Chapter 2 Research Methodology
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Between-Subjects Design / two random-samples design
each subject is measured once, comparisons are made between TWO GROUPS of subjects
Within-Subjects Design / single group repeated-measures design
each subject is measured at least two times, comparisons are made within the SAME SUBJECT
Mixed Method / two-random-samples & repeated-measures design
a combination of between- and within-subjects design
Operational Definition
It translates abstract psychological constructs like "anxiety" into measurable terms, such as a test score or changes in heart rate
Operant Conditioning / Instrumental conditioning
a learning process where voluntary behaviors are modified by associating them with consequences, either rewards or punishment
Classical Conditioning
behaviors are learned by connecting a neutral stimulus with a positive one
Theory
explains how (mechanistic explanation) or why (functional explanation) something happens, or both how and why
Good Theory
a clear, internally consistent explanation of a psychological phenomenon, aligns with empirical data, can be tested and falsified, and generates new hypotheses
The role of a theory
integrates apparently unrelated facts and principles into a coherent whole
Narrative Review
a descriptive and subjective of the literature on a specific topic
Systematic Review
a structured and rigorous examination of the literature on a specific topic
Meta-analysis
an objective examination of published data from many studies of the same research topic identified through a literature search
Reliability
the consistency or dependability of a measurement tool or research finding
Random Errors
unpredictable differences between a measurement and the true value being measured
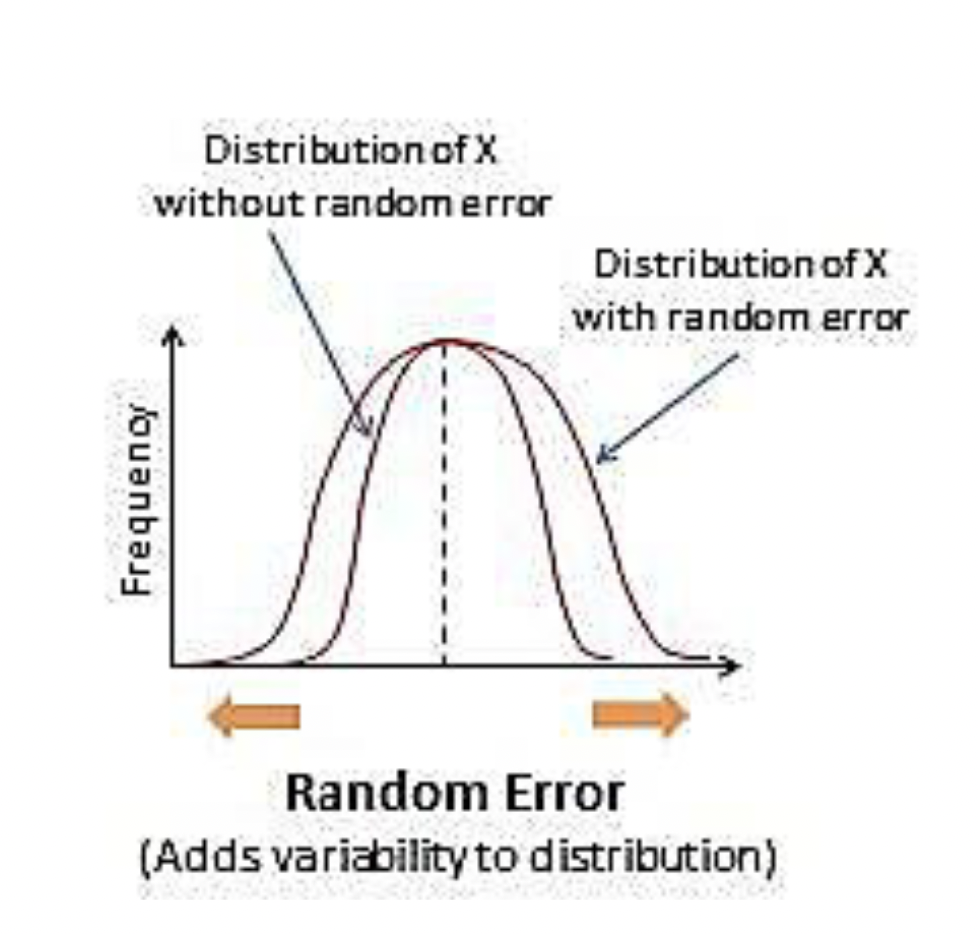
does not affect the average, only the variability around the average
Systematic Errors / Biases
in either the positive or negative direction consistently. They bias the overall measurement
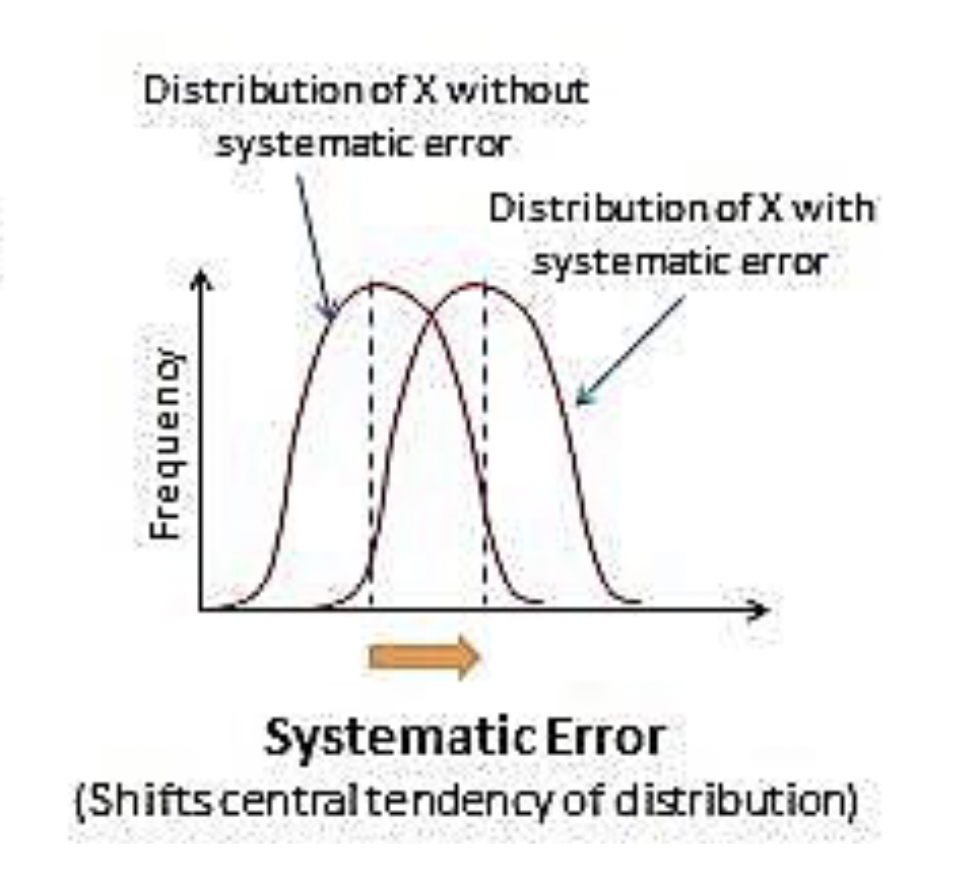
does affect the average, shifting it to the right in this case. We call this a bias
Construct Validity
a test measures the concept it was designed to evaluate
Case Study / n = 1 study (number of observation = 1)
the intensive observation, recording and description of an atypical person, organization, or event
Correlational Studies
non-experimental research designs that explore the relationships between two or more variables, without manipulating or controlling them
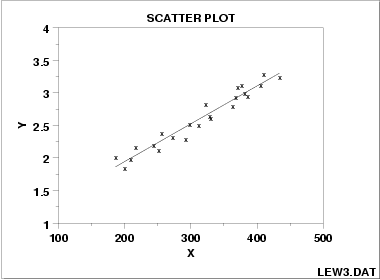
positve correlation
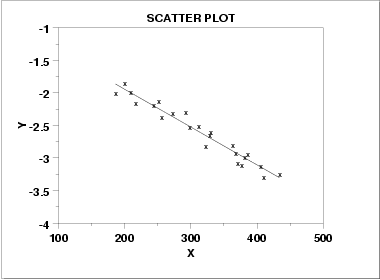
negative correlation
no relation
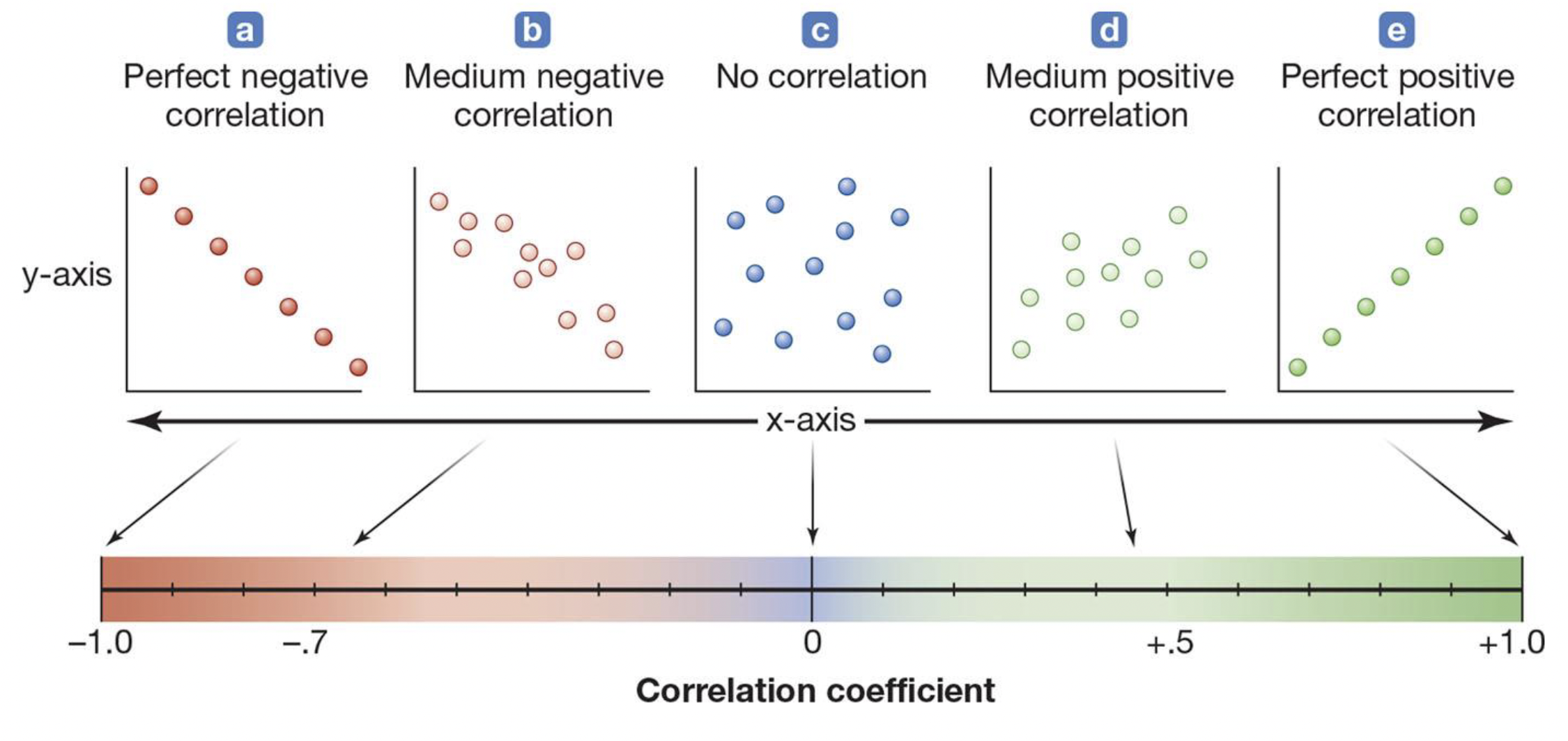
Correlation Coefficient (also called Pearson’s r)
Independent Variable (X variable)
the experimenter controls
Dependent variable (Y variable)
the experimenter measures
Confounding variable (Third variable)
variable that affects a dependent variable and unintentionally varies between experimental conditions of a study
Internal validity
change in the dependent variable is caused by the independent variable and not by the confounding variables
External validity
generalize the findings of a study to other situations, people, settings, and measures, often from the lab to the real world
The control group / the placebo group (in a drug test)
a group of participants who do not receive the experimental treatment or intervention being tested
descriptive statistics
used to organize or summarize a set of data
inferential statistics
ways of analyzing data that allow the researcher to make conclusions about whether a hypothesis was supported by the results