Corneal Deposits and Pigmentations
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What are the symptoms of band keratopathy?
asymptomatic
may cause decreased VA, (+) FBS
white spot on cornea that look like "Swiss cheese"
subepithelial or anterior stromal deposit
calcium phosphate salt crystals
Band keratopathy
How do we treat band keratopathy?
chelation therapy with EDTA
PTK
DALK or PKP
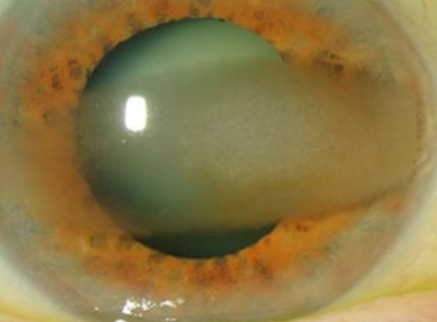
What condition is this?
Band keratopathy
What condition is this?
Band keratopathy
What are the etiologies of band keratopathy?
Ocular: uveitis (JRA — Still's Triad), phthisis bulbi, silicone oil, chronic corneal edema or keratitis
Age-related
Metabolic: elevated serum calcium, phosphorus, hyperuricemia, chronic renal failure
Hereditary: familial cases, ichthyosis
What drugs can cause vortex keratopathy?
amiodarone (HTN med)
chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine (anti-malarial med)
indomethacin (pain reliever / arthritis med)
Rhopressa (netarsudil 0.02% once/day glaucoma medication)
present in —21% of patients at one month visit of 4 clinical trials
What drugs can cause corneal precipitates?
ciprofloxacin (topical fluoroquinolone)
Usually epithelial in nature
Causes: drug-related, Fabry disease
Vortex keratopathy
X-linked lysosomal storage disorder
Alpha-galactosidase-A deficiency
Accumulation of glycosphingolipids
Poor prognosis
Fabry disease
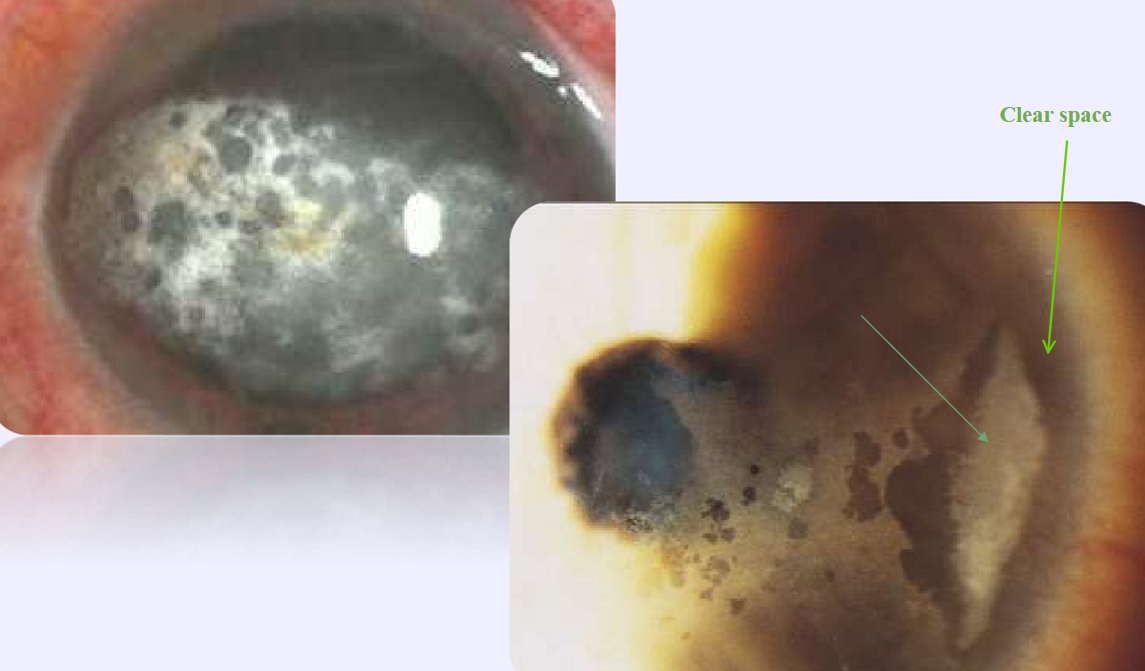
What condition is this?
Vortex keratopathy
What condition is this?
Vortex keratopathy
white corneal deposit
associated with topical ciprofloxacin therapy
3rd generation fluoroquinolone
Tx: bacterial conjunctivitis, microbial keratitis
precipitates occur in area of epithelial defect
higher risk in older patients
spontaneous resolution after d/c therapy
Corneal precipitates
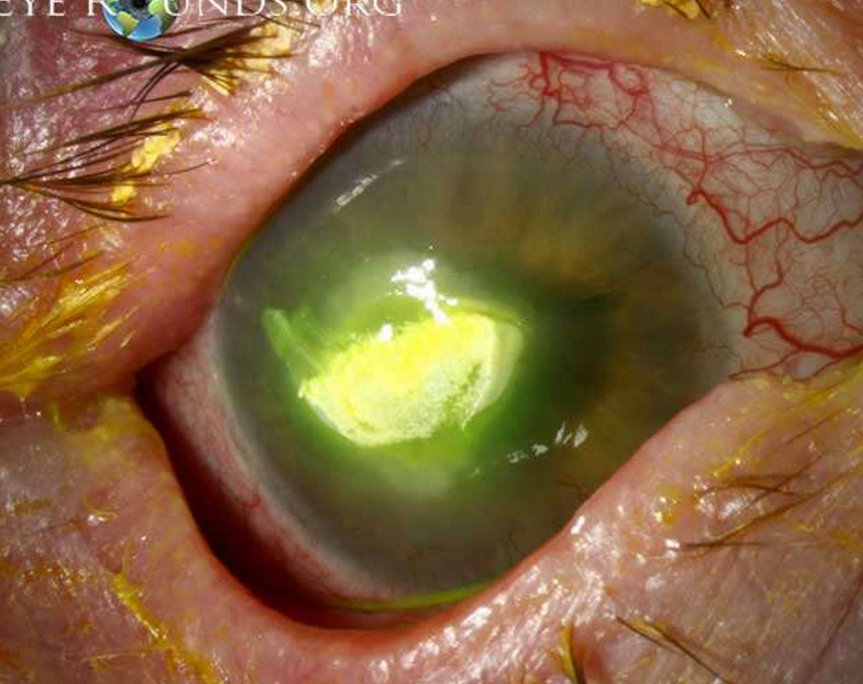
What condition is this?
Corneal precipitates
Systemic diseases with associated corneal deposits
Cystinosis
Mucopolysaccharidosis
Wilson disease
*Kayser-Fleischer ring
Norum disease
Immunoprotein deposits
Fabry disease
*vortex keratopathy
Tyrosinemia Type Il
rare (3.5/1 M births)
defect in amino acid metabolism
accumulation of cysteine crystals in lysosomes
affects cornea, conjunctiva, iris, lens, retina
evert lids; can see in TM with gonioscopy
categorized based on age: infantile (often fatal), intermediate (juvenile), or non-nephropathic (adult) forms
Cystinosis
What is the inheritance pattern of cystinosis?
Autosomal Recessive

What condition is this?
Cystinosis
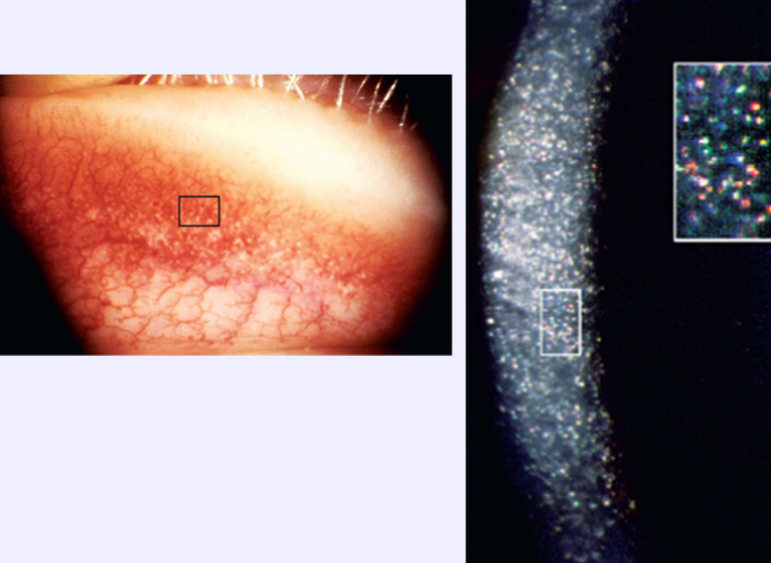
What condition is this?
Cystinosis
What are the symptoms of cystinosis?
Photophobia, eye pain, FBS, corneal abrasion
How do we treat cystinosis?
Topical cysteamine solution (oral is ineffective)
Cystaran 0.44%
Cystadrops 0.37%
inherited deficiencies
unable to hydrolyze mucopolysaccharides
GAGs accumulate in tissues and organs
corneal clouding/opacification - most common reason for ophthalmic consultation
diffuse punctate stromal opacities
corneal edema
Mucopolysaccharidoses
What is mucopolysaccharidoses associated with?
Pigmentary retinopathy, glaucoma, chronic papilledema, optic atrophy
What is the inheritance pattern of Mucopolysaccharidoses?
Autosomal recessive
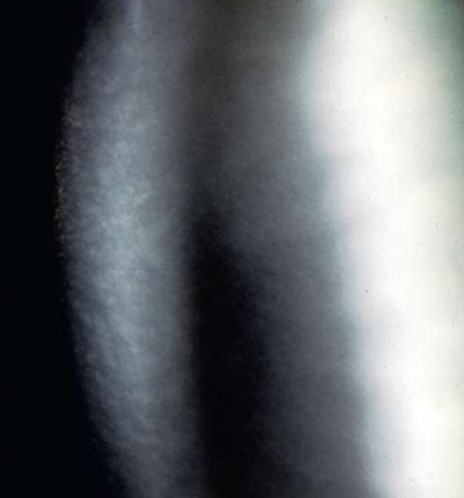
What condition is this?
Mucopolysaccharidoses
Milder adult variant of mucopolysaccharidoses similar to arcus in appearance
MPS I (Hurler syndrome)
How do we treat Mucopolysaccharidoses?
Enzyme replacement therapy, bone marrow transplantation, supportive therapies
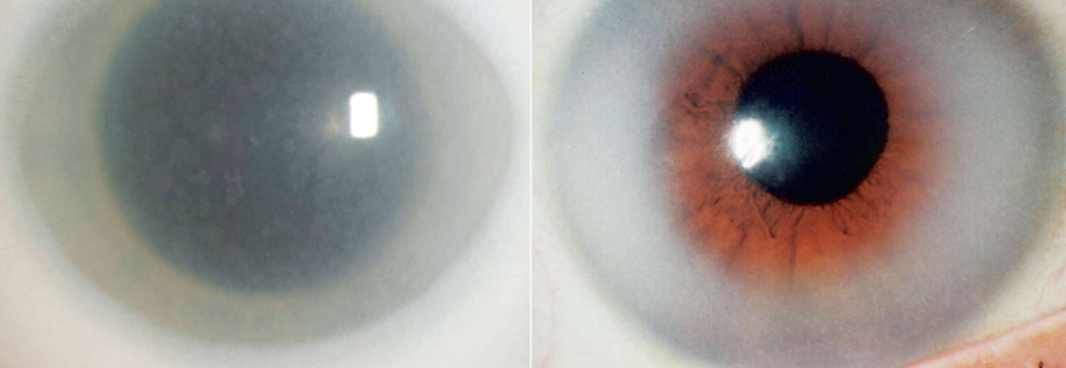
What condition is this?
Mucopolysaccharidoses
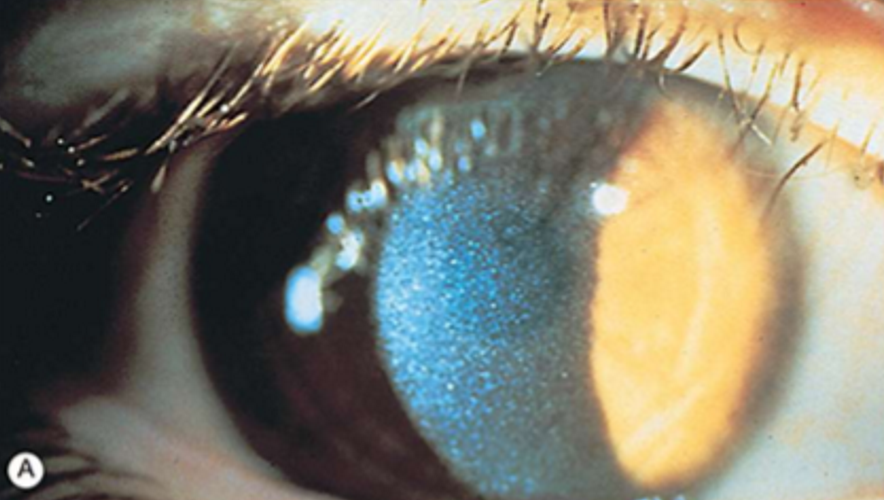
What is the inheritance pattern of Wilson Disease?
Autosomal recessive
Decreased serum ceruloplasmin levels
Widespread copper deposition
Muscle rigidity, tremor, dementia
“Sunflower” cataract
Wilson Disease
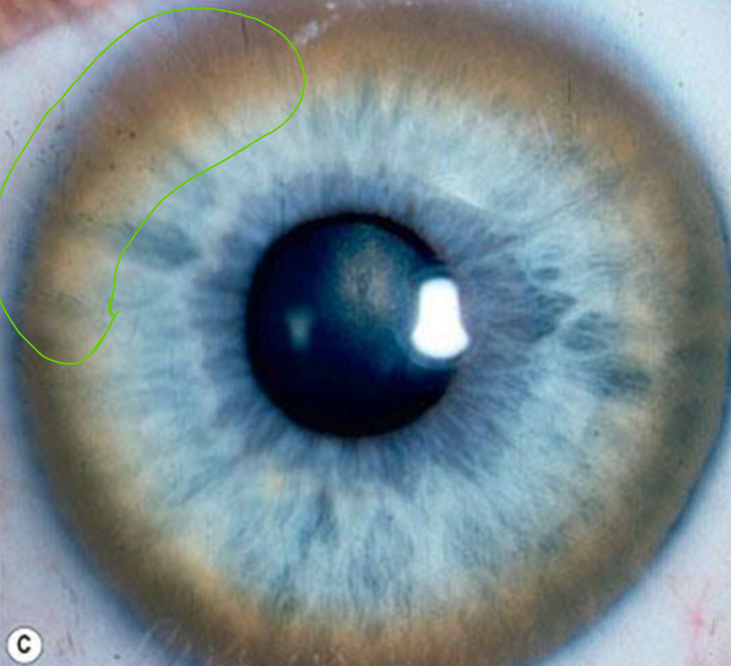
What condition is this?
Kayser-Fleischer ring
Copper deposition in Descemet's membrane
golden-brown, ruby-red, or green ring
can visualize with gonioscopy
starts superiorly, then spreads to meet inferior deposits
not manifested by all patients
Kayser-Fleischer ring
How do you treat a Keyser-Fleischer ring?
Refer to internist!
order testing
serum copper and ceruloplasmin levels
urine copper level
start chelating agents
refer to neurologist
What is the inheritance pattern of Norum Disease/Familial LCAT Deficiency?
Autosomal recessive
complete LCAT deficiency
cholesterol accumulates in plasma and tissue
associated corneal opacification
lipid deposits (a "lipid keratopathy")
Norum Disease/Familial LCAT Deficiency
What are the three things that categorize Norum Disease/Familial LCAT Deficiency?
corneal opacities
hemolytic anemia
renal failure
How do we treat Norum Disease/Familial LCAT Deficiency?
PKP
What is the inheritance pattern of Fish-Eye Disease?
Autosomal recessive
partial LCAT deficiency
corneal opacification
lipid deposits (a "lipid keratopathy")
concentrated peripherally - arcus-like configuration
reduced VA (20/40 to HM)
Fish-Eye Disease
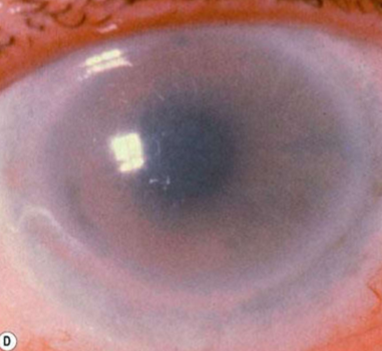
What condition is this?
Fish-Eye Disease
Bilateral bands of punctate, flake-like, crystalline deposits in the cornea
Immunoprotein deposits
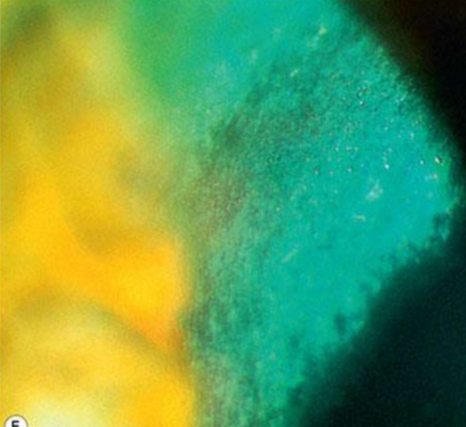
What condition is this?
Immunoprotein deposits
What may be the presenting sign for a serious immunoglobulin disorder?
Immunoprotein deposits
Excess synthesis of immunoglobulins by plasma cells
multiple myeloma (polychromatic)
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (amorphous)
monoclonal gammopathies (iridescent)
rheumatoid arthritis
Immunoprotein deposits
How do we treat immunoprotein deposits?
Systemic therapy; DALK if vision affected
Lysosomal storage disorder
a-galactosidase-A deficiency
accumulation of glycosphingolipids
Vortex keratopathy
wedge-shaped cataract
conjunctival + retinal vascular changes
CN Ill palsy
nystagmus
Fabry Disease
What is the inheritance pattern of Fabry disease?
X-linked
How do you treat Fabry Disease?
Enzyme replacement therapy
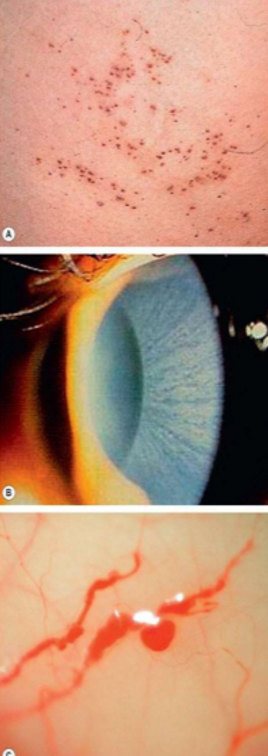
What condition is this?
Fabry Disease
What is the inheritance pattern of Tyrosinemia Type 2?
Autosomal recessive
deficiency in amino acid metabolism
tyrosine aminotransferase
high plasma tyrosine levels
recalcitrant bilateral pseudo-dendritic keratitis
inferotemporal
normal corneal sensitivity
no end bulbs, limited NaFl staining
Tyrosinemia Type 2
What are the symptoms of Tyrosinemia Type 2?
Photophobia, tearing, eye pain, conjunctival injection
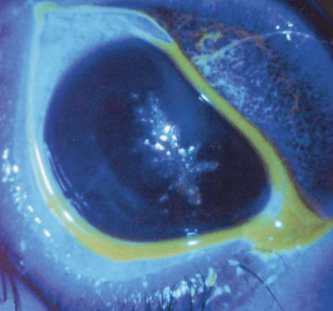
What condition is this?
Tyrosinemia Type 2
What systemic conditions are associated with Tyrosinemia Type 2?
Painful palmar and plantar hyperkeratotic lesions
Cognitive impairment
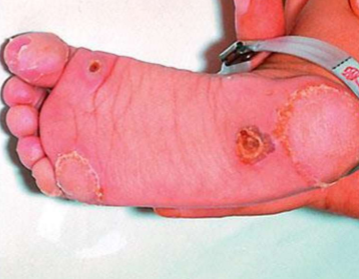
How do we treat Tyrosinemia Type 2?
Dietary restriction
small corneal opacity in white ring-like shape
indicates the presence of a previous FB
deposit contains iron and calcium
superficial corneal stroma
Coats white ring
How do we treat coats white ring?
No treatment indicated
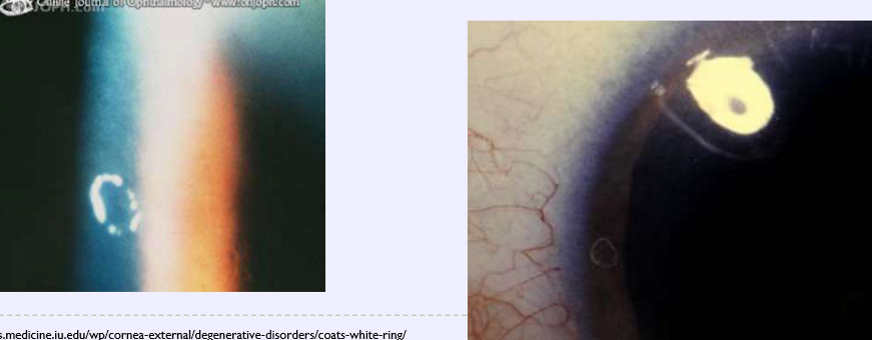
What condition is this?
Coats white ring
What is the histology of epithelial iron deposits?
Iron is deposited intracellularly as a ferritin-like material
Where is the source of iron in epithelial iron deposits?
The tear film
What is the etiology of corneal iron lines?
Altered tear flow secondary to distorted corneal shape
How do we treat corneal iron lines?
No treatment necessary
epithelial deposition of iron due to irregular tear pooling at the base of cone
found in 86% of KCN patients
may be earliest sign of KCN
enhanced visualization with cobalt blue filter
Fleisher ring
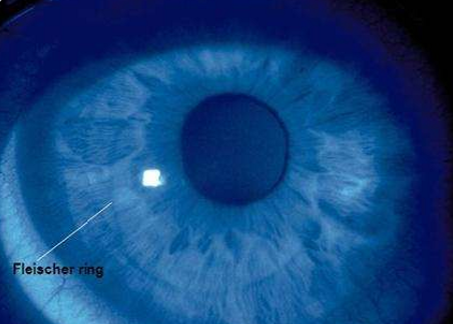
What condition is this?
Fleisher ring
Corneal iron line in the inferior-central cornea
at the junction of middle and lower thirds of the cornea
0.5mm wide and 1-2mm long
central part of the line curves downward (due to epithelial migration)
age-related
Hudson-Stahli line
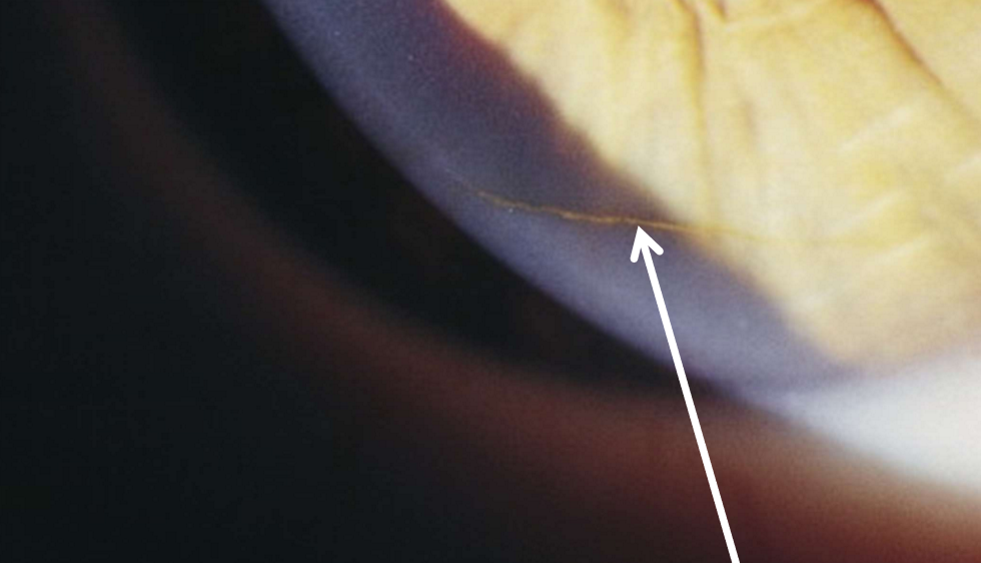
Corneal iron line at the leading edge of a pterygium
Stocker line
Corneal iron line at the edge of a glaucoma filtering bleb
Ferry line
Where can corneal iron lines be found (- the big 3)?
within the margin of corneal grafts
between radial keratotomy (RK) scars
following laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK)
following intrastromal corneal ring placement
during orthokeratology lens wear
adjacent to other corneal elevations, e.g. Salzmann nodule
What condition is this?
Hudson-Stahli
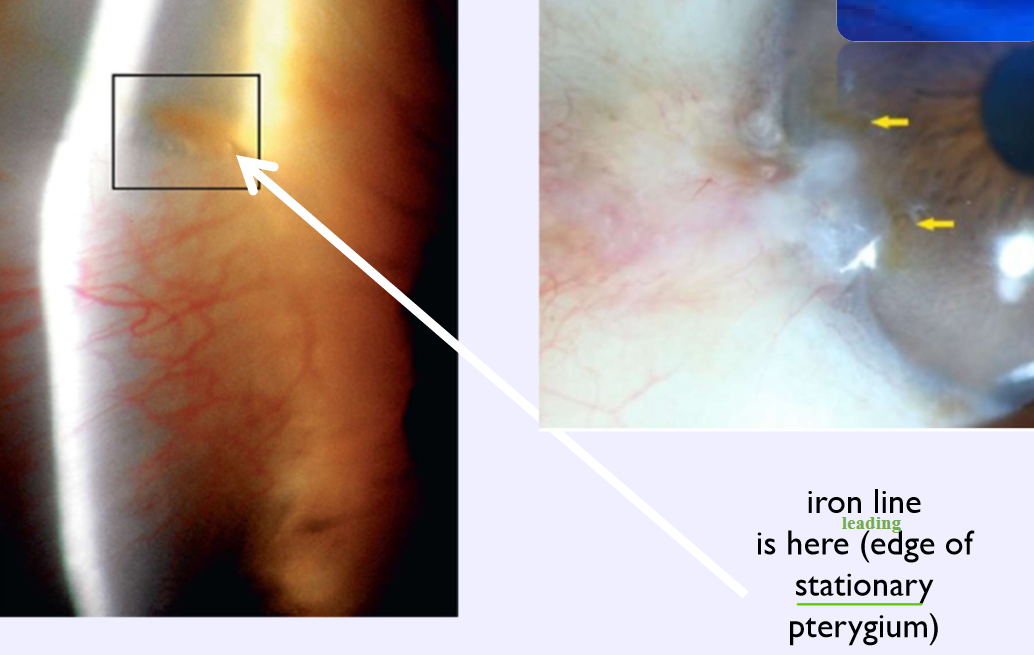
What condition is this?
Stocker line
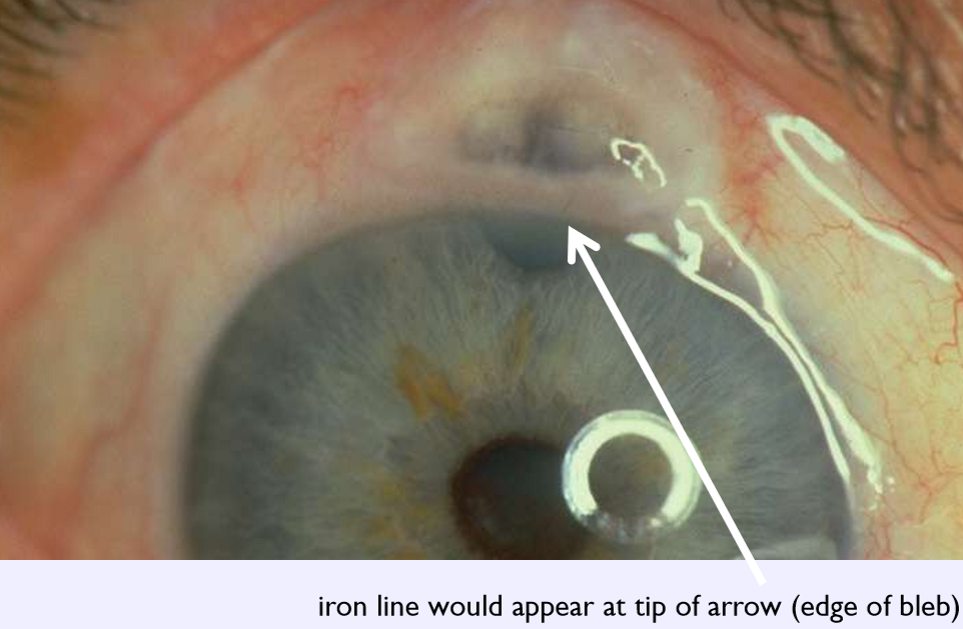
What condition is this?
Ferry line
increased melanin in the basal epithelium (conjunctival or limbal) without elevated mass
can extend onto cornea with streaks/whorls
more common in African American patients (95%)
note in EHR in case changes occur (photodocument)
bilateral
benign
Benign melanosis/melanosis oculi
How do we treat benign melanosis/melanosis oculi?
No treatment necessary
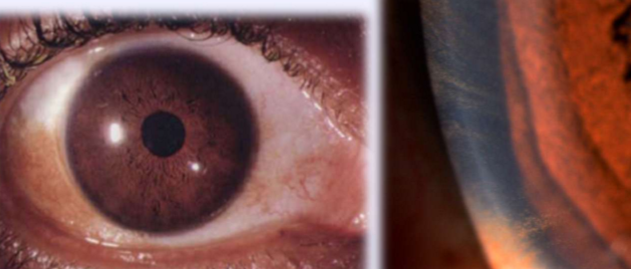
What condition is this?
Benign melanosis/melanosis oculi
traumatic penetration of the globe with iron-containing foreign body
corneal stroma can exhibit a rust-colored hue
Ocular siderosis
What additional testing should you do for ocular siderosis?
DFE
CT scan
B-scan
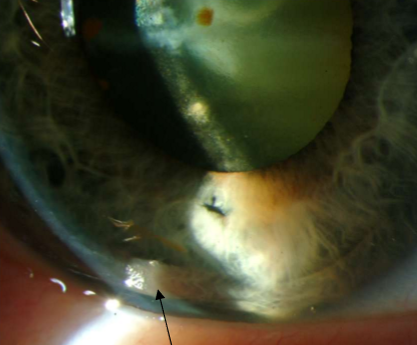
What condition is this?
Ocular siderosis
Deposits on the endothelium due to hyphema (especially 8 ball)
Clears slowly from the periphery
Corneal blood staining
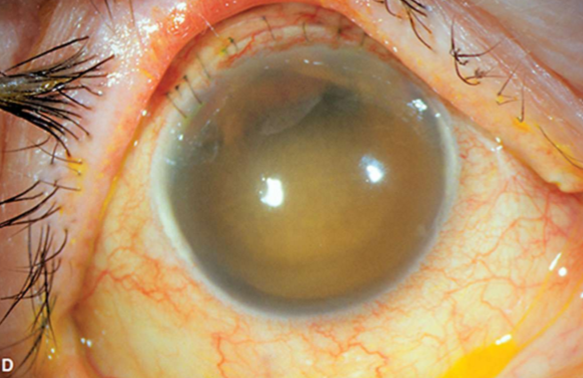
What condition is this?
Corneal blood staining
fine dusting of pigment on endothelium
will be same color as iris
Age related or patholigic
secondary to
inflammation (uveitis)
glaucoma/PDS (Krukenberg spindle)
associated with
guttata
can be an early sign of Fuchs dystrophy
Endothelial pigment dusting
stippled brown vertical line on endothelium
central cornea
shape d/t aqueous humor dynamics
Krukenberg spindle
Where does a Krukenberg spindle
Iris pigmentation liberated after lens zonules rub on iris

What condition is this?
Krukenberg spindle
Found in pigmentary glaucoma/pigment dispersion syndrome
pigment may precede the glaucoma by as much as 20y
Krukenberg spindle
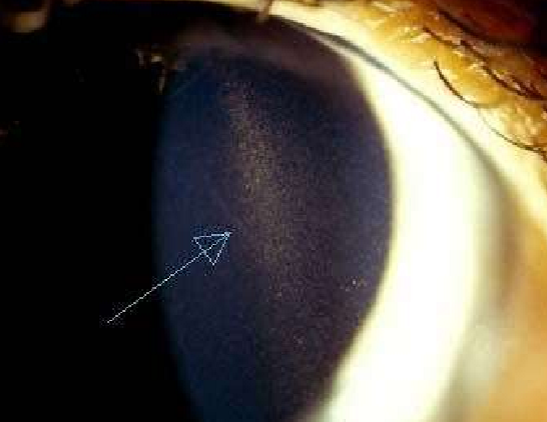
What condition is this?
Krukenberg spindle
form during / after inflammatory events (e.g. uveitis)
lymphocytes (WBCs) on corneal endothelium
may become pigmented with age
Keratic precipitates
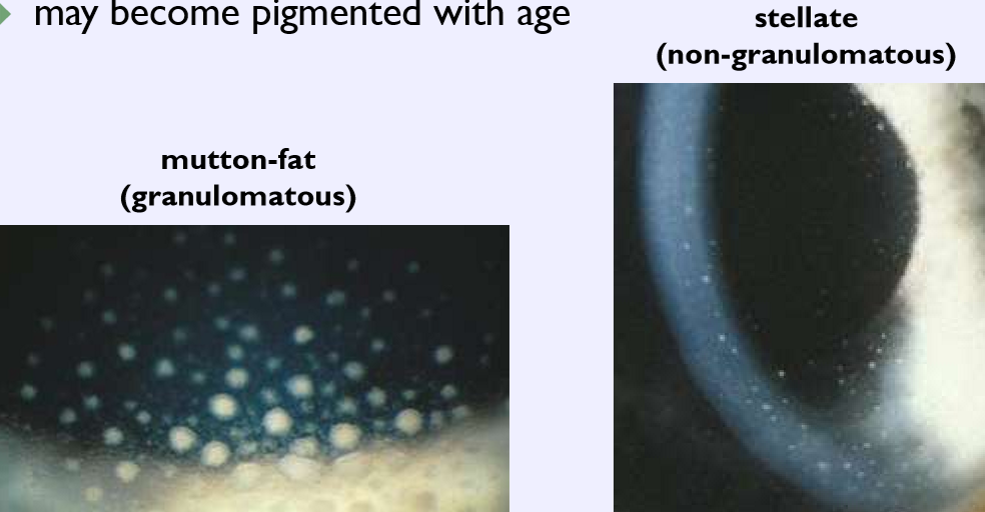
What condition is this?
Keratic precipitates
Epithelial cell proliferation
Common after LASIK
At flat interface
Risk factors
Epithelial defects at/around the time of Sx
EBMD
hypertonic Tx
Repeat Tx
Epithelial ingrowth
Hos do we treat epithelial ingrowths?
If affecting VA, lift flap and irrigate
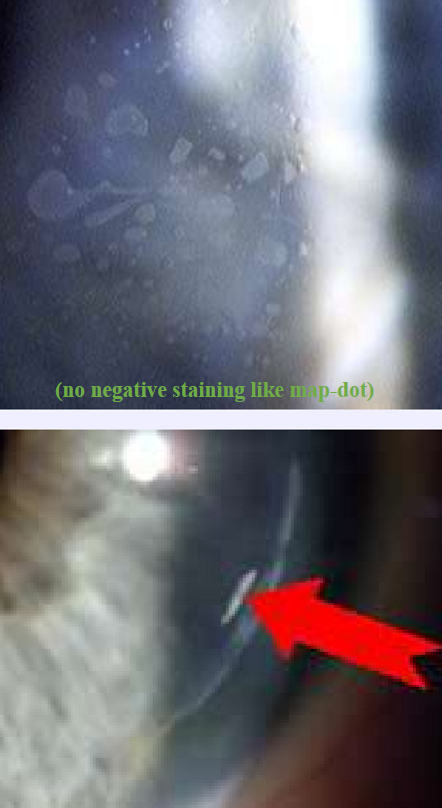

What condition is this?
Epithelial ingrowth
subepithelial open nerve endings
associated with a variety of ocular and systemic diseases
keratoconus
Fuchs dystrophy
Reis-Buckler
multiple endocrine neoplasia
MEN Type lib
neurofibromatosis
NF-I
also easily seen in normal, young patients
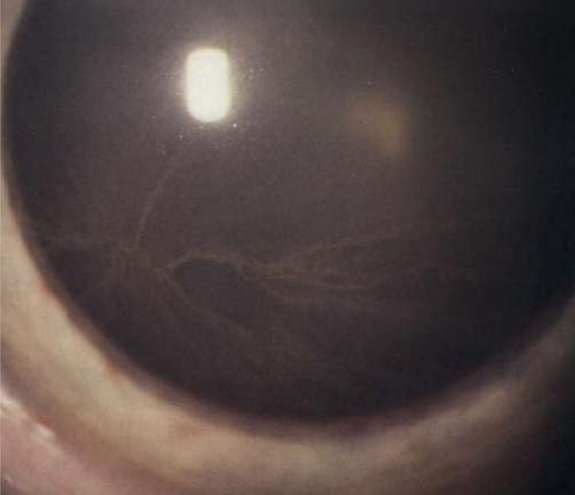
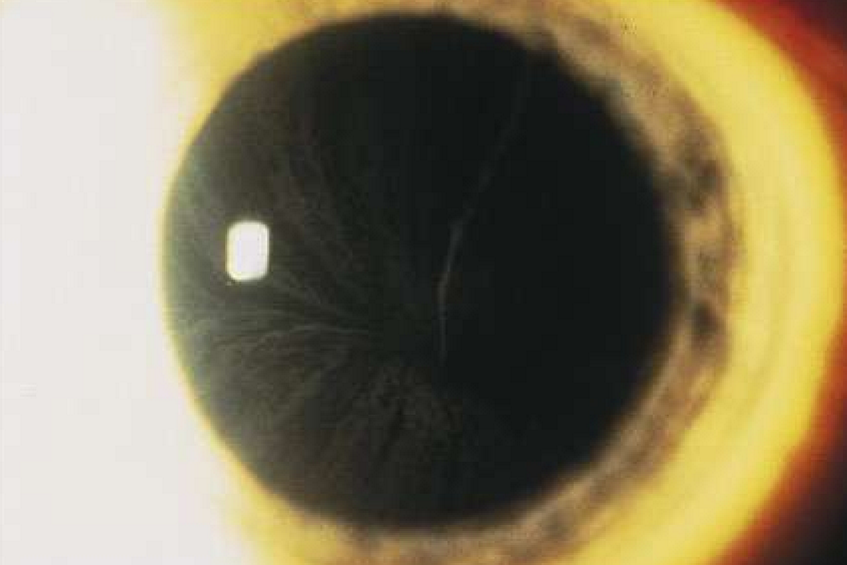
Prominent corneal nerves
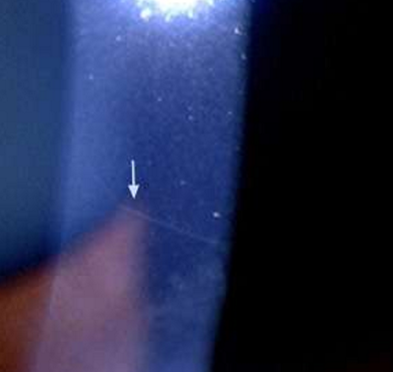
What condition is this?
Prominent corneal nerves