Gram Stains
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the primary stain for Gram staining?
Crystal Violet
What is the mordant for Gram staining?
Gram’s Iodine
What is the purpose of the mordant during staining?
sets the crystal violet into all cells
What is the decolorizer in Gram staining?
acetone-alcohol
How does the decolorizer affect Gram positives?
thick cell wall is dehydrated, trapping the crystal violet in place
What 2 things make up the thick cell wall of Gram positives?
peptidoglycan
teichoic acids
How does the decolorizer affect Gram negatives?
outer thin cell wall is dissolved/forms holes, allowing crystal violet to exit the organism
What does the outer thin cell wall in Gram negatives consist of?
lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
What is the counterstain in Gram staining?
safranin
Blue/Purple organisms are Gram (positive/negative).
positive
Red/Pink organisms are Gram (positive/negative).
negative
What would over-decolorizing do to your stain?
Gram positives would appear Gram negative
What would under-decolorizing do to your stain?
Gram negatives would appear Gram positive
How old should a culture be to use for staining?
18-24 hrs
Why do we not use cultures older than 24 hours?
older cultures can be easily decolorized
Cultures older than 24 hours may appear Gram (positive/negative).
Gram negative
Smears that are too thick can what affect on staining?
Gram negatives will appear Gram positive
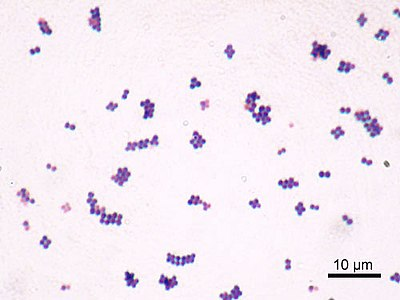
How would you report this stain?
GPC
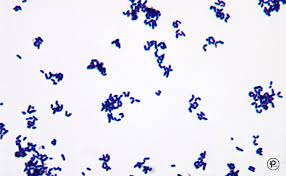
How would you report this stain?
GPR
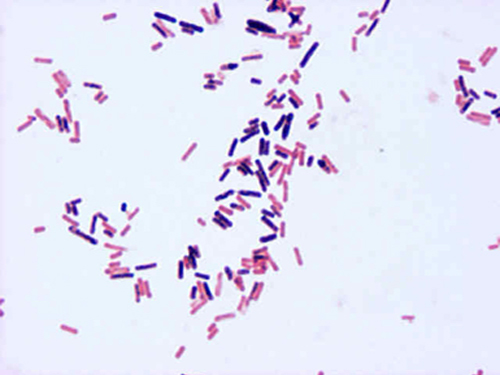
How would you report this stain?
GPR w/ spores
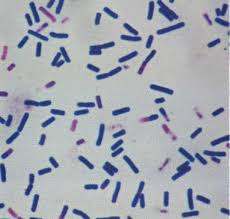
How would you report this stain?
GPR w/ spores
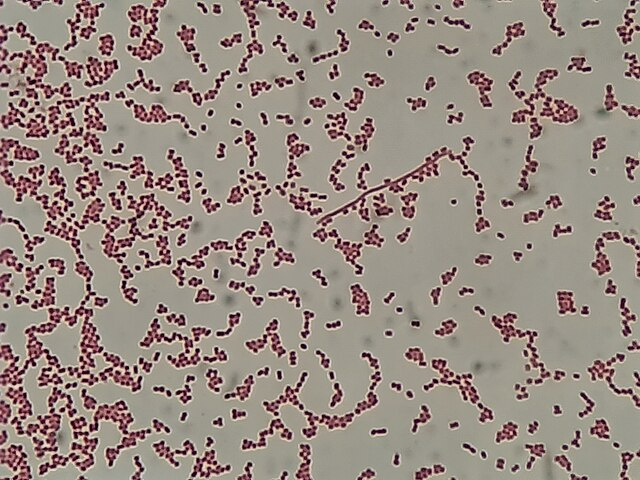
How would you report this stain?
GNC

How would you report this stain?
GNR

How would you report this stain?
yeast
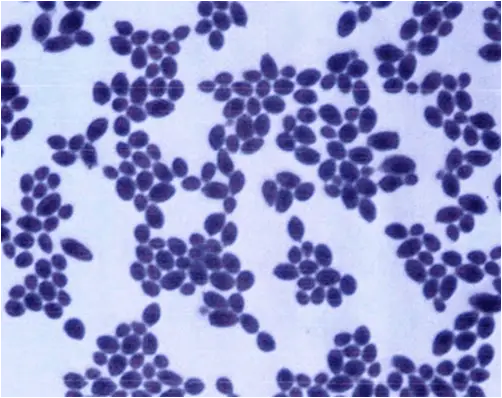
How would you report this stain?
yeast
Nonbacterial cells and cellular debris should appear Gram (positive/negative).
Gram negative