Chemistry Chapter 5
1/45
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Energy Levels
The fixed energies an electron can have.
Quantum
The amount of energy required to move an electron from one energy level to another energy level.
Quantum Mechanical Model
Comes from the Schrodinger equation; it determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus.
Atomic Orbital
A region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron.
How many electrons can an orbital hold?
2 electrons spinning in opposite directions.
How are the energy levels of electrons in the quantum mechanical model labeled?
They are labeled by principal quantum numbers (n). They are assigned the values n=1, 2, 3, 4, etc.
Describe the shape of an s orbital.
Spherical.

Describe the shape of a p orbital.
Dumbell-shaped.

Describe the shape of a d orbital.
Clover-shaped.

Describe the shape of an f orbital.
Clover-shaped as well, although more complex.
What is the formula to find the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a principal energy level?
2n^2
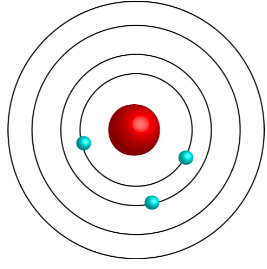
How did Bohr’s model differ from Rutherford’s model of the atom?
He proposed that an electron is found only in specific circular orbits around the nucleus with fixed energies. His discovery included discoveries about how the energy of an atom changes when it absorbs/emits light.
How can electrons in an atom move from one energy level to another?
An electron must gain or lose just the right amount of energy.
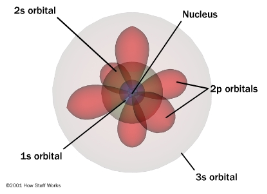
How is the quantum mechanical model different from Bohr’s model?
It does not involve an exact path the electron takes around the nucleus.
Bohr Model Diagram
Electron Cloud/Quantum Mechanical Model Diagram
Electron Configurations
The ways in which electrons are arranged in various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms.
Aufbau Principle
States that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first.
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
States that an atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons. To occupy the same orbital, 2 electrons must have opposite spins and should be paired.
Hund’s Rule
States that electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as large as possible.
How many electrons can the S orbital hold?
It contains 1 orbital, so it can hold a total of 2 electrons.
How many electrons can the P orbital hold?
It contains 3 orbitals, so it can hold a total of 6 electrons.
How many electrons can the D orbital hold?
It contains 5 orbitals, so it can hold 10 electrons.
How many electrons can the F orbital hold?
It contains 7 orbitals, so it can hold 14 electrons.
Amplitude
The wave’s height from zero to the crest.
Wavelength
The distance between the crests.
Frequency
The number of wave cycles to pass a given point per unit of time.
Hertz
The SI units of wave cycles per second.
Electromagnetic Radiation
Includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays (mnemonic: RMI-VUXG).
Spectrum
A collection of what the different frequencies of light (colors) separate into (a rainbow) when sunlight passes through a prism.
Atomic Emission Spectrum
The frequencies of light emitted by an element separated into discrete lines. Each discrete line corresponds to one exact frequency of light (color) emitted by the atom.
Ground State
The lowest possible energy of the electron.
Photons
Light quanta (atoms); they behave like particles.
Louis de Broglie proposed that electrons have some properties of what?
Of waves and light.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
States that it is impossible to know exactly the velocity and position of a particle at the same time.
What is the formula for finding the wavelength or frequency of a wave?
wavelength = the speed of light constant/frequency
What is the symbol and unit for wavelength?
The symbol is the Greek letter lambda (looks like an upside-down V) and the unit is meters (m).
What is the symbol and unit for frequency?
The symbol is the Greek letter nu (looks like a V) and the unit is cycles.
What is the formula of a wave for the speed of light, c?
c = wavelength(frequency)
What is c, the speed of light constant? What is its unit?
2.998 x 10^8 m/s
How are wavelength and frequency of a light wave related?
They are inversely proportional to each other. As wavelength decreases, the frequency increases, and vice versa.
What happens when electrons change energy levels?
They either absorb light (moving up to higher energy levels) or emit light (returning to lower energy levels).
What can the emission spectrum of an element be likened to?
A person’s fingerprint because just as no 2 people have the same fingerprint, no 2 elements have the same emission spectrum.
What is the formula for finding the quantum of energy?
E = hv, where h is equal to 6.626 x 10^-34 Js
What is the unit for energy?
joules (J)
What is the unit for h?
joules (J)