AP Psychology Unit 1
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
nature
Genetics - biology influences who you are
Nurture
Your environment influences who you are
Nuture and Nature
Humans are a product of both
Epigenetics
How does our DNA and genetics change based on environment - nurture effect on nature
LTP
Neurons recall previously learned information
Identical Twins
Share the same DNA, single egg; monozygotic
Fraternal Twins
Dizygotic: Not identical genetic information
If identical twins raised in different environments...
the similarites acounted for are due to genes
If fraternal twins raised in different environments...
the similarities acounted for are due to environment
Heritability
Measurment of variation in individuals attributed to genes and DNA
How many divisions of Nervous System (NS)
2 - Central and Peripheral
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Everything else, and brings information to the CNS
How many divisons of the peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
2 - Somatic and autonomic
somatic nervous system (SNS)
Controls body's skeletal muscle, and uses motor neurons to take information to the CNS, to be processed by the brain. IN short- controls body's skeletal muscle
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Controls all the involuntary things (HR, blood pressure, digestion etc)
How many divisions of the ANS are there
2- parasympathetic and sympathetic
What does the parasympathetic nervous system do?
Its the rest and digest system. Returns body to a resting state after the body's responses were heightened and slowed after fight or flight, and autonomic functions resume
What does the sympathetic nervous system do?
Fight or flight response: Dilates pupils, increases heart rate, and autonomic functions are decreased
What are glial cells?
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons. "Helper cells"
What are the three types of neurons
Motor, inter, and sensory
Motor neuron
a neuron that sends an impulse to a muscle or gland, causing the muscle or gland to react
Interneuron:
a neuron that carries nerve impulses from one neuron to another (sensory ----> motor)
Sensory neuron
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord, then the brain sends a message that the motor neuron should do
What is the neural pathway?
Sensory neuron ---- interneuron ---- motor neuron
Spinal Reflex Arc
Sensory - Inter - motor
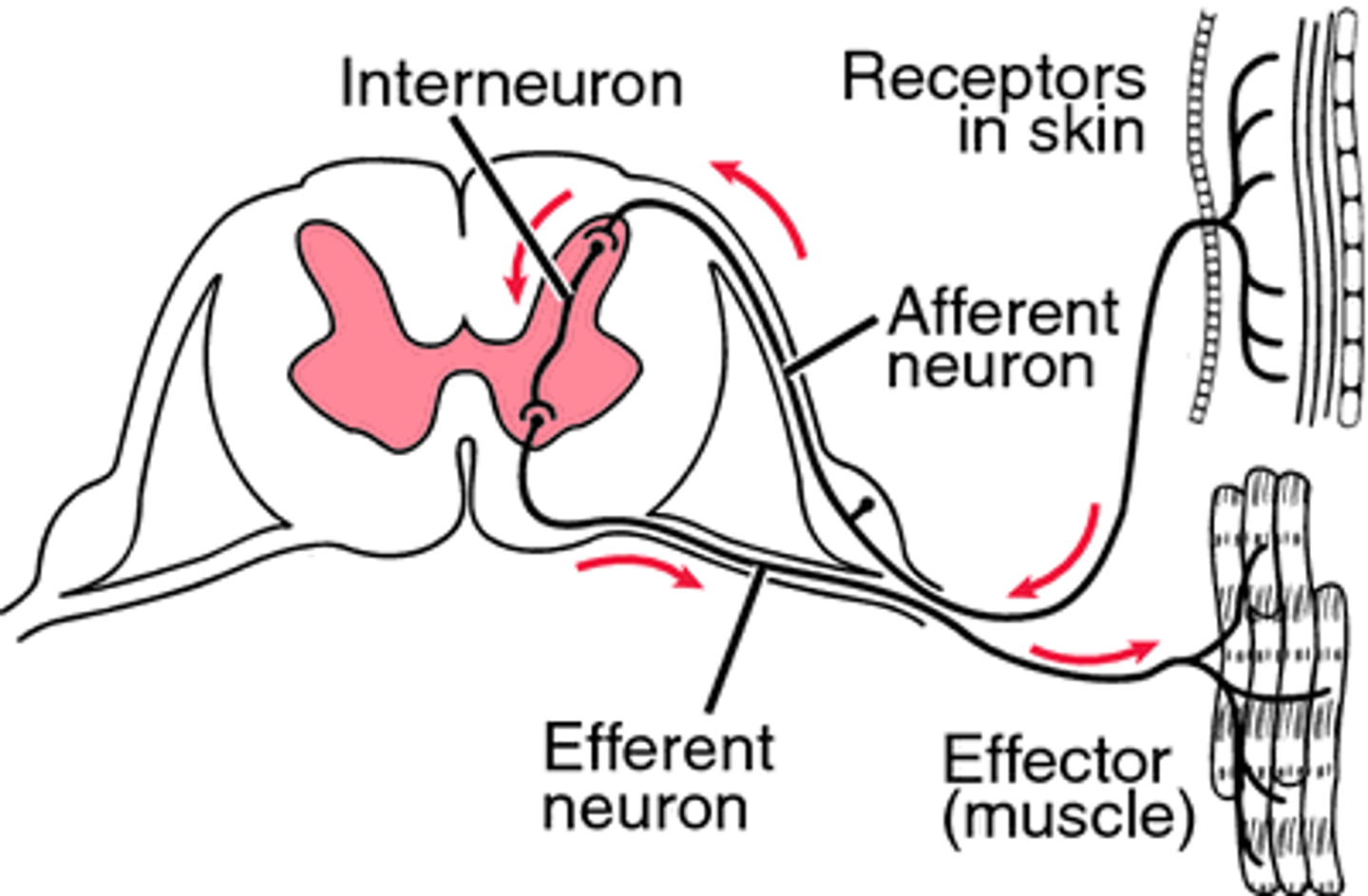
Sensory vs Motor
Sensory: DIfferent for each sense
Respond to NON-chemical stimuli
AFFerent signals (Arrive at the brain)
Motor: Connected to all muscles
Only way people can express thoughts into the world (gestures, actions, speech)
EFFerent signals (Exit the brain
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
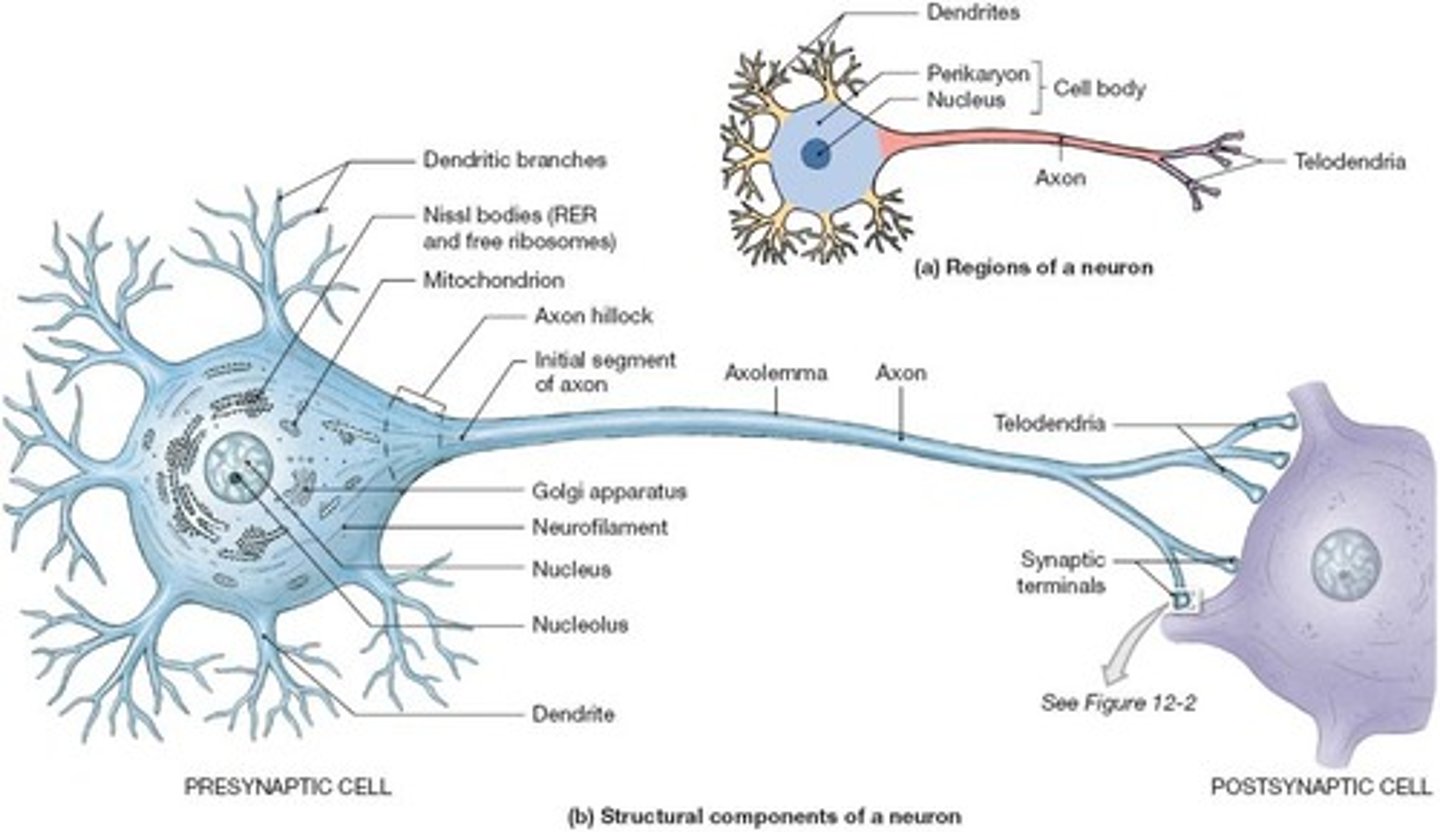
Anatomy of Neuron
Top
Dendrite : recieve messages
Soma: Body
Nucleus: holds information of nerve cell
Axon: the action potential goes down the length of the axon
Myelin sheath: Not all neurons have this, but the electrical charge goes faster with it
Terminal: end of neurson
Terminal buttons: Final point
Synapse: The message from presynaptic neuron passed to a postsynaptic neuron
All or nothing law
Neurons either fully fire or do not; if a neuron needs 3 neurotransmitters to bind to the dendrite, only 2 will not make it partially fire, 3 are needed to fire, and fires are consistent
excitatory neurotransmitters
excite the next cell into firing
inhibitory neurotransmitters
inhibit the next cell from firing
Resting potential
-70 mV, polarized, and positive outside the cell
Action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon, 30 mV, depolarized
Refractory Period
A brief period of inactivity where the neuron can't fire after firing
Reuptake process
Neuron snatches all the neurotrasmitters after the postsynaptic neuron has fired. Some are lost, new ones are generated
Glutamate function
Excitatory neurotransmitter that strengthens synaptic connections.
Increases memory
GABA
Inhibitory neurotransmitte. Related to anxiety disorders
Acetylcholine (ACh)
All movements rely on its release. Triggers muscle contraction. Enables learning and memory
Dopamine
a neurotransmitter that regulates motor behavior, motivation, pleasure, and emotional arousal
Associated with Parkinsons disease and Alzheimers
Endorphins
Natural painkiller. ends pain
Epinephrine
Also known as adrenaline
Its a neurotransmitter and a hormone. Boosts energy in high fight or flight situation or just a high energy situation
Norepinephrine
Noradrenaline.
Arousal and alertness help
Associated with the sleep cycle - low levels
Serotonin
Affects mood hunger sleep and appetite. Associated with depression
What is an antagonist
Drug that is capable of binding to a receptor and blocking neurotransmitter activity by blocking the binding to post synaptic neuron
What is an agonist drug
Enhances the neurotransmitter's activity.
Direct agonists: Mimic the neurotransmitters and bind to receptor
Indirect agonists: Blocks the momentary reuptake period to constantly fire the neuron
Heroin
AGONIST
Enhances the activity of endorphins. The drug mimics the Neurotransmitter sop the receptor cannot distinguish between the two. Further lessens pain
NIcotine
AGONIST
Enhances the activity of acetylcholine (ACh)
Muscle spasms
Prozac
inhibits the reuptake process for seratonin so the neuron constantly fires
Cocaine
inhibits reuptake for dopamine, so dopamine neurotransmitters are always firing.
Botox
ANTAGONIST
Inhibits the function of acetlycholine, slows or stops muscle contraction and wrinkles. ACh cannot reach the receptors
Thorazine
ANTAGONIST
Inhibits function of dopamine. Could help with cases of scizofrenia
Tolerance
Increasing amounts of a drug neede after a while
Physical dependancy
repeated use needed to prevent withdrawal
Blood Human Barrier
allows for some chemicals to pass, but prevents others.
Similar to the plasma membrane of cells; semi-permeable
Depressants
slow or inhibit the nerbous system. Decreases anxiety and inhibitions, increases sleep
Combinations can be fatal

Example of depressant
Alcohol: agonist for GABA. Net slowing effect on the body, judgement, self control.

Opiods
agonist for endorphins
examples of opioids
Heroin, oxycodone, and fentanyl

Stimulants
Activate parasympathetic nervous system functions.
Increase in brain activity, arousal behavior, and mental alertness. Can crash after dose wears off
Examples of stimulants
Caffiene: awake, alert, and fast. Antagonist for adneosine (adenosine induces sleep)
Cocaine: reuptake inhibitor for dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin.

Halucinogens
psychedelic
Sensory and perceptual distortions
alter mood
affect thinking
Examples of halucinogens
THC: mild ingredient in marijuana. Well being, state of relaxation.
Interferes with muscle coordination learning memory and overall cognitive function
THE BRAIN
woah
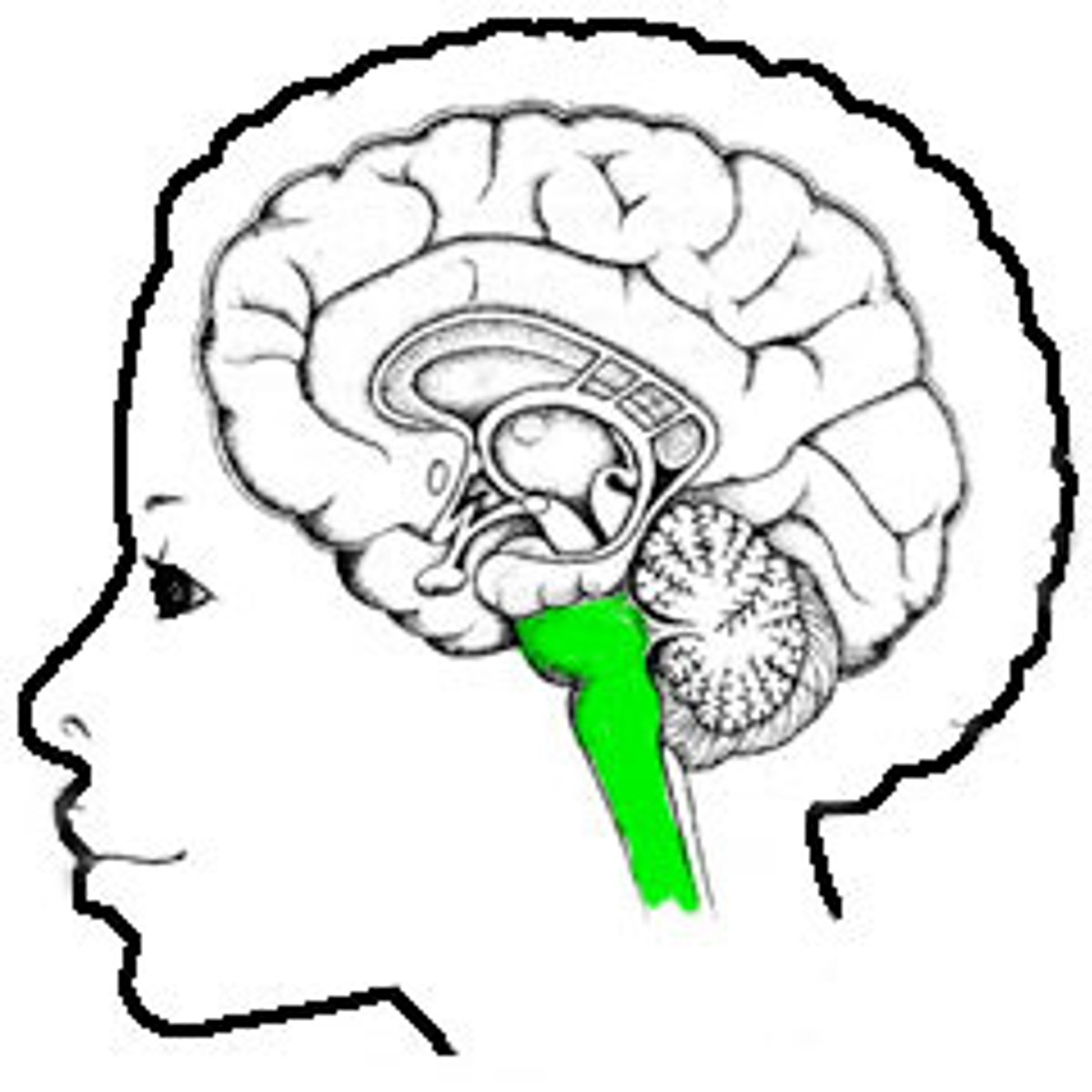
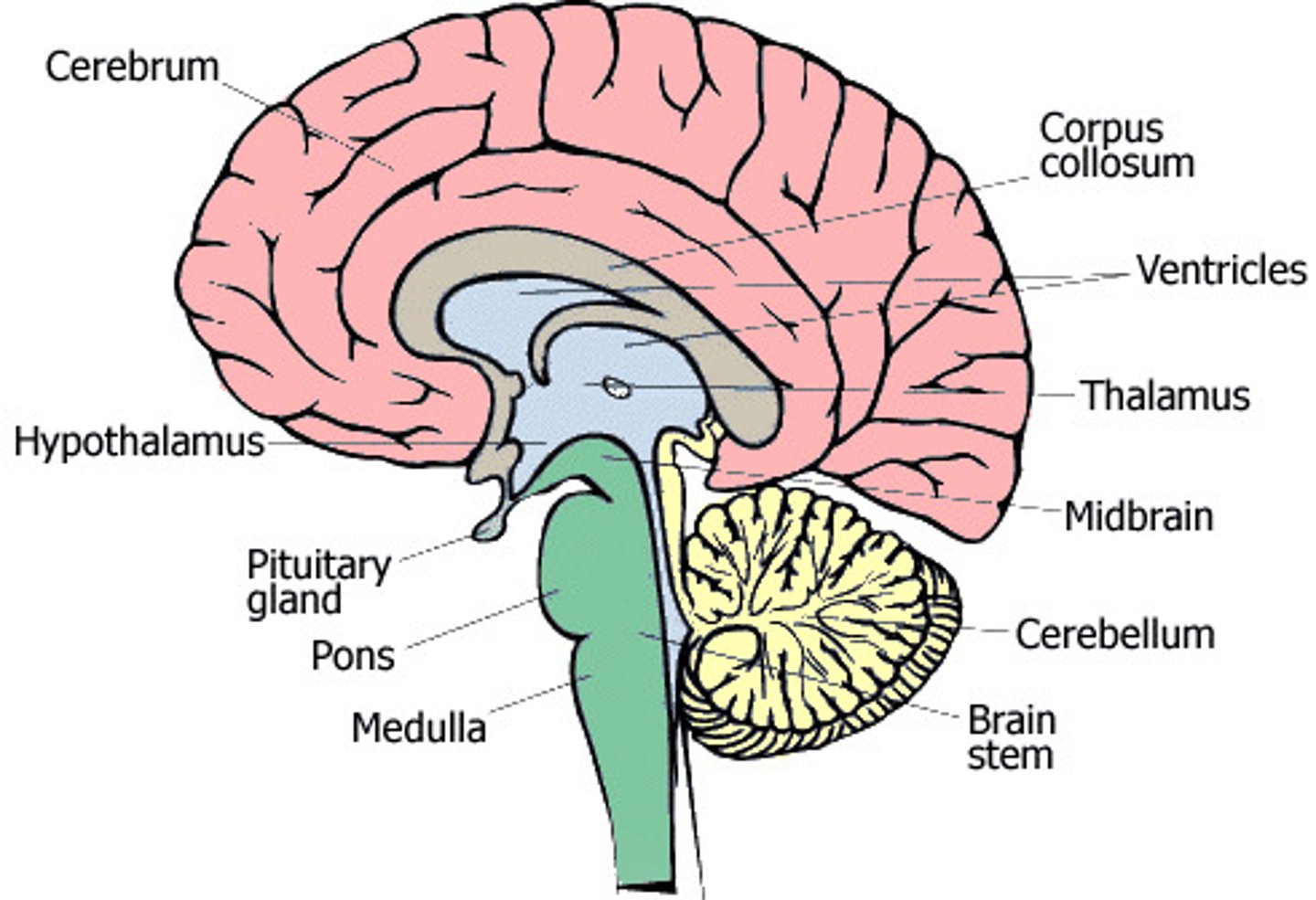
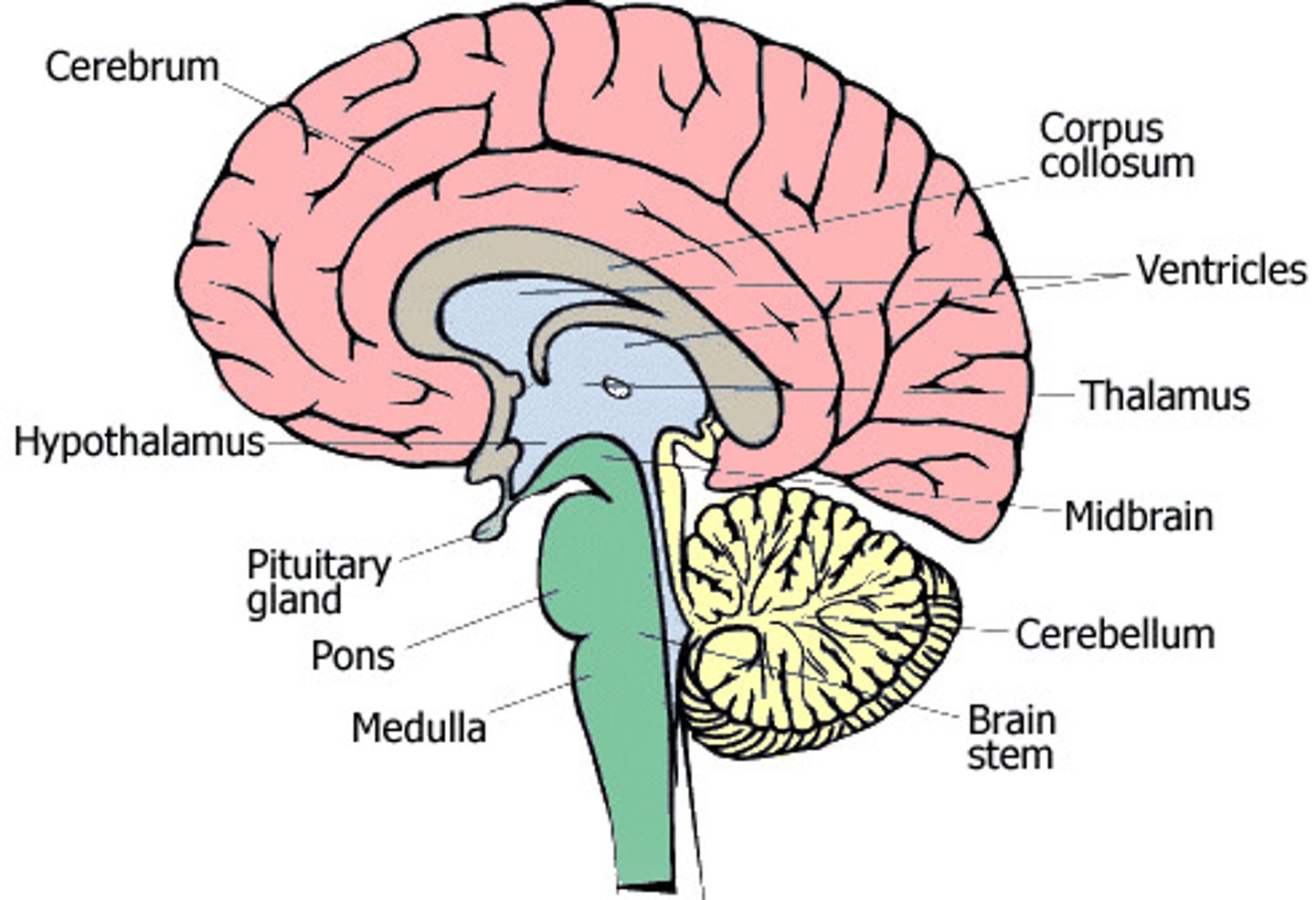
Where is the Medulla, and what is its function
In the bottom portion of the brain.
Deals with all the autonomic functions of the body
(HR, blood pressure, breathing, digestion)
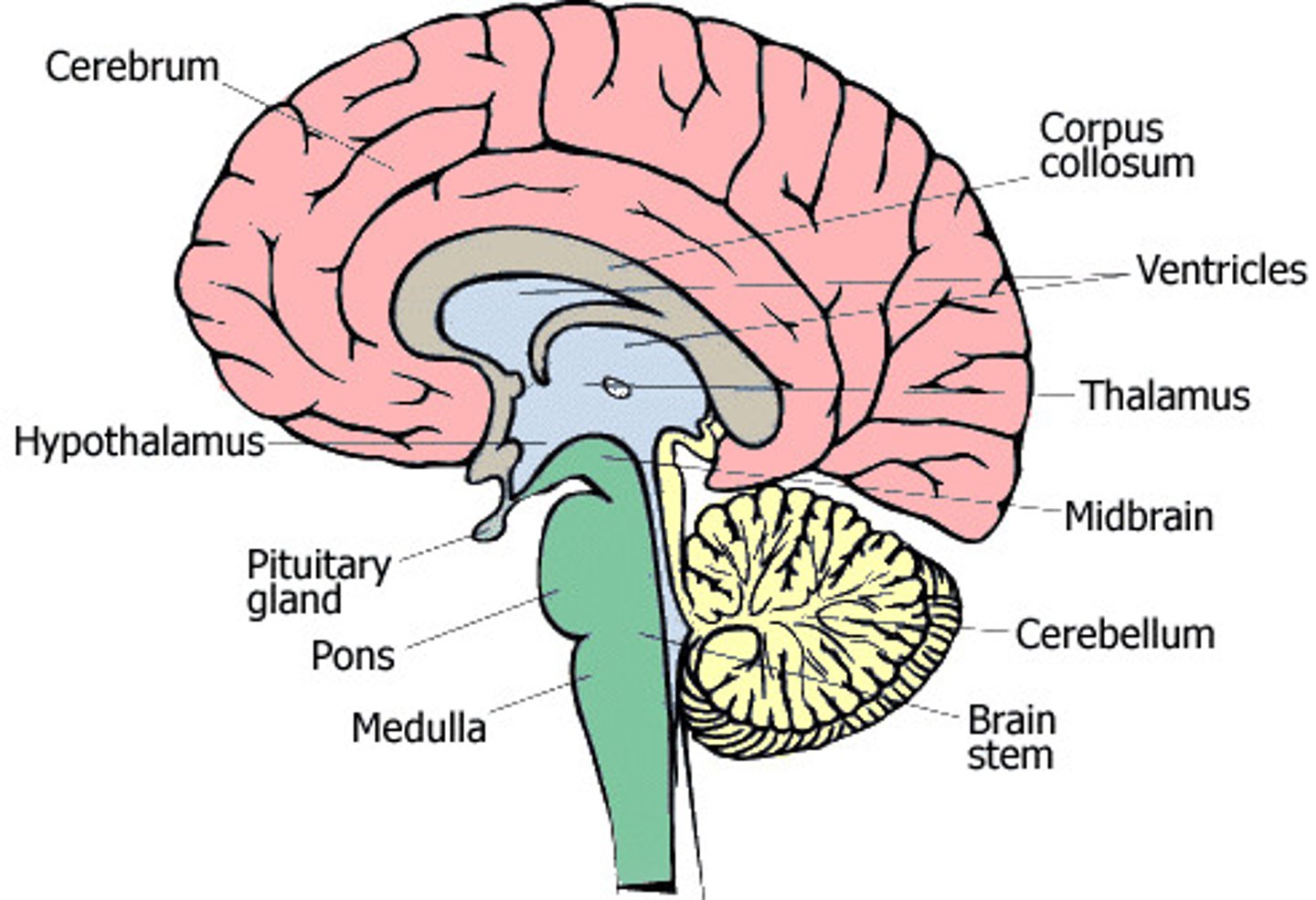
Where is the Pons, and what is its function
Connects the brainstem and the cerebellum.
Plays a role in dreams and sleep
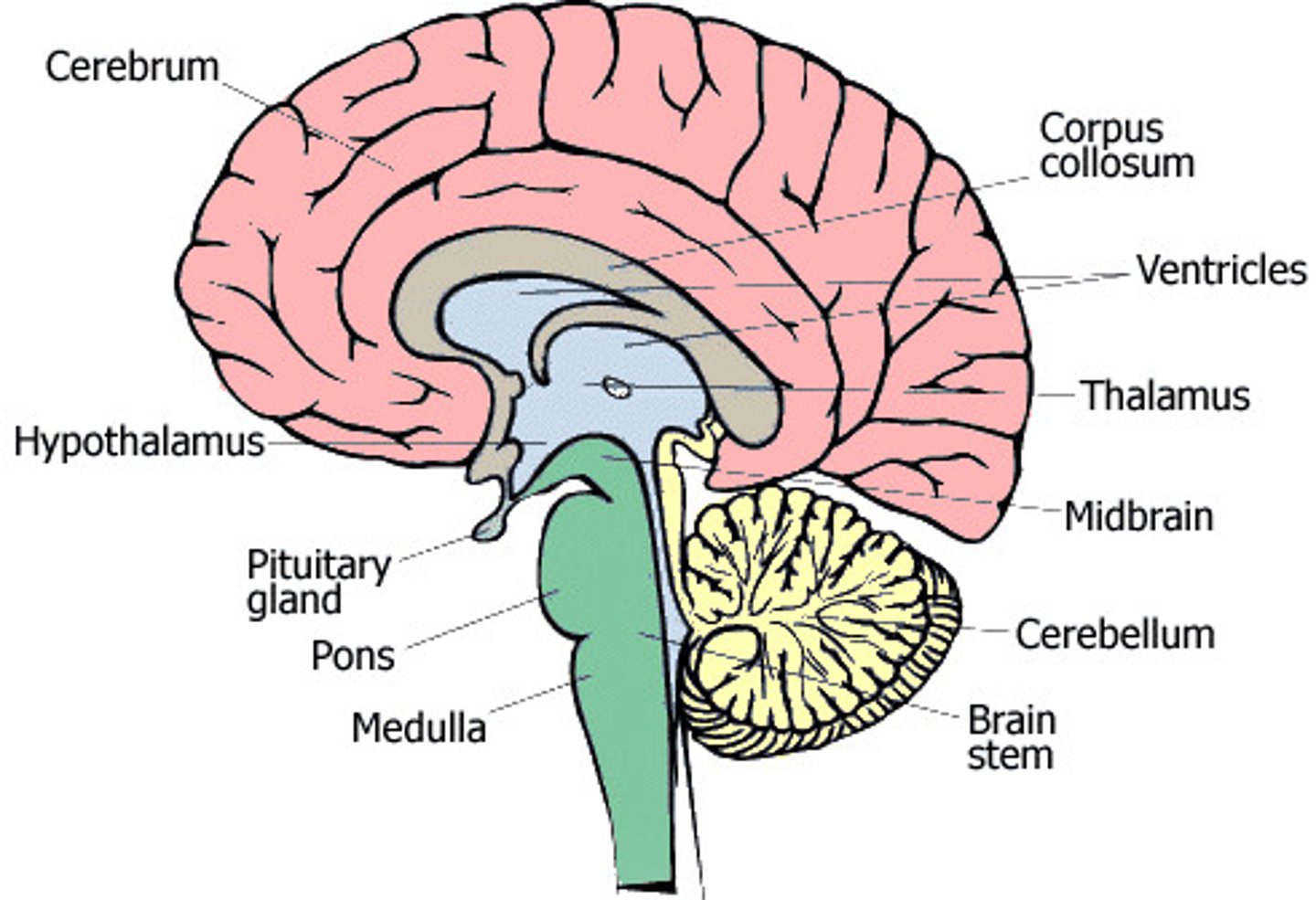
Where is the Cerebellum and what is its function
Back of the brain
In implicit (no thought given) movements, such as walking. Also if in sports: swinging a bat, or a tennis raquet.
Many sequences of movements.
Balance and equilibrium
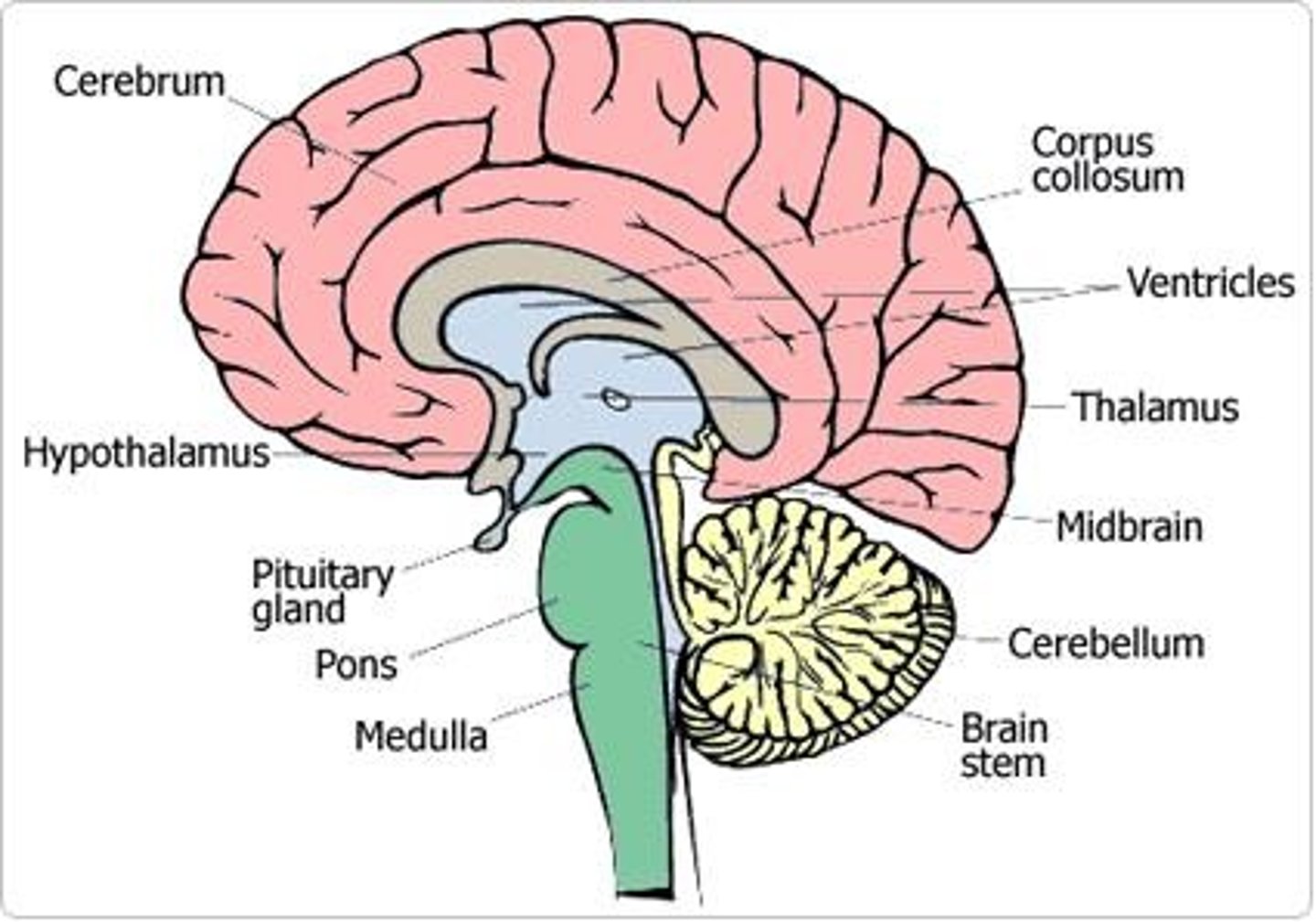
Where is the RAS, what is it, and what is its function
Reticular activating system
On the brainstem
Function: nerve for arousal alertness and attention
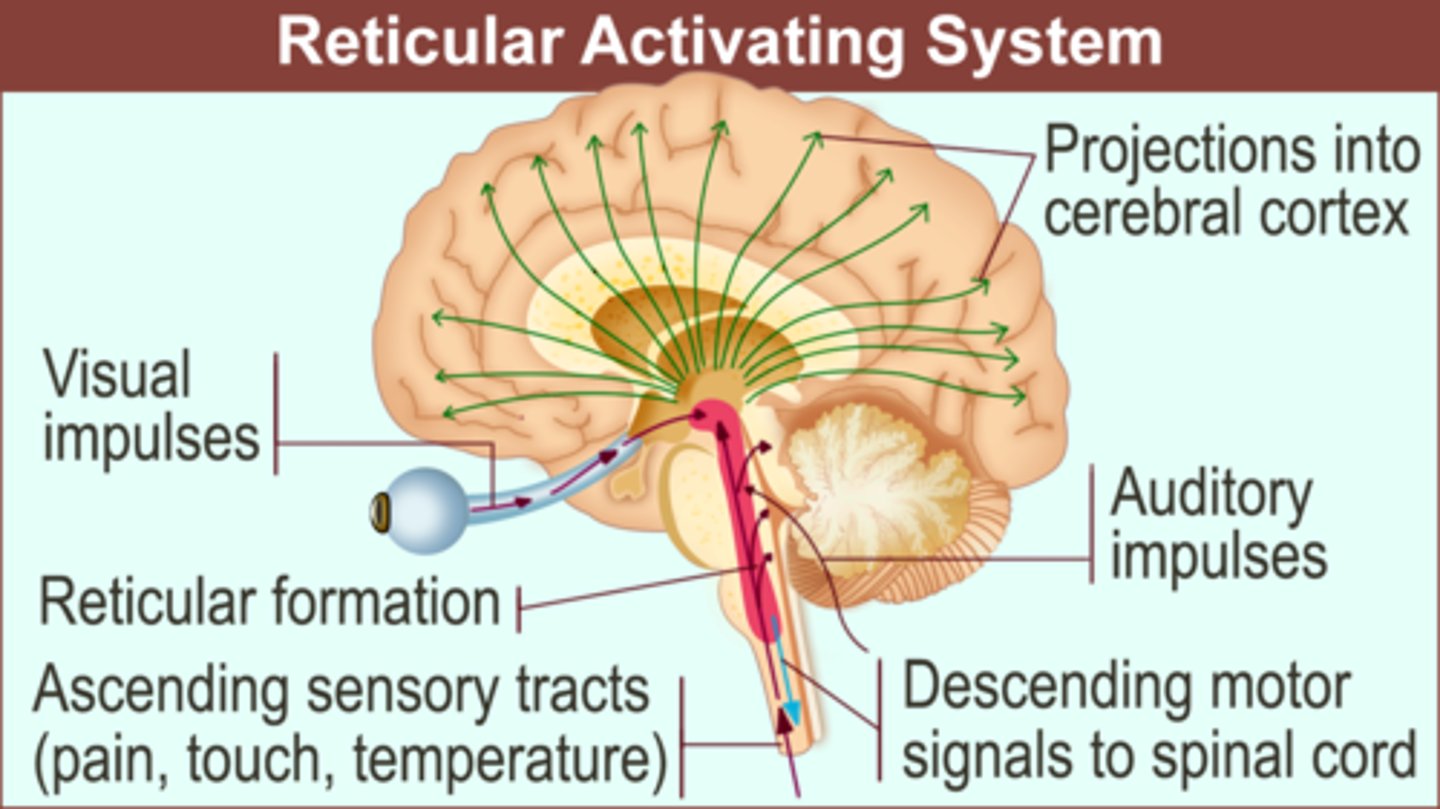
Where is the hippocampus and what is its function
Located above the Pons and Medulla
Function: Creates new memories. Does not store them. Any damage to the hippocampus will result in loss in function of creating new memories, but will not destroy old ones.
Dysfunction: Can cause Alzheimers or anterograde amnesia
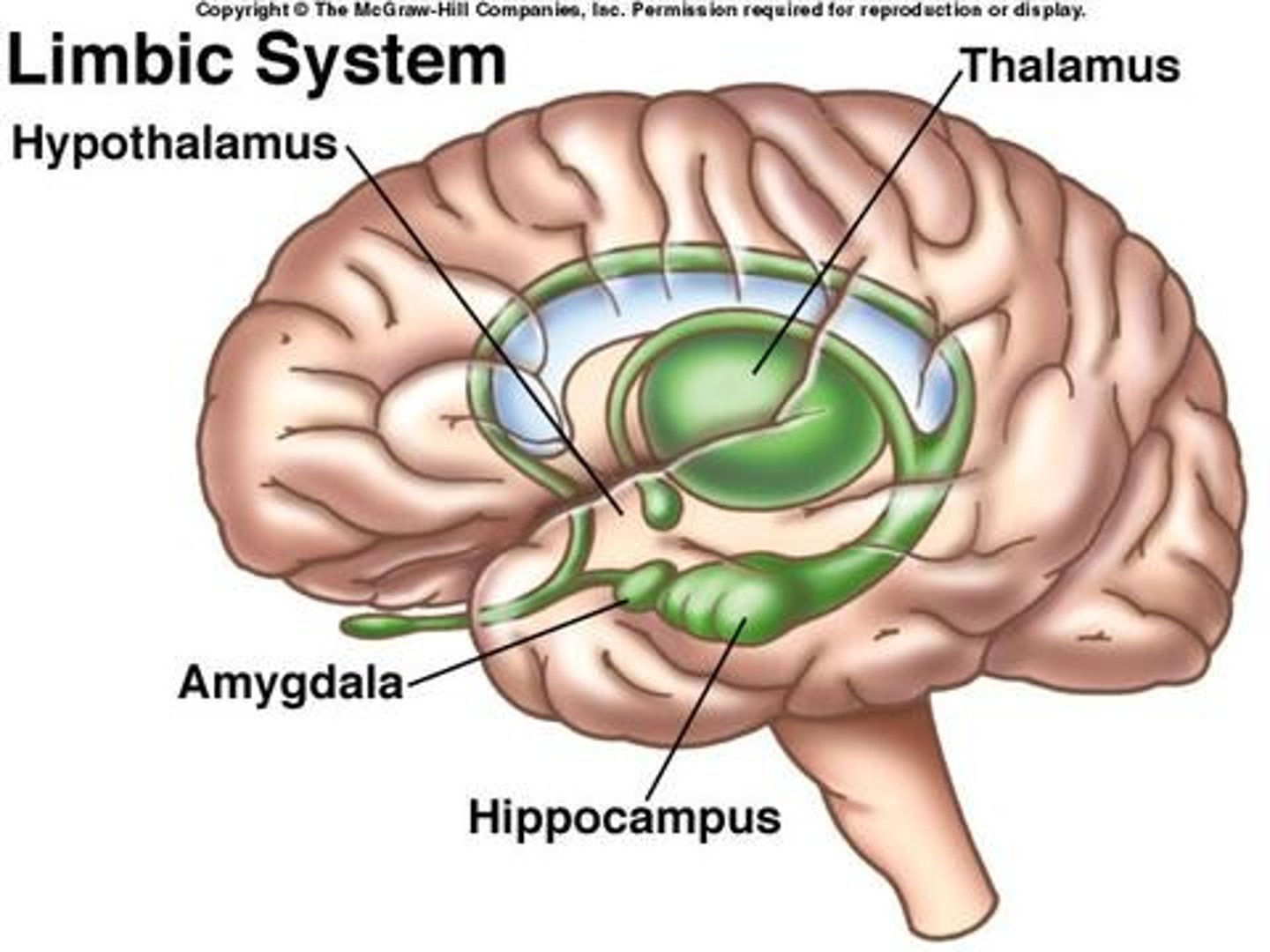
Where is the amygdala, and what is its function
From a left hemisphere lateral view, amygdala is located to the left of the hippocampus
Function: Regulates the A's: Anger, agression and afriad. Emotional memories
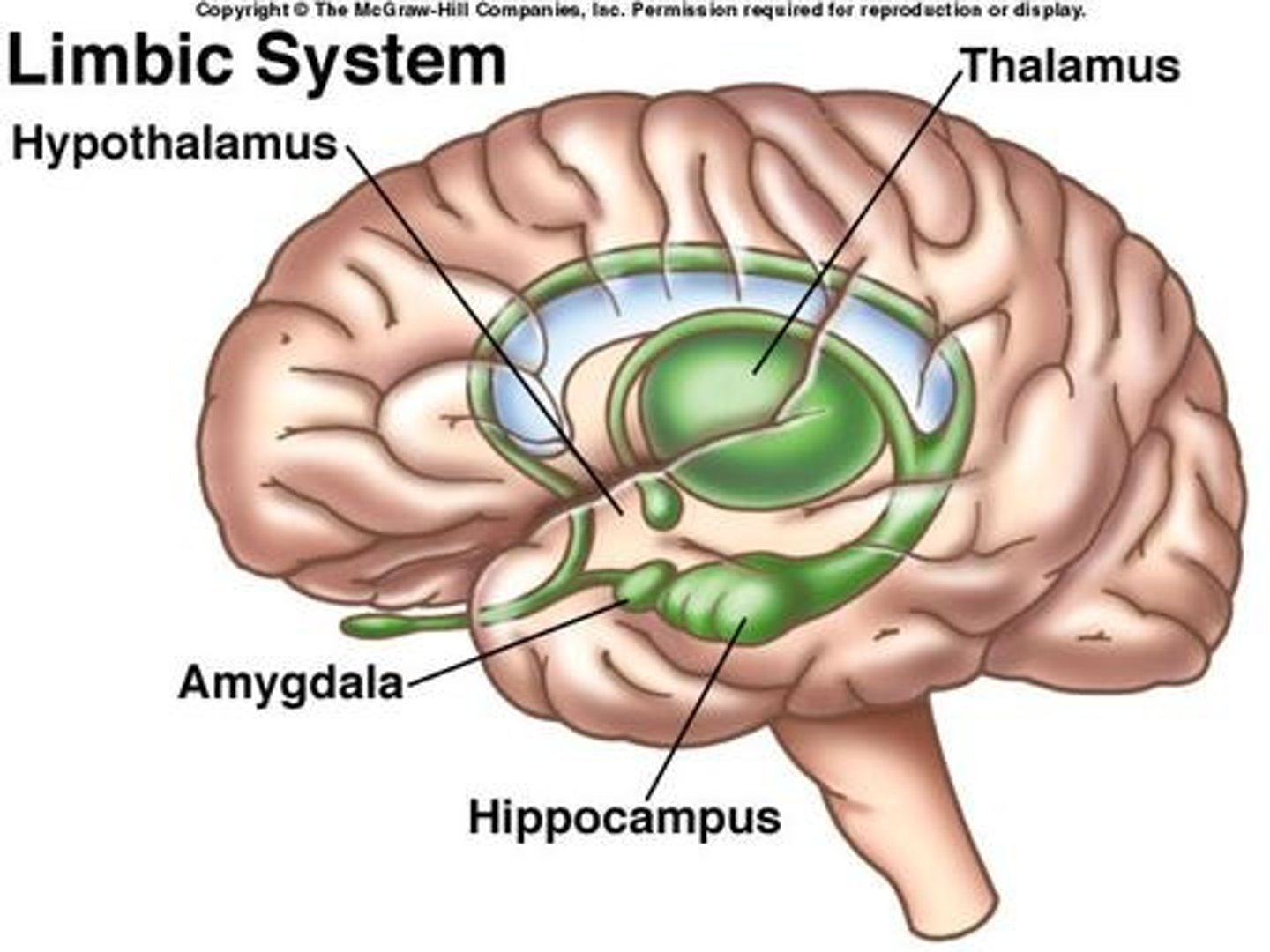
Where is the thalamus and what is its function
Between the midbrain and cerebrum.
Function: Sensory switchboard. All senses go to the thalamus and then to the cortex. ALL senses but smell.
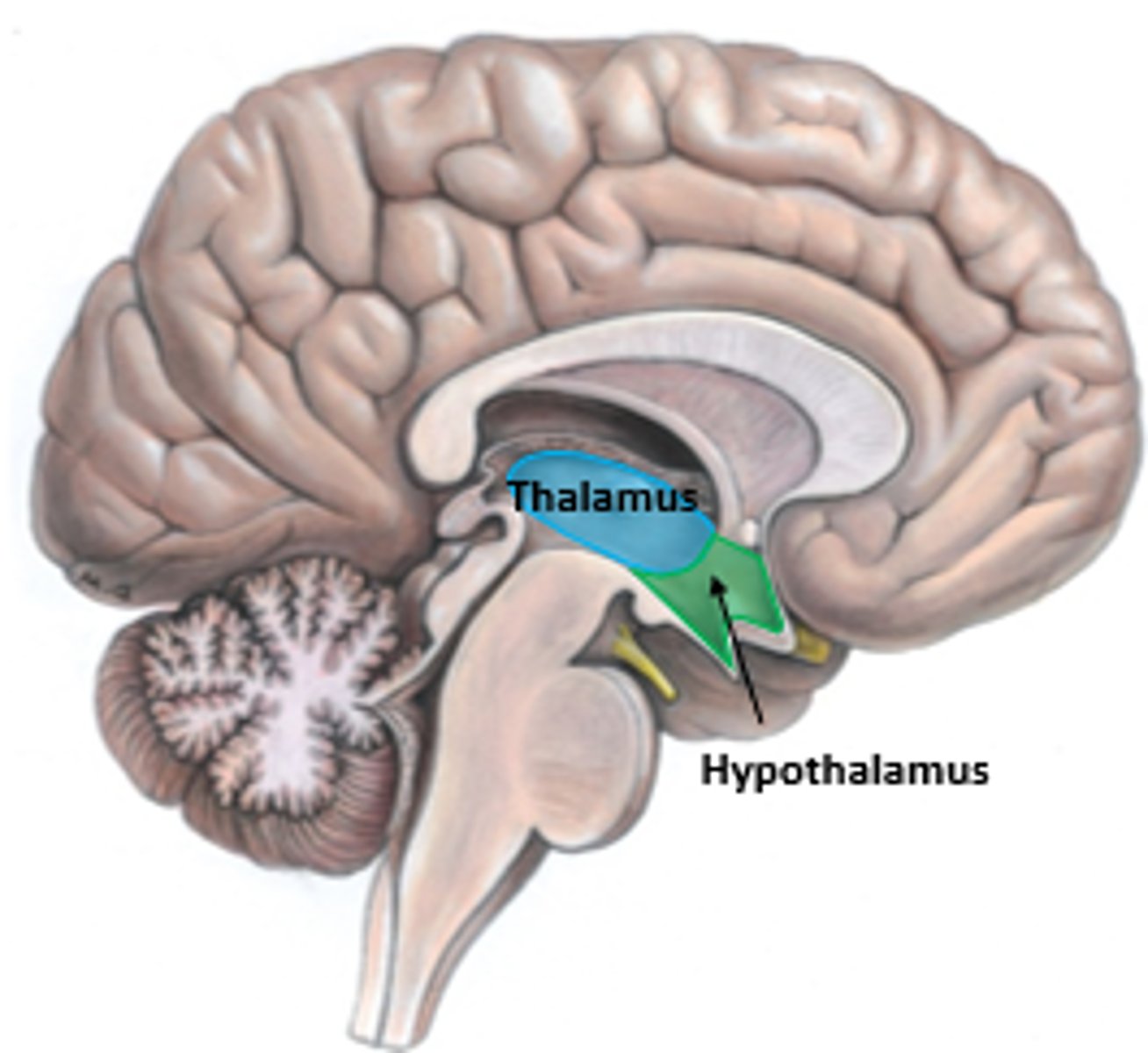
Where is the hypothalamus and what is its function
- Between midbrain and cerebrum, but below the thalamus
Fight or flight responses. Initiation when to eat and when we are full.
Fornication: sexual desire.
Regulates the sympathetic and parasympathetic NS
Recap of Amygdala, Hippocampus, Hypothalamus, and Thalamus
Amygdala: Someone is angry and agressive.
Hippocampus: Creates new memories
Hypothalamus: if damaged, causes you to keep eating and eating...
Thalamus: All incoming sensory information passes through it.