Ascending & Descending pathways
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Three ascending tracts in spinal cord
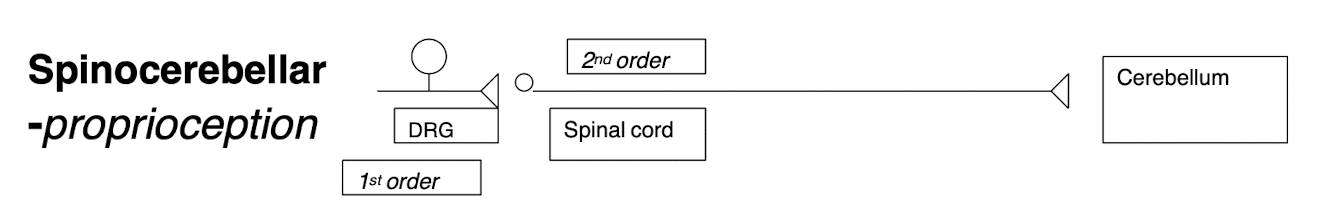
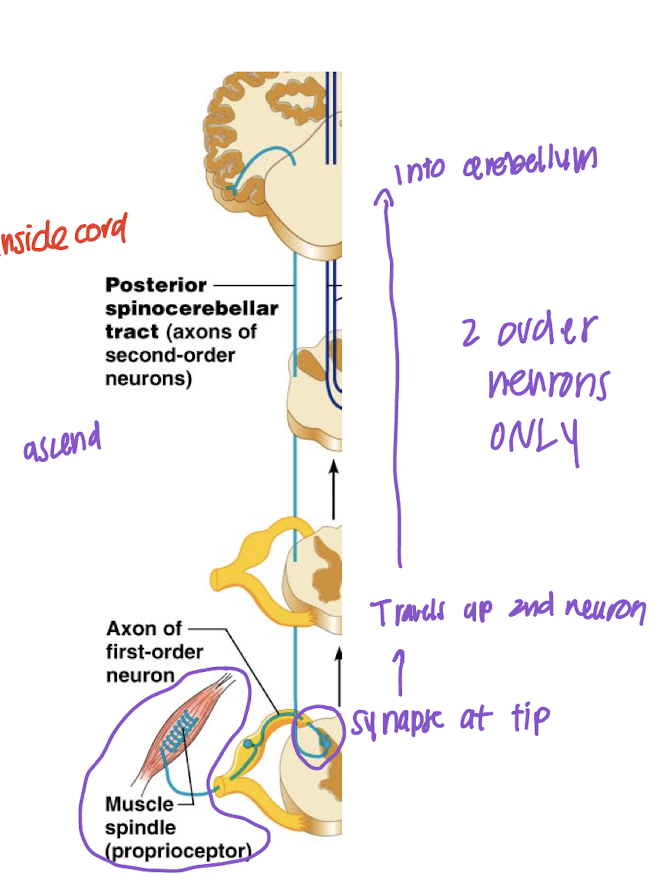
Spinocerebellar
Spinothalmic
Leminiscal
Spinocerebellar
Convey information about propioception from muscle/tendon.
Propioceptors provided information on body position on the same side of the body
1st order neuron: Sensory neuron cell bodies in DRG
2nd: In dorsal horn of spinal cord neuron & synapses at Cerebellum
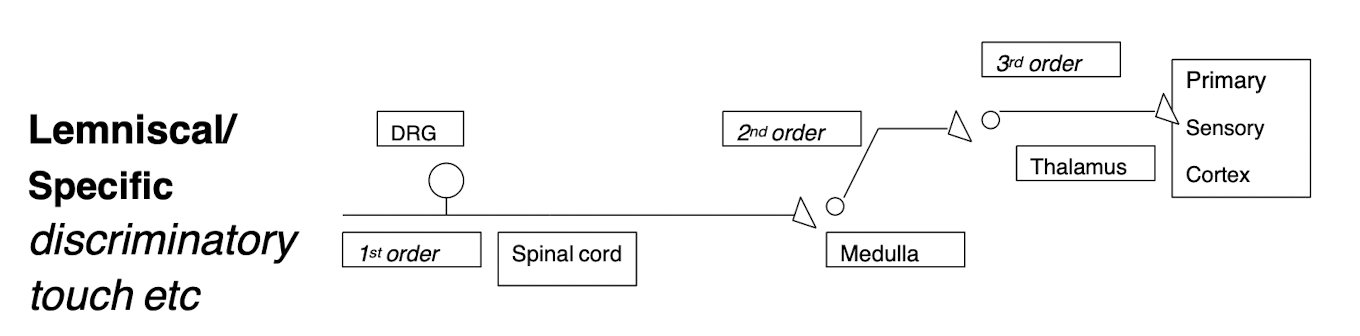
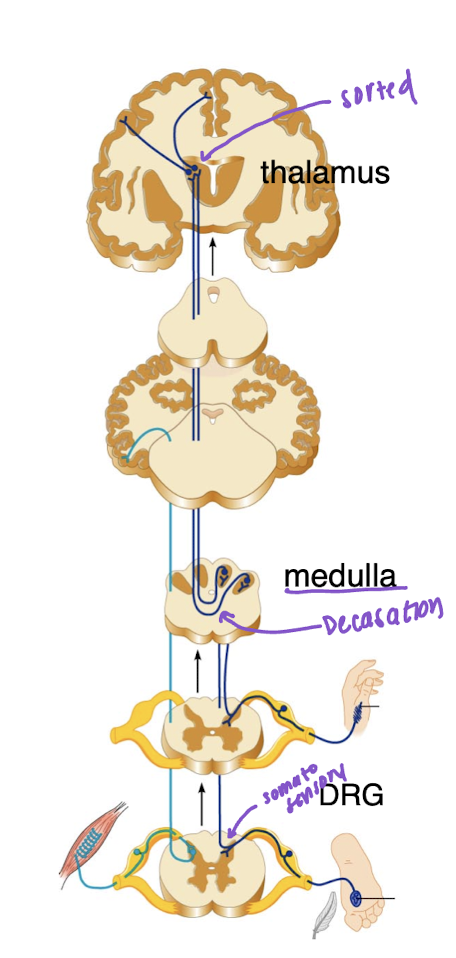
Specific/Lemniscal
Touch/vibration and proprioception crossover in medulla
Carry discriminatory sensation from skin (touch, pressure) and propioception
1st order neuron: Sensory neuron cell bodies in DRG
2nd order neuron: Medulla- these neurons decussate in medulla
3rd order neuron: Thalamus (projects to primary somatosensory area of cortex on opposite side of the brain
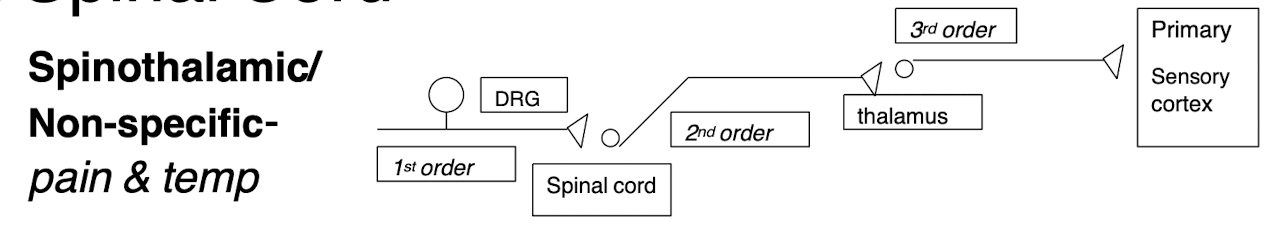
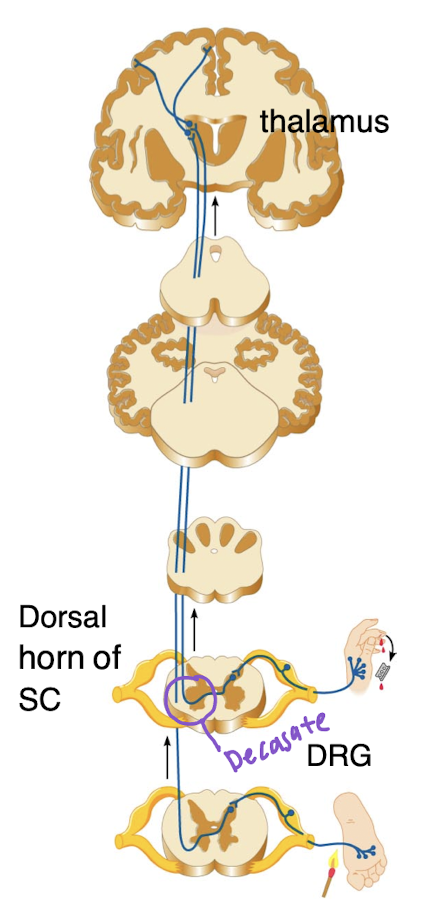
Spinothalamic/Non-Specific
Carries information on pain and temperature and deep pressure
Pathways crossover in spinal cord
1st order neuron: Sensory neuron cell bodies in DRG
2nd order neuron: Dorsal horn of spinal cord’s axons decussate
3rd order neuron: Thalamus projects information to primary somatosensory area of cortex
Descending pathways in spinal cord
Pyramidal (aka corticospinal tracts)
Direct: Descends without synapsing
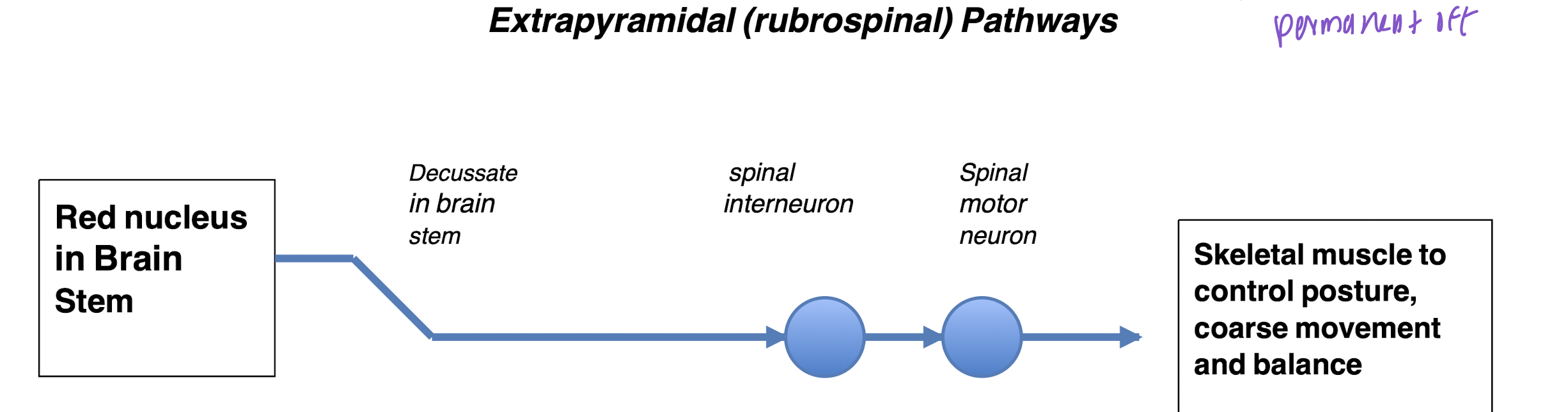
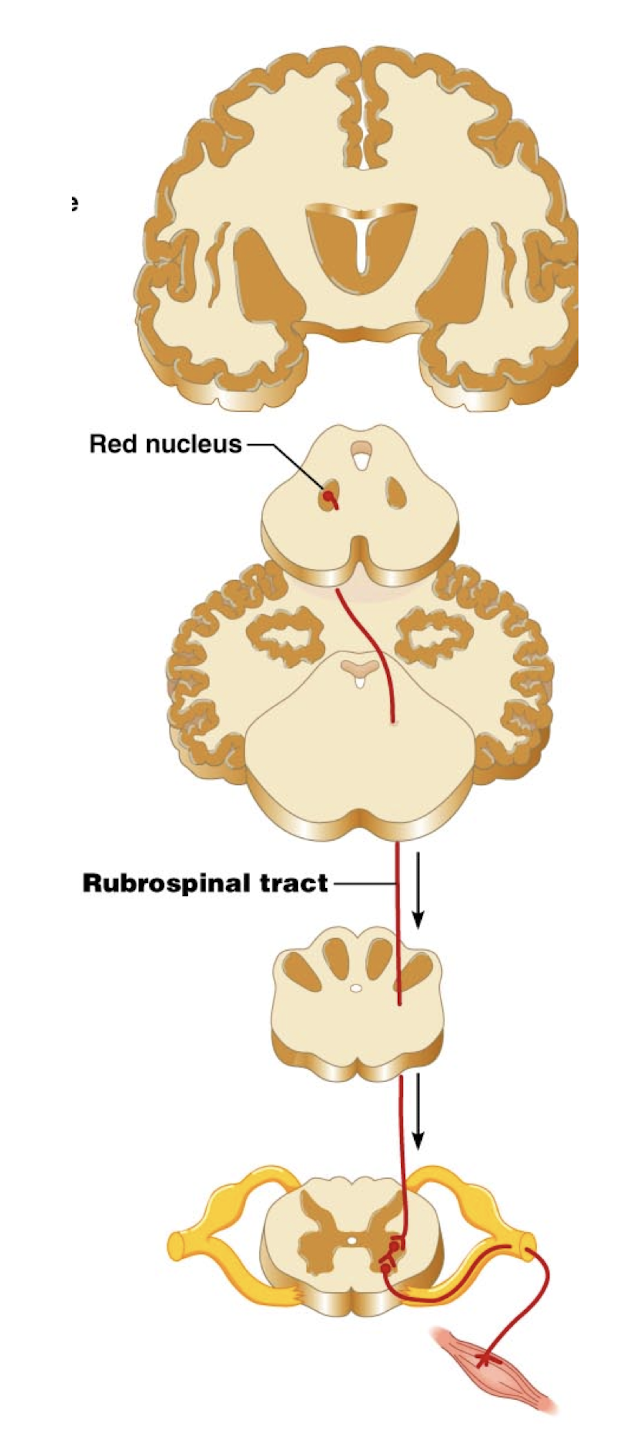
Rubrospinal (aka extrapyrimidal tract)
Indirect: multineuronal pathways
What is Pyramidal (aka corticospinal tracts) for
Regulate fast and fine skulled movement
What is Rubrospinal (aka extrapyrimidal tract) for
Regulate balance, posture, coarse limb movement, head and neck, eye movement
Pyramidal (aka corticospinal tracts)
Control voluntary and conscious movements on the opposite side of the body
Decussate in either medulla or spinal cord
Synapse either directly on spinal motor neuron or on an interneuron (more often) that connects to motor neuron.
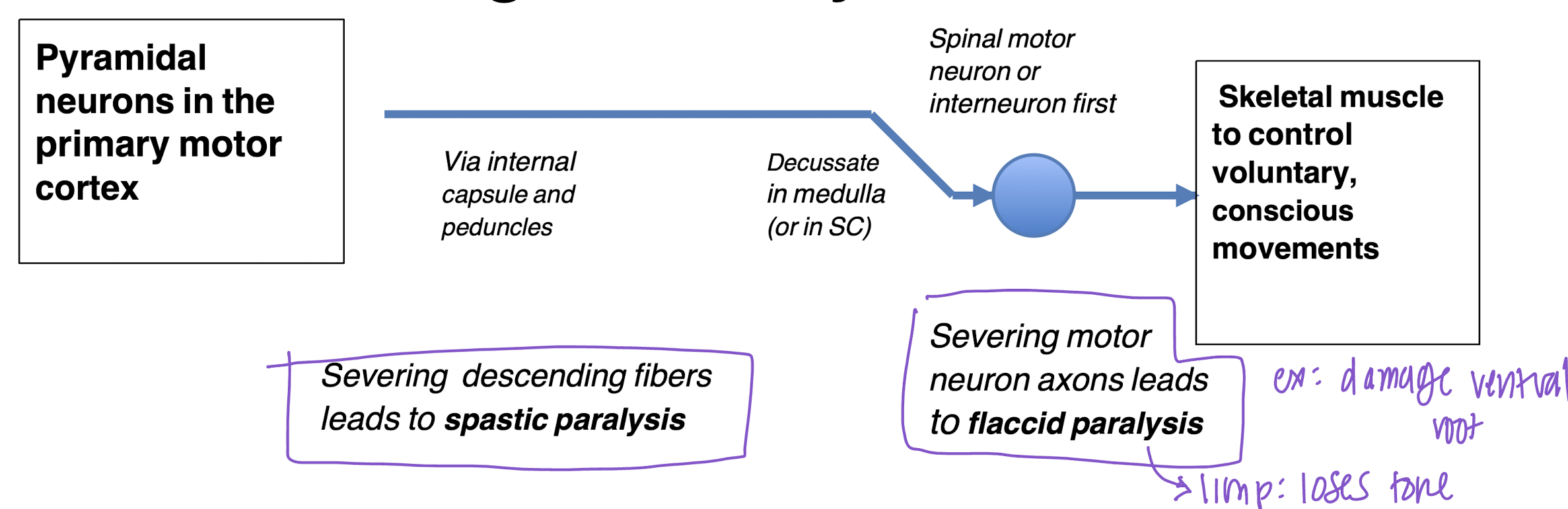
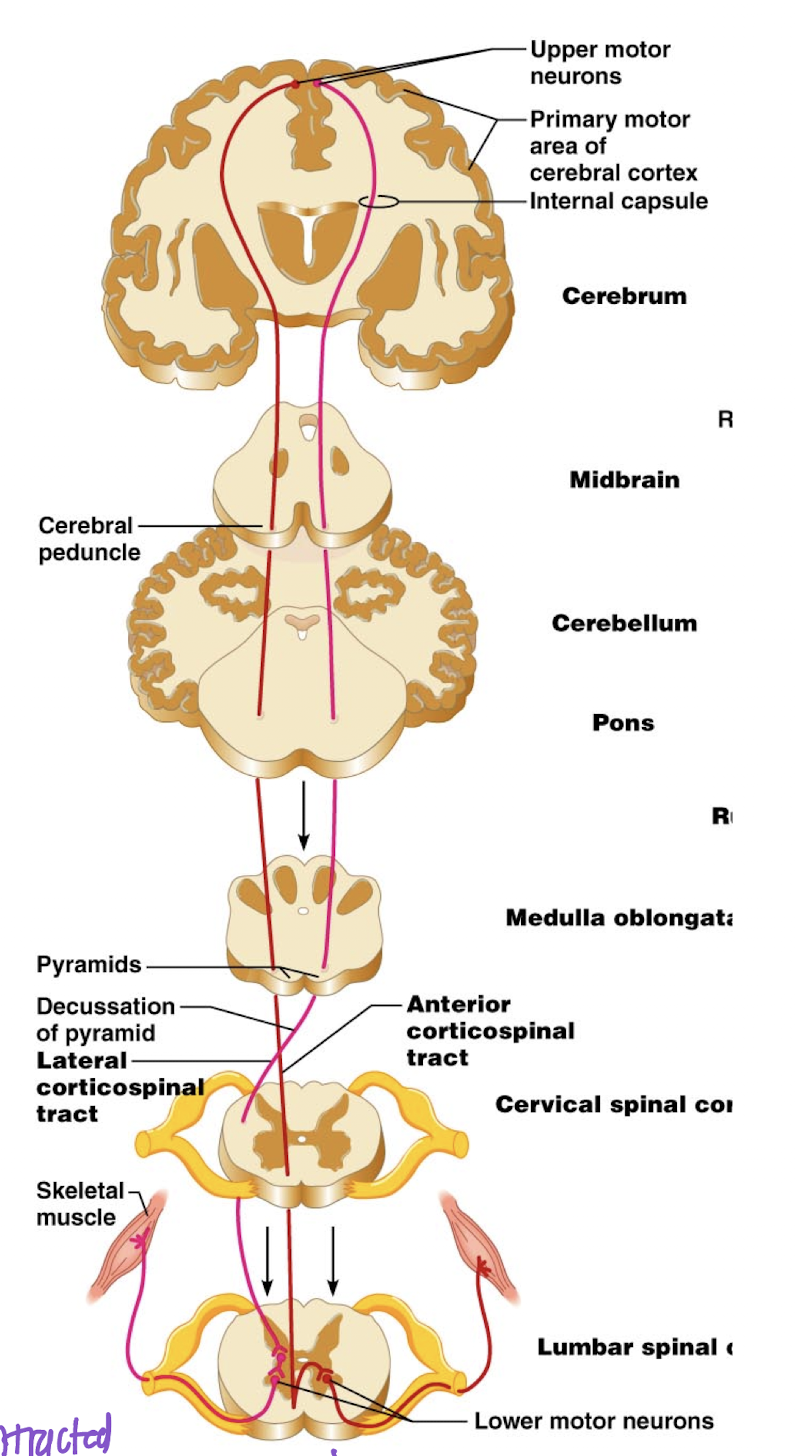
Rubrospinal (aka extrapyrimidal tract)
Controls unconscious, voluntary muscles controlling posture and balance
Always multi-synaptic
Arise in brain stem nuclei (e.g., red nucleus)
Decussate in brain stem (medulla)
Moderated by pyramidal neurons