Chap 8B - Chemical equilibria
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Describe relationship of K and gibbs free
A negative value for ∆G represents a driving force in the forward direction, and POE lies to the right
A positive value represents a driving force in the reverse direction, and POE lies to the left
Define Le Chatelier’s Principle
(Def.): Le Chatelier’s Principle states that when a system at equilibrium is disturbed, the system will counteract by shifting its position of equilibrium in a direction that will reduce that disturbance in order to re-establish the equilibrium
Describe effect of conc on reaction mechanisms
If a substance is added to a system at equilibrium, the system will adjust itself to remove the substance added
If a substance is removed from a system at equilibrium, the system will adjust itself to replace the substance removed
Describe effect of conc (Prediction using Le Chateller’s Principle)
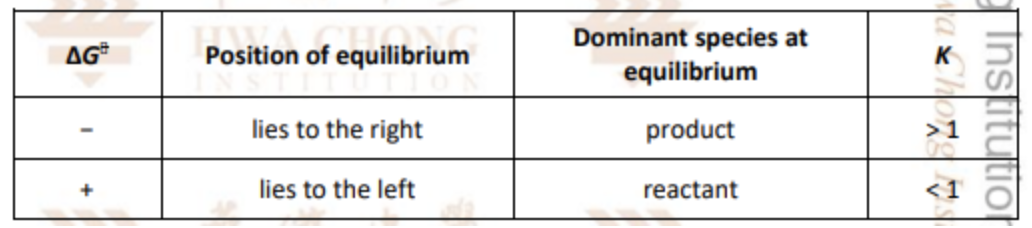
The system will counteract the increase in the amount of H2 by favouring the forward reaction -> POE shift right.
In the new equilibrium mixture, [NH3] and [H2] would be higher than at the previous one, while [N2] would be lower
Describe effect of conc (Effect on rates of reactions)
When more H2 is added, system will adjust to reduce [H2]
The rate of forward reaction will increase, leading to formation of more NH3
The forward rate will then start to decrease while the backward rate starts to increase with
time until both are equal again
At this stage, the system re-established its equilibrium at t2
Describe conc time and rate time graph for N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
Explain why there is no change to the value of Kc when [H2] increase in N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
When [H2] increase, Qc will drop causing Qc < Kc (system no longer at equilibrium) -> POE shifts right to lower [H2]
[N2] will start to decrease while [NH3] will start to increase -> Qc will start to increase until it is equal to Kc
After spiking, the forward rate will then drop as [H2] and [N2] start to fall and the backward rate will increase as [NH3] starts to increase, at new equilibrium, Qc = Kc
Explain effect on POE when more CaCO3 or CaO added in CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Adding more CaCO3 or CaO will not affect the position of equilibrium because the position of equilibrium is unaffected by pure solids or liquids since their concentrations are considered constant
Describe effect of pressure
Only affect reactions with gases involved
Pressure of gas directly proportional to concentration
The effect of changing partial pressure of A on position of equilibrium is the same as changing [A]
Explain how partial pressure can be changed
Adding or removing any of the gaseous components at constant temperature
Removal of some NH3 will lower the partial pressure of NH3.
By Le Chatelier’s Principle, the system will counteract the decrease in partial pressure of NH3 by favouring the forward reaction in order to increase the partial pressure of NH3.
POE will shift right
Changing the volume of the vessel at constant temperature
Compression increases partial pressure of all gasses
Effect on POE depends on stoichiometry of reaction
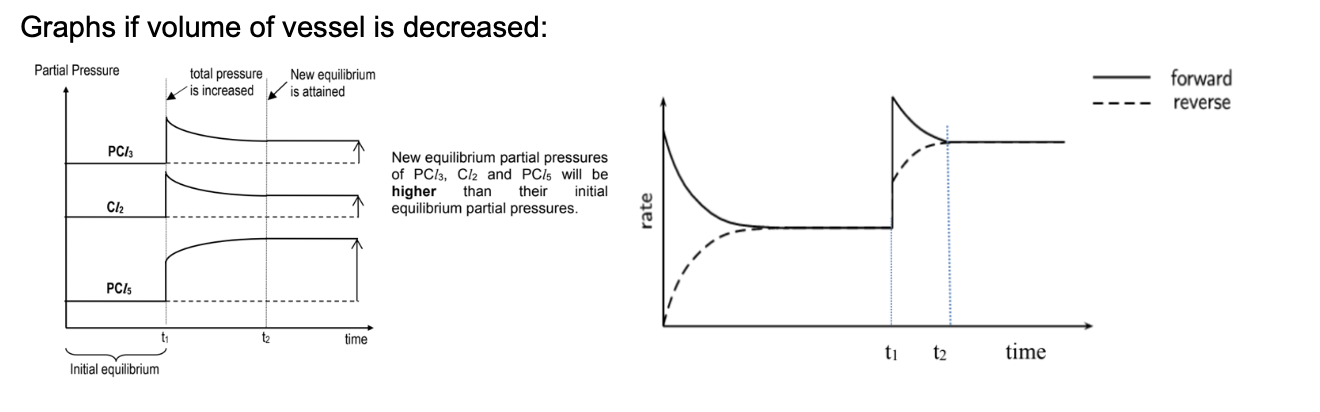
Describe effect when volume of vessel is increased for PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ PCl5(g)
increase and so both forward and backward rates will spike
The system will counteract by favouring forward reaction to reduce the total amount of gas particles in the system -> POE shifts right
As more PCl5 forms, the backward rate will rise while the forward rate will fall until they are equal again
At this stage (t2), equilibrium is re-established
Draw graph for effect when volume of vessel is decreased for PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ PCl5(g)
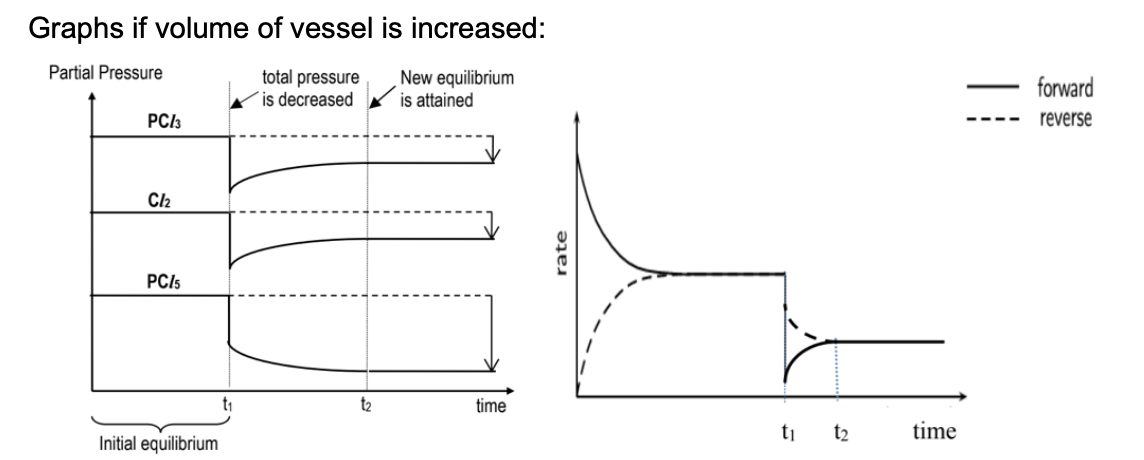
Draw graph for effect when volume of vessel is increased for PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ PCl5(g)
Describe effect on POE if pressure of gases change H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
Since the number of gaseous particles on both sides of the system is equal, changes in partial pressure of gases favour neither the forward nor the backward reaction
Position of equilibrium is unaffected, and the system remains at equilibrium
No change in the composition of the equilibrium mixture