CHM 365 *EXAMS 1-3*
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
1
New cards
A tetrapeptide is treated with trypsin to produce two dipeptides, one of which is composed of Arg When the tetrapeptide is treated with and Gly, and the other one is composed of Ala and Phe. When the tetrapeptide is treated with chymotrypsin, a tripeptide containing Arg, Gly, and Phe is created, and Ala is the other product. When the tetrapeptide is treated with 1. Fluorodinitrobenzene (FDNB) and 2. 6 M HCI at 110 °C for 24 hours Ala, dinitrophenyl-Gly, Arg, and Phe are observed. The sequence of the tetrapeptide is
A. Ala-Phe-GIy-Arg
B. Ala-GIy-Arg-Phe
C. GIy-Arg-Phe-Ala
D. Gly-Phe-Arg-Ala
A. Ala-Phe-GIy-Arg
B. Ala-GIy-Arg-Phe
C. GIy-Arg-Phe-Ala
D. Gly-Phe-Arg-Ala
C. GIy-Arg-Phe-Ala
2
New cards
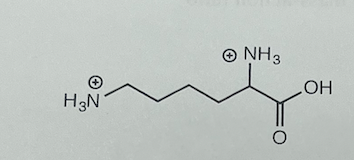
The structure of fully protonated lysine is given below. For lysine, pK1 is 2.16, pK2, is 9.18, and pKR is 10.79 The isoelectric point pl of lysine is
A. 5.67
B. 6.48
C. 9.18
D. 9.99
A. 5.67
B. 6.48
C. 9.18
D. 9.99
(10.79 + 9.18)/2 = 9.99
why?
* uncharged: (pk1 + pk2)/2
* cationic: (pkr + pk2)/2
* neutral acid: (pk1 + pkr)/2
why?
* uncharged: (pk1 + pk2)/2
* cationic: (pkr + pk2)/2
* neutral acid: (pk1 + pkr)/2
3
New cards
3\. What intermolecular forces could the side chain ammonium group of lysine experience with a phosphodiester group in DNA? Provide the best answer
a. H-bonding and hydrophobic forces
b, H-bonding and electrostatic attraction
c. Hydrophobic forces and electrostatic repulsion
d. London dispersion and electrostatic repulsion
a. H-bonding and hydrophobic forces
b, H-bonding and electrostatic attraction
c. Hydrophobic forces and electrostatic repulsion
d. London dispersion and electrostatic repulsion
H-bonding and electrostatic attraction
4
New cards
4\. When one mole of ammonium chloride dissolves completely in water to a final volume of 1 L, the solution absorbs heat. Which statement is false?
a. ΔG° is negative because the process is spontaneous
b. ΔH° is positive because the process is endothermic
c. TΔS° is always positive when a salt dissolves in water
d. TΔS° is positive, and it is larger in magnitude than AH°
a. ΔG° is negative because the process is spontaneous
b. ΔH° is positive because the process is endothermic
c. TΔS° is always positive when a salt dissolves in water
d. TΔS° is positive, and it is larger in magnitude than AH°
TΔS° is always positive when a salt dissolves in water
5
New cards
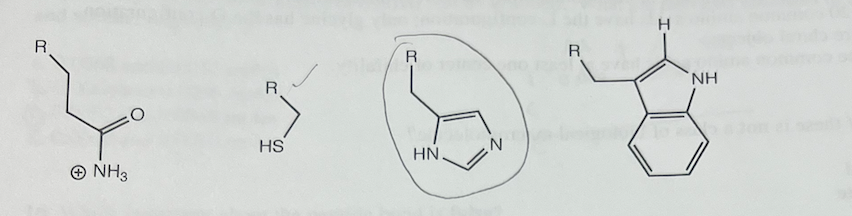
Which amino acid structure is not correct? R is the rest of the amino acid, the carboxylate group, the ammonium group and HCα
A.
6
New cards
6\. Which statement about ATP and biochemical work is false? a. Hydrolysis at the gamma-phosphoryl group proceeds with a large, negative value of ΔG.
B. Hydrolysis at the alpha-phosphoryl group proceeds with a large, negative value of ΔG°:
C. other than water, no nucleophiles may react with ATP in a cell
D. Enzymes couple the cleavage of ATP to uphill processes in order to accomplish biological work
B. Hydrolysis at the alpha-phosphoryl group proceeds with a large, negative value of ΔG°:
C. other than water, no nucleophiles may react with ATP in a cell
D. Enzymes couple the cleavage of ATP to uphill processes in order to accomplish biological work
other than water, no nucleophiles may react with ATP in a cell
7
New cards
The pH of a 0.200 M phosphate buffer is 7.15. The pKa for H2PO4^-1, the phosphate monoanion, is 7.20. What are the concentrations in moles/liter of H2PO4^-1' and HPO4^-2? respectively?
a. 0.106, 0.094
b. 0.094, 0.106
c. 0.100, 0.100
d. 0.112, 0.088
a. 0.106, 0.094
b. 0.094, 0.106
c. 0.100, 0.100
d. 0.112, 0.088
0\.106, 0.094
8
New cards
When individual fatty acid molecules in water combine to form a micelle, the sign of ΔS is
a. negative because a micelle is a highly disordered structure
b. positive because water molecules gain freedom
c.negative because the process is not spontaneous
d. positive because heat is released
a. negative because a micelle is a highly disordered structure
b. positive because water molecules gain freedom
c.negative because the process is not spontaneous
d. positive because heat is released
positive because water molecules gain freedom
9
New cards
Which statement about the chelate effect is false?
a. one molecule with n-points of attachment binds more strongly to another chemical species than n molecules with one point of attachment
b. the chelate effect is primarily an entropic phenomenon
c. the binding of two strands of DNA to make duplex DNA is an example of the chelate effect
d. The chelate effect refers to the release of energy when a high-energy bond in ATP is broken
a. one molecule with n-points of attachment binds more strongly to another chemical species than n molecules with one point of attachment
b. the chelate effect is primarily an entropic phenomenon
c. the binding of two strands of DNA to make duplex DNA is an example of the chelate effect
d. The chelate effect refers to the release of energy when a high-energy bond in ATP is broken
The chelate effect refers to the release of energy when a high-energy bond in ATP is broken
10
New cards
Which statement about the stereochemistry of biological molecules is false?
a. Two molecules that form a pair of enantiomers may have very different biological effects.
b. 19 of the 20 common amino acids have the L-configuration; only glycine has the D-configuration.
C. Proteins are chiral objects
d. Most of the common amino acids have at least one center of chirality.
a. Two molecules that form a pair of enantiomers may have very different biological effects.
b. 19 of the 20 common amino acids have the L-configuration; only glycine has the D-configuration.
C. Proteins are chiral objects
d. Most of the common amino acids have at least one center of chirality.
19 of the 20 common amino acids have the L-configuration; only glycine has the D-configuration.
11
New cards
Which of these is not a class of biological macromolecule?
a. nucleic acid
b. carbohydrate
c lipid
d. ribosome
a. nucleic acid
b. carbohydrate
c lipid
d. ribosome
ribosome
12
New cards
Which statement about the Ramachandran diagram and dihedral angles is false?
a. residues in the same type of 2° structure have similar values of the dihedral angles Φ and φ (lowercase)
b. Forbidden regions of the Ramachandran diagram occur when atoms approach each other too closelv.
c. The allowed and forbidden areas within the Ramachandran diagram refer to the dihedral angles within disulfide bonds
d. residues that are in 2° structure have values of Φ and φ (lowercase) that are within the allowed regions of the Ramachandran diagram
a. residues in the same type of 2° structure have similar values of the dihedral angles Φ and φ (lowercase)
b. Forbidden regions of the Ramachandran diagram occur when atoms approach each other too closelv.
c. The allowed and forbidden areas within the Ramachandran diagram refer to the dihedral angles within disulfide bonds
d. residues that are in 2° structure have values of Φ and φ (lowercase) that are within the allowed regions of the Ramachandran diagram
The allowed and forbidden areas within the Ramachandran diagram refer to the dihedral angles within disulfide bonds
13
New cards
Protein A (MW = 80,000) has a pI value of 6.0. Protein B (MW =15,000) has a pI value of 6.0. Which technique would have the greatest chance for success in separating a mixture of A and B in their native states?
a. cation exchange chromatography at pH 7
b. gel filtration chromatography at pH 7
c. anion exchange chromatography at pH 5
d. none of the above
a. cation exchange chromatography at pH 7
b. gel filtration chromatography at pH 7
c. anion exchange chromatography at pH 5
d. none of the above
gel filtration chromatography at pH 7
14
New cards
After the chromatography in the previous question, which is the best technique to prove whether or not proteins A and b are now pure (whether or not they had been separated completely from each other)?
a. a colorimetric assav with 2-mercaptoethanol
b. boiling point
c. sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS PAGE)
d. unfolding in the presence of guanidinium chloride
a. a colorimetric assav with 2-mercaptoethanol
b. boiling point
c. sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS PAGE)
d. unfolding in the presence of guanidinium chloride
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS PAGE)
15
New cards
In a buffer the starting amounts of acetic acid and acetate are 0.0060 moles and 0.0060 moles respectively. A 0.0020-L aliquot of 0.40 M NaOH is added. What are the final amounts of acetic acid and acetate, respectively?
a. 0.0068 and 0.0052 moles
b. 0.0064 and 0.0056 moles
c. 0.0052 and 0.0068 moles
c. 0.0060 and 0.0060 moles
a. 0.0068 and 0.0052 moles
b. 0.0064 and 0.0056 moles
c. 0.0052 and 0.0068 moles
c. 0.0060 and 0.0060 moles
0.0052 and 0.0068 moles
16
New cards
16\. Which statement about the peptide bond is false?
a. peptide bonds are planar
b. there is only one significant resonance structure for the peptide bond
c. peptide bonds are a subclass of amide bonds
peptide bonds can be both hydrogen bond donors and acceptors
a. peptide bonds are planar
b. there is only one significant resonance structure for the peptide bond
c. peptide bonds are a subclass of amide bonds
peptide bonds can be both hydrogen bond donors and acceptors
there is only one significant resonance structure for the peptide bond
17
New cards
Which statement about protein secondary structure is false?
a. Residues in the same type of 2° structure have a regular pattern of hydrogen bonds.
b. Two strands in a ß-sheet may be parallel or anti-parallel.
c. In a-helices there are intra-helix hydrogen bonds.
d. secondary structure is held together by hydrogen bonds from one R group (side chain) to another.
a. Residues in the same type of 2° structure have a regular pattern of hydrogen bonds.
b. Two strands in a ß-sheet may be parallel or anti-parallel.
c. In a-helices there are intra-helix hydrogen bonds.
d. secondary structure is held together by hydrogen bonds from one R group (side chain) to another.
secondary structure is held together by hydrogen bonds from one R group (side chain) to another.
18
New cards
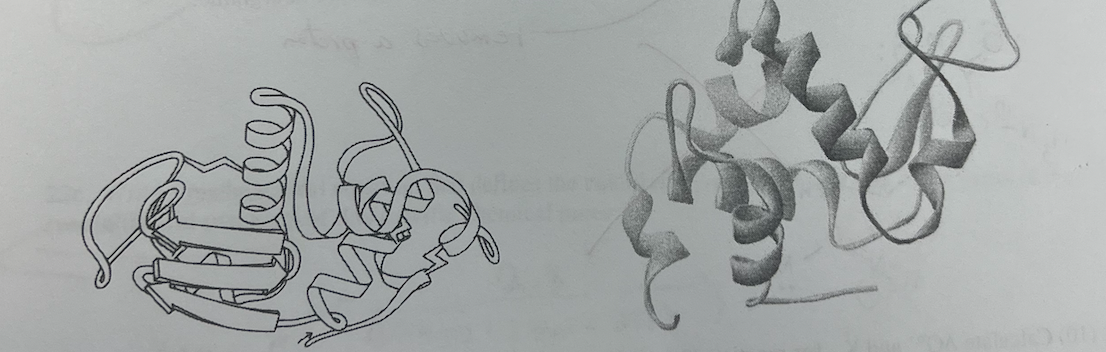
18\. Two drawings with different perspectives of the same protein, lysozyme, are shown. Which statement about lysozyme is false?
a. the helix-turn-helix motif is present
b. the hairpin-beta (beta-turn-beta) motif is present .
c. an antiparallel beta-sheet is present
d. the beta-alpha-beta motif is present
a. the helix-turn-helix motif is present
b. the hairpin-beta (beta-turn-beta) motif is present .
c. an antiparallel beta-sheet is present
d. the beta-alpha-beta motif is present
the beta-alpha-beta motif is present
19
New cards
Which statement about protein structure and diversity is false? a. some proteins have quaternary structure, and some do not
b. the number of possible protein primary structures is extremely large (astronomical)
c. some out not all proteins have disulfide bonds
d. none of the above
b. the number of possible protein primary structures is extremely large (astronomical)
c. some out not all proteins have disulfide bonds
d. none of the above
20
New cards
Which of the following amino acids has a non-polar side chain?
a. methionine
b. aspartate
c. asparagine
d. serine
a. methionine
b. aspartate
c. asparagine
d. serine
methionine
21
New cards
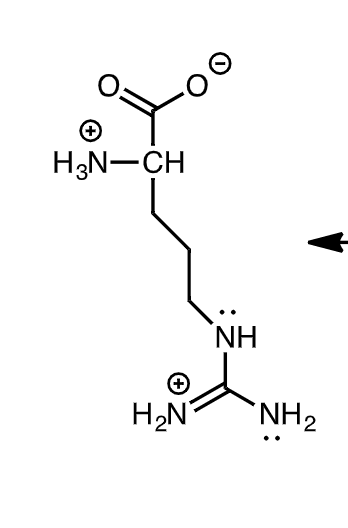
21a. (4) The structure of arginine (pK, = 2.17: pK, = 9.04; pK = 12.48) is shown. Draw an additional resonance form for the side chain of Arg
\
\
answer in pic
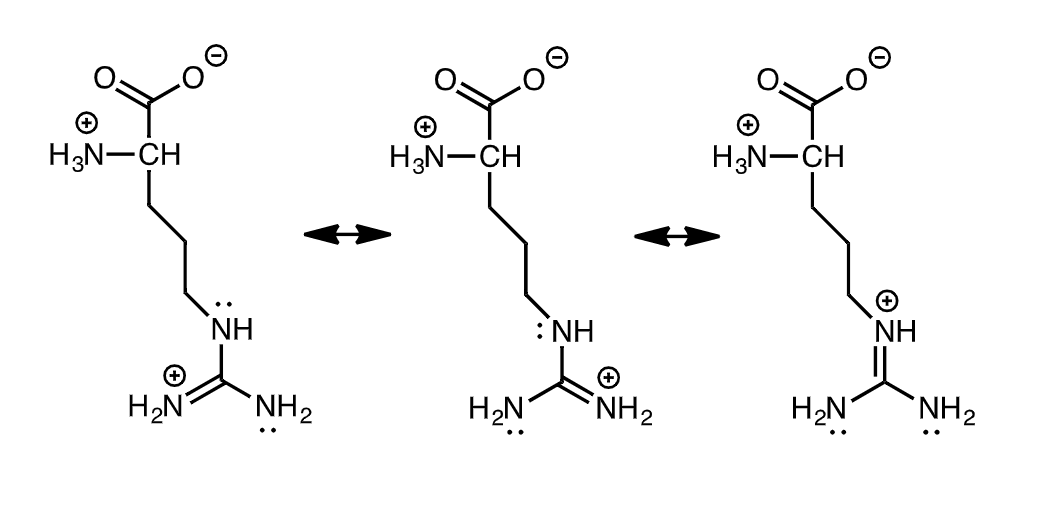
22
New cards
21b. Assume one equivalent of hydroxide ion (OH^-1) is added and draw the structure of arginine
ans
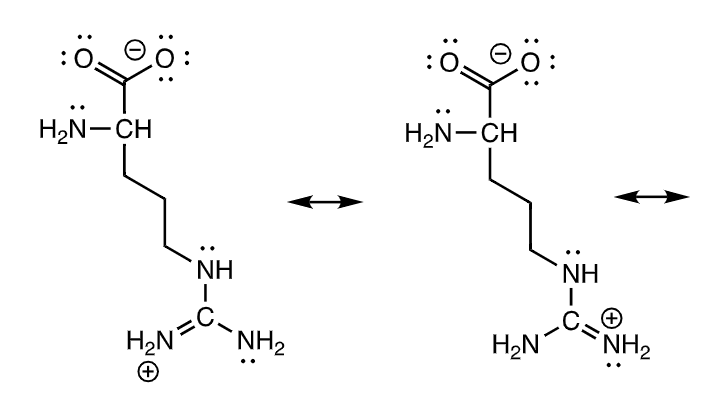
23
New cards
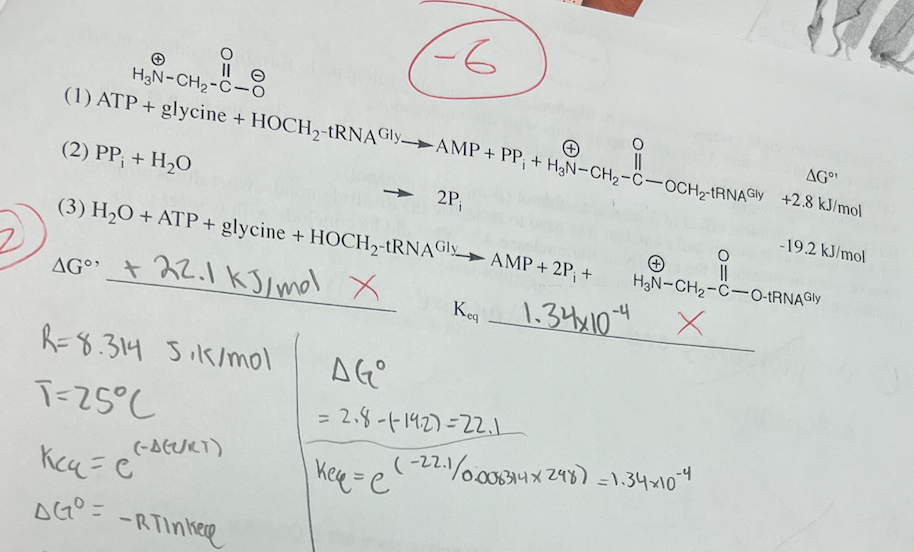
22a. (10) Calculate ΔG°' and Keq for reaction (3) at 25 °C and place answers on the lines below, showing all work. HO-tRNAgly is a transfer RNA molecule. "HOCH2" is a primary alcohol group, a portion of the tRNA^gly molecule. Pi is inorganic phosphate and PPi is inorganic pyrophosphate.
ΔG°’ = -16.4 kJ/mol. Keq = 749
24
New cards
22b. Using the values of ΔG°' for reactions 1-3, discuss biochemical coupling in the synthesis of the covalent adduct between glycine and transfer RNA. The term "biochemical coupling" does not refer to the joining of glycine with tRNA
Reaction (1) is unfavorable under biochemical standard state conditions: ΔG°’ = +2.8, which indicates that Keq = 0.323. However, reaction (2) is quite favorable. The sum of the two \n reactions, (3), is more favorable than reaction (1), and the value of Keq for reaction (3) is about 2300-fold larger than the value of Keq for reaction (1) is. One type of biochemical coupling is to follow an unfavorable reaction with a favorable one that removes one of the products. In this case it is pyrophosphate that is removed. This kind of biochemical coupling can also be explained by invoking LeChatelier’s principle
25
New cards
22c. Write a mathematical equation that defines the equilibrium constant Keq of eqn.(1) in terms of the reactants and products of this specific chemical process.
the equilibrium constant is the ratio of concentrations of the products over the concentrations of the reactants, with each concentration taken to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient. In this case, all of the stoichiometric coefficients are unity, which means that each concentration is taken to the first power (when the exponent is one, it is usually not written out).
Keq = \[AMP\]\[pyrophosphate\]\[Gly-tRNAGly\]/\[ATP\]\[glycine\]\[HO-tRNAGly\] \n The molecule HO-tRNAGly has a free hydroxyl group, and Gly-tRNAGly is the molecule with a covalent bond between glycine and tRNAGly
Keq = \[AMP\]\[pyrophosphate\]\[Gly-tRNAGly\]/\[ATP\]\[glycine\]\[HO-tRNAGly\] \n The molecule HO-tRNAGly has a free hydroxyl group, and Gly-tRNAGly is the molecule with a covalent bond between glycine and tRNAGly
26
New cards
23\. There are eight cysteine residues in ribonuclease A, and all participate in forming disulfide bonds With respect to Christian Antinson's experiments with ribonuclease A
(a) What did the presence of urea do to the structure of ribonuclease A? Be specific, and answer with more man a single word.
(b) Discuss the chemical effect of 2-mercaptoethanol (B-mercaptoethanol)
(c) After urea was removed and a catalyst was used to reshuffle the disulfide bonds, what did Anfinson observe when he measured the activity of ribonuclease A? What did he conclude with respect to the primary and tertiary structures of ribonuclease A?
(a) What did the presence of urea do to the structure of ribonuclease A? Be specific, and answer with more man a single word.
(b) Discuss the chemical effect of 2-mercaptoethanol (B-mercaptoethanol)
(c) After urea was removed and a catalyst was used to reshuffle the disulfide bonds, what did Anfinson observe when he measured the activity of ribonuclease A? What did he conclude with respect to the primary and tertiary structures of ribonuclease A?
Christian Anfinson used urea to unfold ribonuclease A, meaning that this enzyme lost some \n or all of its secondary and tertiary structure. This denatured the enzyme, meaning that it had no \n biological activity. He used 2-mercaptoethanol to reduce the four disulfide bonds, turning four \n cystine residues into eight cysteine residues. Using dialysis he then removed the urea and \n allowed random disulfide bonds to form via oxidation (there are 105 possible arrangements of \n four disulfide bonds). The enzyme had little activity (about 1%) at this stage of the experiment. \n Finally, he used a small amount of 2-mercaptoethanol as a catalyst to break the disulfide bonds \n temporarily and reform them in the most stable arrangement (this can also be done using the \n enzyme protein disulfide isomerase). At this point the solution of ribonuclease A regained \n almost full enzymatic activity. This experiment showed that the information for the correct \n three-dimensional state of this enzyme was present in the primary structure, the amino acid \n sequence itself.
27
New cards
exam 1 end
formula sheet
28
New cards
exam 2 start
formula sheet
29
New cards
If a mutation of a charged residue near the surface of hemoglobin (distant from the site where oxygen binds) to alanine (R = -CH3) strenethens the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin the most likely explanation is that the mutation
a. destabilized oxyhemoglobin by removing a salt bridge
b. destabilized deoxyhemoglobin by removing a salt bridge R
c. destabilized oxyhemoglobin by creating a new salt bridge
d. destabilized deoxyhemoglobin by creating a new salt bridge
a. destabilized oxyhemoglobin by removing a salt bridge
b. destabilized deoxyhemoglobin by removing a salt bridge R
c. destabilized oxyhemoglobin by creating a new salt bridge
d. destabilized deoxyhemoglobin by creating a new salt bridge
destabilized deoxyhemoglobin by removing a salt bridge R
30
New cards
When oxygen binds to hemoglobin, four of the atoms around Fe(I) are nitrogen atoms from heme. The fifth and sixth coordination sites of the Fe(Il) ion are occupied by
a. two O2 molecules
b. one O2 molecule and one atom from bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
c. two O2 atoms
d. one O2 molecule and one atom from the side chain of Histidine F8
a. two O2 molecules
b. one O2 molecule and one atom from bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
c. two O2 atoms
d. one O2 molecule and one atom from the side chain of Histidine F8
one O2 molecule and one atom from the side chain of Histidine F8
31
New cards
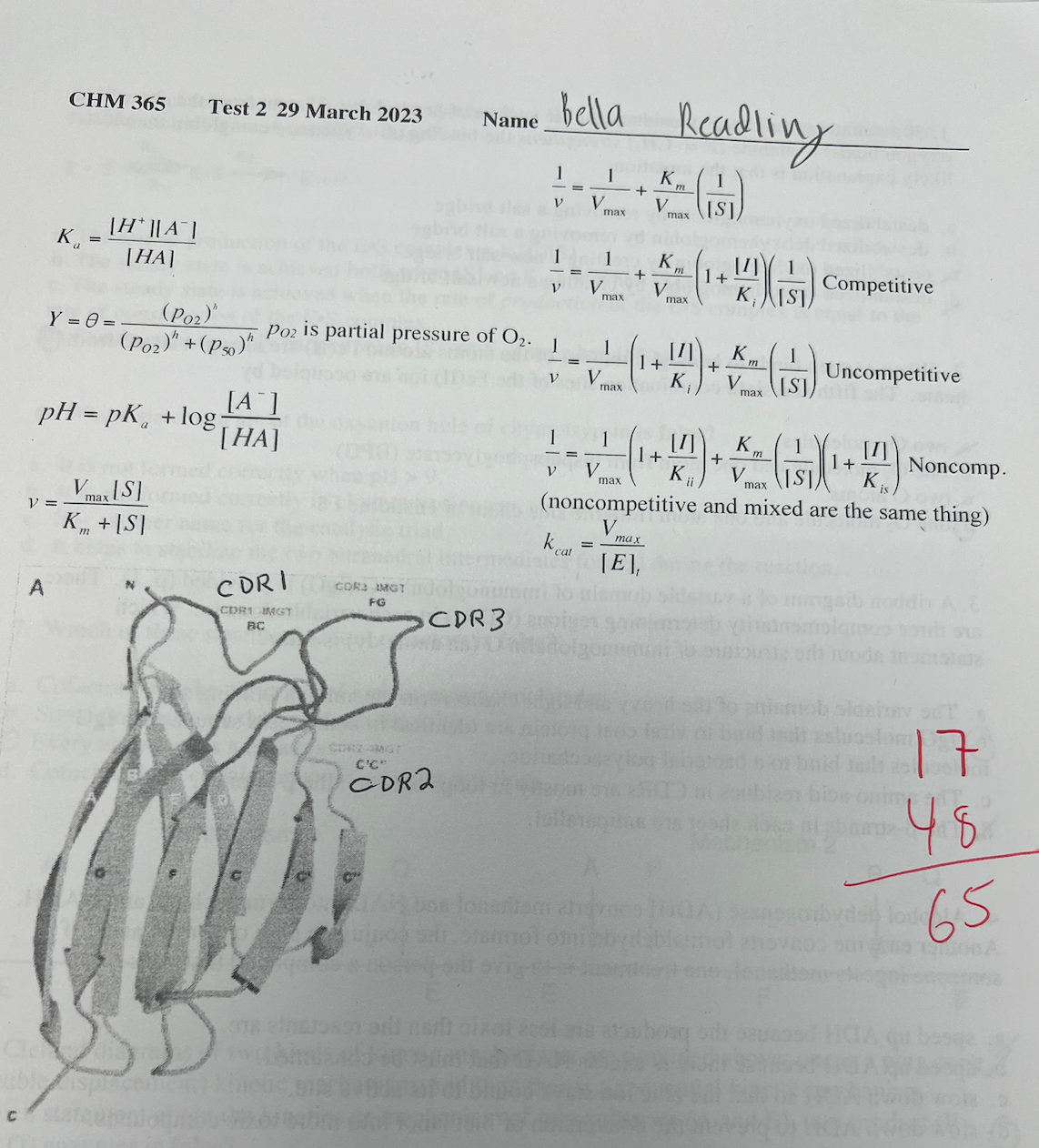
3\. A ribbon diagram of a variable domain of immunoglobulin G (IgG) is provided (p. 1). There are three complementarity determining regions (DRs) in each variable domain. Which statement about the structure of immunoglobulin G (an antibody) is false?
a. The variable domains of the heavy and light chains form the antigen-binding site.
b. IgG molecules that bind to viral coat protein are identical in amino acid sequence to IgG molecules that bind to a bacterial polysaccharide
c. The amino acid residues in CDRs are mostly in loops between the ß-strands.
d. The ß-strands in each sheet are antiparallel.
a. The variable domains of the heavy and light chains form the antigen-binding site.
b. IgG molecules that bind to viral coat protein are identical in amino acid sequence to IgG molecules that bind to a bacterial polysaccharide
c. The amino acid residues in CDRs are mostly in loops between the ß-strands.
d. The ß-strands in each sheet are antiparallel.
IgG molecules that bind to viral coat protein are identical in amino acid sequence to IgG molecules that bind to a bacterial polysaccharide
32
New cards
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) converts methanol and NAD into formaldehyde and NADH. Another enzyme converts formaldehyde into formate, the conjugate base of formic acid. If someone ingests methanol, one treatment is to give the person a compound that will:
a. speed up ADH because the products are less toxic than the reactants are
b. speed up ADH because there is excess NAD that must be consumed.
c. slow down ADH so that the zinc ion stays bound to its active site.
d. slow down ADH to prevent the conversion of methanol into more toxic compounds.
a. speed up ADH because the products are less toxic than the reactants are
b. speed up ADH because there is excess NAD that must be consumed.
c. slow down ADH so that the zinc ion stays bound to its active site.
d. slow down ADH to prevent the conversion of methanol into more toxic compounds.
slow down ADH to prevent the conversion of methanol into more toxic compounds.
33
New cards
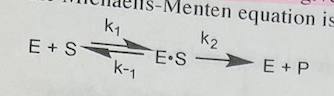
The Michaelis constant is given the symbol Km. Which statement about the steady-state and Michaelis-Menten equation is false?
a. The rate of production of the E•S complex = k1IEl|S|.
b. The steady-state is achieved both when |S| >> Kn and when |S| >> KM.
c. The steady state is achieved when the rate of production of the E•S complex is equal to the rate of consumption of the E•S complex
d. Steady state can only happen when IS| << Km, not when ISI >> KM.
a. The rate of production of the E•S complex = k1IEl|S|.
b. The steady-state is achieved both when |S| >> Kn and when |S| >> KM.
c. The steady state is achieved when the rate of production of the E•S complex is equal to the rate of consumption of the E•S complex
d. Steady state can only happen when IS| << Km, not when ISI >> KM.
\
Steady state can only happen when IS| << Km, not when ISI >> KM.
Steady state can only happen when IS| << Km, not when ISI >> KM.
34
New cards
Which of these statements about cofactors is false?
a. Cofactors may be either metal ions or organic molecules
b. Some cofactors are derived from vitamins.
c. Every enzyme has a cofactor.
d. Cofactors help certain enzymes catalyze reactions.
a. Cofactors may be either metal ions or organic molecules
b. Some cofactors are derived from vitamins.
c. Every enzyme has a cofactor.
d. Cofactors help certain enzymes catalyze reactions.
Every enzyme has a cofactor.
35
New cards
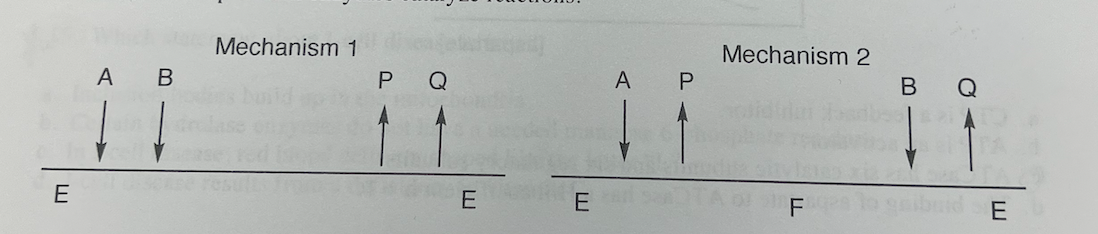
Cleland diagrams of two kinds of kinetic mechanisms are provided above; one is a ping pong (double displacement) kinetic mechanism, and the other is a sequential kinetic mechanism. Which statement about the kinetics or mechanism of two-substrate (A and B), two-product (P and Q) enzymes is false?
a. In a ping-pong mechanism, a ternary complex (E•A•B) forms
b. In a sequential mechanism, a ternary complex (E•A•B) forms.
C. Enzymes having ping pong mechanisms use covalent catalysis.
d. In a ping-pong mechanism, the first product departs before the second substrate binds.
a. In a ping-pong mechanism, a ternary complex (E•A•B) forms
b. In a sequential mechanism, a ternary complex (E•A•B) forms.
C. Enzymes having ping pong mechanisms use covalent catalysis.
d. In a ping-pong mechanism, the first product departs before the second substrate binds.
In a ping-pong mechanism, the first product departs before the second substrate binds.
36
New cards
Which statement about enzymes and catalysis is false?
a. Strong bases make poor leaving groups
b. The side chain of histidine may bring about general acid or general base catalysis.
c. Some enzymes use salt bridges to help bind their substrates.
d. Enzymes are more complementary in shape & charge to the substrate than to the transition
a. Strong bases make poor leaving groups
b. The side chain of histidine may bring about general acid or general base catalysis.
c. Some enzymes use salt bridges to help bind their substrates.
d. Enzymes are more complementary in shape & charge to the substrate than to the transition
Enzymes are more complementary in shape & charge to the substrate than to the transition
37
New cards
Which statement about Symmetry model of allosteric proteins is false?
a. Activators bind more tightly to the Taut state than to the Relaxed state.
b. L= (Taut |/IRelaxed\], and in the absence of other compounds L >> 1.
c. All subunits must change conformation together.
d. Substrates bind more tightly to the Relaxed state than to the Taut state.
a. Activators bind more tightly to the Taut state than to the Relaxed state.
b. L= (Taut |/IRelaxed\], and in the absence of other compounds L >> 1.
c. All subunits must change conformation together.
d. Substrates bind more tightly to the Relaxed state than to the Taut state.
Activators bind more tightly to the Taut state than to the Relaxed state.
38
New cards
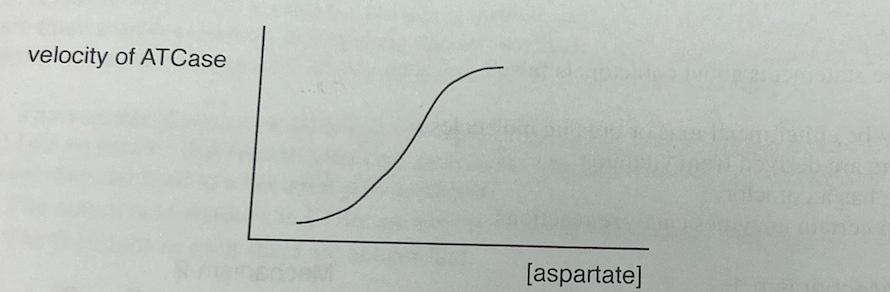
11\. A graph of velocity vs. (aspartate| is provided. Which statement about aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) is false?
a. CTP is a feedback inhibitor.
b. ATP is an activator.
c. ATCase has six catalytic subunits and six regulatory subunits
d. The binding of aspartate to ATCase has a Hill coefficient h = 1.
a. CTP is a feedback inhibitor.
b. ATP is an activator.
c. ATCase has six catalytic subunits and six regulatory subunits
d. The binding of aspartate to ATCase has a Hill coefficient h = 1.
the binding of aspartate to ATCase has a Hill coefficient h = 1.
39
New cards
Which statement about the regulation of glycogen phosphorylase is true?
a. The covalent modification of glycogen phosphorylase b into a is irreversible.
b. Glycogen phosphorylase a but not b has a phosphoryl group (-PO,2) on serine-14
c. Glycogen phosphorylase b is more active (faster) than glycogen phosphorylase a is.
d. Conversion of glycogen phosphorylase b into a occurs when oxygen binds to a heme group.
a. The covalent modification of glycogen phosphorylase b into a is irreversible.
b. Glycogen phosphorylase a but not b has a phosphoryl group (-PO,2) on serine-14
c. Glycogen phosphorylase b is more active (faster) than glycogen phosphorylase a is.
d. Conversion of glycogen phosphorylase b into a occurs when oxygen binds to a heme group.
Glycogen phosphorylase a but not b has a phosphoryl group (-PO3^-2) on serine-14
40
New cards
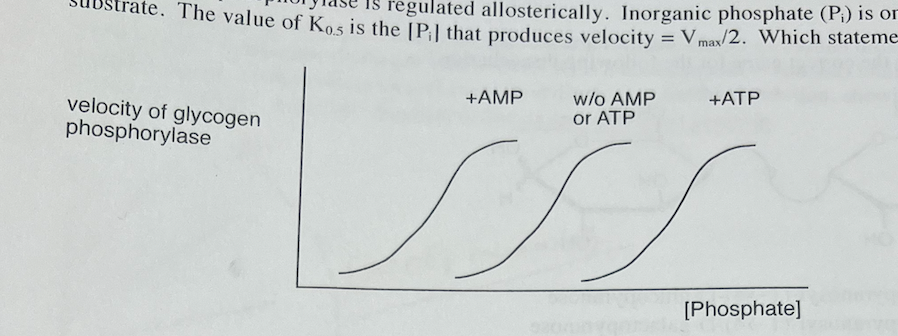
Glycogen phosphorylase is regulated allosterically. Inorganic phosphate (Pi) IS one substrate. The value of K0.5 is the Pi. that produces velocity = Vmax/2. Which statement is true?
a. AMP lowers the value of K0.5 between phosphate and glycogen phosphorylase.
b. AMP inhibits glycogen phosphorylase.
c. A high concentration of AMP is a sign that the cell is rich in energy.
d. ATP activates glycogen phosphorylase.
a. AMP lowers the value of K0.5 between phosphate and glycogen phosphorylase.
b. AMP inhibits glycogen phosphorylase.
c. A high concentration of AMP is a sign that the cell is rich in energy.
d. ATP activates glycogen phosphorylase.
AMP lowers the value of K0.5 between phosphate and glycogen phosphorylase.
41
New cards
14\. Which statement about glycoconjugates is true?
a. In N-glycoproteins an oligosaccharide is linked to a threonine residue.
b. Glycoproteins and glyconucleic acids are the two major classes of glycoconjugates.
c. Some glycoproteins are found on the outer surface of the plasma membrane.
d. In O-glycoproteins an oligosaccharide is linked to a leucine residue.
a. In N-glycoproteins an oligosaccharide is linked to a threonine residue.
b. Glycoproteins and glyconucleic acids are the two major classes of glycoconjugates.
c. Some glycoproteins are found on the outer surface of the plasma membrane.
d. In O-glycoproteins an oligosaccharide is linked to a leucine residue.
Some glycoproteins are found on the outer surface of the plasma membrane.
42
New cards
Which statement about I-cell disease is true?
a. Inclusion bodies build up in the mitochondria.
b. Certain hydrolase enzymes do not have a needed mannose 6-phosphate residue
c. In 1-cell disease, red blood cells are shaped like the letter "I."
d. I-cell disease results from a deficiency in vitamin C.
a. Inclusion bodies build up in the mitochondria.
b. Certain hydrolase enzymes do not have a needed mannose 6-phosphate residue
c. In 1-cell disease, red blood cells are shaped like the letter "I."
d. I-cell disease results from a deficiency in vitamin C.
Certain hydrolase enzymes do not have a needed mannose 6-phosphate residue
43
New cards
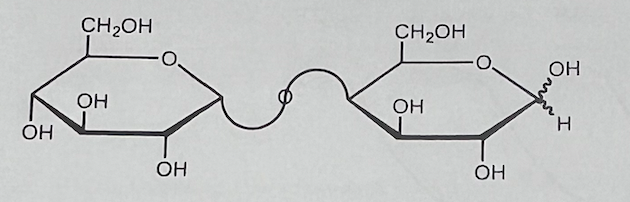
What is the correct name for the following disaccharide?
a. a-D-glucopyranosy|-(1->4)-D-glucopyranose
b. a-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)-D-galactopyranose
c. ß-D-galactopyranosyl-(1-›4)-D-glucopyranose
d. ß-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)-D-galactopyranose
a. a-D-glucopyranosy|-(1->4)-D-glucopyranose
b. a-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)-D-galactopyranose
c. ß-D-galactopyranosyl-(1-›4)-D-glucopyranose
d. ß-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)-D-galactopyranose
a-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)-D-galactopyranose
44
New cards
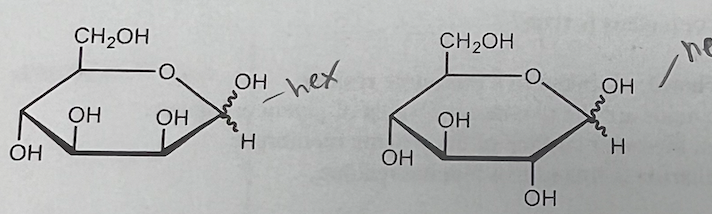
Epimers are a special class of diastereomer. The structures of glucose and mannose are shown. Which statement is false?
a. They are both pyranoses.
b. They are both hexoses.
c. They are both ketoses.
d. They are epimers of each other
a. They are both pyranoses.
b. They are both hexoses.
c. They are both ketoses.
d. They are epimers of each other
They are both ketoses.
45
New cards
Which statement about polysaccharides is false?
a. Cellulose is made by plants to store energy.
b. Glycogen is polymer of glucose, linked by alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
c. Cellulose is a polymer of glucose, linked by beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
d Glycogen is made by mammals to store energy.
a. Cellulose is made by plants to store energy.
b. Glycogen is polymer of glucose, linked by alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
c. Cellulose is a polymer of glucose, linked by beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
d Glycogen is made by mammals to store energy.
Cellulose is made by plants to store energy.
46
New cards
(4) Formate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction formate +NAD
Noncompetitive (mixed) inhibitors reduce both the apparent values of V max and V max /K m . The equations on the front of the exam can be used to produce this inhibition pattern. Recall that y = ax +b, where a is the slope, and b is the y-intercept. Increases in the concentration of the inhibitor increase both the slope and the y-intercept, unlike competitive or uncompetitive inhibition.
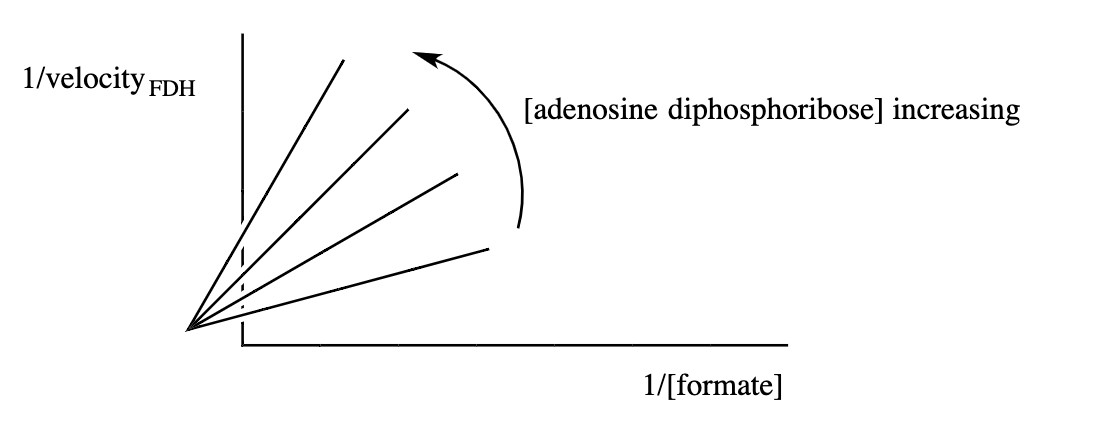
47
New cards
20) The mechanism of NADH reacting with oxaloacetate is shown below.
(a) Complete the structures of the His residue in malate dehydrogenase, the second reactant, and both of the products. Include H's, charges, bonds, and lone pairs on nitrogen atoms.
(b) Use curved arrows to show the flow of electrons in this reduction reaction
(a) Complete the structures of the His residue in malate dehydrogenase, the second reactant, and both of the products. Include H's, charges, bonds, and lone pairs on nitrogen atoms.
(b) Use curved arrows to show the flow of electrons in this reduction reaction
When NADH reduces oxaloacetate, NAD and L-Malate are the products. The reaction is a hydride transfer from NADH to oxaloacetate. The ketone group is reduced to a secondary \n alcohol. A histidine residue is the general acid. The nitrogen atom of NADH has a lone pair, and the nitrogen atom of NAD is positively charged
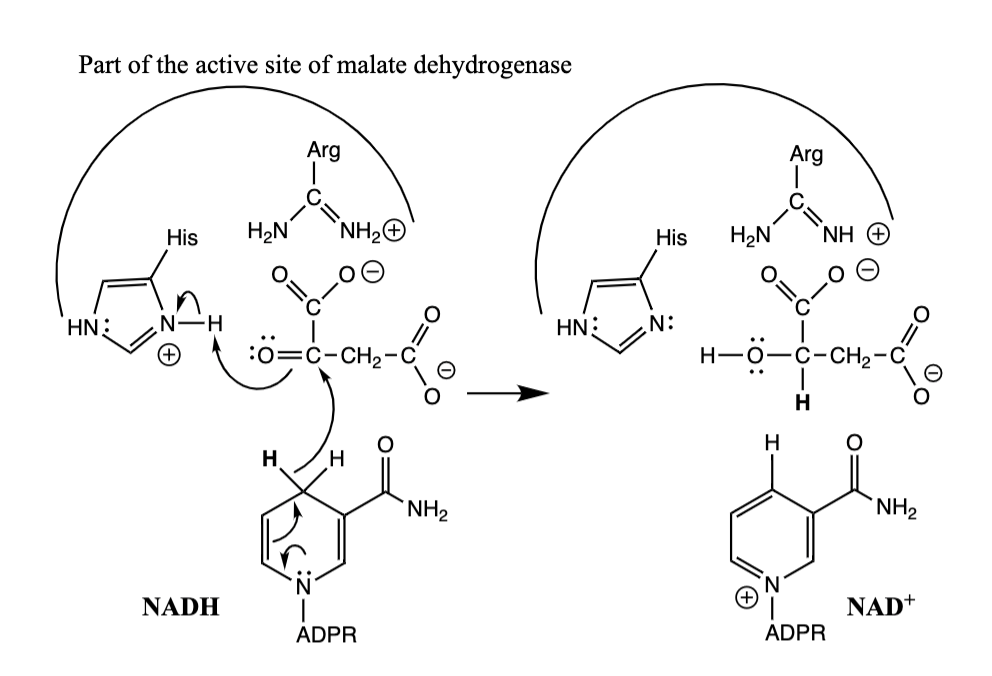
48
New cards
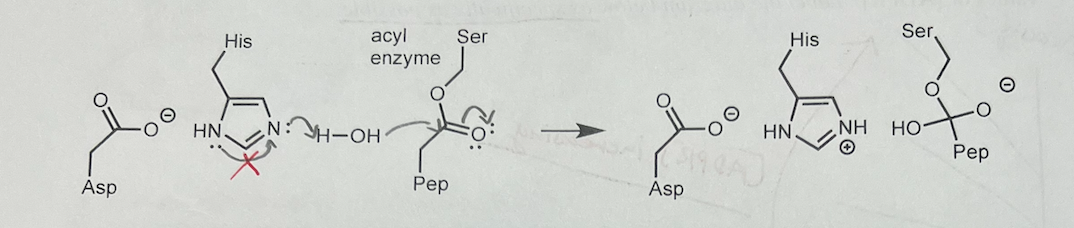
21\. (6) Chymotrypsin is an enzyme that hydrolyzes peptide bonds. In the third step (below), the enzyme starts the process of hydrolyzing the acyl enzyme intermediate.
(a) Add curved arrows to the third step of the mechanism of chymotrypsin (shown below)
(b) How does His57 make this step faster? Use chemical terminology
(a) Add curved arrows to the third step of the mechanism of chymotrypsin (shown below)
(b) How does His57 make this step faster? Use chemical terminology
21b. His57 is a general base. By removing the proton from water (a poor nucleophile), His \n makes water a stronger nucleophile: water gains additional electron density that is freed up \n when the proton leaves. Pep is a portion of the polypeptide, and the product of this step is the \n second tetrahedral intermediate. The fourth and final step is the expulsion of the side chain of \n serine
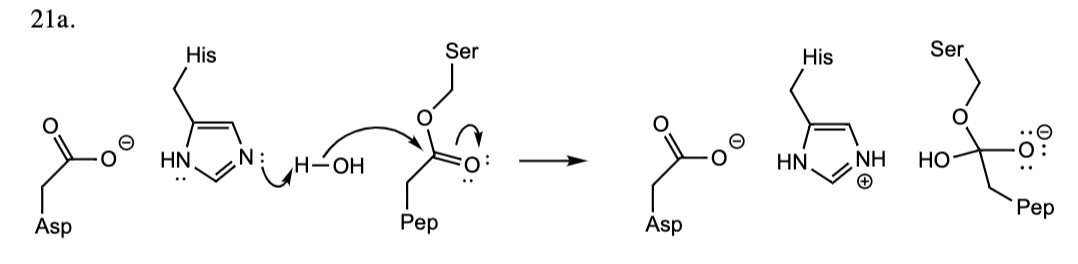
49
New cards
22a. (12) For hemoglobin (H) the Hill coefficient h = 3 and pso = 26 torr. The partial pressure Of Oxygen IS Po2. Assume that po2 lungs = 100 torr and po2 muscle = 20 torr. For myoglobin (Mb) h = 1. and P50 = 3 torr. Let Po2 lungs = 100 torr and po2 muscle = 20 torr.
(a) Calculate ΔθHb and ΔθMb for each protein traveling from muscles to lungs. To what importal physiological quantity is Δθ proportional? In other words, why is it significant?
(a) Calculate ΔθHb and ΔθMb for each protein traveling from muscles to lungs. To what importal physiological quantity is Δθ proportional? In other words, why is it significant?
ΔθHb = 0.670, and ΔθMb = 0.101. Dq is the change in fractional saturation as Hb moves from the muscles to the lungs, and it is proportional to how much oxygen Hb can transport.
50
New cards
22b. (b) Draw a graph of fractional saturation θHb versus po2. Indicate po2 lungs, Po2 muscle, and ΔθHb
See the course pack on p. 93 for a similar diagram. Y is an alternate symbol for fractional saturation θ. The shape of the curve should be sigmoidal. There should be marks for pm and p1 on the x-axis, and there should be marks for Ym and Y1 on the Y axis. ΔY = Y1 – Ym .
51
New cards
22c. Discuss two chemical factors that make Δθ smaller for Mb than it is for Hb. Interpret what h = 3 means chemically as part of your answer.
Mb binds oxygen more strongly than Hb does (as can be seen by their respective values of p50 ); therefore, Mb would not release oxygen when it moved from the lungs to muscle tissue. \n However, Hb also binds oxygen with partial positive cooperativity (h = 3), whereas myoglobin does not bind oxygen cooperatively (h = 1). Even if Mb and Hb had equal affinity for oxygen, ΔθMb would be smaller than ΔθHb . A high degree of cooperativity makes the slope of θ vs. pO2 steep in the vicinity of p 50 ; therefore, small changes in the value of pO2 bring about large changes in θ for values of p O2 near p 50 .
A common incorrect answer is that Hb has four binding sites and Mb has only one, but this is immaterial. The values of both ΔθHb and ΔθMb must lie between 0 and 1; therefore this answer does not make sense mathematically. The 4-versus-1 answer does not make sense physiologically, either. Mb is about one-fourth as large as Hb; therefore, having four times as \n many moles of Mb as Hb would make the two proteins equivalent. Yet even if Mb were present in fourfold greater quantities than Hb, Mb would still not be able to transport as much oxygen as Hb, for the reasons given above and mentioned below
A common incorrect answer is that Hb has four binding sites and Mb has only one, but this is immaterial. The values of both ΔθHb and ΔθMb must lie between 0 and 1; therefore this answer does not make sense mathematically. The 4-versus-1 answer does not make sense physiologically, either. Mb is about one-fourth as large as Hb; therefore, having four times as \n many moles of Mb as Hb would make the two proteins equivalent. Yet even if Mb were present in fourfold greater quantities than Hb, Mb would still not be able to transport as much oxygen as Hb, for the reasons given above and mentioned below
52
New cards
22d. Could myoglobin substitute for hemoglobin? Explain by discussing two chemical properties that are different in the two proteins to support your answer. Do not discuss bisphosphoglycerate (BPG).
Myoglobin would not be able to transport as much oxygen as hemoglobin, as can be seen by their respective values of \n Δθ in part (a). The difference in values of h and p 50 are the reasons behind the difference in Dq between the two proteins. See the course pack, p. 98 for a diagram.
53
New cards

exam 3 start
formula sheets
54
New cards
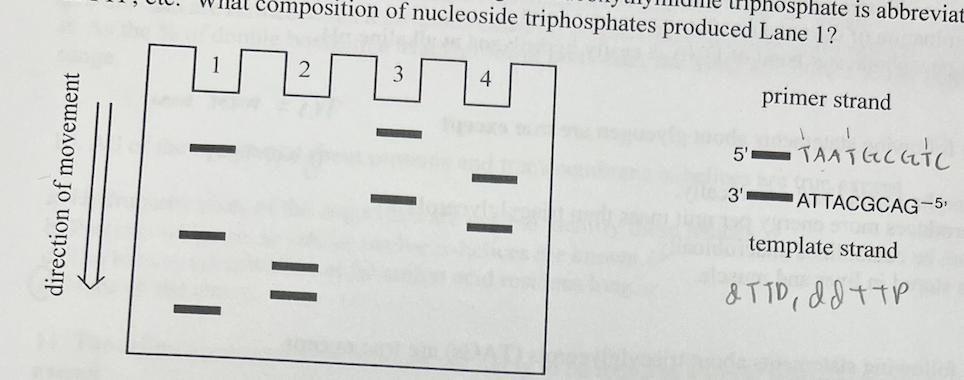
In a DNA sequencing experiment, the bottom strand in the drawing is the template, and the top strand is the primer. The reaction includes DNA polymerase, and only the strand containing the primer is seen below. A gel electrophoresis experiment is run, and lane 1 below is observed Each band represents DNA of a certain length. Dideoxythymidine triphosphate is abbreviated ddTTP, etc. What composition of nucleoside triphosphates produced Lane 1?
a. dTTP, dATP + ddTTP, dCTP, dGTP
b. dTTP, dATP, dCTP + ddCTP, dGTP
c. dTTP + ddTTP, dATP, dCTP, dGTP
d. dTTP, dATP, dCTP, dGTP + ddGTP
a. dTTP, dATP + ddTTP, dCTP, dGTP
b. dTTP, dATP, dCTP + ddCTP, dGTP
c. dTTP + ddTTP, dATP, dCTP, dGTP
d. dTTP, dATP, dCTP, dGTP + ddGTP
dTTP + ddTTP, dATP, dCTP, dGTP
55
New cards
Tm is the melting temperature of double stranded DNA into single strands. As the % of A: T base pairs in DNA increases, Tm *; as the [NaCI] increases, Tm*
a. rises; rises
b. rises; falls
c. falls; rises
d. falls: falls
a. rises; rises
b. rises; falls
c. falls; rises
d. falls: falls
falls; rises
56
New cards
3\. Differences between double stranded DNA and double stranded RNA include all of the following except:
a. Uracil is not found in DNA but is common in RNA.
b. In double stranded RNA the two strands are antiparallel, but in double stranded DNA the two strands are parallel.
c. The presence of a 2' -OH group in RNA but not DNA
d. Thymine is rarely found in RNA but is common in DNA.
a. Uracil is not found in DNA but is common in RNA.
b. In double stranded RNA the two strands are antiparallel, but in double stranded DNA the two strands are parallel.
c. The presence of a 2' -OH group in RNA but not DNA
d. Thymine is rarely found in RNA but is common in DNA.
In double stranded RNA the two strands are antiparallel, but in double stranded DNA the two strands are parallel.
57
New cards
4\. UV stands for ultraviolet. Which statement about DNA damage is false?
a. Thymine dimers are formed because of the absorption of UV light.
b. Thy mine dimers may be formed by adjacent T residues on the same strand of DNA.
c. Deamination of cytosine residues produces uracil.
d. The phosphodiester bond of DNA is easily hydrolyzed at alkaline pH.
a. Thymine dimers are formed because of the absorption of UV light.
b. Thy mine dimers may be formed by adjacent T residues on the same strand of DNA.
c. Deamination of cytosine residues produces uracil.
d. The phosphodiester bond of DNA is easily hydrolyzed at alkaline pH.
the phosphodiester bond of DNA is easily hydrolyzed at alkaline pH.
58
New cards
5\. The following statements about glycogen are true except
a. It can be catabolized aerobically.
b. it produces more energy per unit mass than triacylelycerols
c. It can be catabolized anaerobically.
d. It is stored in liver and muscle.
a. It can be catabolized aerobically.
b. it produces more energy per unit mass than triacylelycerols
c. It can be catabolized anaerobically.
d. It is stored in liver and muscle.
it produces more energy per unit mass than triacylelycerols
59
New cards
The following statements about triacylglycerols (TAGs) are true except
a. TAGs are used for the long-term storage of energy
b. TAGs are esters between fatty acids and sphingosine.X
c. The average carbon atom is highly reduced (has an oxidation number less than 0
d. TAGs are hydrolyzed by the enzyme hormone-sensitive lipase.
a. TAGs are used for the long-term storage of energy
b. TAGs are esters between fatty acids and sphingosine.X
c. The average carbon atom is highly reduced (has an oxidation number less than 0
d. TAGs are hydrolyzed by the enzyme hormone-sensitive lipase.
TAGs are esters between fatty acids and sphingosine.
60
New cards
7\. Essential nutrients are those that we cannot synthesize in sufficient quantities and must take in as part of our diet. Prostaglandins and thromboxanes are two classes of eicosanoid hormones. Which statement about lipids is false?
a. Lack of vitamin D is associated with improper bone formation and the disease rickets.
b. Vitamin K is needed for blood coagulation to occur properly.
c. A few fatty acids are nutritionally essential.
d. Aspirin speeds up the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes.
a. Lack of vitamin D is associated with improper bone formation and the disease rickets.
b. Vitamin K is needed for blood coagulation to occur properly.
c. A few fatty acids are nutritionally essential.
d. Aspirin speeds up the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes.
Aspirin speeds up the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes.
61
New cards
Which statement about sphingolipids is false?
a. Phosphosphingolipids are used for the medium-term storage of energy.
b. Tay-Sachs disease is caused by a deficiency in the enzyme the hydrolyzes a glycosidic bond within GM2
c. Differences in the oligosaccharide of one sphingolipid is the basis for the ABO blood group system.
d. Sphingolipids are found in the plasma membrane.
a. Phosphosphingolipids are used for the medium-term storage of energy.
b. Tay-Sachs disease is caused by a deficiency in the enzyme the hydrolyzes a glycosidic bond within GM2
c. Differences in the oligosaccharide of one sphingolipid is the basis for the ABO blood group system.
d. Sphingolipids are found in the plasma membrane.
Phosphosphingolipids are used for the medium-term storage of energy.
62
New cards
Which statement about fatty acids or fatty acyl groups in lipids is false?
a. Fatty acids are joined to glycerol via glycosidic bonds.
b. The carbon chains of fatty acids usually have an even number of carbon atoms.
c. trans-fats are formed when a cis-double bond is isomerized to a trans-configuration.
d. As the % of double bonds in a triacylglycerol increases, the TAG will have a lower melting range.
a. Fatty acids are joined to glycerol via glycosidic bonds.
b. The carbon chains of fatty acids usually have an even number of carbon atoms.
c. trans-fats are formed when a cis-double bond is isomerized to a trans-configuration.
d. As the % of double bonds in a triacylglycerol increases, the TAG will have a lower melting range.
Fatty acids are joined to glycerol via glycosidic bonds.
63
New cards
All of the statements about proteins and transmembrane -helices are true except
a. Hydropathy plots of the sequences are used to identify these helices.
b. Proteins with one, seven, or twelve -helices are known. c. The helices are often about 20 amino acid residues long.
d. none of the above
a. Hydropathy plots of the sequences are used to identify these helices.
b. Proteins with one, seven, or twelve -helices are known. c. The helices are often about 20 amino acid residues long.
d. none of the above
none of the above
64
New cards
The following amino acid residues are likely to be found in a single transmembrane helix except
a. leucine
b. methionine
c. lysine
d. tryptophan
a. leucine
b. methionine
c. lysine
d. tryptophan
lysine
65
New cards
Assume that a proton is moving from outside of the mitochondrial inner membrane to the inside. The pH in the interior of the mitochondria is 8, and the pH on the outside of the inner membrane is 5. The membrane potential is 0.080 volts more negative on the inside of the membrane than on the outside. T = 37 °C. What is the value of the protonmotive force?
a. -25,222 J/mol
b. -10.085 J/mol
c. -9843 J/mol
d. +10.085 J/mol
a. -25,222 J/mol
b. -10.085 J/mol
c. -9843 J/mol
d. +10.085 J/mol
\-25,222 J/mol
66
New cards
The flagellum is a supramolecular complex that moves bacteria through its environment. The protonmotive force (ΔGH+) =-2.3025RT(ΔpH) + F(Δφ). Which statement about the protonmotive force (pmf) is false?
a. The pmf in mitochondria provides the driving force for ATP synthesis.
b. The pmf provides the driving force for active transport of lactose in the bacterium E. coli.v
c. The value of the pmf is independent of the value of the membrane potential.
d. In bacteria the pmf provides the driving force for rotation of the bacterial flagella.
a. The pmf in mitochondria provides the driving force for ATP synthesis.
b. The pmf provides the driving force for active transport of lactose in the bacterium E. coli.v
c. The value of the pmf is independent of the value of the membrane potential.
d. In bacteria the pmf provides the driving force for rotation of the bacterial flagella.
The value of the pmf is independent of the value of the membrane potential.
67
New cards
14\. All of the following are true of facilitated diffusion across membranes except
a. It may be inducible.
b. Enantiomers may be transported at different rates.
c. It may show saturation kinetics.
d. Only ions may move via facilitated diffusion, not electrically neutral molecules.
a. It may be inducible.
b. Enantiomers may be transported at different rates.
c. It may show saturation kinetics.
d. Only ions may move via facilitated diffusion, not electrically neutral molecules.
Only ions may move via facilitated diffusion, not electrically neutral molecules
68
New cards
Which statement about the Na\* K\* ATPase is false?
a. This enzyme couples ATP hydrolysis to electrochemical work.
b. Sodium moves downhill, meaning with its electrochemical potential.
c. This reaction maintains the membrane potential (inside negative relative to outside).
d. This enzyme consumes a significant fraction of ATP in neurons and intestinal epithelial cells,
a. This enzyme couples ATP hydrolysis to electrochemical work.
b. Sodium moves downhill, meaning with its electrochemical potential.
c. This reaction maintains the membrane potential (inside negative relative to outside).
d. This enzyme consumes a significant fraction of ATP in neurons and intestinal epithelial cells,
Sodium moves downhill, meaning with its electrochemical potential.
69
New cards
16\. The following processes directly use the cleavage of ATP except Cleav=conv
a. the conversion of aspartate into asparagine
b. the conversion of glutamate into glutamine
c. the active transport of protons by bacteriorhodopsin
d. Myosin and actin producing contraction of muscle tissue
a. the conversion of aspartate into asparagine
b. the conversion of glutamate into glutamine
c. the active transport of protons by bacteriorhodopsin
d. Myosin and actin producing contraction of muscle tissue
the active transport of protons by bacteriorhodopsin
70
New cards
17\. A table of free energies is provided on page 2. The following compounds are high-energy Except
a. Acetyl phosphate = -42.2
b. glycerol phosphate = -9.2
c. phosphocreatine = -43
d. acetyl coenzyme A = -31
a. Acetyl phosphate = -42.2
b. glycerol phosphate = -9.2
c. phosphocreatine = -43
d. acetyl coenzyme A = -31
glycerol phosphate = -9.2
71
New cards
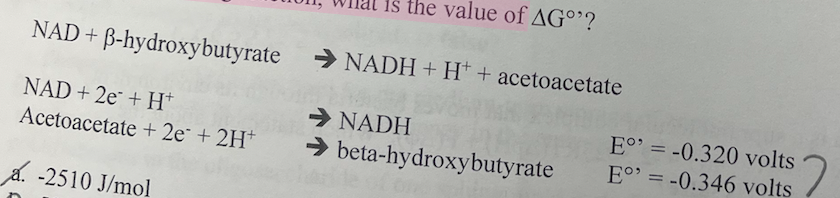
18\. For the following reaction, what is the value of ΔGº?
a. -2510 J/mol
b. -5020 J/mol
c. +2510 J/mol
d. +5020 J/mol
a. -2510 J/mol
b. -5020 J/mol
c. +2510 J/mol
d. +5020 J/mol
b. -5020 J/mol
72
New cards
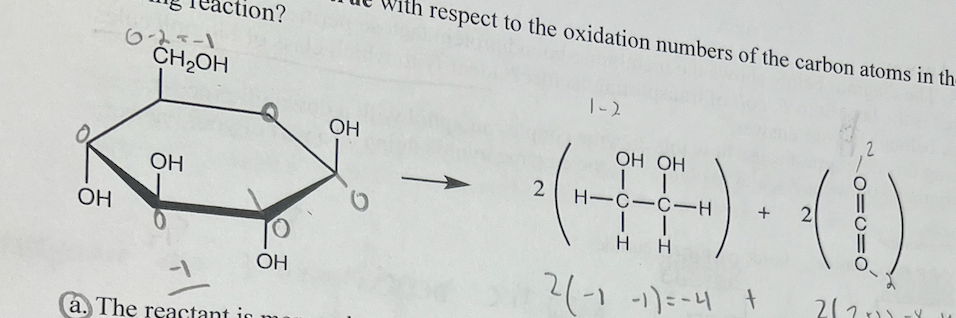
Which statement is true with respect to the oxidation numbers of the carbon atoms in the following reaction?
a. The reactant is more reduced than the products by 4 electrons
b. The reactant is more oxidized than the products by 1 electron
c. The reactant and the products have an equal number of electrons
d. The reactant is more reduced than the products by 3 electrons
a. The reactant is more reduced than the products by 4 electrons
b. The reactant is more oxidized than the products by 1 electron
c. The reactant and the products have an equal number of electrons
d. The reactant is more reduced than the products by 3 electrons
the reactant is more reduced than the products by 4 electrons
73
New cards
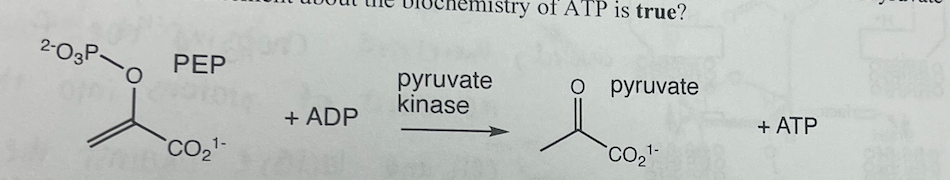
Pyruvate kinase catalyzes the reaction: Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) + ADP -> Pyruvate + ATP. Which statement about the biochemistry of ATP
a. ATP is very labile to nonenzymatic hydrolysis in solution.
b. No nucleophile except water cleaves ATP in biochemical reactions.
c. The transphosphorylation from PEP to ADP is favorable partially because of an enol-to-ketone tautomerization.
d. ATP mav only be cleaved at the y-phosphorus, not the ß- or a-phosphorus atoms.
a. ATP is very labile to nonenzymatic hydrolysis in solution.
b. No nucleophile except water cleaves ATP in biochemical reactions.
c. The transphosphorylation from PEP to ADP is favorable partially because of an enol-to-ketone tautomerization.
d. ATP mav only be cleaved at the y-phosphorus, not the ß- or a-phosphorus atoms.
The transphosphorylation from PEP to ADP is favorable partially because of an enol-to-ketone tautomerization.
74
New cards
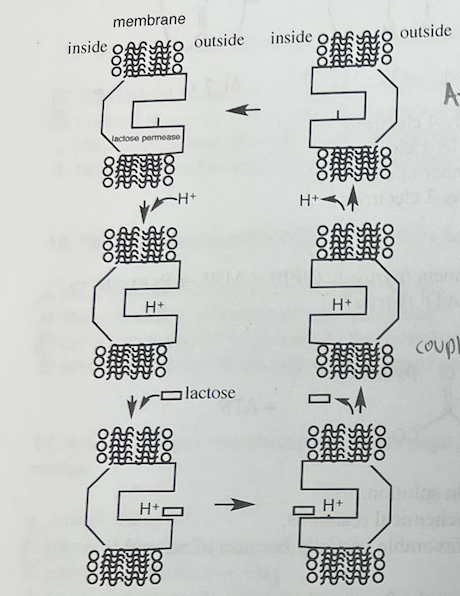
The diagram below shows the membrane-bound protein lactose permease in E. coli
a What is the benefit to E. coli of transporting lactose? Identify to which class of biomolecules lactose belongs in your answer.
a What is the benefit to E. coli of transporting lactose? Identify to which class of biomolecules lactose belongs in your answer.
Lactose is a disaccharide of glucose and galactose. It transported into the bacterial cells so \n that it can be catabolized for energy. The first step is its hydrolysis to glucose and galactose. \n Glucose can be used to make ATP via glycolysis. Galactose also provides energy, but the \n pathway for galactose is somewhat different.
75
New cards
Using this diagram. discuss how this enzvme couples an uphill with a downhill process. Identifv the two processes, and explain what the enzyme avoids doing as a part of your answer
Lactose permease couples the thermodynamically favorable movement of protons into the cell with the unfavorable movement of lactose against its concentration gradient. Lactose permease has two conformations, one in which the binding site faces outside the cell and one in \n which the site faces inwards. This transporter avoids transporting only protons by changing conformations only when both a proton and lactose are bound, or when neither one is bound. If it changed conformation with only a proton bound, the protons would move across the \n membrane without useful work (the active transport of lactose) being accomplished. In other words, the potential energy of the pmf would be spent for nothing. See Problem 3 in Chapter 11 and the course pack on pages 215-216.
76
New cards
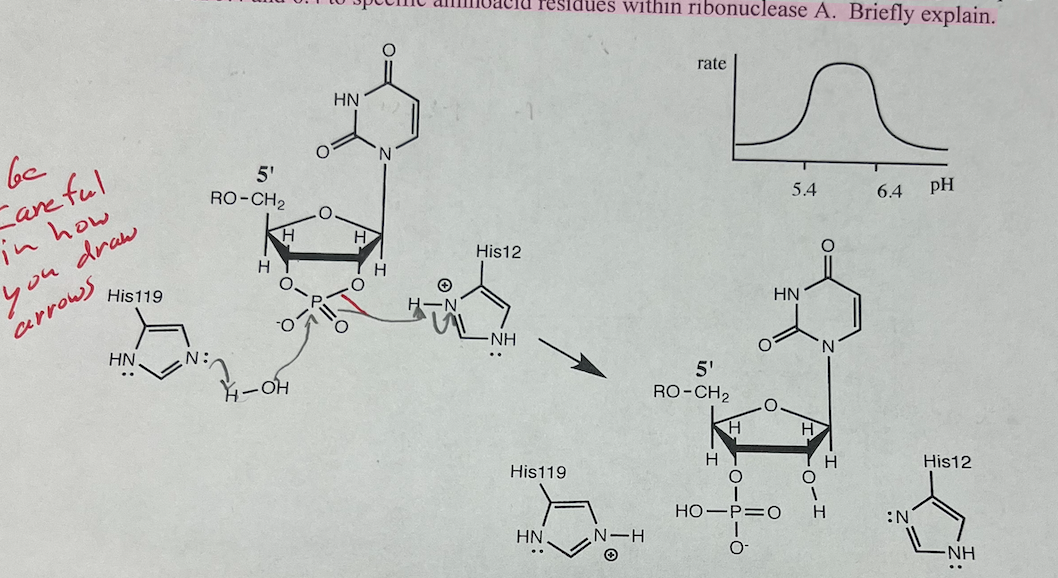
22a. Add arrows to the second half of the reaction catalyzed by ribonuclease A.
The base of each arrow starts at a lone pair of electrons or a bond, and the tip points toward a new bond or new lone pair.
77
New cards
22b. The pH-rate profile (graph of rate versus pH) for ribonuclease A is shown. Assign the pKa values of 5.4 and 6.4 to specific amino acid residues within ribonuclease A. Briefly explain.
\
ribonuclease A will not function quickly below pH 5.4 because His119 becomes protonated and cannot act as a general base. Its role is to activate the water molecule so that it becomes a stronger nucleophile. His12 becomes deprotonated above pH 6.4; therefore, it cannot make the oxygen atom a better leaving group via general acid catalysis. See Problem 15 in Chapter 8
ribonuclease A will not function quickly below pH 5.4 because His119 becomes protonated and cannot act as a general base. Its role is to activate the water molecule so that it becomes a stronger nucleophile. His12 becomes deprotonated above pH 6.4; therefore, it cannot make the oxygen atom a better leaving group via general acid catalysis. See Problem 15 in Chapter 8
78
New cards
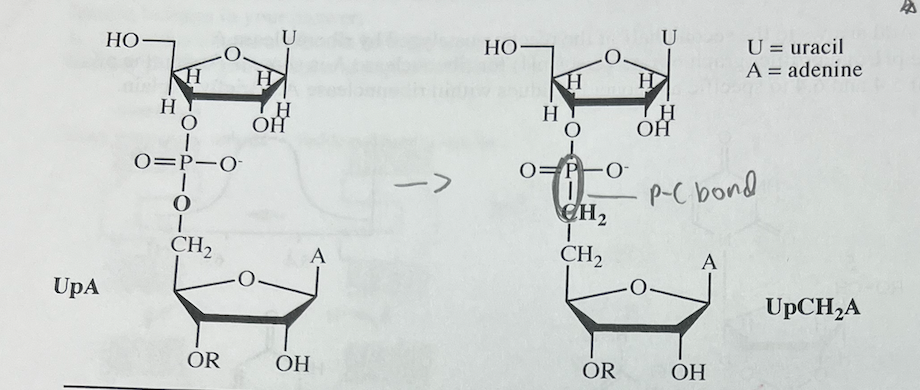
(3) Indicate in which direction and why the rate of ribonuclease-catalyzed hydrolysis of the dinucleotide UpA changes when UpCHA is added to the solution. Use terminology appropriate to enzyme Kinetics.
UpCH2A inhibits Ribonuclease A (it slows down the hydrolysis of RNA). UpCH2A competes against UpA for binding to the active site of Ribonuclease A. When UpCH2A binds, no reaction occurs. Inhibitors typically bind rapidly and reversibly to the active site of their \n target enzyme, and competitive inhibitors prevent the enzyme from binding the substrate. \n Ribonuclease A cannot hydrolyze the P-C bond of UpCH2A because a carbanion is an extremely poor leaving group. See homework problem 16 in Chapter 8. Other inhibitors also use a P-C bond in place of a P-O bon
79
New cards
24 .The structure of a minor tautomer of thymidine is shown. Draw the major tautomer. Would the minor tautomer form a Watson-Crick base pair with an adenine residue? Briefly explain.
The lack of a hydrogen atom on N3 means that the minor tautomer cannot be a hydrogen bond donor to adenine. The H-bond donor and acceptor have switched places in the minor tautomer versus the major tautomer. See homework problem 17 in Chapter 8