MICR5842 L18: Current Vaccines and Immunization Strategies
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is the history of variolation in vaccination?
Variolation has been practiced for over 2000 years, originating in China, and was introduced to Europe in 1719 by Lady Mary Wortley Montague.
Who is credited with the first vaccination and what was it for?
Edward Jenner is credited with the first vaccination in 1796, which was for smallpox.
What vaccines did Louis Pasteur develop, and when?
Anthrax vaccine in 1881 and the rabies vaccine in 1885.
What was the compulsory vaccination for smallpox in England?
Smallpox vaccination was compulsory from 1853 to 1946 in England.
List the vaccines introduced in the UK routine vaccination schedule from 1941 to 2008.
Diphtheria (1941), Tetanus (1950), BCG (1953), Pertussis (1957), Polio (1955, live 1962-2004), Measles (1968), Rubella (1971), Mumps (1988), Haemophilus influenzae type B (1992), Meningococcus C (1999), Pneumococcus (2006), HPV (2008).
What is the purpose of the Expanded Programme of Immunisation (EPI)?
The EPI aims to ensure that all children receive routine vaccinations to prevent infectious diseases.
What is the significance of the 'Green Book' in UK vaccination?
The 'Green Book' is a comprehensive document by the Department of Health that provides guidelines on immunisation against infectious diseases.
What are the recommended vaccines for infants at 2 months in the UK?
DTaP/IPV/Hib + PCV.
What is the efficacy of the BCG vaccine against pulmonary tuberculosis in South India?
The efficacy of the BCG vaccine against pulmonary tuberculosis in South India is approximately 0%.
What are the estimated protection rates for the RTS,S malaria vaccine?
The RTS,S malaria vaccine provides about 18-36% protection against clinical malaria.
What does the abbreviation DTP stand for in vaccination?
DTP stands for Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis.
What is the recommended schedule for the DTP vaccine?
Three doses are recommended during infancy, with booster doses at 18 months or preschool age.
What is the controversy surrounding the pertussis component of the DTP vaccine?
There is major controversy over the efficacy and reactogenicity of the pertussis component.
What type of vaccine is BCG and how is it administered?
BCG is a live attenuated vaccine administered via intradermal or percutaneous injection.
What is the target population for the BCG vaccine in the UK?
The BCG vaccine targets high-risk populations in the UK.
What was the impact of UNICEF's 'UCI 90' initiative?
UNICEF's 'UCI 90' initiative aimed for 90% of children to receive routine vaccines by 1990.
What is the vaccine coverage situation when the EPI started in 1974?
When the EPI started in 1974, only 15% of the world's children were receiving routine vaccines.
What are the recommended vaccines for children aged 12-13 years in the UK?
HPV vaccine (3 doses, girls only) is recommended for children aged 12-13 years.
What is the efficacy of measles vaccines if well administered?
Measles vaccines can achieve over 90% efficacy if well administered in most populations.
What is the recommended vaccination for children aged 3-5 years in the UK?
dTaP/IPV + MMR + PCV.
What is the significance of the year 2013 in the UK vaccination schedule?
In 2013, the routine vaccination schedule included Influenza for 2-year-olds and Zoster for ages 70 and 79.
What are the potential issues with vaccine efficacy estimates?
Vaccine efficacy estimates can vary and do not always clarify what is being protected against (disease vs. infection).
What recent policy change was introduced in the USA regarding pertussis vaccination?
The adolescent booster aP is being introduced.
What has contributed to the recent increase in whooping cough cases in newborns?
Waning immunity from the aP vaccine.
What is the purpose of maternal immunization?
To increase passive protection of young infants through maternal antibodies.
Which vaccines are recommended routinely for maternal immunization?
1) Tetanus toxoid, 2) Influenza vaccine, 3) Pertussis vaccine (as dTaP/Tdap booster plus IPV).
What was the impact of the Swine Flu vaccine scare on influenza vaccine uptake?
There was a decreased uptake following the scare.
What is the current status of the Group B streptococcal vaccine?
It is in Phase 3 clinical trials as of 2015.
What is the significance of maternal antibodies in vaccination?
Pre-existing maternal antibodies can interfere with vaccines for measles, polio, and rotavirus.
What are the two types of polio vaccines used in most countries?
1) IPV (Inactivated Polio Vaccine) and 2) OPV (Oral Polio Vaccine).
Why have wealthy countries shifted back to IPV from OPV?
Due to safety concerns regarding vaccine-associated paralytic polio (VAPP).
What was the goal of the global polio eradication program?
To eradicate polio globally, primarily using OPV and national immunization days (NIDs).
What major issue surrounds the efficacy of OPV in tropical regions?
Low efficacy and the persistence of vaccine-derived polio viruses (VDPVs).
What reduced the incidence of acute paralytic poliomyelitis from 1912 to 1999 in England and Wales?
The incidence decreased significantly after the introduction of the Salk and Sabin vaccines.
What progress was made in polio eradication from 1988 to 2003?
Cases decreased from 350,000 in 1988 to less than 1,000 in 2003.
What is the current status of wild type Polio serotype 2?
All cases of wild type Polio serotype 2 have been eradicated.
What recommendation did the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts make regarding IPV?
To introduce at least one dose of IPV into the routine immunization schedule before the end of 2015.
What are some new vaccine technologies being explored for polio?
Monovalent IPV-2, aluminum salt adjuvants, double-mutant heat-labile enterotoxin adjuvants, intradermal delivery of IPV, and genetically stable OPV strains.
What is the significance of the polio endgame strategy?
To provide immunity against type 2 poliovirus and facilitate the transition from trivalent OPV to bivalent OPV.
What challenges does IPV face in developing countries?
High costs and operational issues pose a threat to timely introduction.
What was the last wild virus case of polio in the New World?
The last wild virus case occurred in 1991.
How many countries were involved in the polio eradication efforts in 1988?
125 countries.
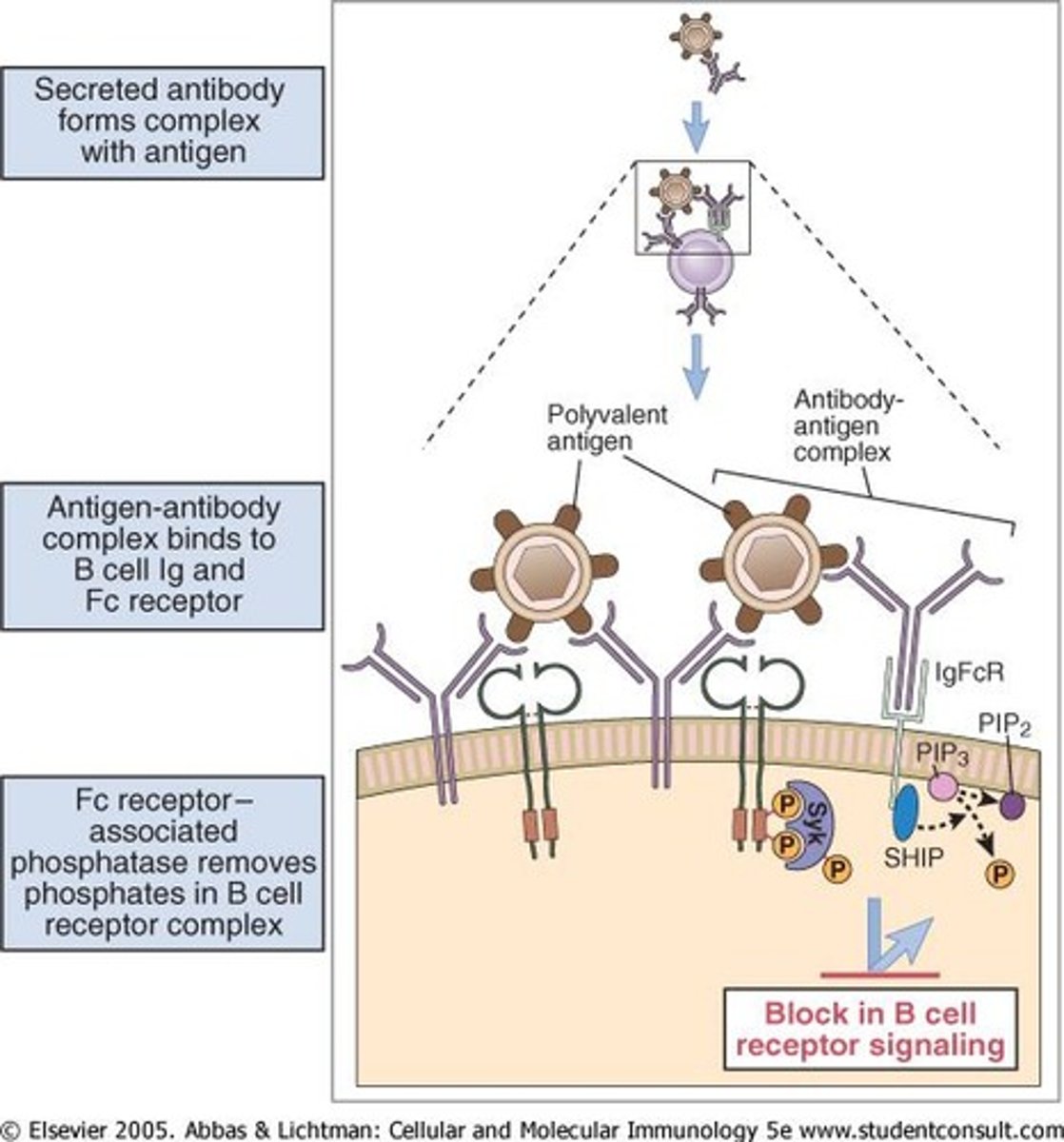
What is the relationship between maternal antibodies and B cell activation?
B cell activation is blocked by co-engagement with the inhibitory FcgRII.
What is the potential impact of non-protective antibody levels?
They can still be inhibitory to immune responses.
What was the outcome of polio vaccination efforts in India?
India is now polio 'free'.
What is the significance of the 2015 recommendation for OPV using countries?
To ensure immunity against type 2 poliovirus and boost immunity against types 1 and 3.
What type of vaccine is used for measles in most countries?
Live attenuated virus, freeze-dried, administered via SubQ or IM injection.
At what age is the single dose of measles vaccine recommended?
12-15 months of age, or younger if incidence of measles is high.
What is the efficacy of the measles vaccine if given at the recommended age?
High efficacy if a potent vaccine is given at 12-15 months.
What factors can lower the efficacy of the measles vaccine?
Lower efficacy if given earlier due to interference by maternal antibodies.
What controversy surrounds the measles vaccination schedule in tropical countries?
Debate over the optimal schedule due to high incidence of measles in infants.
What was the issue with high titre vaccines for young infants?
They were withdrawn due to safety concerns.
Which countries have a two-dose schedule for measles vaccination?
Brazil, Sweden, USA, UK.
What is the target for measles elimination in Europe?
Measles 'elimination' target for Europe in 2007.
What is the annual death toll from pneumonia in children under 5 years?
2 million deaths annually, with over 800,000 due to Streptococcus pneumoniae.
What is the problem with pneumococcal vaccines regarding serotype immunity?
There are about 90 different serotypes, leading to serotype-specific immunity issues.
What is the name of the 23-valent capsular polysaccharide vaccine?
Pneumovax 23.
Why do young children not respond well to polysaccharide vaccines?
They do not respond well to polysaccharide alone.
What is the purpose of the new broad strain pneumococcal vaccines?
To expand the number of serotypes covered and improve vaccination in S. America and Africa.
What is the expected impact of new pneumococcal vaccines by 2015?
Expected to vaccinate 110 million children and save 700,000 lives by 2015.
What are some vaccines currently in development or rollout?
Mosquirix, Denvaxia, Bexsero, and vaccines for Rotavirus, Malaria, HIV, Tuberculosis, Shigella, Lyme disease, Respiratory syncytial virus, Dengue, Ebola, and MenB.
How many deaths per year are attributed to rotavirus?
1.3 million deaths per year, with one-third due to Rotavirus.
What was the issue with the Rotashield vaccine?
It was withdrawn in 1999 due to safety issues related to intussusception.
What is the effect of vaccines on human populations?
Direct effect reduces disease risk in vaccinees; indirect effect reduces disease in non-vaccinees through reduced transmission.
What does 'herd immunity' imply?
A threshold of immunity above which infection incidence will decline, potentially leading to eradication.
What are the effects of vaccines on microbial populations?
Eradication of diseases (like smallpox), reduced circulation in the community, and strain replacement.
What is the current annual spending on vaccination in the poorest countries?
$2.5 billion per year, needing to reach $3.5 billion to achieve 90% coverage.
What is the cost-benefit of vaccination?
Vaccination confers approximately $1 billion in cost benefit.
What is the role of GAVI in vaccination efforts?
GAVI has vaccinated 288 million children and saved 5 million lives since 2000.
What is the Advance Market Commitment by GAVI?
Guarantees delivery of new vaccines to low-income countries for $3.50 per dose for 10 years.