cell transport test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
what are the two kinds of cell transport?
passive transport and active transport
2
New cards
what is passive transport?
movement across the cell membrane that does not require energy (high concentration to low concentration & moves WITH the concentration gradient)
3
New cards
what is active transport?
movement across a cell membrane that does require energy (low concentration to high concentration & moves AGAINST the concentration gradient)
4
New cards
what is the main component of the cell membrane?
phospholipids
5
New cards
polar
hydrophilic
hydrophilic
hydrophilic
6
New cards
non-polar
hydrophobic
7
New cards
head
polar (hydrophilic)
8
New cards
tail
non-polar (hydrophobic)
9
New cards
what is another name for the cell membrane?
phospholipid bilayer
10
New cards
what types of substances can pass through the cell membrane? (2 examples)
small and hydrophobic
* carbon dioxide
* oxygen
* carbon dioxide
* oxygen
11
New cards
what types of substances need a transport protein?
large and hydrophilic
* sodium
* potassium
* calcium
* fluoride
* sodium
* potassium
* calcium
* fluoride
12
New cards
what does it mean that the cell membrane is selectively permeable?
only allows certain molecules to enter
* extremely small
* hydrophobic (non-polar) molecules
* extremely small
* hydrophobic (non-polar) molecules
13
New cards
concentration gradient
a difference in the distribution of substances across a space
14
New cards
solute
the substance that is being dissolved
15
New cards
solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves
16
New cards
what is it called when concentration is equal inside and outside of the membrane?
* equilibrium
* homeostasis
* homeostasis
17
New cards
what are the types of active transport?
ion pumps, exocytosis and endocytosis.
18
New cards
what are the types of passive transport?
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
19
New cards
What are ion pumps?
Membrane-spanning proteins that allow ions to pass in/out but they require energy
20
New cards
What is exocytosis?
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
21
New cards
What is endocytosis?
process by which the cell takes in materials that are too large to pass through by folding in the cell membrane.
22
New cards
What is diffusion?
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. **DOES NOT REQUIRE ENERGY!**
23
New cards
What is facilitated diffusion?
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels. **DOES NOT REQUIRE ENERGY!**
24
New cards
What is osmosis?
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. **DOES NOT REQUIRE ENERGY!**
25
New cards
hypotonic
A solution that causes cell to swell (hypo - hippo)/a solution with the greater concentration of solvents
26
New cards
hypertonic
A solution that causes cell to shrivel/a solution with the greater concentration of solutes
27
New cards
isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
28
New cards
equillibrium
a condition in which molecules are spread evenly(equally)
29
New cards
Phagocytosis
process in which extensions of cytoplasm surround and engulf large particles and take them into the cell also called "cell eating"
30
New cards
Pinocytosis
process by which a cell takes in liquid from the surrounding environment also called "cell drinking"
31
New cards
aquaporins
channel proteins that facilitate the passage of water
32
New cards
permeability
how well a substance can pass through something
33
New cards
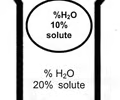
what is the missing percentage? hyper, iso, or hypo? what direction does the water travel in(in or out of the cell)?
cell: 90% H20 solution: 80% H20 water travels out the cell hyper because water is exiting the cell (causes cell to shrivel)
34
New cards
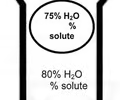
what is the missing percentage? hyper, iso, or hypo? what direction does the water travel in(in or out of the cell)?
cell: 25% solute solution: 20% solute water travels into the cell hypo because water is because water is entering the cell (causes the cell to expand
35
New cards

what is the missing percentage? hyper, iso, or hypo? what direction does the water travel in(in or out of the cell)?
cell: : 90% H20 solution: 90% H20 water travels both in and out cell iso because both have the , water travels both ways
36
New cards
diffusion occurs because of
random movement of particles
37
New cards
Diffusion can be accelerated by
increasing temperature
38
New cards
dynamic equilibrium
when materials pass into and out of a cell at equal rates, there is no net change in concentration inside the cell.
39
New cards
what is ATP and what does it stand for?
ATP- Adenosine Tri Phosphate it is an energy molecule that helps power cells
40
New cards
what type of biomolecule is ATP
nucleic acids
41
New cards
what is a vesicle and what makes it?
membrane bound sac made from ER and golgi apparatus
42
New cards
what substances are transported by vesciles and do they require energy?
large substances they do require energy