(Week 4) How Does Life Evolve? - Evolutionary Processes BSC 101 ISU
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Evolution
Descent with modification from a common ancestor
Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
Allele
Different variations of a gene that leads to a different phenotype for that given trait
Mutation
A random error in gene replication. Can be beneficial, detrimental or have no effect
Antibiotics
Drugs that block the growth and reproduction of bacteria. Most commonly through interrupting protein synthesis
Genetic Variation
Differences in DNA sequences among individuals within a species. Can arise through mutations, genetic recombination and other processes
(Horizontal) Gene Transfer
The movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the transmission of DNA from parent to offspring
Natural Selection
The idea that
a) Individuals within a population vary
b) Some traits are heritable
c) More offspring are produced than can survive
d) Organisms best adapted to the environment have the best chance to survive and reproduce
Sexual Selection
A form of natural selection. Traits are 'selected' for because they increase an individual's chance of reproduction
Genetic Drift
A mechanism for evolution. A change in the allele frequency of a population as a result of chance events rather than natural selection. (Non-adaptive evolution)
Gene Flow
Transfer of genetic materials between
populations. Increases genetic diversity and can alter allele frequencies in the receiving population
Mutagen
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and makes mutations more likely to occur
Directional Selection
Form of natural selection in which the entire curve moves; occurs when individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve
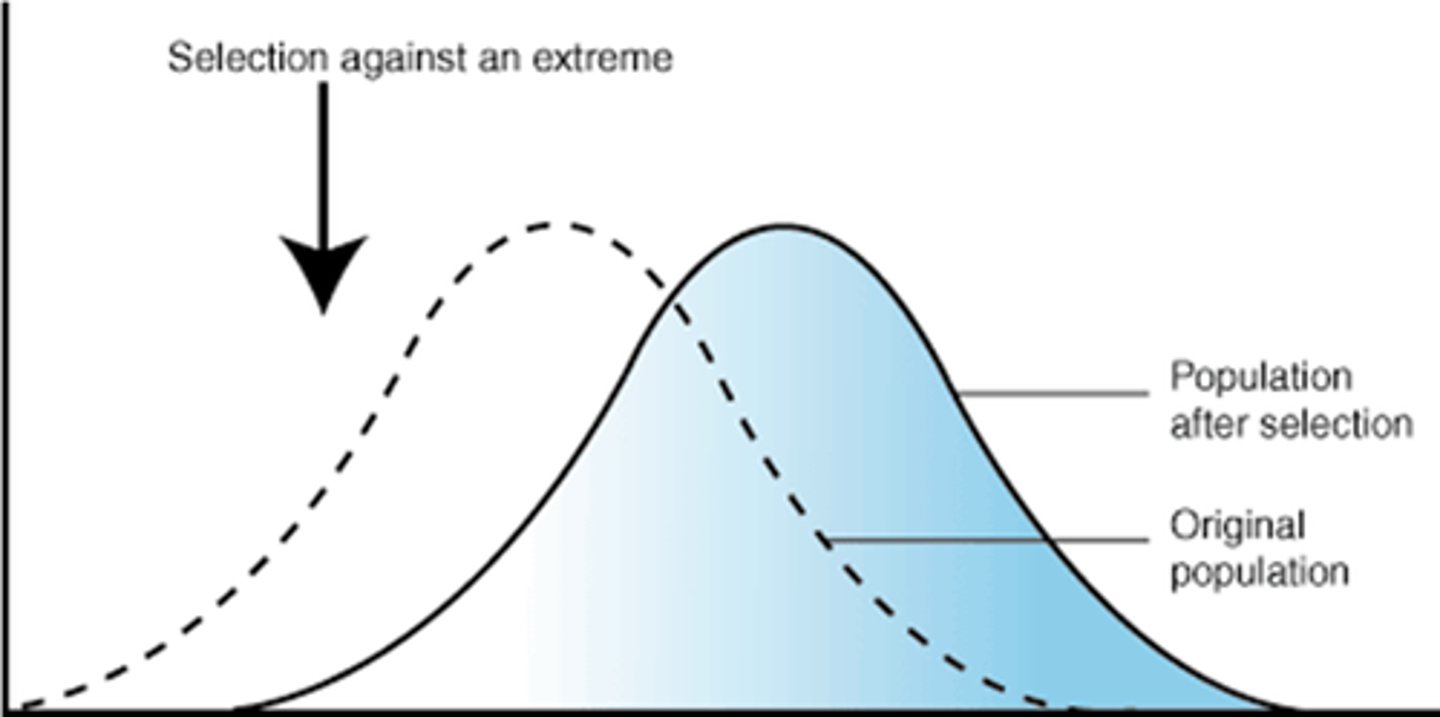
Stabilizing Selection
Form of natural selection in which the curve bulges in the middle; occurs when individuals in the middle of the distribution have higher fitness than individuals at either end of the curve
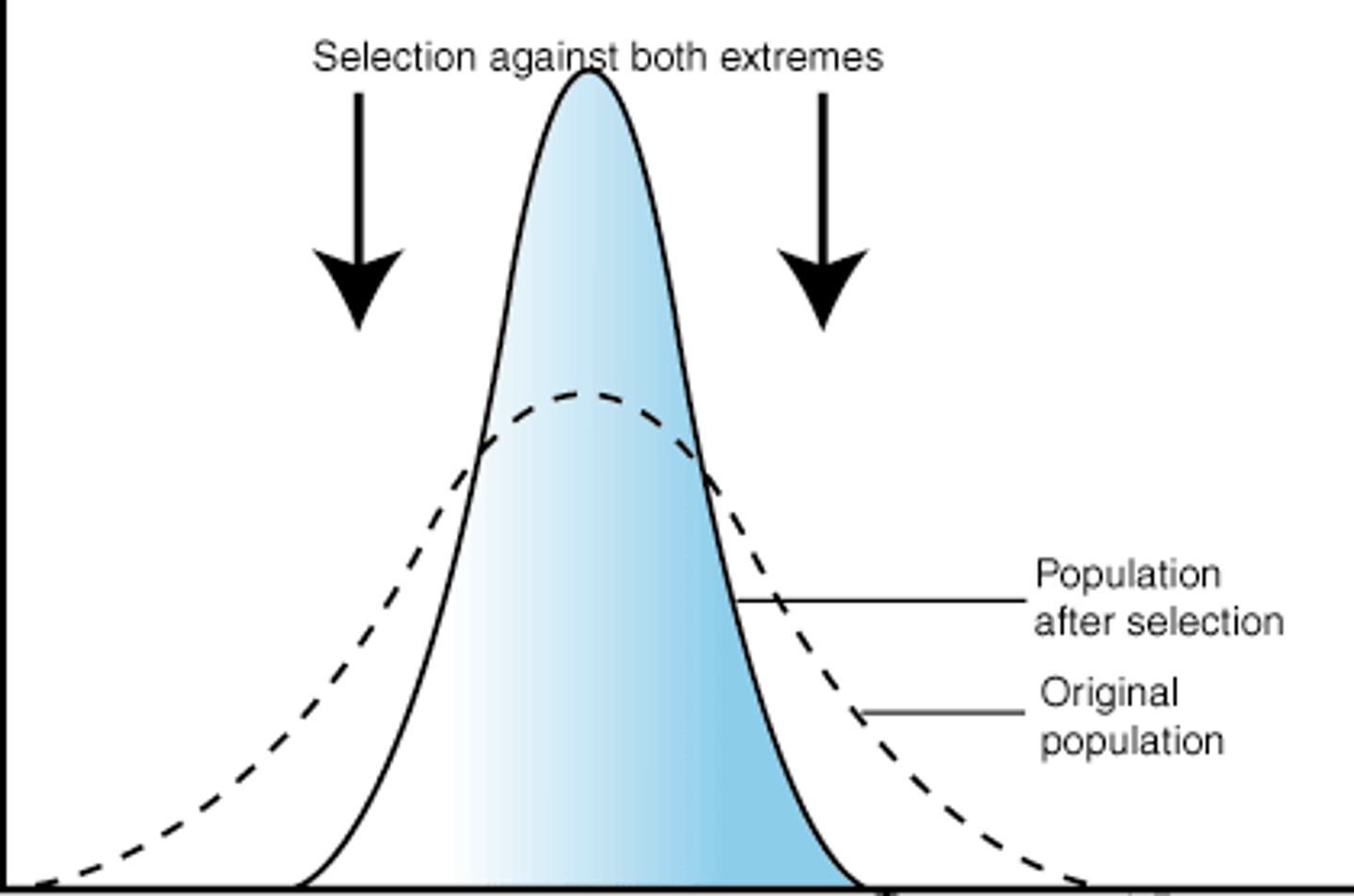
Diversifying Selection
Form of natural selection in which the curve bulges at both ends; occurs when individuals at both ends of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle of the curve
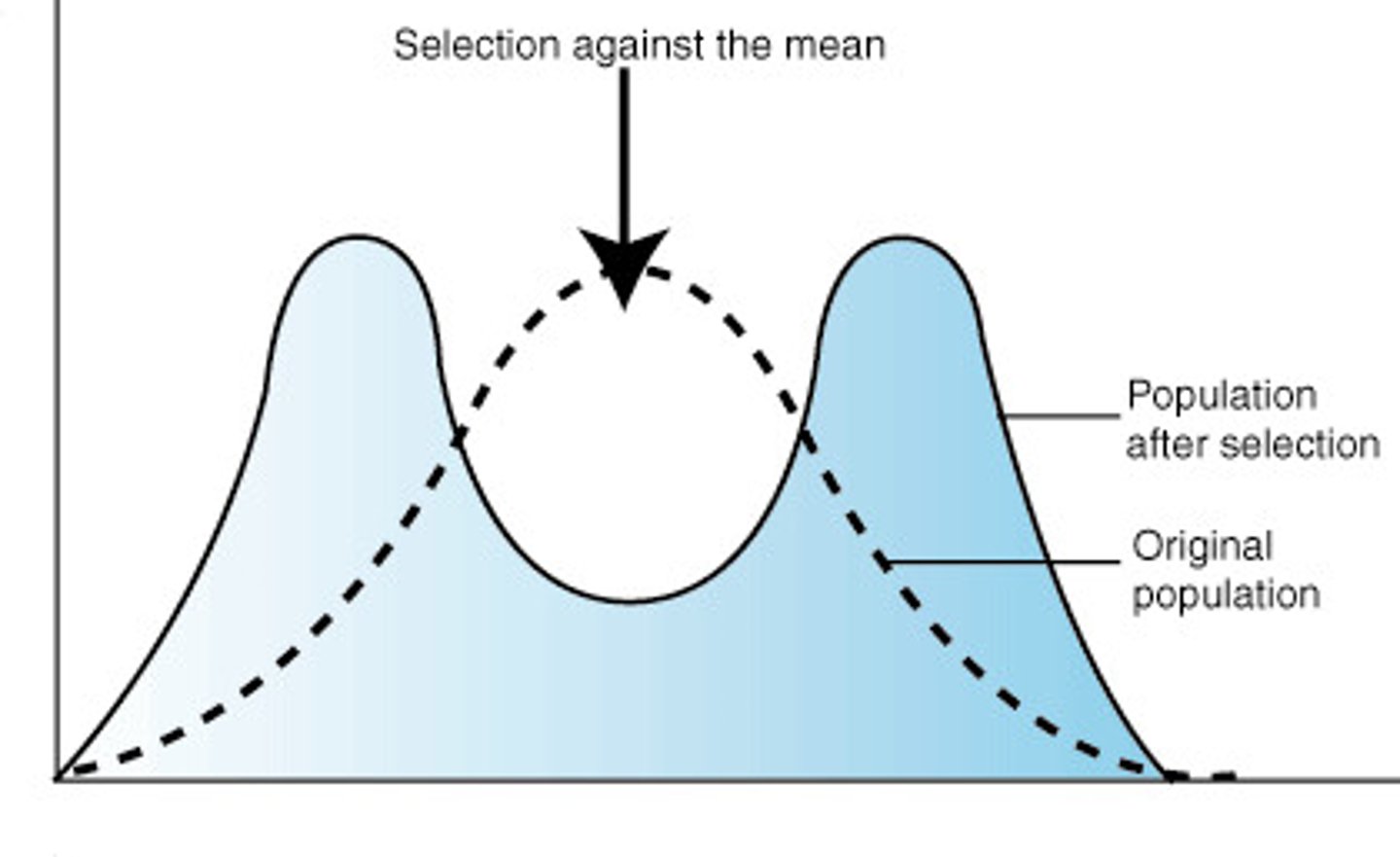
Speciation
The formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution. Occurs when a portion of a parent species becomes unable to reproduce with the rest of the species
Allopatric Speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another. Gene flow between the populations stops and genetic differences accumulate
Sympatric Speciation
The formation of new species in populations that live in the same geographic area. Often occurs through niche differentiation, reproductive isolation or chance mutations in offspring