Electromagnetism 1 & 2
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Radi 121
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
electromagnet
coil or wire wrapped around an iron core that intensifies the magnetic field
solenoid
helical winding of current-carrying wire that produces a magnetic field along the axis of the helix
flux linkage
the interaction of one line of force and one loop of a conductor
permeability
defined as the ability of a material to attract the magnetic lines of force
faradays law
states that electric current cannot be induced in a circuit merely by the presence of a magnetic field, rather, the flux line must be changing
describe hans oersteds discovery
concluded any moving charge also produces a magnetic field
what did hans oersted discover
any moving particle generates a magnetic field
as the conducting wire is looped, the flux density of a solenoid
increases
when a ferromagnetic core is added, as with an electromagnet, the flux density is
increased
when a ferromagnetic core is added, as with an electromagnet, the magnetic field strength
increases
what are three ways in which the strength of the magnetic field lines in solenoids and electromagnets can be increased
increasing number of turns or loops
by increasing voltage of current flow
permeability of the core
where might we find electromagnets
detent locks in x-ray
circuit breakers and relays
slator electromagnets
another name for faradays law
first law of electromagnets
what law must the magnetic field (flux lines or lines of force) must be changing in order to induce electrical current
faradays law
list three ways to create motion between the lines of force and a conductor (wire) include
move the conductor through a stationary, unchanging strength magnetic field
move the magnetic lines of force through a stationary conductor with an unchanging conductor
vary the magnetic flux strength from a stationary magnet through a stationary conductor
what is the magnitude of the included EMF determined by
the number of the flux linkages per second
what happens to the flux density of a solenoid as the conducting wire is looped
increases
what happens when the electromagnet as a ferromagnetic core is introduced
enhance permeability
dipoles in same direction
increase magnetic field strength resulting in a stronger magnetic field.
can electric current be induced in a circuit merely by the presence of a magnetic field
no
what must the magnetic flux lines do in order to induce electrical current
changing
what happens when a conductor cuts across the magnetic flux or when a conductor is cut by a magnetic field
an electromotive force or potential difference is induced in the conductor
what are four factors influencing the magnitude of induced current
STRENGTH of magnetic field
VELOCITY of the magnetic field as it moves past the conductor
ANGLE of the conductor to the magnetic field
NUMBER OF TURNS in the conductor
describe strength of magnetic field
stronger magnetic field = greater the number of flux
describe velocity of the magnetic field as it moves past the conductor
faster the conductor is traveling = more flux linkages per second
describe angle of the conductor to the magnetic fields
closer to 90 degrees = more flux linkages per second
describe number of turns in the conductor
greater number of turns in conductor = more flux linkages per second; more EMF
stronger magnetic field =
greater the number of lines of flux
faster the conductor is traveling =
more flux linkages per second
closer to 90 degrees =
more flux linkages per second
greater number of turns in the conductor =
more flux linkages per second; more EMF
lens law
induced current flows in a direction such that it opposes action that induces it
what is lens law also known as
the second law of electromagnetic
right hand thumb rule… along a conductor
thumb: points w/ current flow
fingers: direction of magnetic field
right hand thumb rule… solenoid and electromagnetic
fingers = current
thumb = direction of north pole
right hand generator rule
index finger = magnetic lines of force
middle = current flow
thumb = movement of conductor on armature
left hand motor rule
index finger = magnetic lines of flux
middle finger = current flow
thumb = movement of conductor on rotor
list two items in x-ray circuitry that make use of faradays law
transformers
slator electromagnets
describe current flow verses electron flow in a circuit
current flow and electron flow are exact opposite of one another
electron flow means opposite of
current flow
when the question is talking about "generator" which hand should you use
right
when the question is talking about "motor" which hand should you use
left
is current a positive or negative
positive
is electron a positive or negative
negative
should you always start at the negative or the positive end
positive (current)
for finding north and south, which hand should you use
right
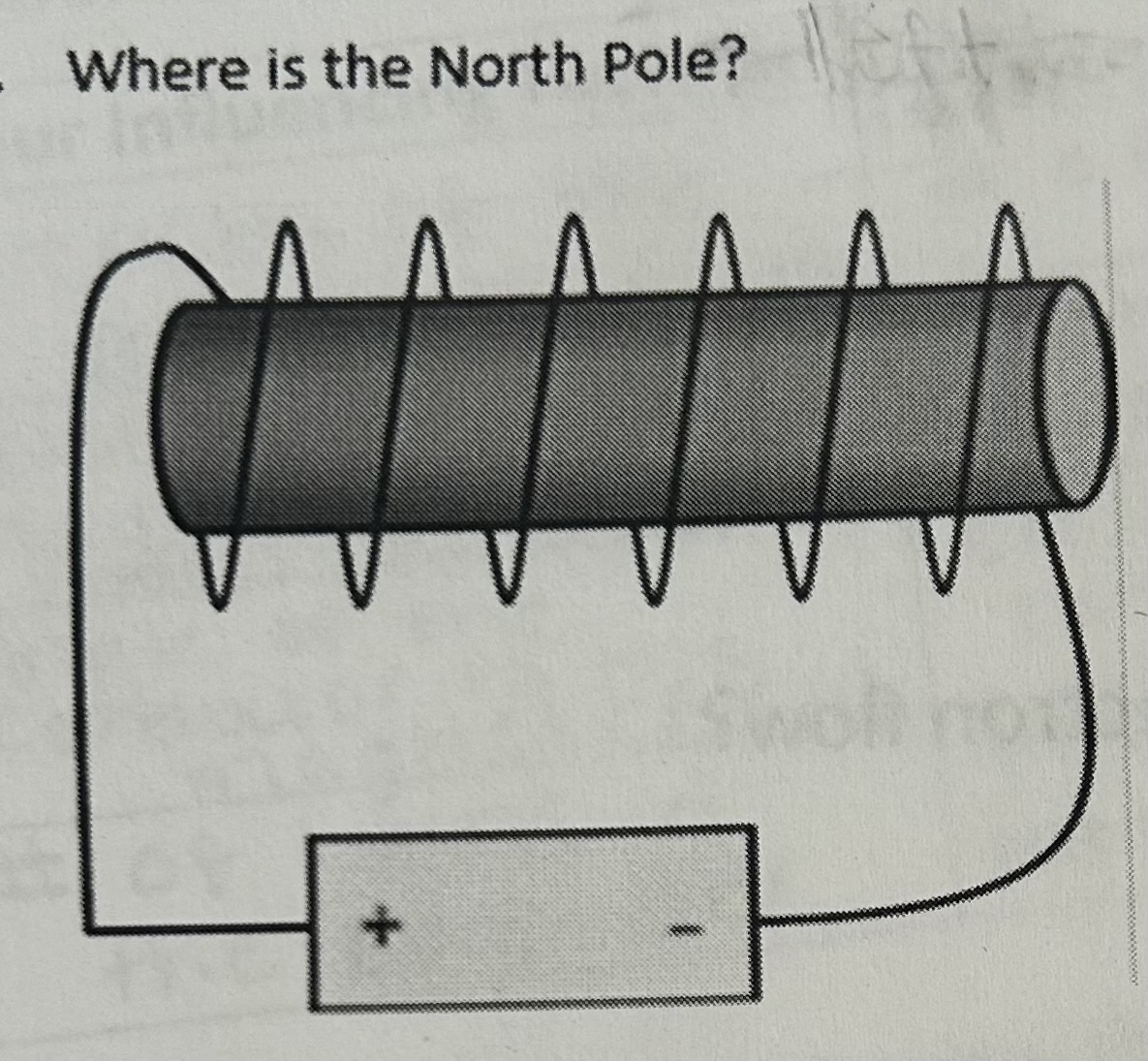
Where is the North Pole
Left
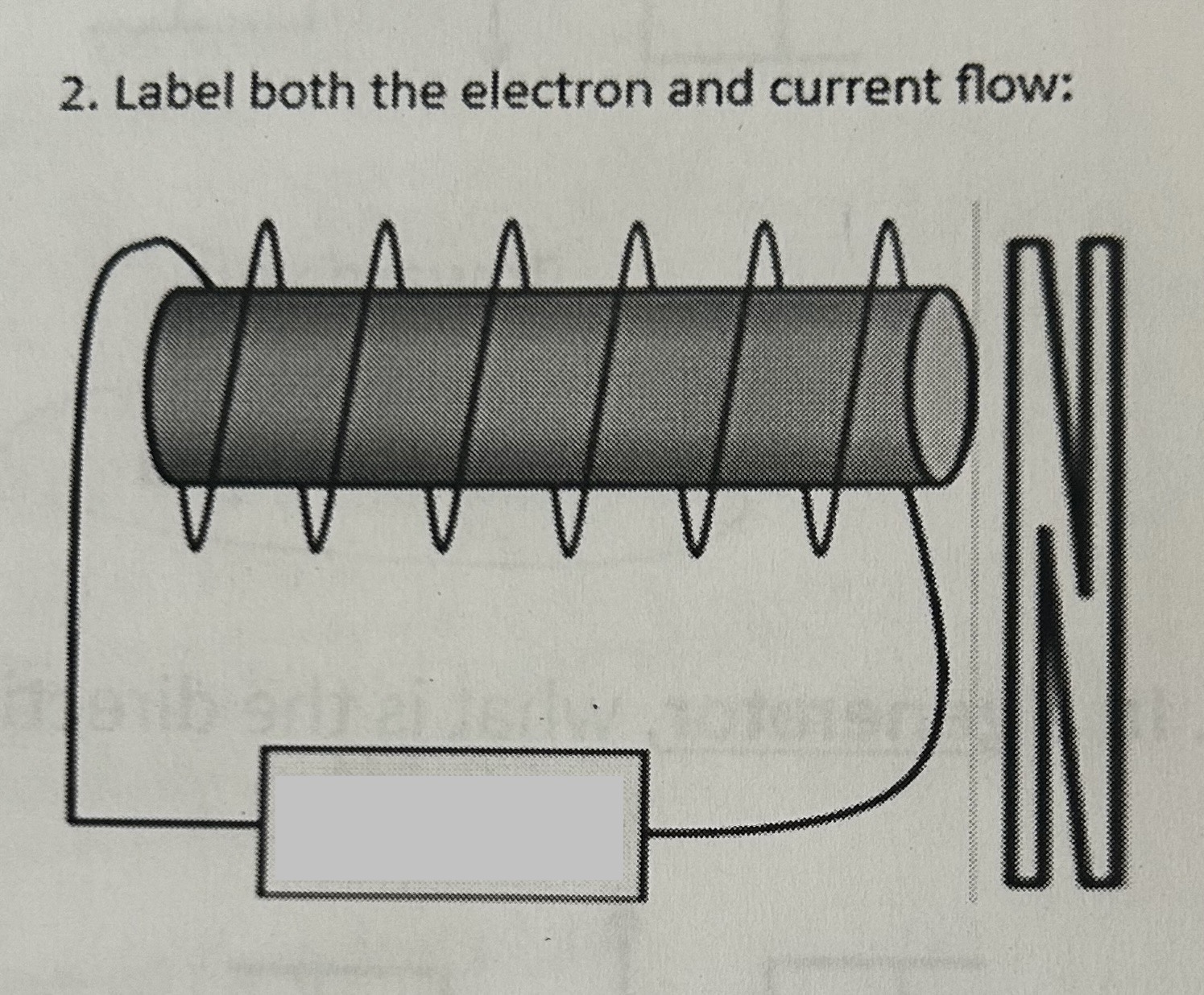
Label both the electron and current flow
- +
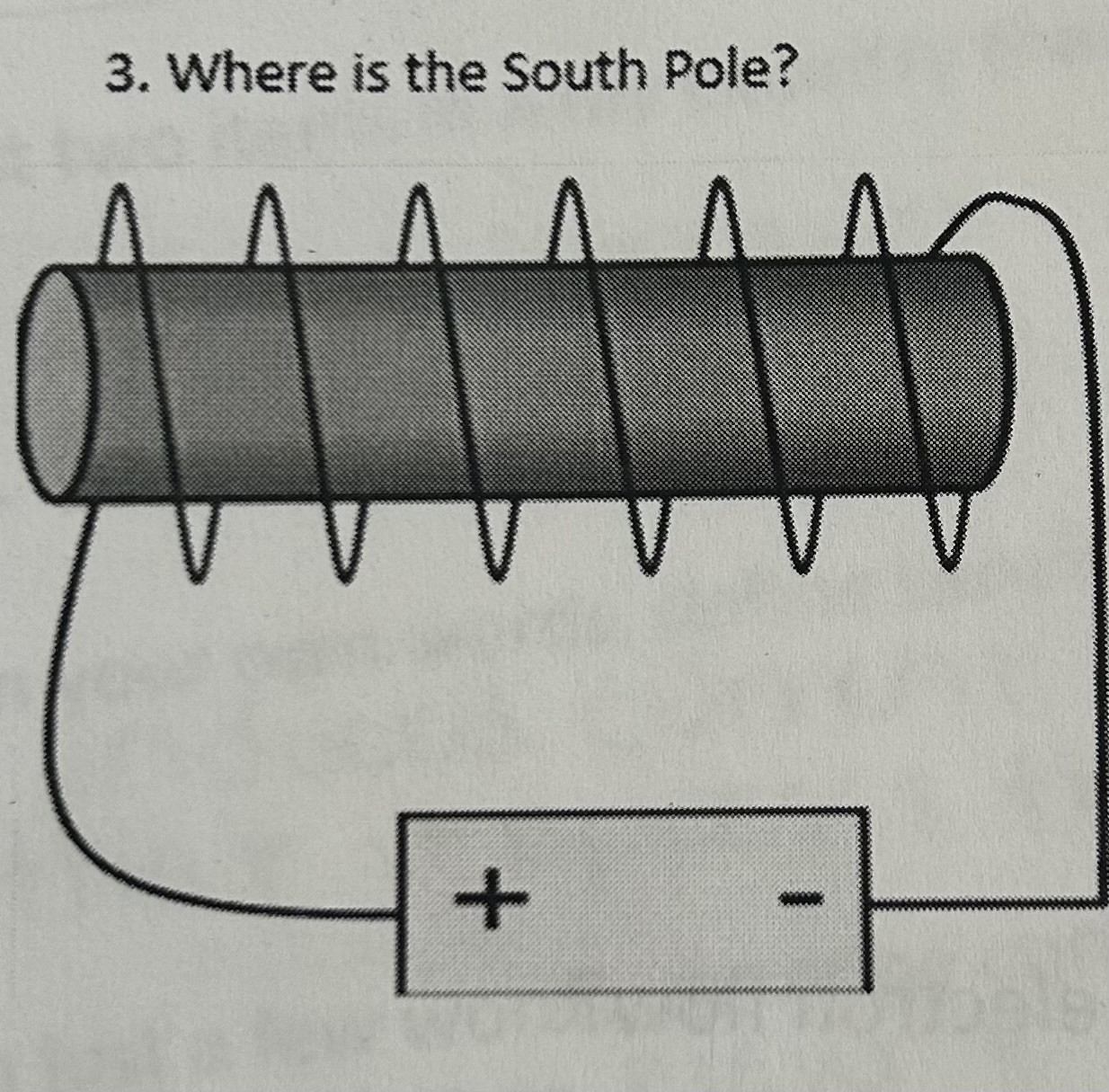
Where is the South Pole
Left
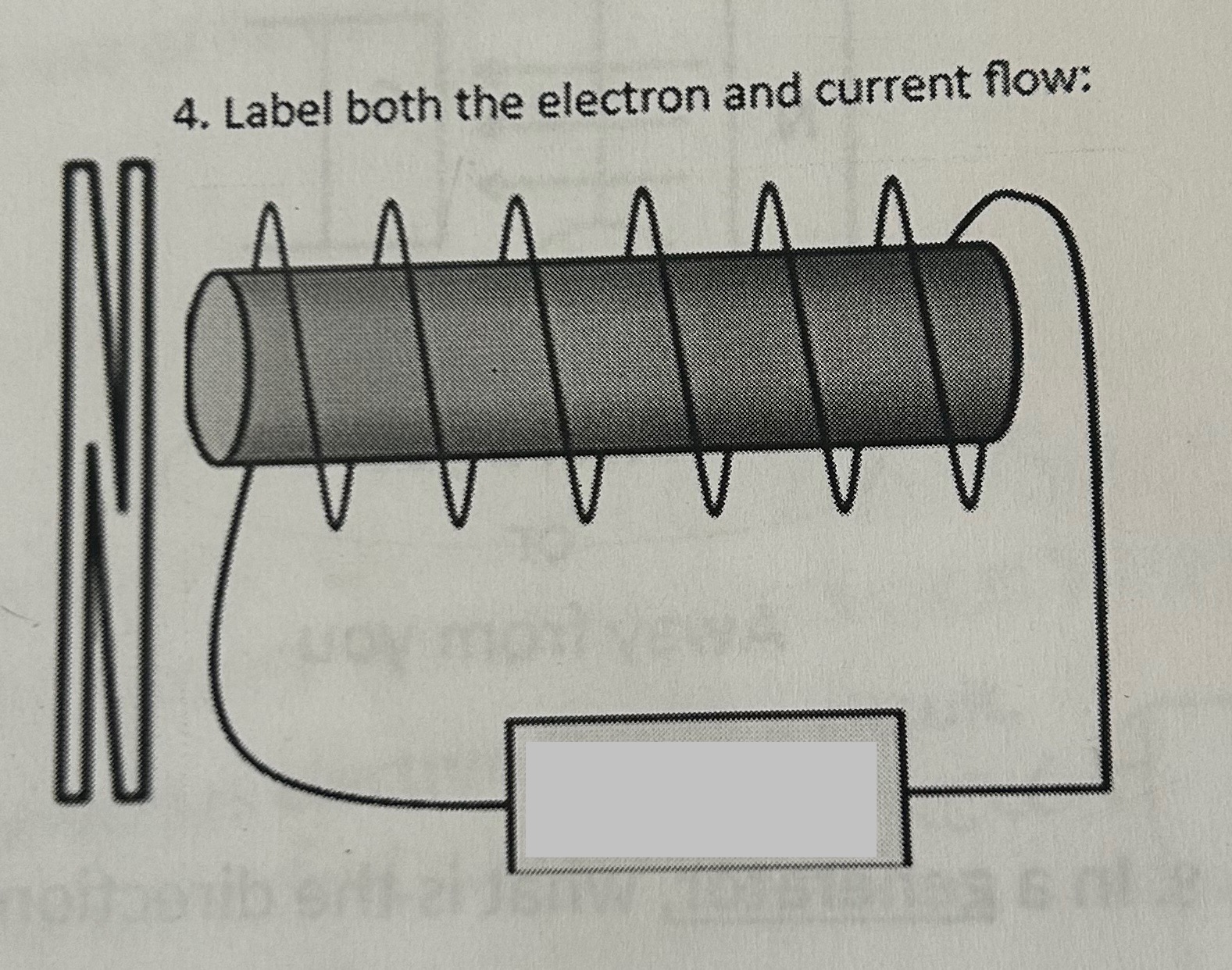
Label both the electron and current flow
- +
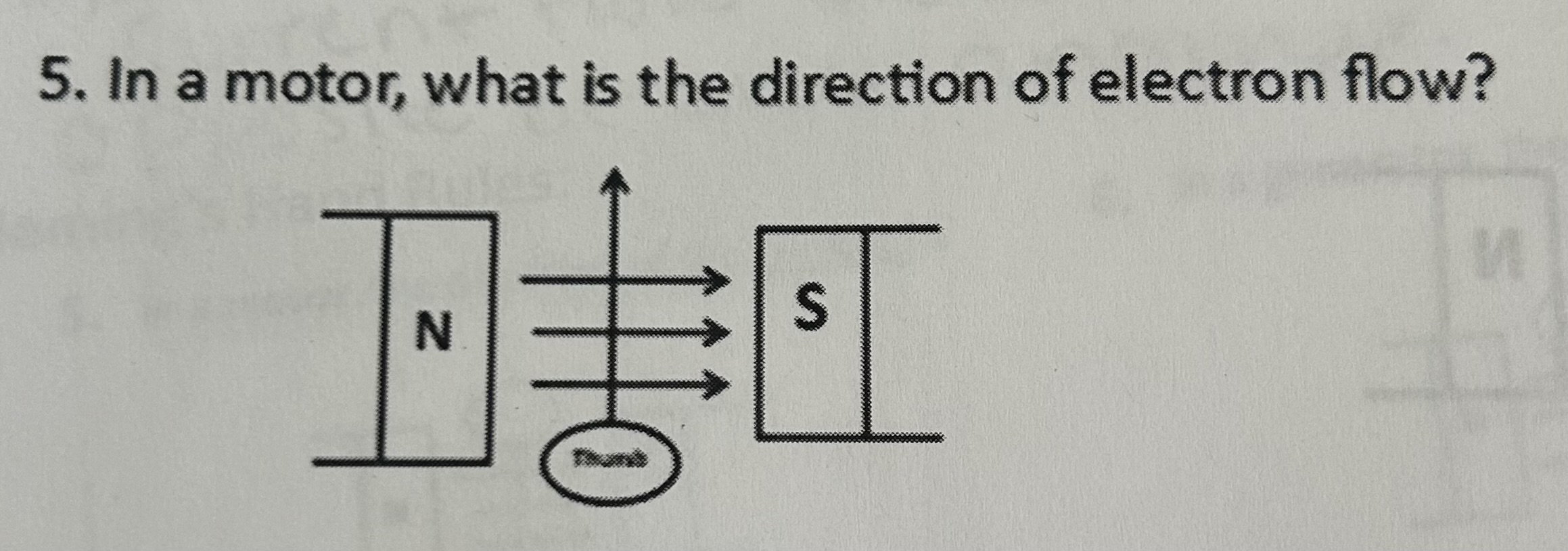
In a motor, what is the direction of the electron flow
Away from you
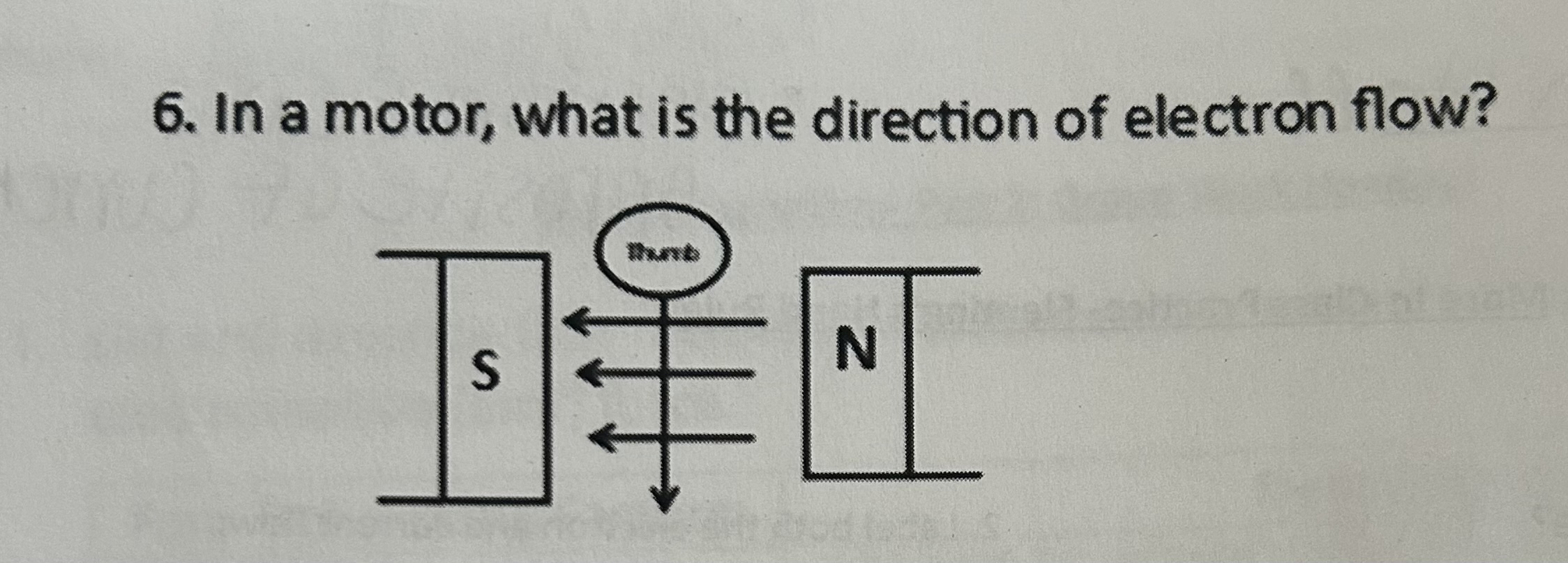
In a motor, what is the direction of electron flow
Away from you
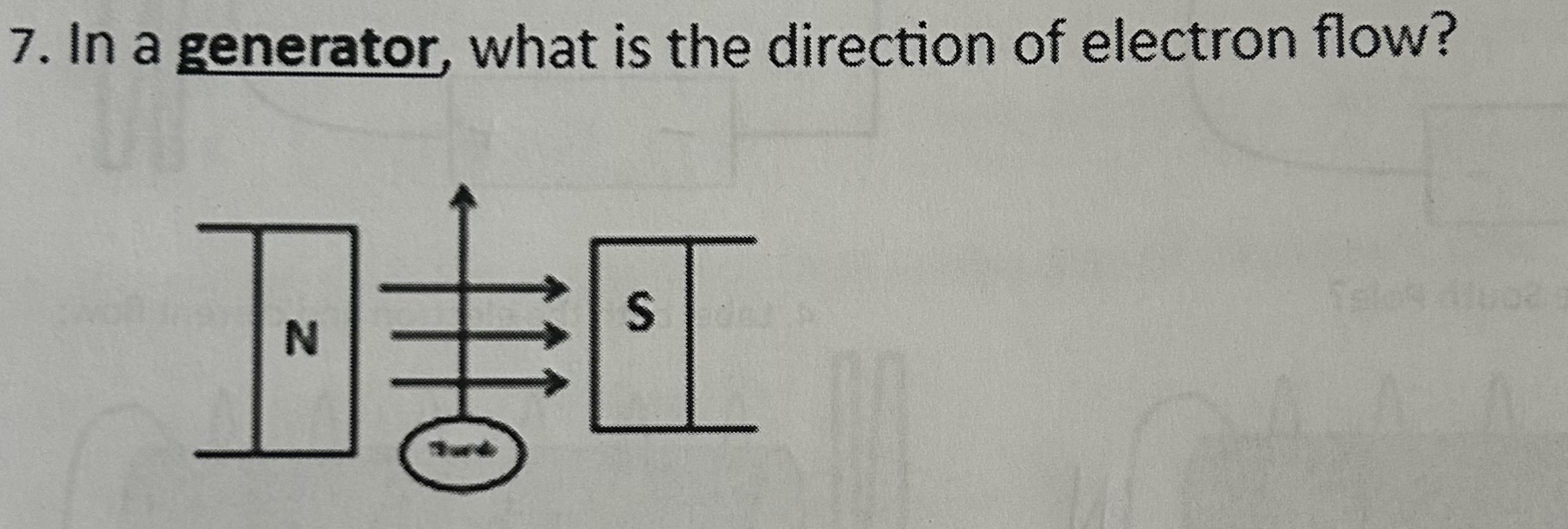
In a generator, what is the direction of electron flow
Toward you
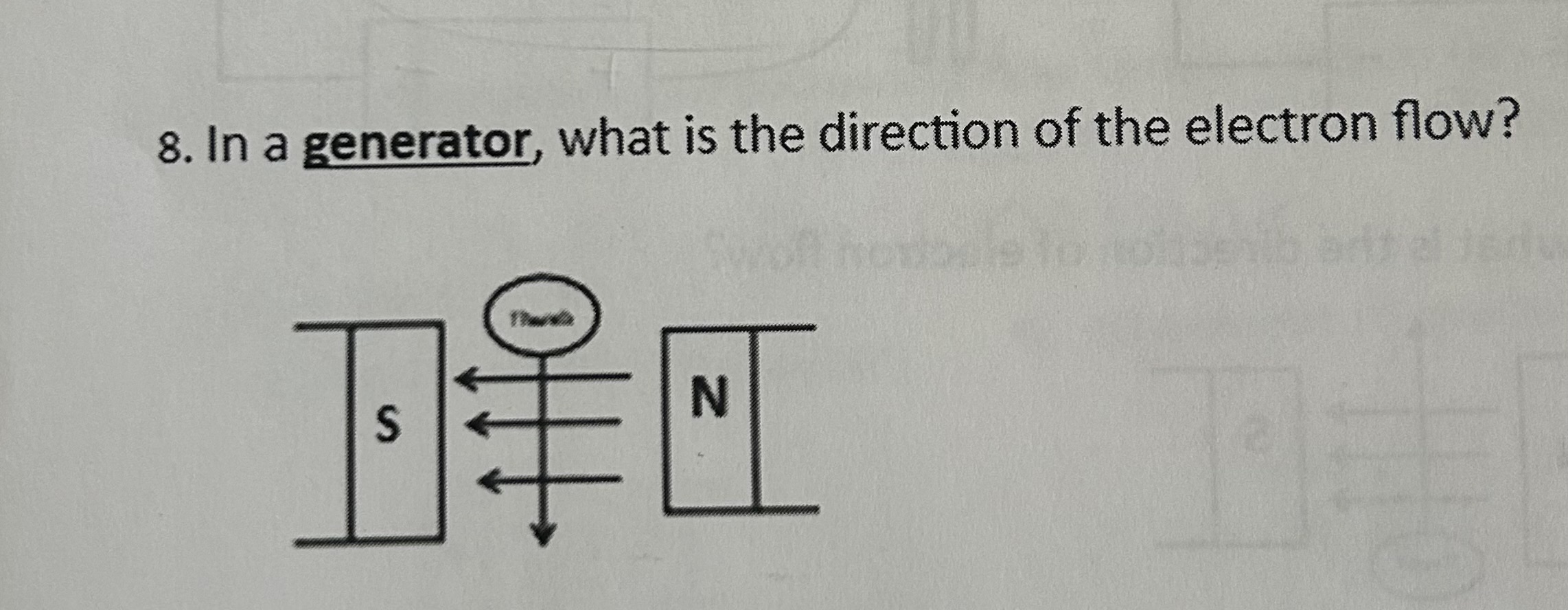
In a generator, what is the direction of the electron flow
Toward you
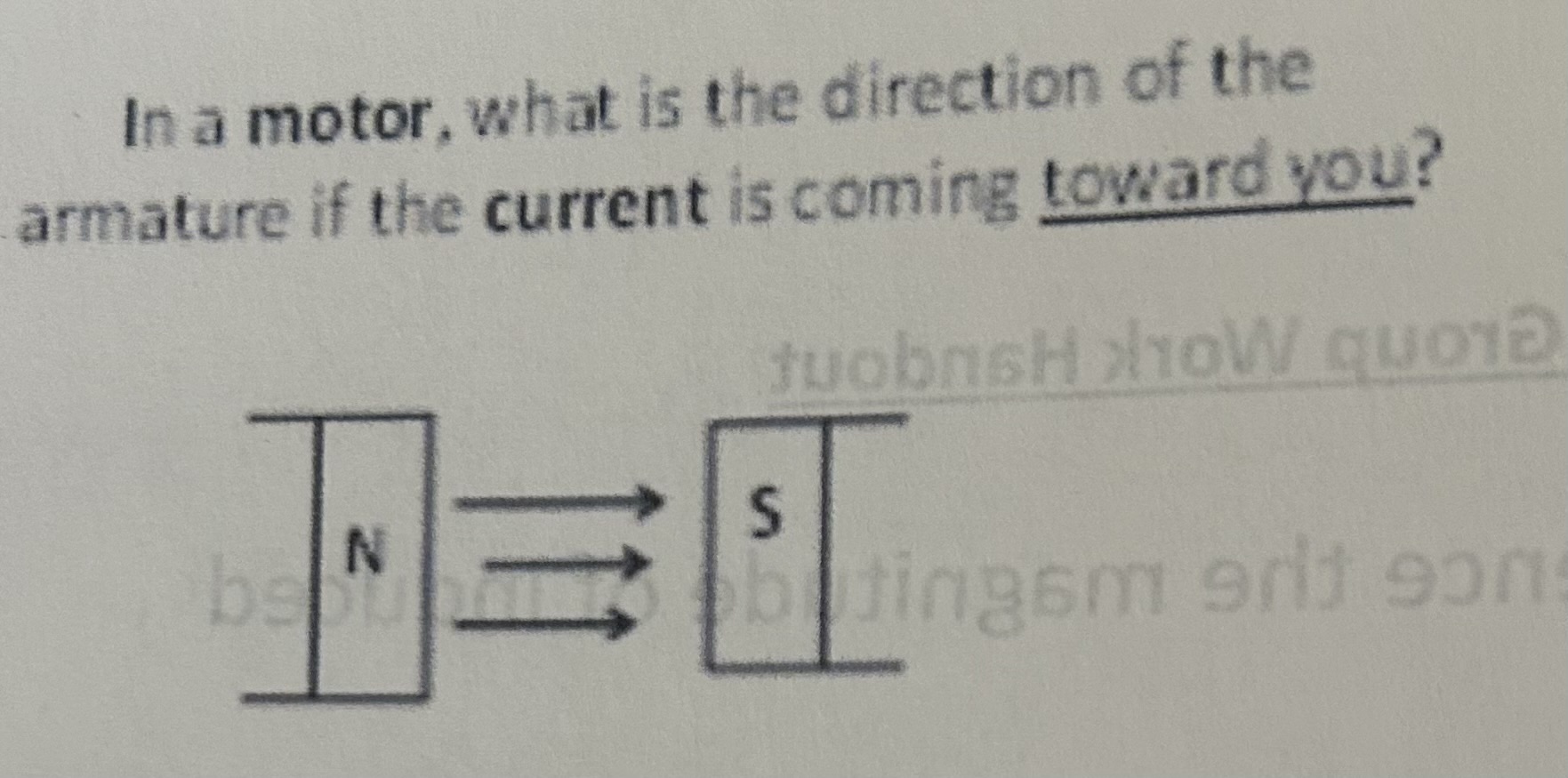
In a motor, what is the direction of the armature if the current is coming toward you
Up

In a motor, what is the direction of the armature if the current is going away from you
Up
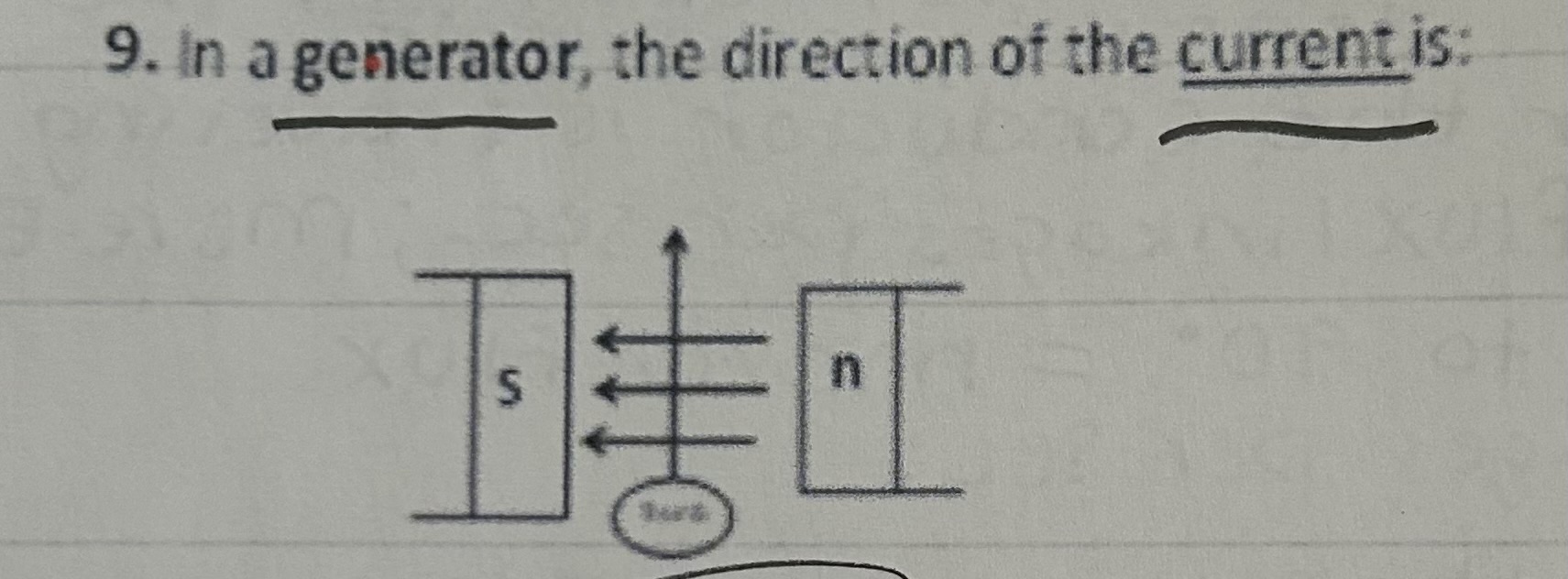
In a generator, the direction of the current is
Toward you
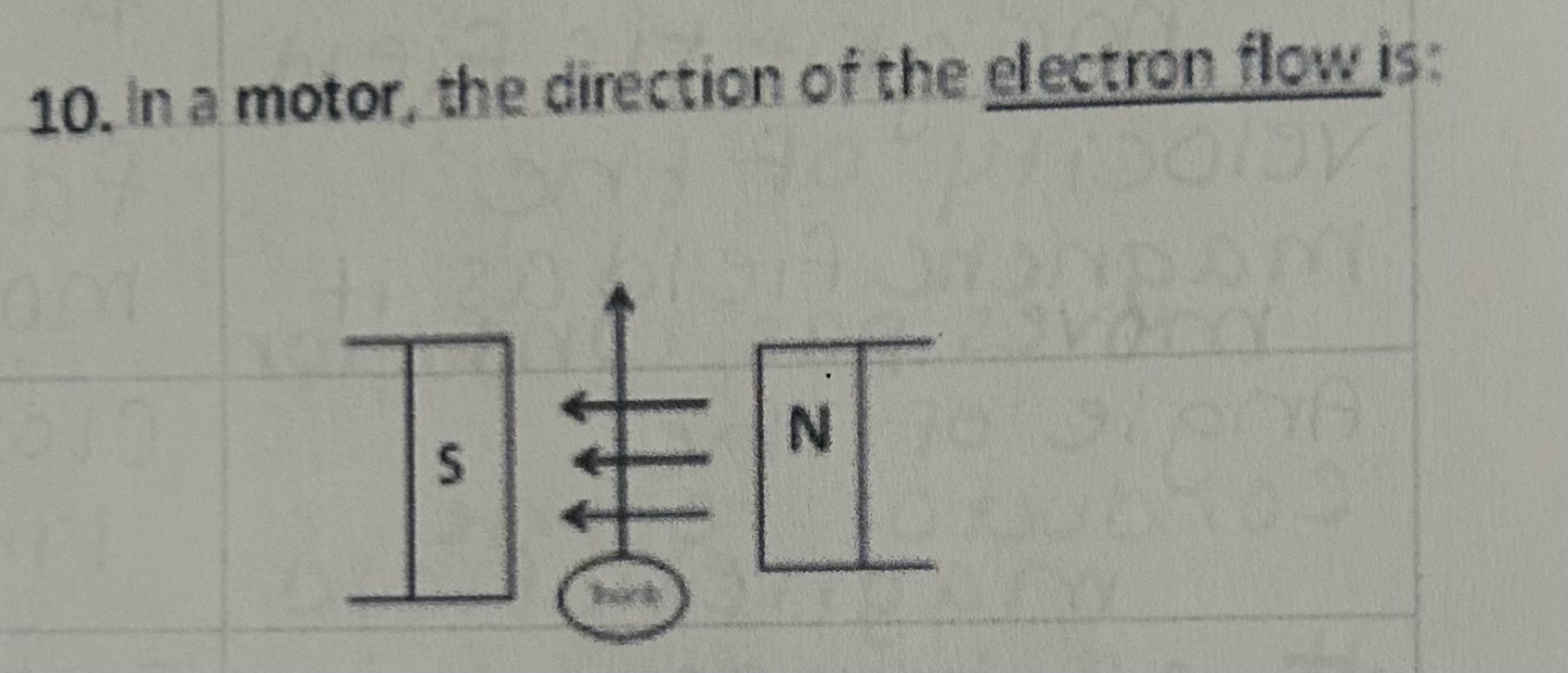
In a motor, the direction of the electron flow is
Toward you
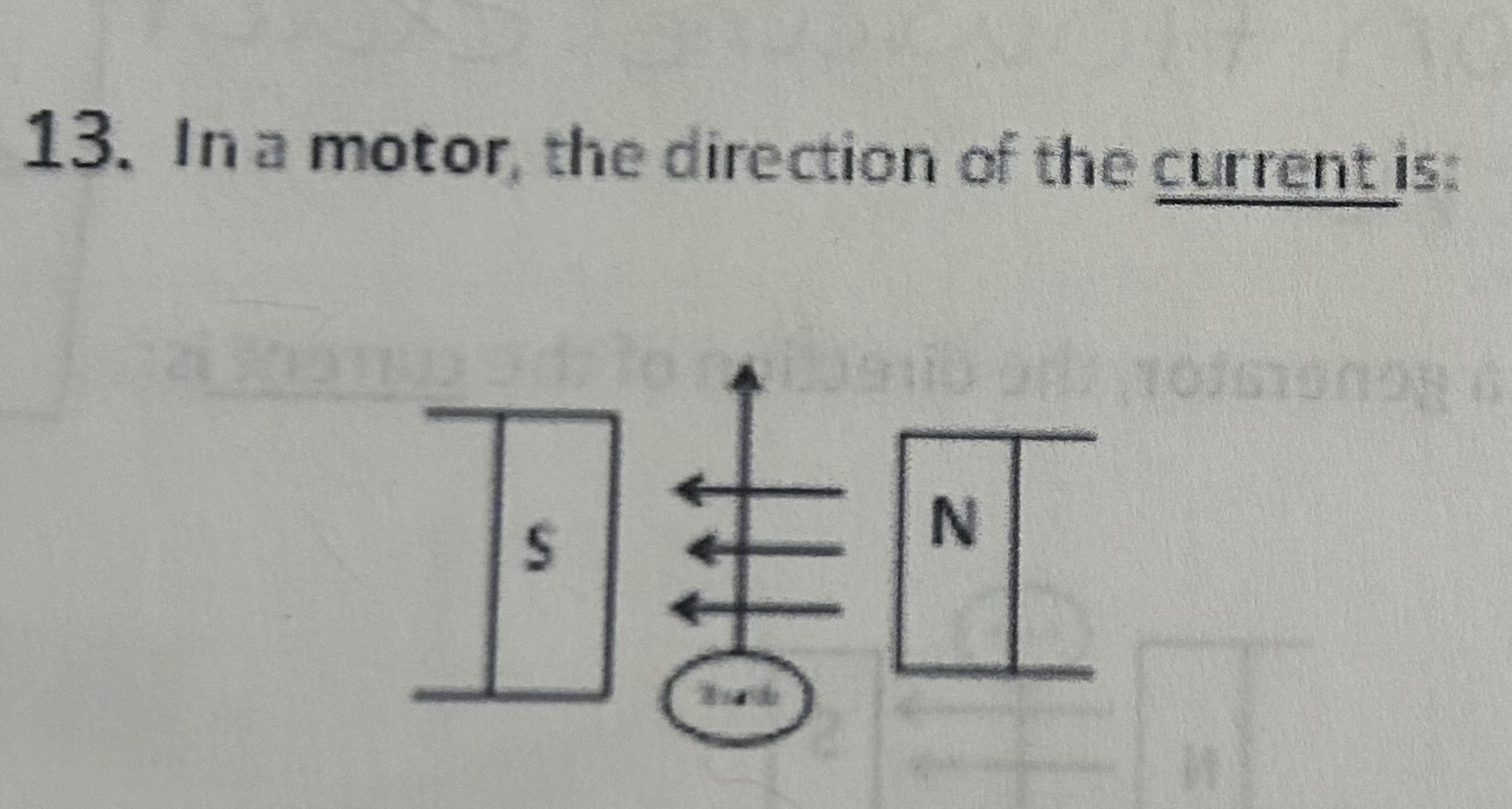
In a motor, the direction of the current is
Away from you
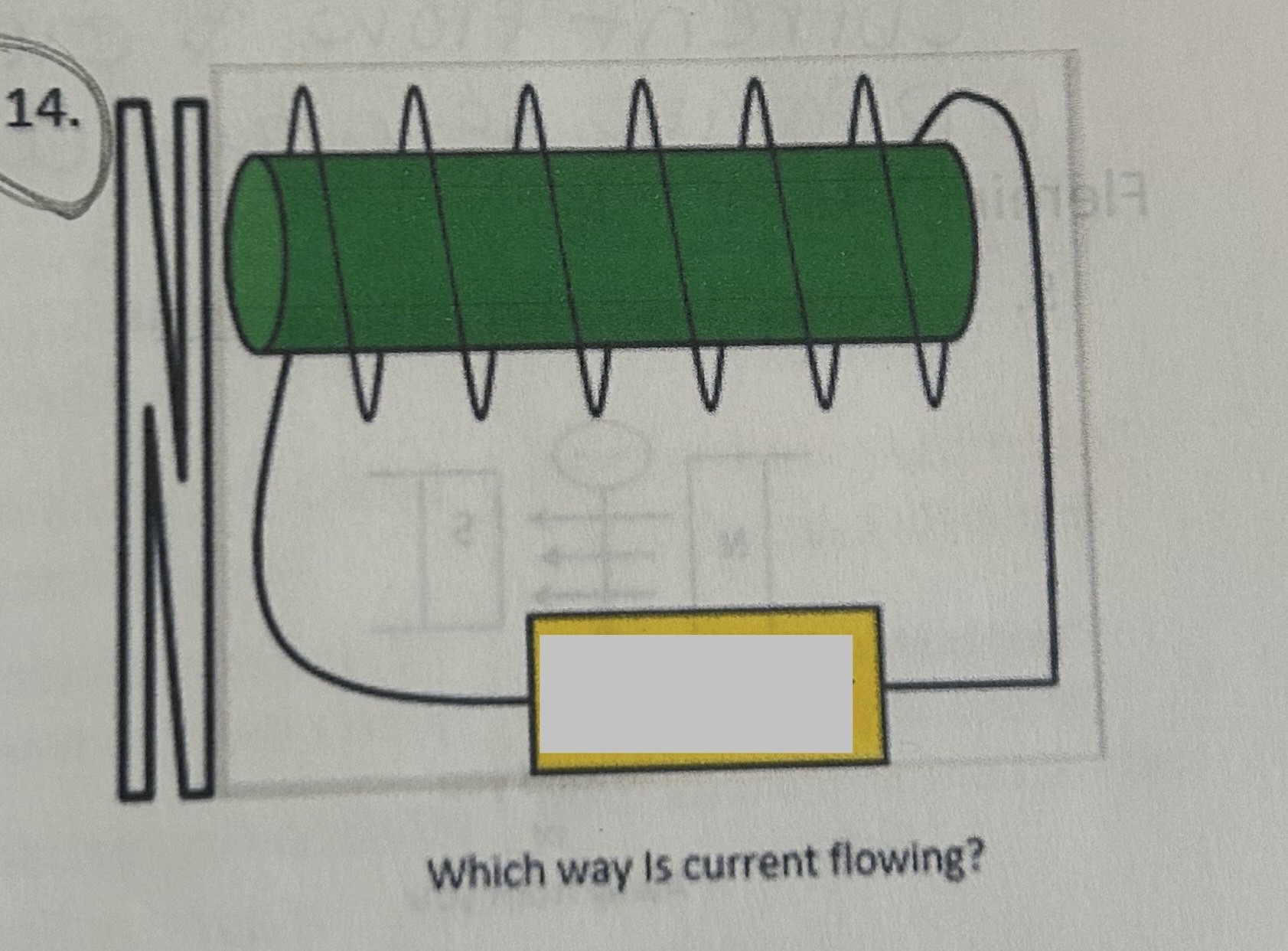
Which way is current flowing
- +
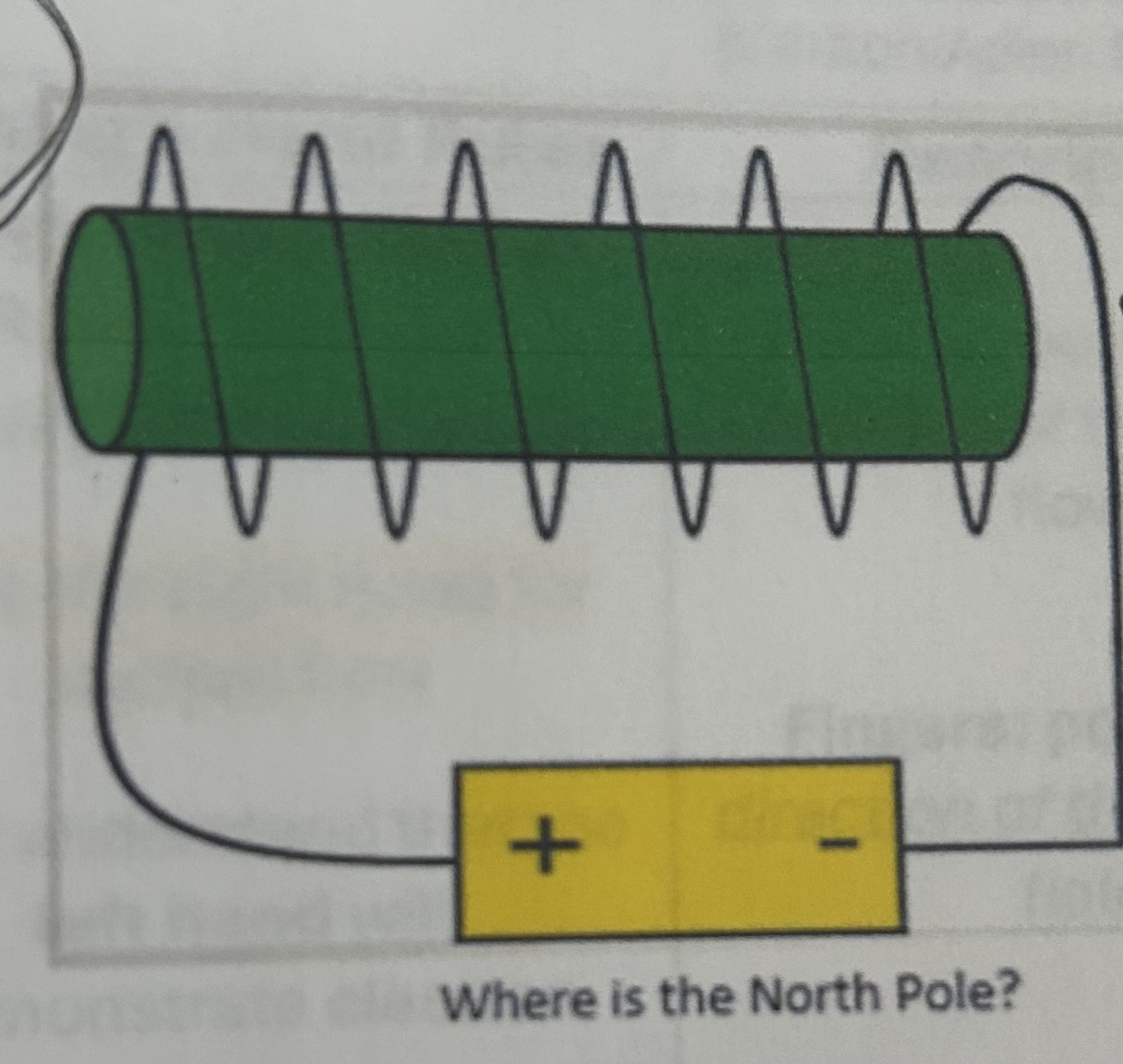
Where is the North Pole
Right
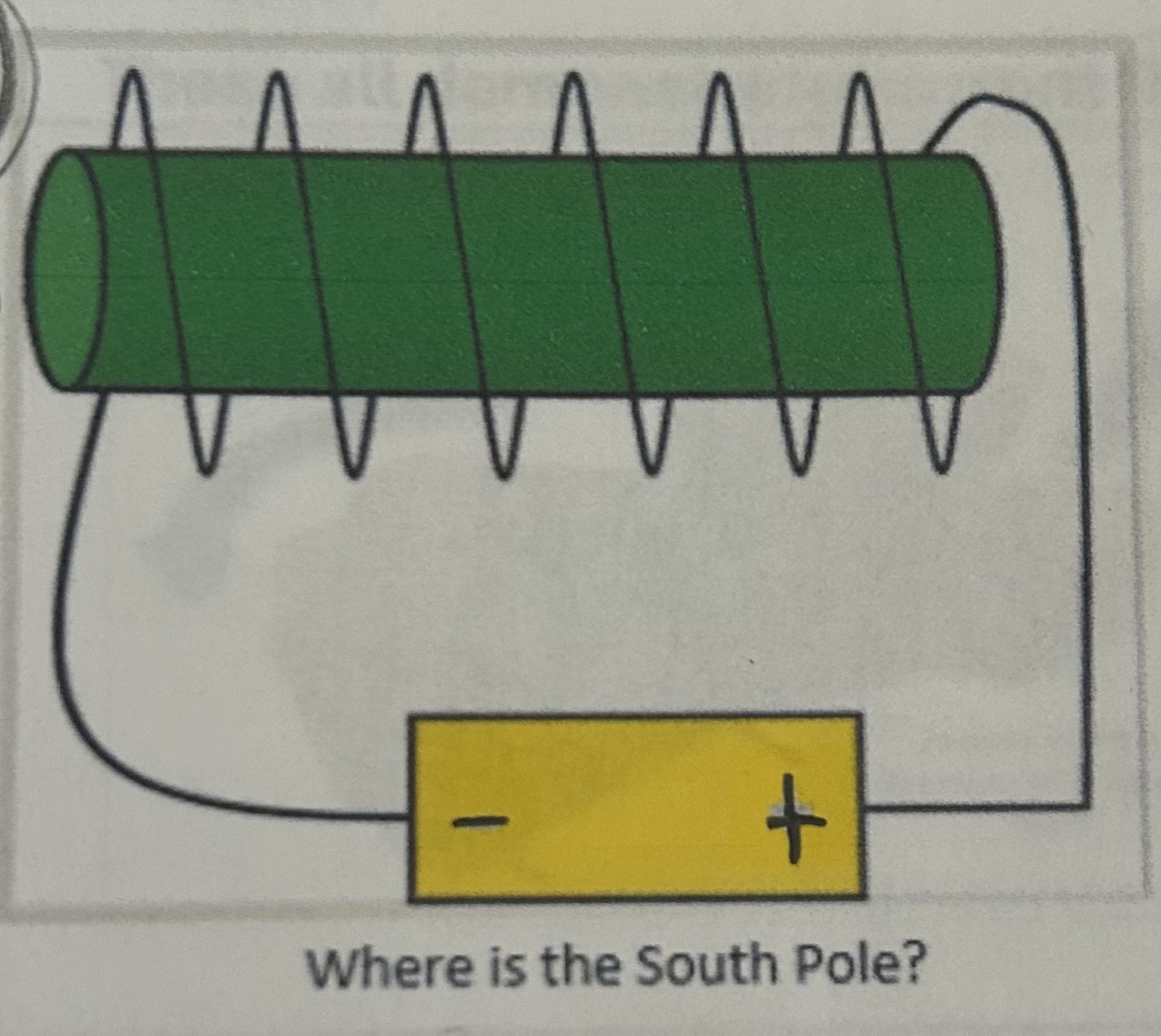
Where is the South Pole
left
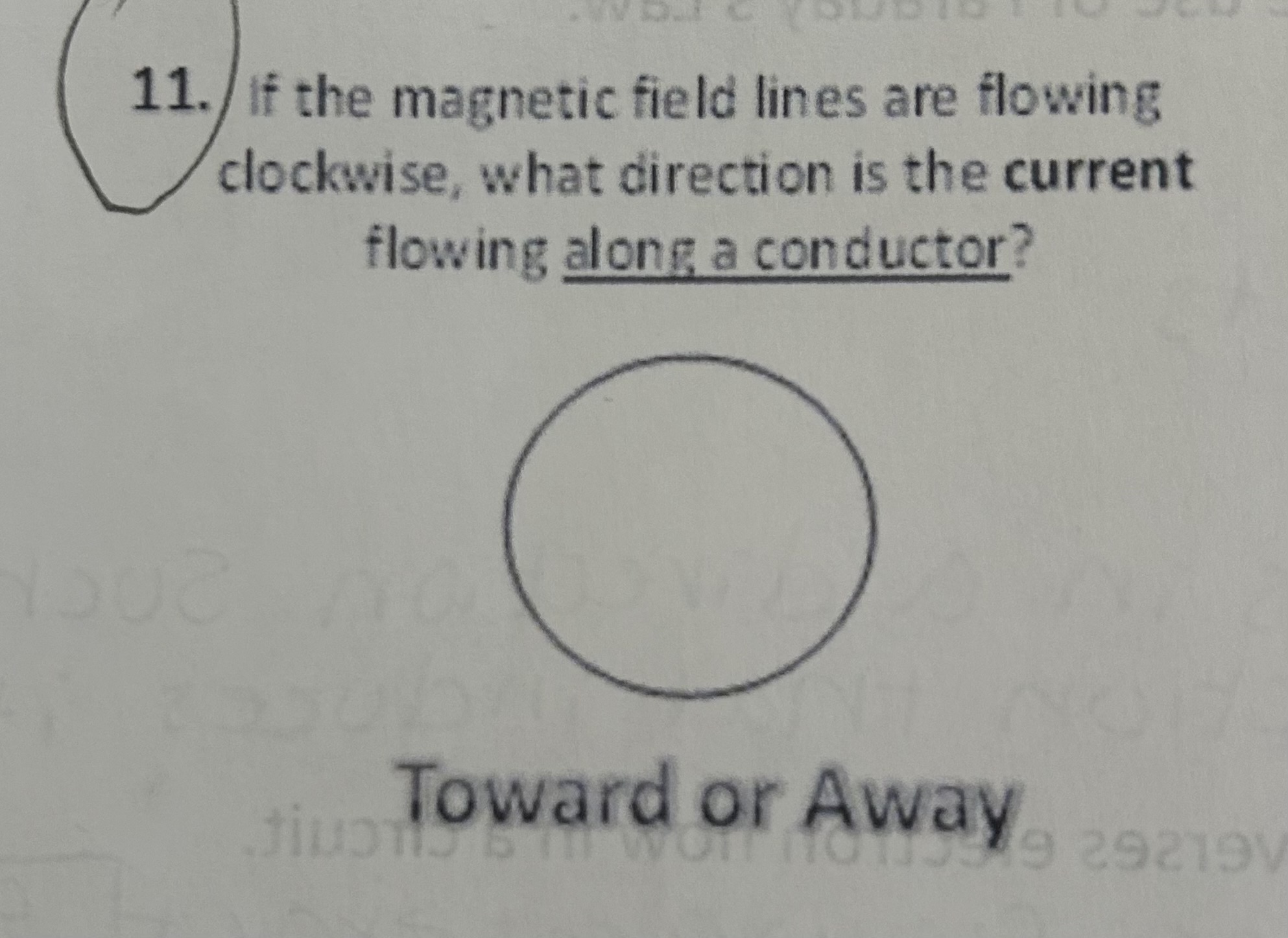
If the magnetic field lines are flowing clockwise, what direction is the current flowing along a conductor
Away

If the magnetic field lines are flowing clockwise, what direction is the electrons flowing along a conductor
Toward