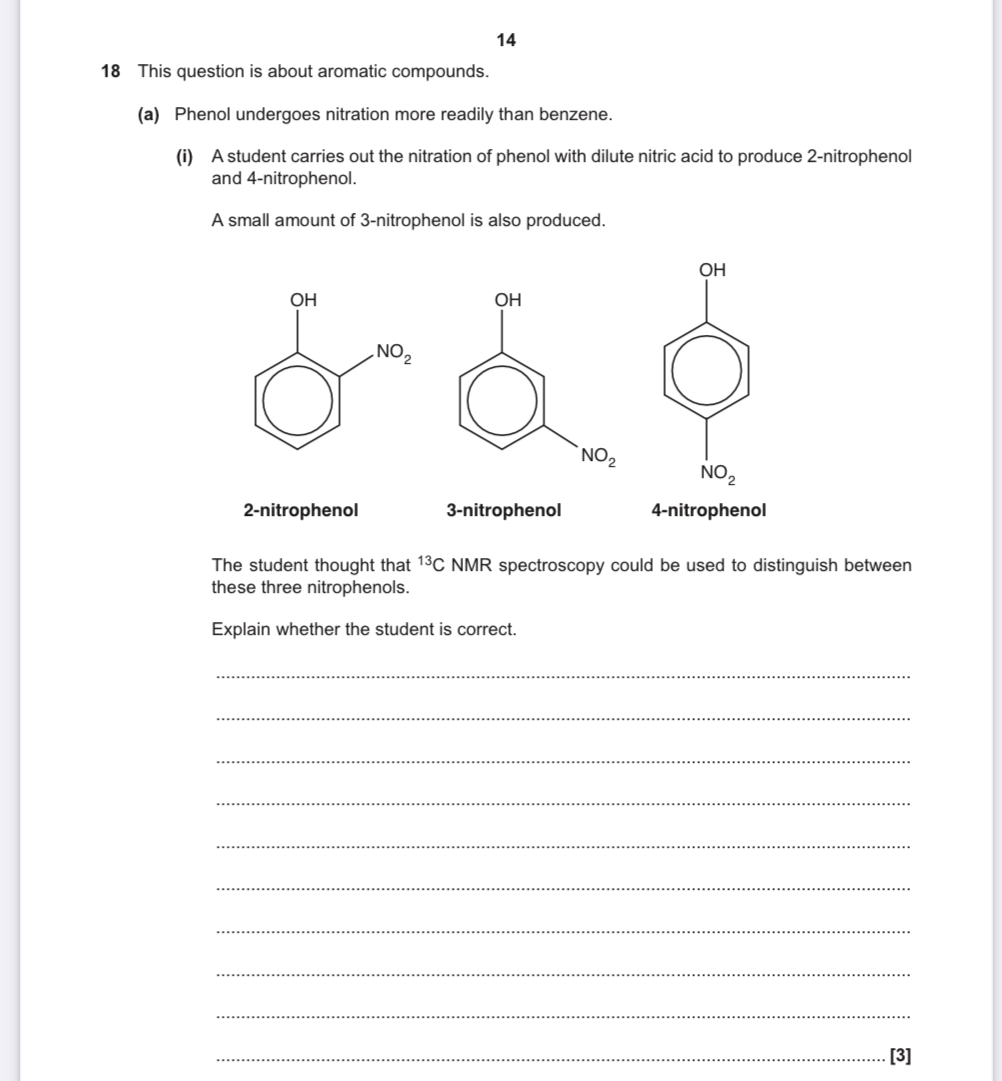
How to answer this type of question
Say which ones have the same carbon environments
Which ones have different carbon environments
Whether they can be distinguished (one that has different environments can be distinguished)