Patterns of Inheritance, Patterns of Inheritance
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Gregor Mendel
the Father of Genetics; studied inherited traits of pea plants
Mendels 3 important ideas
1) Traits are dominant and recessive
2) Genes and alleles
3) Segregation of alleles
Dominant Gene
Dominant variant is displayed in hybrids; shown
Recessive gene
Recessive variant is masked by dominant; not shown.
Codominant
Inheritance pattern in which a heterozygote expresses the distinct trait of both alleles.
autosomal dominant
inheritance pattern of a dominant allele on an autosome
autosomal recessive
inheritance pattern of a recessive allele on an autosome
X-linked recessive
What pattern of genetic transmission affects only M and has no M-to-M transmission, and mother is usually an unaffected carrier?
X- linked dominant
a mode of genetic inheritance by which a dominant gene is carried on the X chromosome
Genes ; alleles
A ________ has 2 forms, or _______; every individual has two ________, one from mom and other from dad
Segregation of alleles
allele pairs separate randomly from each other during production of gametes
Genotype
The genetic composition of an individual. Provides the plan to create phenotype.
TT
homozygous dominant
Tt
Heterozygous
tt
homozygous recessive
Phenotype
Physical or behaviorial characteristics that are the result of gene expression.
ex)
TT and Tt are tall
tt is short
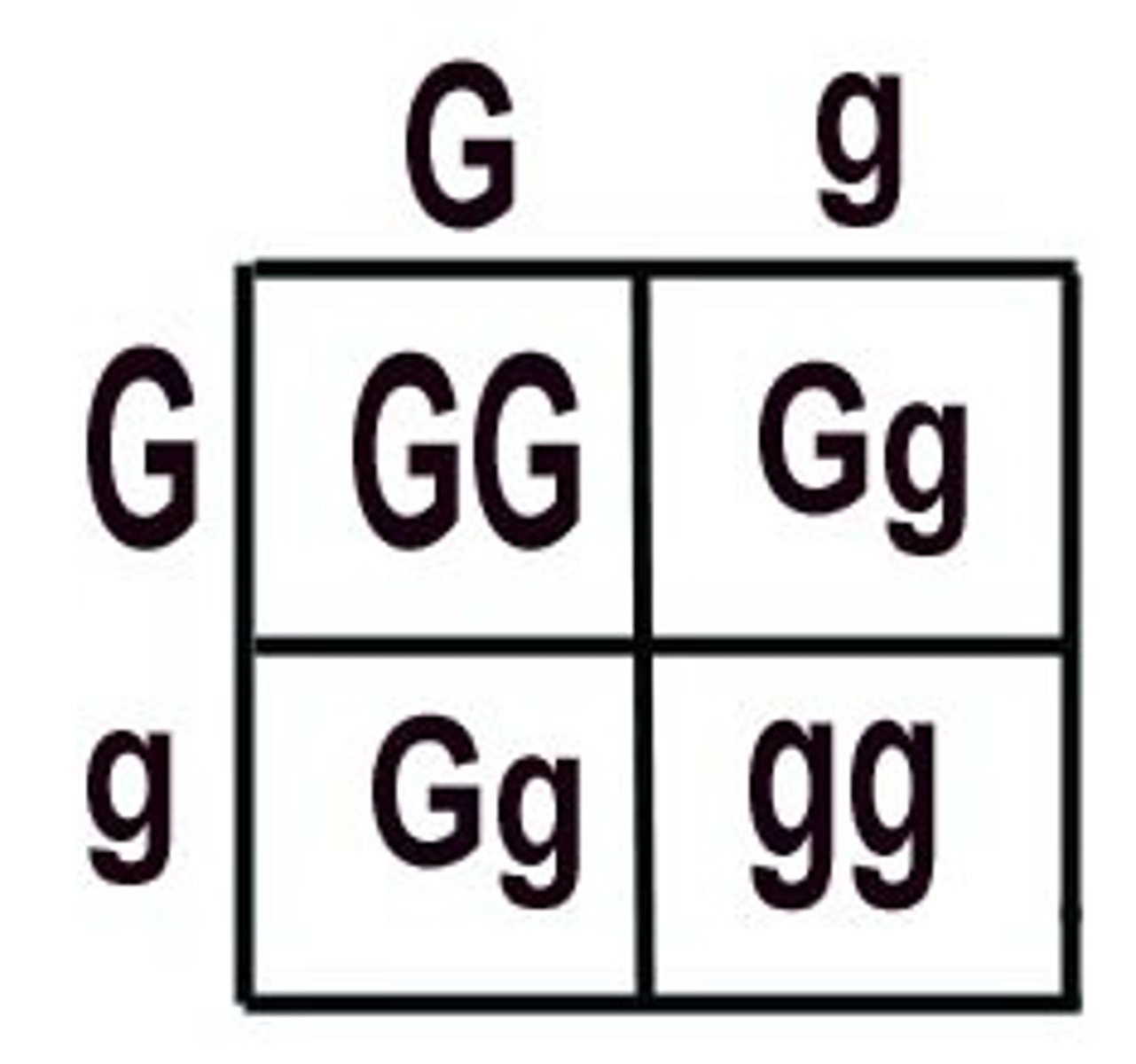
Punnett Square
Make sure to practice, with genotype and phenotype ratios.
Law of independent assortment
Alleles of different genes assort independently of each other during gamete formation.
Simple mendelian inheritance
Alleles are dominant or recessive; Phenotype ratios follow mendels laws.
Complex forms of inheritance
Incomplete dominance and Codominance are....
Autosomes
All chromosomes except the sex chromosomes
(X and Y) are called?
Autosomal dominant
Where the disease is dominant and more common to get then not (Ex. Huntington's disease)
Codominance
A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive.
environment
What plays a significant role on the phenotype of genes?
Male sex chromosome pattern
XY
Female sex chromosome pattern
XX
X chromosome
Which is larger and carries more genes? X or Y?
X-Linked genes
Genes found on the X but not the Y
Maternal inheritance
inheritance of DNA that occurs through the cytoplasm of the egg
Biparental inheritance
inheritance from two parents
Gregor Mendel
"father of genetics" studied peas to figure out if the differences in how the peas looked. He looked at wrinkled vs. smooth peas. he found the principle of independent assortment
Mendellian Genetics
1 gene= 1 trait
independent assortment
autosomal chromosome traits
genetics
study of how the traits were passed down from parent to offspring
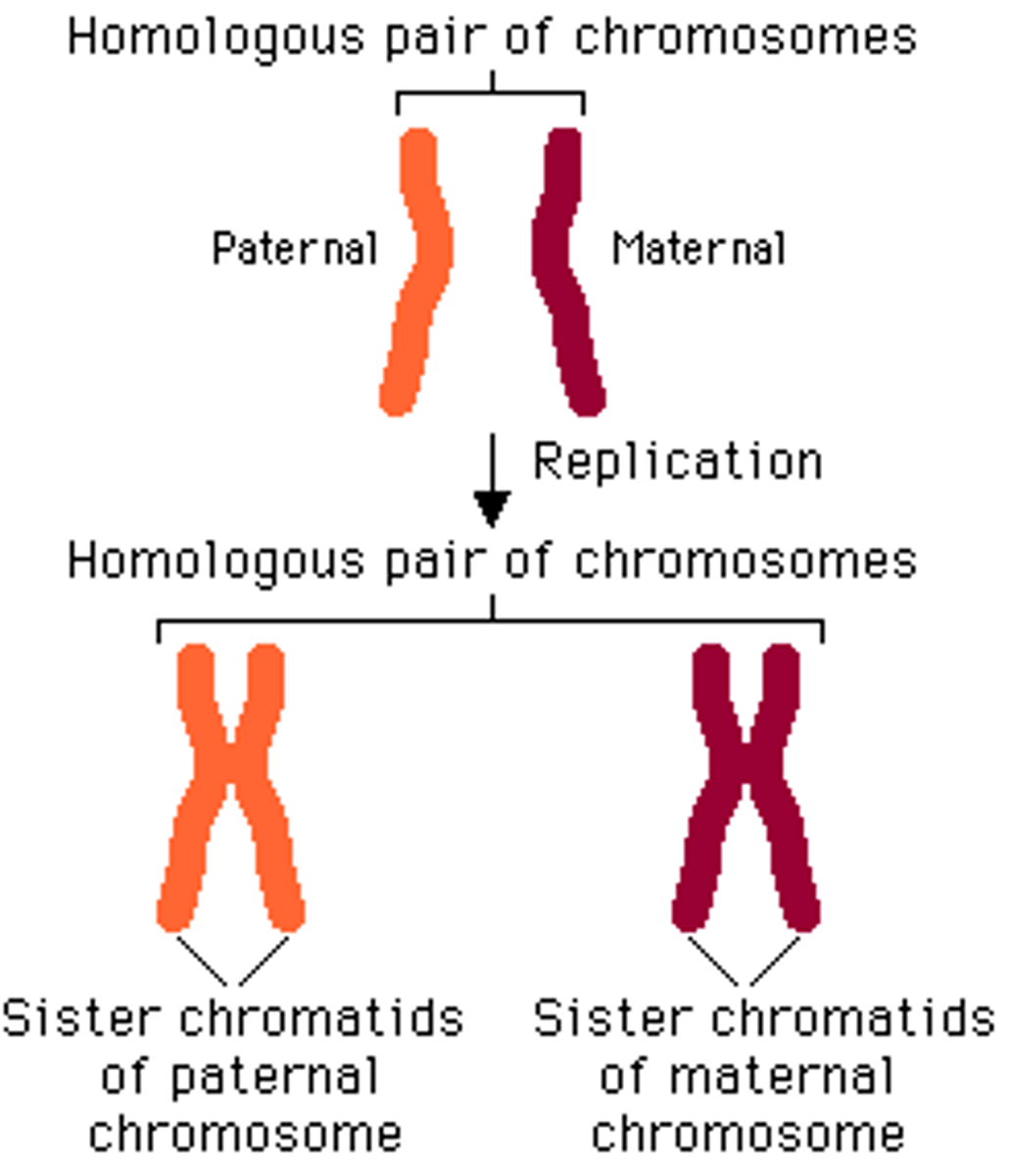
homologous pairs
one maternal one paternal chromosome come together to make.....
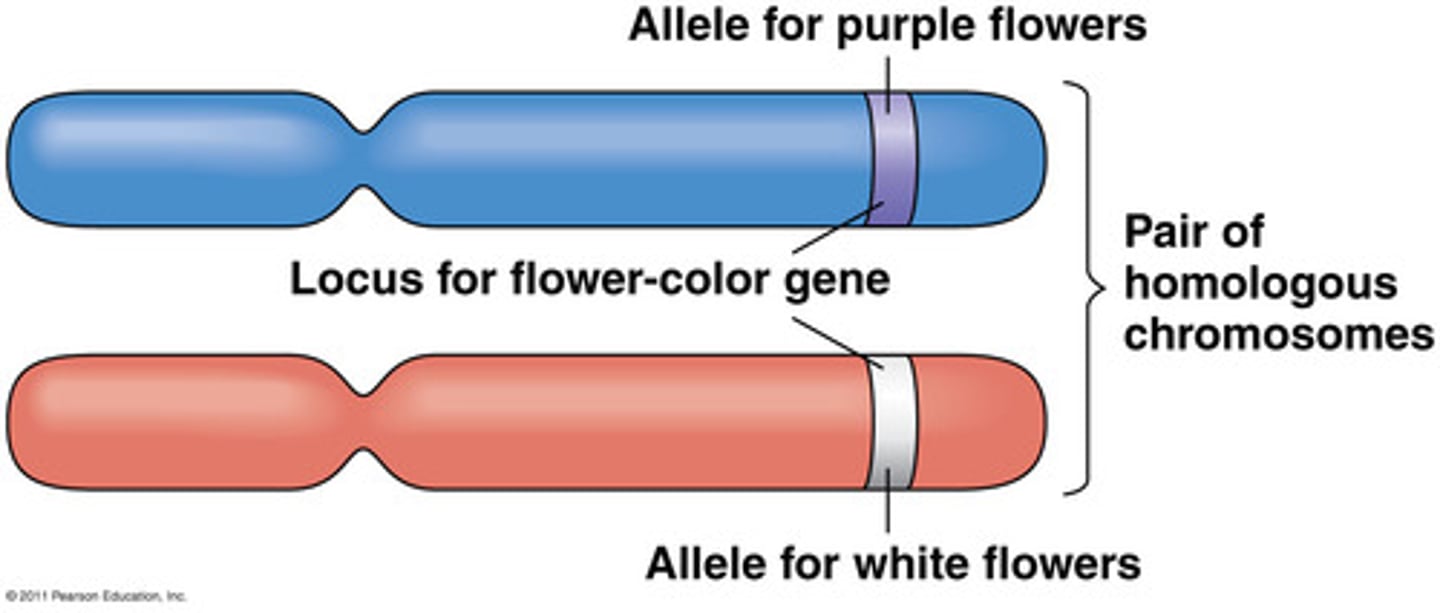
Alleles
different genes (possibilities) for the same trait
ex: blue eyes or brown eyes
sex chromosomes
The last pair of chromosomes on a karyotype
Letters
= 2 alleles given for a gene
capital letter
dominant gene
lowercase letters
recessive gene
genotype
Ex. sS; dd ; DD
how many alleles so you get from your parents?
dad gives you one because sperm is haploid and mom gives you one because egg is haploid
Homozygous
two alleles that are the same
Homozygous dominant
TT
homozygous recessive
tt
Heterozygous (Hybrid)
Tt
Punnet Square
used to predict the possible gene makeup of offspring
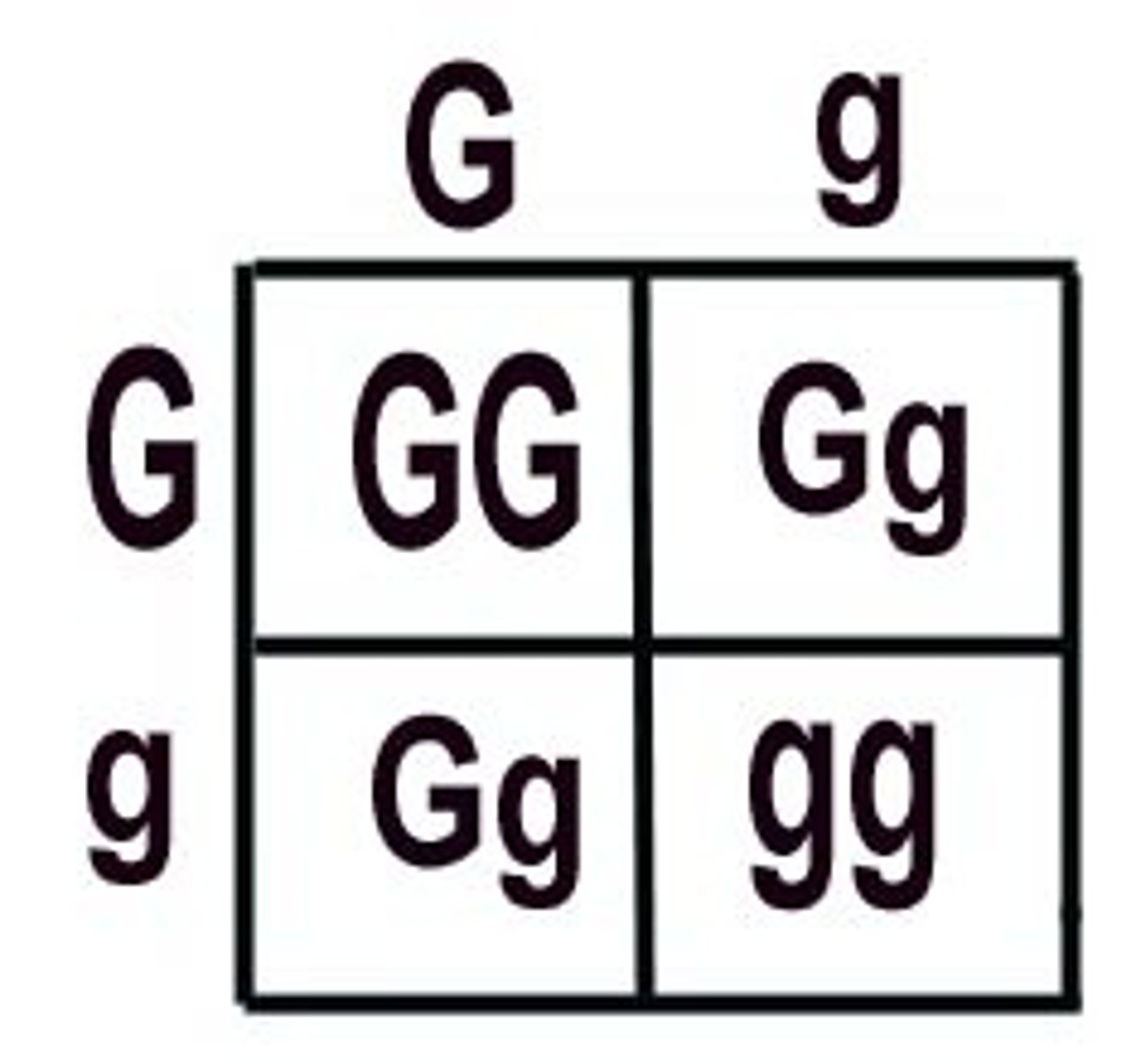
The recessive allele will be masked by a dominant
Why does a recessive allele not kill you?
Incomplete dominance
combination of two alleles
two alleles are mixed (mixed person white and black) RR red x rr white = 100% pink
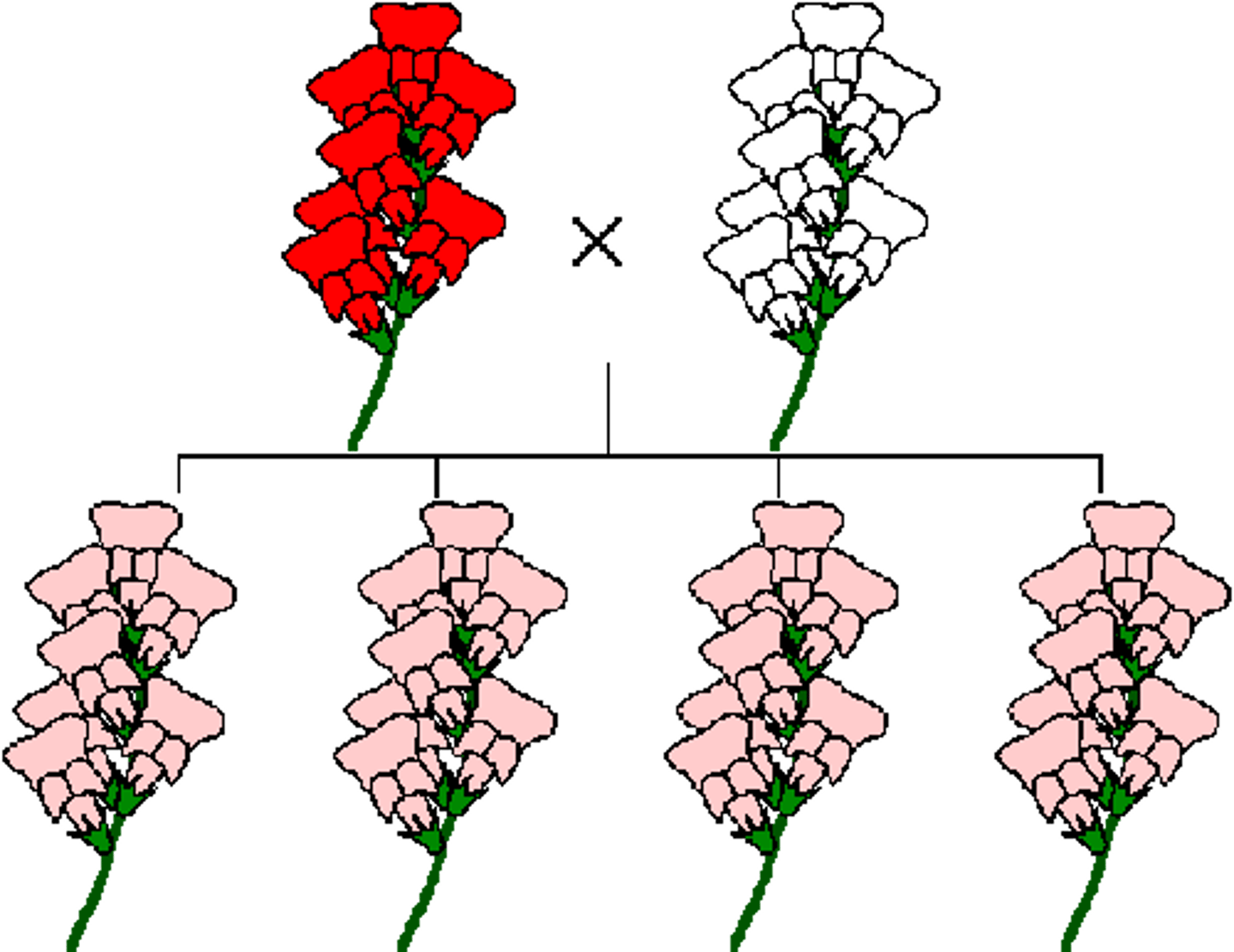
Co Dominance
full expression of both alleles in the heterozygous individual
makes an individual with alleles from both parents (no mixing)
3 alleles for blood
IA(A oligosaccharides on the surface of red blood cells)
IB( B oligosaccharides on the surface of red blood cells)
i (O) (no oligosaccharides on the surface of red blood cells)
Universal reciever
type AB- type AB blood can receive blood from all types
-A because it has blood type A
-B because it has blood type B
-O because there are no antigens attached so it wont cause a reaction
universal donor
type O
-no antigens on the blood so no reaction will happen if any blood type enter an O blood type cell
Polygenic Inheritance
multiple genes combining together and contributing to one phenotype
-the large distribution of a single characteristic
ex: skin color, eye color, intelligence
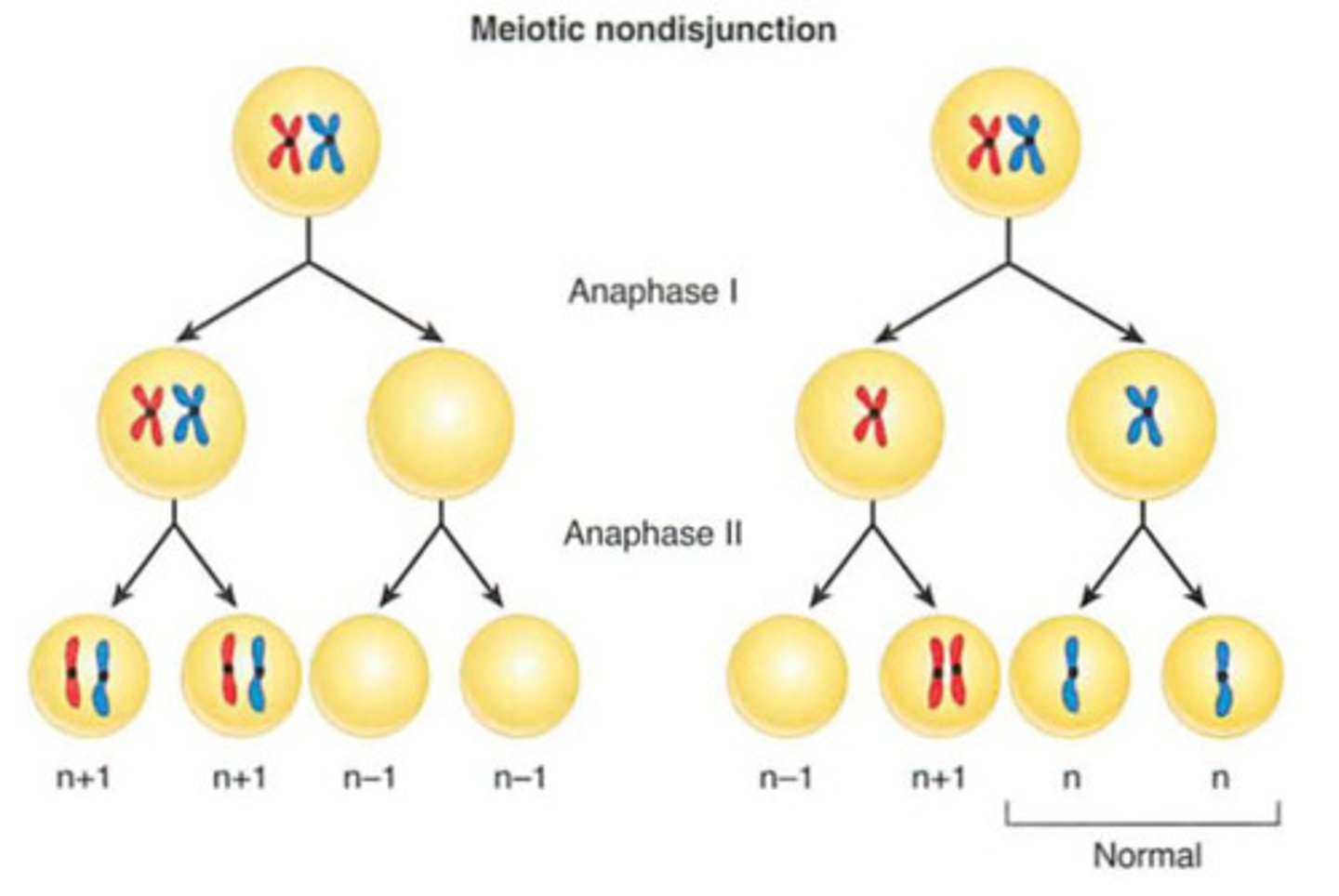
Nondisjunction of chromosome #21
down syndrome
Colorblindness
inherited from dad, when you have Xb and cannot see color
Hemophilia
missing a blood clotting protein and can bleed to death
-X linked
Huntington's Disease
loss of muscle control and mental functions; causes death 35-45 years old within 10 years of symptom appearance
-autosomal dominant
Sickle Cell Anemia
when the red blood cells are very thin and shape in a crescent moon shape and cause lack of blood flow and oxygen for major organs; immunity to malaria

Phenyiketonuria (PKU)
they lack the able to convert amine=o acid to other amino acids
tay sachs
defective enzyme with fatal death within ages of 3-5 and causes to break down a section of brain lipids; causes seazure, blindness, and muscle
Albinism
lack pigment or melanin at all. no cure and bad sunburns

dad because he has the y chromosomes and those determine gender
Which parent determined your gender?
Mom only has Xs
why cant you get an y from mom?
Pedigrees
a genetic family tree showing disease (circle is woman square is male and colored in box or circle that the disease has affected the individual )
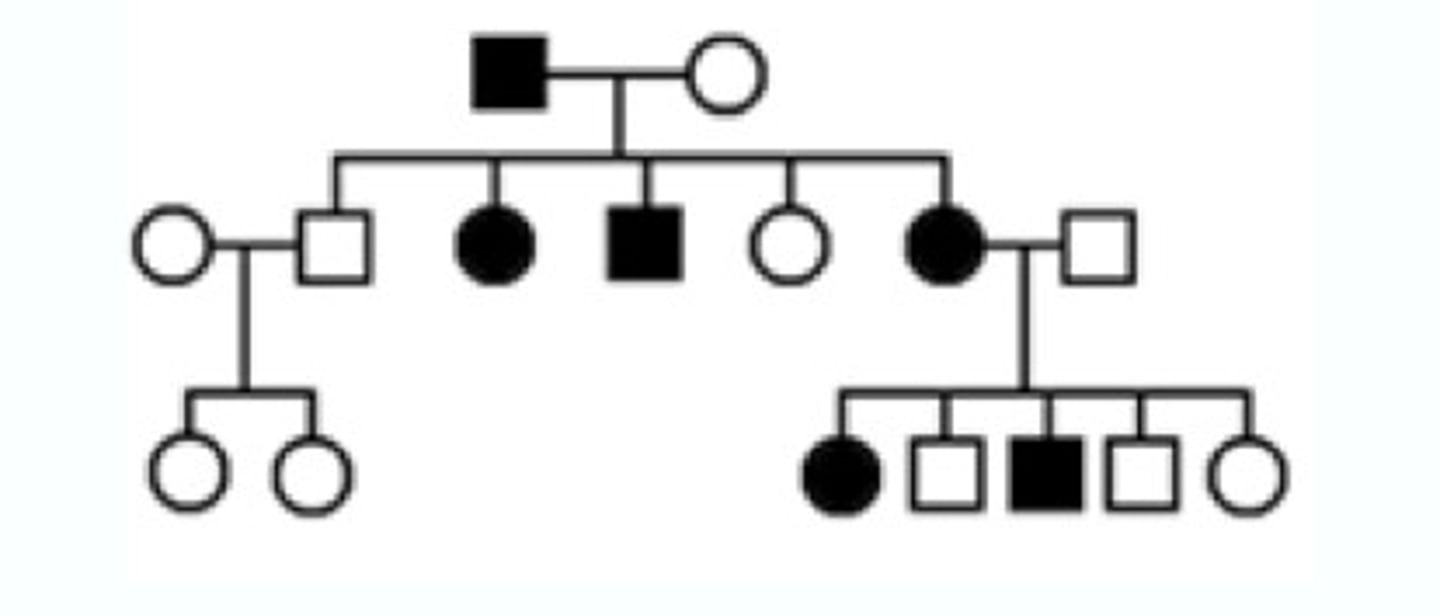
Carriers
Males can never be.....
A carrier
A female who is heterozygous for a disorder
nondisjunction
missing chromosomes or chromosome sections occur
-too may or not enough chromosomes in each gamete after cell formation
Cystic Fibrosis
Disorder that affects the mucus build up in the lungs
polydactyly
Have extra digits on your extremities
-1/500 has more than 5 fingers/toes
-499/500 are homozygous recessive (aa) (arent affected)
environmental affect on genes
-phenotype is controlled by both environment and genes
(pH, condition, heat sensitive alleles)
duchenne muscular dystrophy
loss of voluntary muscle
xlinked
Turner
XO
missing other X chromosome (women)
kleinfelter
XXY
extra X chromosome (men)
karyotype
shows the complete sets of chromosomes in an individual
Phenotype
Ex. Big ears vs. small ears