Motor Control
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is an area of study dealing w/ understanding of neural, physical, & behavioral aspects of biological movement?
Motor control
What is defined as an idea or plan for purposeful mvmt & is made up of components of motor programs?
Motor Planning
What is an abstract representation that, when initiated, results in production of a coordinated mvmt sequence?
Motor Program
What has a set of internal processes associated w/ practice or xp leading to relatively permanent changes in capability for skilled behavior?
motor learning
What is a higher-level motor program that allows flexible output in mvmt by encoding order of events, force of contractions, & muscles/limbs used?
generalized motor program (GMP)
Which theory proposes that movement is the result of chains of reflexes triggered by sensory stimuli?
Reflex theory (does not fully work)
What theory describes the nervous system as a top-down hierarchy where higher centers control lower ones?
Hierarchical theory (does not fully work)
What is an example of the hierarchical theory? ("higher level" brain plans action, sends instructions to "middle level", which then communicates w/ "lower level" spinal cord to activate specific muscles needed; sensory feedback constantly adjusting mvmt as needed)
grabbing a cup, must coordinate arm mvmts, to reach & grasp cup
Which theory explains mvmt thru interaction of body systems, internal/external forces, & control via synergies?
Hierarchical control exists to simplify control of body’s multiple ° of freedom. Muscles work in synergies to complete a task, like a string of sentences.
Systems theory (considers the environment)
What is an example of the systems theory?
transition from walking to running, ↑ walking speed, a critical point is reached causing a sudden shift in mvmt pattern, spontaneously switching to new gait (running) due to interaction of multiple factors; muscle activation, jt angles, & environment; "phaseshifting" to a new stable state as result of small change in input (speed)
Shumway-Cook have defined a somewhat integrated theory as systems theory. Key take aways are it’s critical to recognize that mvmt emerges from an
interaction between individual, task, & environment in which task is carried out.
Mvmts results from a dynamic interplay between perception, cognition, & action systems (muscles)
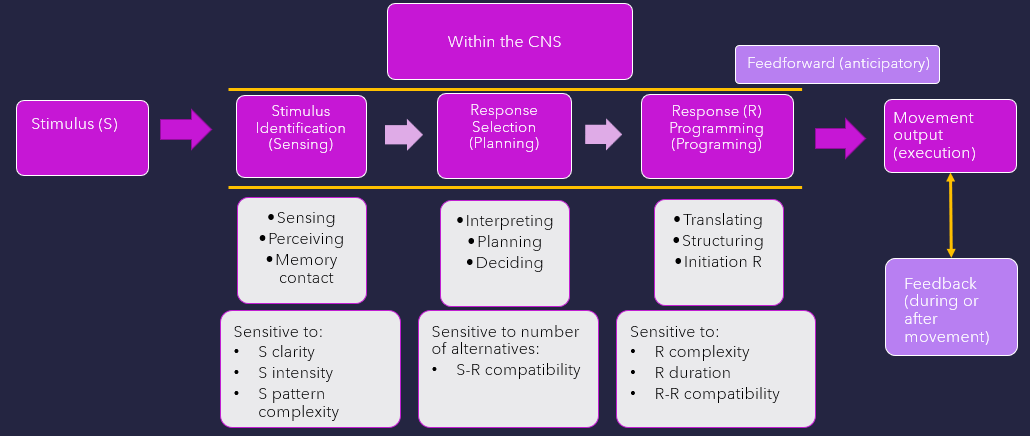
what stage is w/in CNS as current body state, environmental context, meaning is attached based on past sensorimotor experiences. Memory, attention, motivation, & emotional control all play a role
Stimulus identification (sensing)
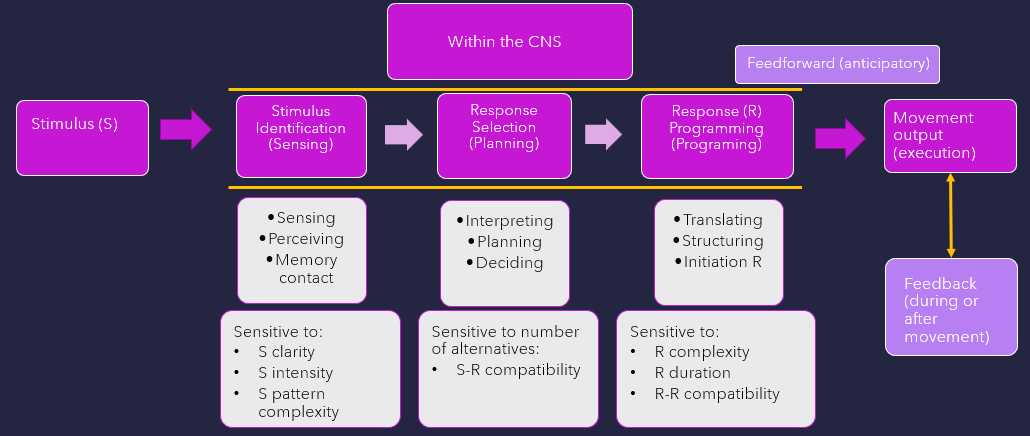
what stage is w/in CNS that motor plans, prototype of final mvmt is being created?
eg well-learned mvmt vs not, crossing street at cross walk w/ green light, vs at cross-walk w/ cross guard telling you to go when light is red; you would most likely hesitate
Response selection (planning)
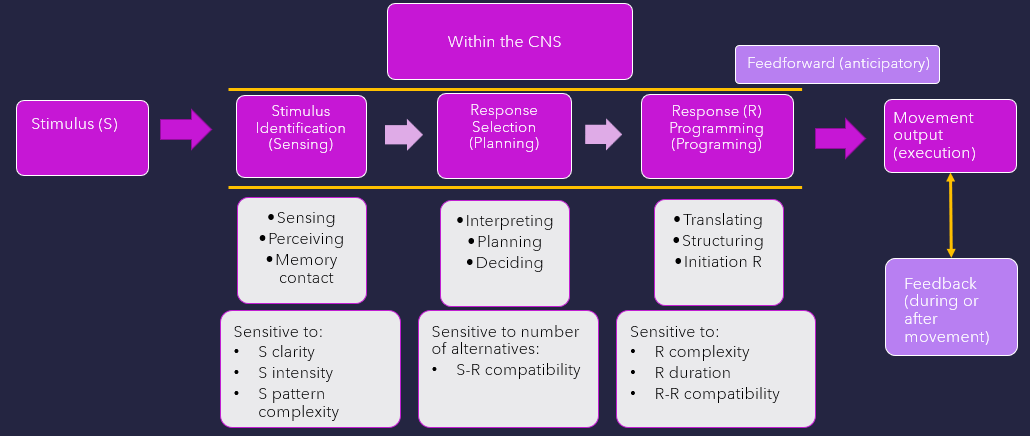
What stage comes after response selection? Neural control centers translate & change idea for mvmt into actions defined by a motor program. A set program ID created from specific parameters: synergistic components parts, force, direction, timing, duration, & extent of mvmt. There are constraints of individual, task, & environment.
The more complex activity the longer process occurs.
Response programming
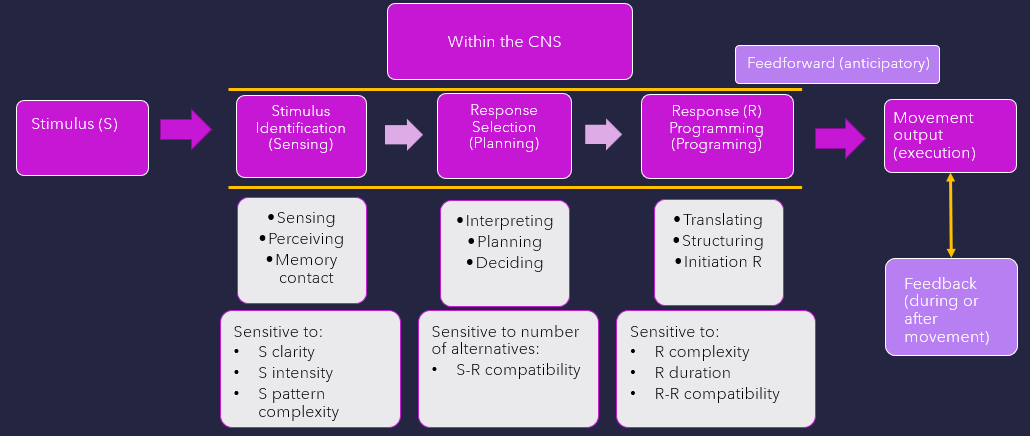
what is defined as compatibltiy for dual movement tasks that either occur simultaneously
Response compatibility
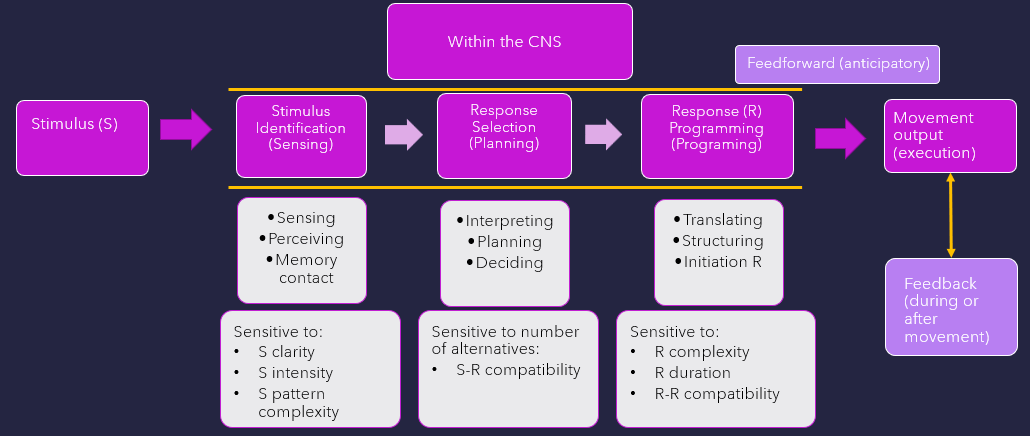
what mechanism sends signals in advance of mvmt to ready system, allows for anticipatory adjustments in postural activity
feedforward (anticipatory)
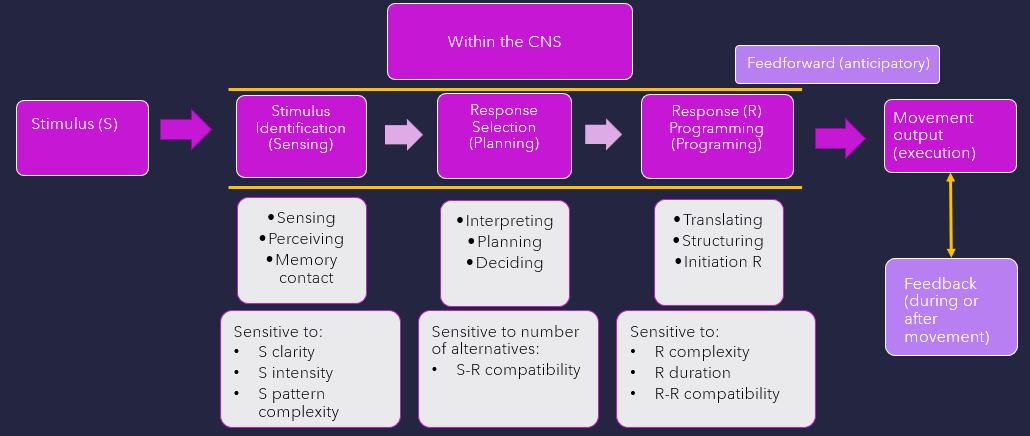
what mechanism that response-reproduced information receives during or after mvmt, is used to monitor output?
feedback
The first step in motor planning has voluntary mvmt occur in subcortical & cortical motivational areas. Conscious “Prime drive” sends signals to
association areas of cortex (different from motor cortex) → creates rough draft of planned mvmt from a stock of subroutines
Info related to plan of mvmt is sent to cerebellum & basal nuclei → convert rough draft into
precise temporal & spatial excitation programs
Cerebellum important for making fast movements; Basal nuclei for
slow or deliberate movements
Next, precise program is sent thru thalamus to motor cortex → forwards message down to spinal neurons for
“spinal tuning” & finally to skeletal muscle
Feedback from the CNS from muscle receptors/proprioceptors allows for
modifications of motor programs if necessary
What stage of motor learning develops an overall understanding of skill, cognitive map/plan. “what to do” phase
High level of cognitive process, lots of brain power, trial-&-error phase
Cognitive stage
what stage of motor learning includes:
Refinement of motor strategy, continuous practice, “how to do” phase
Spatial & temporal aspects become organized as mvmt develops into a coordinated pattern
Decrease in errors
Associative stage
What stage of motor learning includes:
Motor performance that after considerable practice is largely automatic, min level of cognitive load
“how to succeed” phase
Every portion of action is highly organized, learner is capable of coordinated motor patterns
Autonomous Stage
what type of practice has a higher likely hood of injury & fatigue?
massed practice
what type of practice is better for long term retention but may not start with?
random practice
Massed (Rest time is less than practice time) vs Distributed Practice (Practice time is equal to rest time) example
spaced repetition studying vs cram studying
Random (Variety of Tasks ordered randomly) vs Blocked Practice (1 task performed repeatedly followed by next) example
stroke research
Whole (Complete full movement) vs Part Training (Break task into parts) example
side kick
Closed (Stable or predictable) vs Open Environment (Variable environment adds complexity) example
PT clinic vs game field
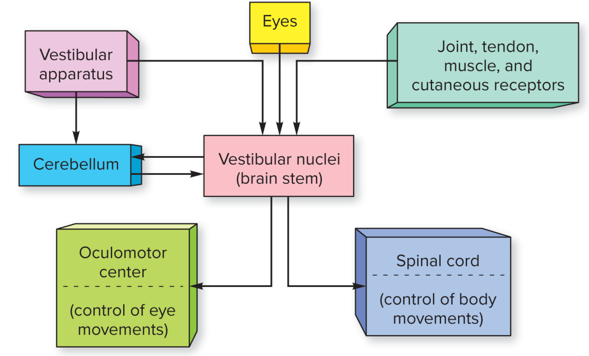
Head mvmt stims receptors in vestibular apparatus, this transmits info to cerebellum & vestibular nuclei located in brain stem. Vestibular nuclei relay message to oculomotor center & to the
neurons in spinal cord that control mvmt of head & limbs
What are the three general stages in acquiring and refining motor skills?
Cognitive, Associative, Autonomous
What type of practice involves repeating the same task many times before switching to another?
Blocked Practice
What is a major limitation of Reflex Theory that makes it less applicable to voluntary or novel actions?
It doesn’t explain voluntary or non-stimulus-driven movements
Which brain region stores learned motor experiences?
Cerebral Cortex
Which cortical area is primarily responsible for initiating voluntary movements?
Primary Motor Cortex
Which brain region handles vital reflexes, postural tone, & integrates CNS input for motor control?
brainstem
What structure w/in brainstem helps control muscle tone & postural adjustments via integration of CNS information?
Reticular Formation
Where are rapid, automatic reflexes like limb withdrawal coordinated w/out ascending to brain?
spinal cord
What training method uses unexpected disturbances to improve reactive balance & adaptability?
Perturbation Training
What is the difference between in-phase & anti-phase movement in bimanual tasks?
In-phase: both hands move same way simultaneously; Anti-phase: hands move in opposite directions