AP Psychology Unit 1 - Part 1
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
neuron
a nerve cell that is the basic building block of the nervous system
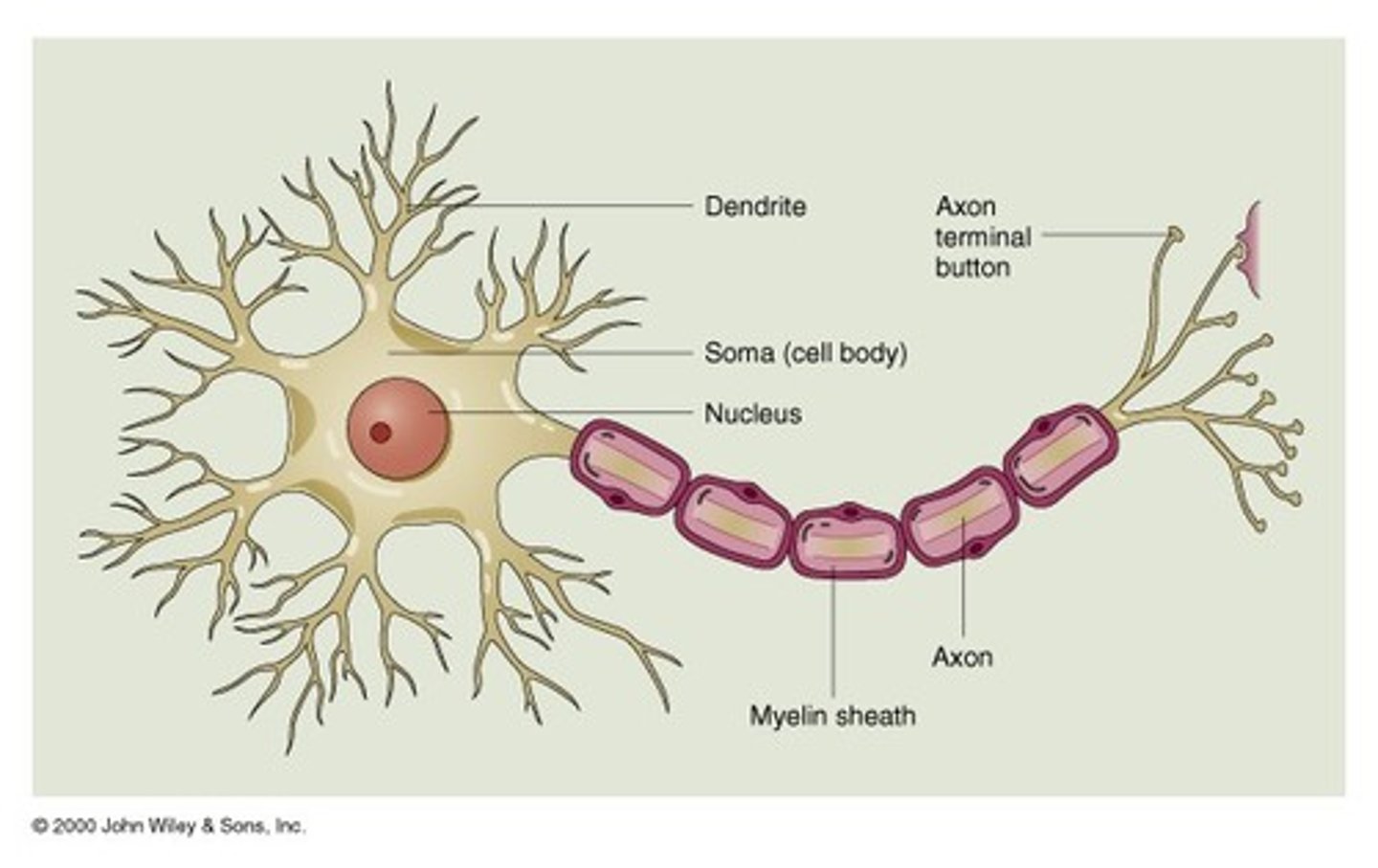
cell body (soma)
the part of the neuron that contains the nucleus
dendrites
bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrate messages, conducting impulses toward the cell body
axon
attached to soma, passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
myelin sheath
fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing axons of neurons; increases transmission speed and provides insulation
terminal branches
ends of axon containing terminal buttons which hold synaptic vesicles that store transmitters
neural impulse
chemical signals exceed threshold, neuron fires, transmitting an electrical impulse (action potential) down its axon by means of chemistry-to-electricity process
glial cells
cells that support, nourish, and protect neurons; they also play a role in learning, thinking, and memory
threshold
level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
all-or-none response
neural firing happens at full response or not at all
excitatory signal
signals trigger action
inhibitory signal
signals depress action
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neutron
substance p
influences the brain's response to pain and inflammation
acetylcholine (ACh)
enables muscle action
dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal
GABA (gama-aminobutyric acid)
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
glutamate
a major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory
endorphins
neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure
agonists
drug molecules that increases a neurotransmitter's actions
antagonists
drug molecules that inhibits a neurotransmitter's actions
reuptake inhibitors
blocks reabsorption of neurotransmitters back into neuron
psychoactive drugs
chemicals that change perception and moods
depressant
slow down neural activity
stimulants
excites neural activity
hallucinogens
distort perceptions and sensory images
opioids
type of depressant that reduces pain by acting an an endorphin
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
nerves
bundles axons of many neurons that form neural cables connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs
central nervous system
decision maker; it is responsible for coordinating incoming sensory messages and outgoing motor messages
peripheral nervous system
made up of sensory and motor neurons
somatic nervous system
controls body's skeletal muscles also called the skeletal nervous system
autonomic nervous system
controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs
sympathetic nervous system
arouses the body, mobilizing its energy
parasympathetic nervous system
calms body, conserving its energy
endocrine system
secretes hormones into the bloodstream
adrenaline
fight or flight response
leptin
fullness hormone
ghrelin
appetite and energy balance
melatonin
sleepiness
oxytocin
love hormone
lesion
brain tissue is destroyed and researchers study the impact on functioning
stimulation
brain regions are stimulated electronically, chemically, or magnetically and researchers study impact on functioning
fMRI
continuously measures blood flow to parts of brain using magnetic imaging
EEG
electrodes placed on scalp measure electrical activity of neurons
pituitary gland
regulates growth and control of other endocrine glands
frontal lobe
associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving
motor-cortex
controls voluntary movements
sensory-cortex
registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
parietal lobe
receives sensory input for touch and body position
wernicke's area
language comprehension (hearing)
occipital lobe
vision
cerebellum
Balance and coordination
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
brocas area
speech production
hypothalamus
directs several maintenance activities such as eating, drinking, and body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system
amygdala
agression and fear
hippocampus
memory
thalamus
brain's sensory control center
reticular formation
arousal and multitasking
brainstem
automatic survival function
pons
coordinate movements and control sleep
medulla
heartbeat and breathing
plasticity
the brain's ability to change by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
corpus callosum
wide band of axon fibers connecting two hemispheres of the brain
split brain
results when fibers of the corpus callous are severed isolating each hemisphere from the other