Unit 5.4 - Improving Cash Flow and Profits
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Payables
the amount of time taken by a business to pay its suppliers and other creditors i.e a supplier may give trade credit of 50 days
Receivables
the amount of time taken by debtors (businesses customers) to pay for the products that has been supplied i.e a business may offer trade credit to a customer of 50 days
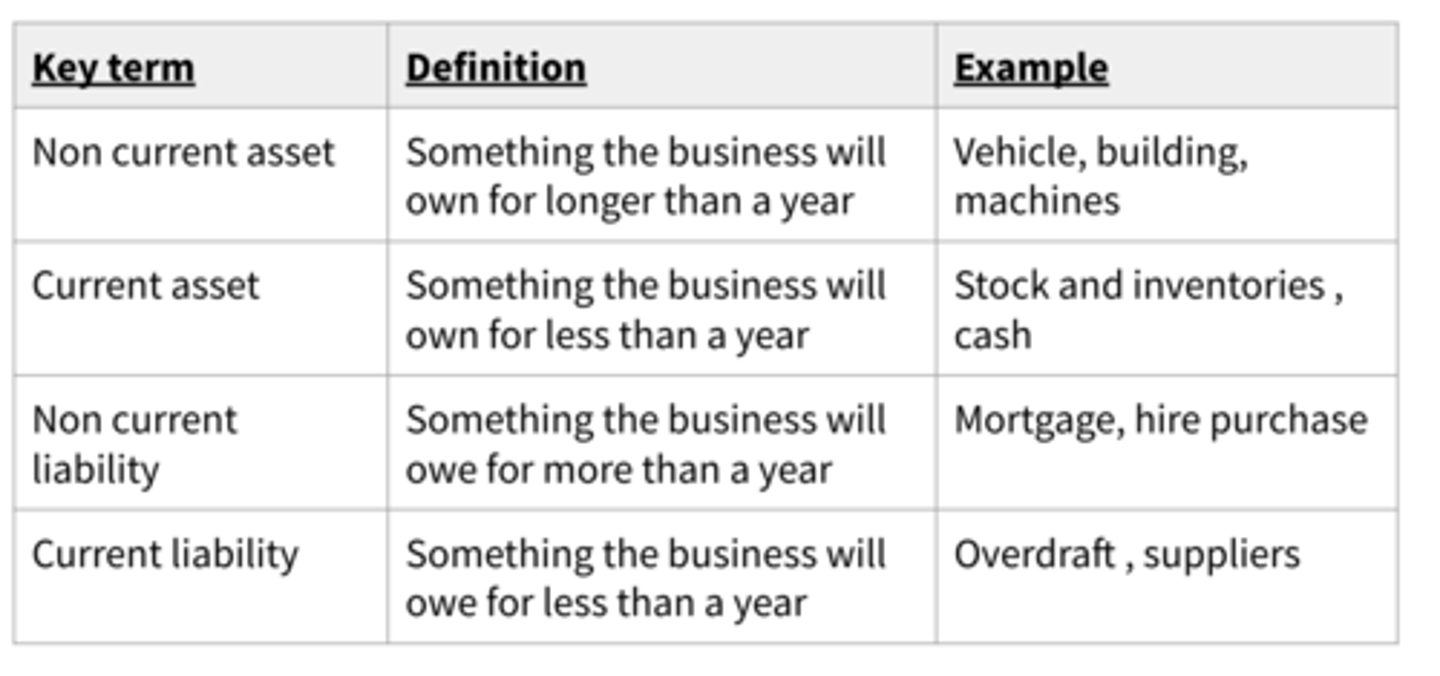
Current assets
Assets that companies expect to convert to cash or use within one year.
Non-current assets
Items owned by the business for more than one year
Current liabilities
Debts that a business will have to pay back within a year
Non-current liabilities
Debts a business pay back for more than a year
Balance sheet
Financial statement recording the assets and liabilities of a business on a particular day at the end of an accounting period (a snapshot). May also be called a statement of financial position
Main features on a balance sheet (in order typical order)
Non-current assets
Current assets
Current liabilities
working capital
non-current liabilities
net assets
total equity
can also calculate capital employed by adding total equity and non-current liabilities
Working capital
current assets - current liabilities (sometimes called net current assets)
net assets
total assets - total liabilities
capital employed
Total equity + non current liabilities
Different types of assets and liabilities (table)
Causes of cash flow issues
Overtrading - business expands quickly without organising funds to finance the expansion
Allowing too much trade credit
Poor credit control - getting customers to pay on time
Inaccurate cash flow forecasting
Trade credit
Periods of time given by suppliers before being paid for the good or service provided
Methods to improve cash flow
Bank overdraft
Debt factoring
Sale and lease back
Leasing non current assets
Improved working capital
Bank overdraft to improve cash flow
- Allows a business to overdraw its current account
- A negative bank balance is held
- A cash flow forecast is needed to support the request, to prove the cash flow problem isn't permanent
- Usually a low rate of interest, if anything at all
- Allows a business to spend money even with no cash so can pay suppliers, employee etc
debt factoring to improve cash flow
Coverts the value of receivables into immediate cash
The receipt of cash helps a business to survive
Sale and lease back to improve cash flow
Selling assets, injection of cash
The business then rents it back i.e a building
Gives flexibility to the business
Leasing non-current assets to improve cash flow
Kept longer than a year
Renting instead of buying i.e vehicles
No large outflow of cash
Four ways to improve working capital
Cash management
Debt management
Inventory management
Management of payables
Importance of working capital
Needed to fund the day-to-day finance available for
running a business. If there is not enough cash for the
business then it may not be able to pay its bills on time.
pay for raw materials and running costs.
•
Working capital is also needed to fund the credit
offered to customers (debtors) when making a
sale. Customers may go to a competitor if a business
cannot offer credit.
•
If a business has too little working capital it may
struggle to finance increased production without
straining its liquidity position.
Improving working capital - cash management
- Agree an overdraft with the bank
- Set aside a contingency fund to allow the company to meet unexpected payments or cope with a loss of income
- Retain profits as reserves
Improving working capital - debt management
Largely managing receivables/trade credit a business must decide whether to offer credit to customers - it may consider
- Obtaining a credit rating - testify to ability to pay
- Controlling product quality - more likely to pay if they are happy
- Scrutinising the offer of credit - costs do not outweigh the profit gained
- Managing credit control - monitor and chase customers
Why businesses offer credit to customers
Giving customers credit encourages them to buy products (helps profits)
However this adds to short term cash flow issues
This is because wages and materials have to be paid before cash is received
Must evaluate the benefits (more sales and profit) against the risks (late or non payment)
Offering credit makes a business more competitive -its depend on the product
Improving working capital - inventory management
Operating JIT systems is more efficient and reduce holding costs, overall having efficient inventory management reduces the level of working capital required within a business
Improving working capital - managing payables
- Get extended credit from suppliers
- Moving payment dates to avoid times of significant outflows
- Balancing payables and receivables to ensure inflows occur before outflows
Benefits of effective cash flow management
- Avoid being unable to find day to day operations, which could lead to employees leaving if they go unpaid
- ensure production is not halted
- Reduce borrowing costs as if managed well borrowing can be minimised
- Good relations with suppliers as they will be paid on time
- Public relation, customers will be confident of the businesses ability to continue supplying goods
Difficulties with improving cash flow
- Seasonal demand and supply
- Overtrading can happen quickly as it will be when the business is in a period of success
- Over investment in long term assets
- Unforeseen changes i.e Machinery breaking down (internal) or new H+S laws (external)
- Losses or low profits will lead to lower cash also Creditors/investors may be reluctant to put money into a business that isn't expected to make profit
Profitability
A measure of financial performance that compares a business's profits to some other factors such as revenue
Profits
Revenue - total costs
Methods of improving profits and profitability
Increase the price - decreasing costs - increasing sales volume
Increasing prices to improve profits and profitability
Works only when a product has price elasticity of demand that is inelastic
Reducing costs to improve profits and profitability
Variable:
- Raw material cost through different suppliers
- Any variable wages by cutting working hours
- Improve production efficiency reducing errors and defects
- Cut products that are low margin (i.e dog products)
- Improve labour productivity reducing unit costs
Fixed:
- Reduce wage bill with redundancies or lowering wages
- Use full capacity therefore spreading fixed costs
- Change location to cheaper site
- Reduce marketing budget i.e less advertising
- Shut down stores or operations in less successful areas
Increasing sales volume to improve profits
Any methods that lead to customer buying more:
- Create a new tv advert
- Promotion i.e tasters
- Accessories to products
- Define a USP
- Reduce price if demand is elastic
- HR to improve training or motivation of staff
- Product development
Internal issues when trying to improve profits and profitability
- Changing the price - difficult to predict, depends on elasticity
- Decreasing costs:
Reducing wages - impact on morale
Cutting raw material costs - loss in quality
Cutting marketing budget - lower sales
- Increasing sales volume - requires good quality products and effective coordination, could increase costs
- Changing production can lead to the need to invest in technology or upsetting labour causing higher costs and worse productivity
External issues when trying to improve profits and profitability
PESTLE-C - could include:
Competition - price war could lead to less revenue for all
Market conditions - with less competition comes regulation issues (competition and markets authority) (CMA)
Consumer incomes - less likely to increase sales
Interest rates - high interest rates could reduce sales when using credit (especially relevant at the moment 2023)
Demographic factors - changes in population can alter demand patterns
Environmental issues - can lead to greater costs