Bio D1 - DNA and Genes
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
How are nucleotide monomers linked together to form a single strand?
Nucleotide monomers are linked together via condensation reactions in which the phosphate grouch of one nucleotide attaches to the sugar of another nucleotide at the 3’ of the 5 carbon sugar, resulting in a phosphodiester bond.
What is RNA and its role in the cell?
RNA is a more versatile single stranded form of nucleic acid that transfers genetic information for decoding
what are sone similarities between DNA and RNA
both have adenine, guanine, cytosine
both polymers of nucleotides
both have five carbon sugars
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
phosphate group (circle)
5 carbon pentose sugar (pentagon)
nitrogenous base (rectangle)
what are two types of nucleic acids present in cells?
RNA and DNA
What is DNA and what is its role in the cell?
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a stable double stranded form of nucleic acid and acts as the genetic blueprint of a cell
How does DNA and RNA differ in terms of composition?
DNA
deoxyribose pentose sugar
AGCT
adenine
guanine
cytosine
thymine
double stranded
longer
antiparallel
double helix
RNA
ribose pentose sugar
AGCU
Adenine
guanine
cytosine
uracil
single stranded
shorter
How are two polynucleotide chains of DNA held together?
Two polynucleotide chains of DNA are held together via hydrogen bonding between complementary nitrogenous bases.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) via two hydrogen bonds
Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) via three hydrogen bonds
Why must the strands of DNA be running in opposite directions for the bases to be able to pair?
The strands of DNA must be running in opposite directions for the bases to be able to pair because the nitrogenous bases are only complementary in a specific orientation.
How are the two strands of DNA described in terms of their directionality and how do they organise themselves?
The two strands of DNA are described as being antiparallel.
As the antiparallel chains lengthen, the atoms will organise themselves into the most stable energy configuration
This atomic arrangement results in the double-stranded DNA forming a double helix
What is DNA?
DNA is the genetic blueprint which codes for, and determines, the characteristics of an organism, including the physical, behavioural, and physiological features.
How is DNA packaged and organized in a cell?
DNA is packaged and organized into discrete structures called chromosomes.
What is a gene?
A gene is a sequence of DNA that encodes for a specific trait. Traits may also be influenced by multiple genes.
What is the name given to the position of a gene on a particular chromosome?
The position of a gene on a particular chromosome is called the locus (plural = loci).
How do genes determine the characteristics of an organism?
Genes contain the information necessary to produce specific proteins, which in turn determine the traits of an organism.
What are alleles and how do they differ from one another?
Alleles are alternative forms of a gene that code for the different variations of a specific trait.
As alleles are alternative forms of the one gene, they possess very similar gene sequences
Alleles only differ from each other by one or a few bases
What is an example of a gene that has alleles that encode different variations of a trait?
The gene for eye colour has alleles that encode different shades/pigments.
What is a gene mutation?
A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a section of DNA coding for a specific trait.
and also forms new alleles
What is a beneficial mutation?
Missense Mutation
A beneficial mutation changes the gene sequence (missense mutations) to create new variations of a trait that is an advantage to the organism.
What is a detrimental mutation?
Nonsense Mutation
A detrimental mutation truncates the gene sequence (nonsense mutations) to abrogate the normal function of a trait, which can negatively impact the organism's survival or reproductive success.
What is a neutral mutation?
Silent Mutation
A neutral mutation has no effect on the functioning of the specific feature (silent mutations), and does not confer an advantage or disadvantage to the organism.
What is a genome?
The genome is the totality of genetic information of a cell, organism or organelle
What does the human genome consist of?
46 chromosomes (barring aneuploidy)
~3 billion base pairs
~21,000 genes
What is the DNA organisation of prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes do not possess a nucleus – instead genetic material is found free in the cytoplasm in a region called the nucleoid, bacterial chromosomes have long uncoiled DNA
Some have shorter DNA strands called plasmids that only contain a few genes and are capable of self-replication
What is the organisation of DNA in a Eukaryotic cell?
consist of multiple linear molecules of DNA that are associated with histone proteins
DNA coiled and wrapped around a set of 8 histones form a nucleosome
where genes are found and is a locus for gene position
has pairs of chromosomes = homologous chromosomes
same genes, loci, length, centromere position
What is a homologous pair?
sexually reproducing organisms inherit their genetic sequences from both parents
organisms possess two copies of each chromosome (1 mom and 1 dad)
same genes at the same loci but not the always the same allele
what are the difference between diploids and haploids?
as sexually reproducing organisms receive genetic material from both parents, that have two sets of chromosomes (23 pairs of 46 chromosomes), called diploids
however, to reproduce, organisms must create gametes with half the number of chromosomes in order to fuse with another chromosome’s gametes, called haploids
What does a diploid possess?
Nuclei possessing pairs of homologous chromosomes
These nuclei will possess two gene copies (alleles) for each trait
All somatic (body) cells in the organism will be diploid, with new diploid cells created via mitosis
What does a haploid possess?
Nuclei possessing only one set of chromosomes
These nuclei will possess a single gene copy (allele) for each trait
only gametes
What is a heterosome?
sex is determined by a pair of chromosomes called the sex chromosomes (or heterosomes) 23rd pair in a karyogram
Female is XX
Male is XY (y is short)
female is default without the y present
what is an autosome?
any other chromosome in the organism and do not determine sex
What is a karyogram?
a process to determine the number and types of chromosomes in a eukaryotic cell
chromosomes obtained by chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis (placenta or white blood cells)
inducing cell division then arresting mitosis when chromosomes are supercoiled in P1
stained to generate an image
How are karyograms organised and used for?
chromosomes of an organism are arranged into homologous pairs according to size, length
Determine the gender of the unborn child (via identification of the sex chromosomes)
Test for chromosomal abnormalities
What is down syndrome?
disjunction of chromosome 21, where there is an extra chromosome
The extra genetic material causes mental and physical delays in the way the child develops
What is autoradiography?
process to measure the length of DNA
grow prokaryotic cells in radioactive thymine and there is no T in RNA
DNA extracted from cells and fixed onto photographic paper
radiation released and after a period of exposure an image appears on the page and can be visualised
What is random assortment?
the order line up of chromosomes in the equator of the cell in metaphase with mom left and dad right or dad left and mom right
order is completely random
What is non-disjuction and where are the two places they can occur in meiosis?
chromosomes failing to spearate correctly, resulting in gametes with one extra or one less chromosome
occurs via:
Failure of homologues to separate in Anaphase I (resulting in four affected daughter cells)
Failure of sister chromatids to separate in Anaphase II (resulting in only two daughter cells being affected)
What is the Law of Dominance?
alleles can be dominant or recessive
the dominant phenotype is expressed with one or two dominant alleles: homozygous dominant or heterozygous genotypes. PP, Pp
the recessive phenotype is expressed with two recessive alleles: homozygous recessive genotype. pp
What is the law of Segregation?
each phenotype is controlled by two alleles
only one allele for a trait is passed on through gametes to offspring from each parent
offspring receive one allele for a trait from each parent
What is the Law of Independent Assortment?
the inheritance of one gene does not affect the inheritance of another gene
homologous chromosomes undergo random orientation in Metaphase I
genes on non-homologous chromosomes are randomly assorted in Anaphase I
What is a haploid gamete?
only carry one allele of each gene
the two alleles of each gene is separated into different haploids during meiosis
what are Punnett grids?
A monohybrid cross determines the allele combinations for potential offspring for one gene only

What is cystic fibrosis?
autosomal recessive disease
extra info: thick and sticky mucus clogs bronchioles and secretory ducts; leads to respiratory failure and pancreatic cysts

What is sickle cell anaemia?
autosomal codominant disease
causes fibrous hemoglobin rather than globular; cells become sickle shaped; leads to poor oxygen transport, clogged vessels, and malaria resistance

What is Hemophilia and Red-green colorblindness?
sex-linked recessive disorders
extra info: hemophilia is a blood clotting disorder; colorblindness is the inability to perceive certain colors

What are the Human ABO blood types?
multiple alleles (≥2): IA IB i
autosomal dominant-recessive and codominant
controls type of glycoprotein used for cell recognition

What are the inheritance patterns?

What is a pedigree chart and what does is do?
A pedigree is a chart of the genetic history of a family over several generations
Males are represented as squares, while females are represented as circles
Shaded symbols mean an individual is affected by a condition, while an unshaded symbol means they are unaffected
A horizontal line between man and woman represents mating and resulting children are shown as offshoots to this line
Generations are labeled with roman numerals and individuals are numbered according to age (oldest on the left)
Nitrogenous Bases
- Adenine | A
- Thymine | T
- Cytosine | C
- Guanine | G
- Uracil | U
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
DNA Function
Holds the code for protein synthesis within a cell, called genes. Processes of protein synthesis is called “transcription” and “translation”.
It’s able to copy itself for cell division called replication within the S-phase of the cell cylce.
DNA Structure
It’s a double helix, it’s double strands are attached to each other by hydrogen bonds which are twisted into a spiral. The backbones are made of phosphate and sugars while the rungs are composed of nitrogenous base pairs.
These nucleotides are composed of phosphate, 5 C-sugar/deoxyribose and a nitrogenous base.
Nitrogenous Bases: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine & Cytosine.
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid
RNA Function
There are several functions:
mRNA - Copy of a gene that leaves the nucleus and carries the message into the cytoplasm and to a ribosome for protein synthesis.
tRNA - Reads the mRNA and carries amino acids to the correct ribosome.
RNA Structure
It only has a single strand of nucleotides which are composed of 5-C sugar ribose.
Nitrogenous Bases: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine & Uracil.
Nucleotides
In a chain connected to each other by covalent bonds, meaning electrons are shared between atoms.
Complementary nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds which are weak bonds where there’s a proton in one atom while the other one is an electron.
Protein Synthesis
DNA is the holder of codes responsible for protein synthesis.
Transcription Summary
Makes a copy of a gene on DNA to turn into a molecule of RNA.
Transcription Steps
Happens in the nucleus.
Enzyme RNA polymerase is needed to open the hydrogen bonds between the double-stranded DNA which makes a strand of mRNA next to one of the DNA strands.
RNA nucleotides are already present in the nucleus and places the nitrogenous bases into complementary pairs.
C —> G | A —> U
The mRNA leaves the nucleus and the DNA goes back together.
Translation Summary
Translates the code on mRNA into amino acids in correct order.
Translation Steps
Happens on the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
mRNA has the code copy of DNA and goes to the ribosome.
The code is read in groups of three nitrogenous bases called codons.
tRNA reads the code and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome for each codon. tRNA has a complementary anticodon which will bind with the mRNA codon.
When two tRNAs are in the ribosome a peptide bond will form between the amino acids and the chain will further longate.
The ribosome will move further along the mRNA until it hits a certain codon. All parts will separate and the protein can leave the ribosome.
What is mitosis?
the division of a cell into two identical daughter cells
What are sister chromatids?
replication to form chromosome in S phase, genetically identical DNA molecules
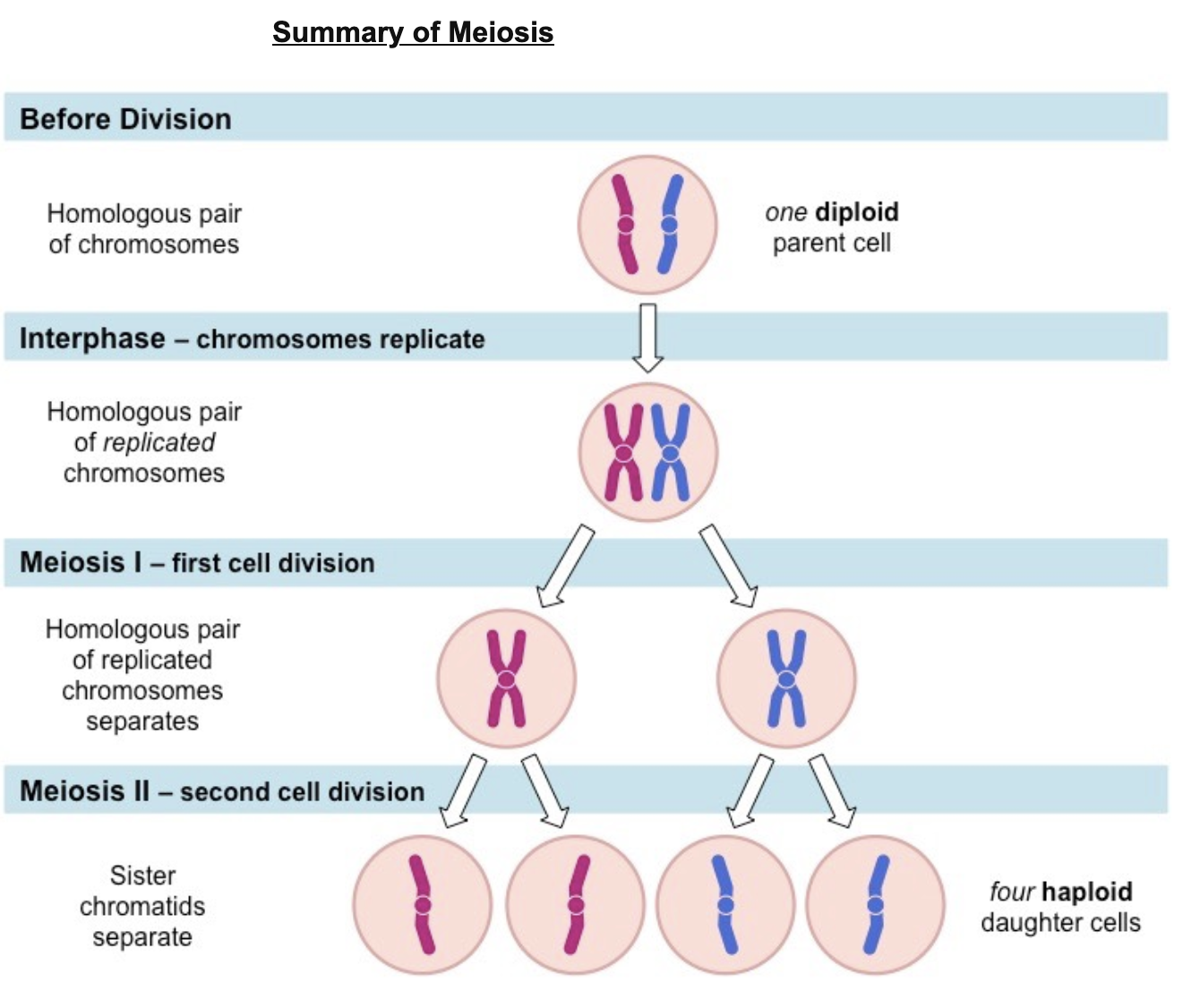
What processes occur in Meiosis 1?
The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated
P-I: Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs
M-I: Spindle fibres from opposing centrosomes connect to bivalents (at centromeres) and align them along the middle of the cell
A-I: Spindle fibres contract and split the bivalent, homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
T-I: Chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane may reform, cell divides (cytokinesis) to form two haploid daughter cells
What occurs in Meiosis 2?
The second division separates sister chromatids (these chromatids may not be identical due to crossing over in prophase I)
P-II: Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrosomes move to opposite poles (perpendicular to before)
M-II: Spindle fibres from opposing centrosomes attach to chromosomes (at centromere) and align them along the cell equator
A-II: Spindle fibres contract and separate the sister chromatids, chromatids (now called chromosomes) move to opposite poles
T-II: Chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane reforms, cells divide (cytokinesis) to form four haploid daughter cells
What is crossing over?
when two homologous chromosomes pair up in prophase 1 and one of each sister chromatids cross over and trade genetic material, then when separated in metaphase 1, each chromatid is genetically unique. and sisters are no longer identical