Political Violence and Democratic Regimes: Key Concepts
1/322
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
323 Terms
Political Violence
Violence outside state control, politically motivated.
Contentious Politics
Collective political struggle including revolutions and protests.
Institutional Explanations
Focus on state and social systems' role in violence.
Ideational Explanations
Impact of political and religious ideas on violence.
Individual Explanations
Motivations of individuals engaging in political violence.
Determinism
Belief that behavior is determined by external factors.
Free Will
Belief that individuals can make independent choices.
Particularistic Approach
Focus on specific contexts in political explanations.
Universal Approach
General principles applicable across various contexts.
Revolution
Public seizure of state to overturn government.
Coup d'état
Elite overthrow of government, unlike public revolutions.
Relative Deprivation Model
Revolution occurs when expectations exceed actual conditions.
Institutional Explanations of Revolution
Power competition leads to reforms inciting revolutions.
Consequences of Revolutions
Revolutionary states often become less democratic, more violent.
Terrorism
Violence by nonstate actors against civilians for political goals.
State-Sponsored Terrorism
State support of terrorism as foreign policy tool.
Guerrilla War
Nonstate violence targeting the state, follows war rules.
Economic Factors in Terrorism
Weak economies and education linked to terrorism.
Political Institutions
Weak state capacity may incentivize political violence.
Ideological Explanations
Specific ideologies or religions blamed for violence.
Violence and Interstate War
Revolutionary states may engage in external conflicts.
Psychological Approach to Revolution
Focus on individual psychology in revolutionary contexts.
Phases of Revolution Scholarship
Evolving focus from descriptive to psychological to institutional.
Terrorism
Violent acts aimed at instilling fear for political goals.
Nihilism
Belief that life lacks meaning, leading to violence.
Apocalyptic viewpoints
Beliefs that destruction leads to a new order.
Political impact of terrorism
Disrupts economies and destabilizes political systems.
Democratic erosion
Weakening of democratic institutions due to security measures.
Regime instability
Terrorism can lead to the collapse of governments.
Revolutionary motivations
Desire to transform or destroy existing institutions.
Guerilla groups
Accept opponents as legitimate, open to negotiation.
Indiscriminate violence
Terrorist violence targets civilians without discrimination.
Religious fundamentalism
Ideological belief system linked to political violence.
Hostility to modernity
Rejection of modern institutions causing societal suffering.
Cosmic war
Belief in a divine struggle against modern states.
Messianic beliefs
Expectation of ultimate victory for righteous believers.
Democratic participation
Political engagement that may reduce violence likelihood.
Surveillance state
Increased government monitoring in response to violence.
Iran's ethnicity
Majority Persian, not Arab, distinct cultural identity.
Farsi language
Language spoken in Iran, distinct from Arabic.
Pan-Islamic movement
Iranians do not identify with broader Islamic unity.
State violence
Government's harsh response to protests and dissent.
Rolling protests
Widespread demonstrations challenging the Iranian regime.
1979 Iranian Revolution
Event marking the establishment of the current regime.
Political violence solutions
Democracies may mitigate violence through political options.
Long-term goals of terrorism
Generally unsuccessful in achieving lasting political change.
Persians
Ethnic group migrated from Central Asia to Persia.
Islam's Arrival
Brought by Arabs in 7th century after Muhammad's death.
Shiism
State religion adopted to differentiate from Sunni Ottomans.
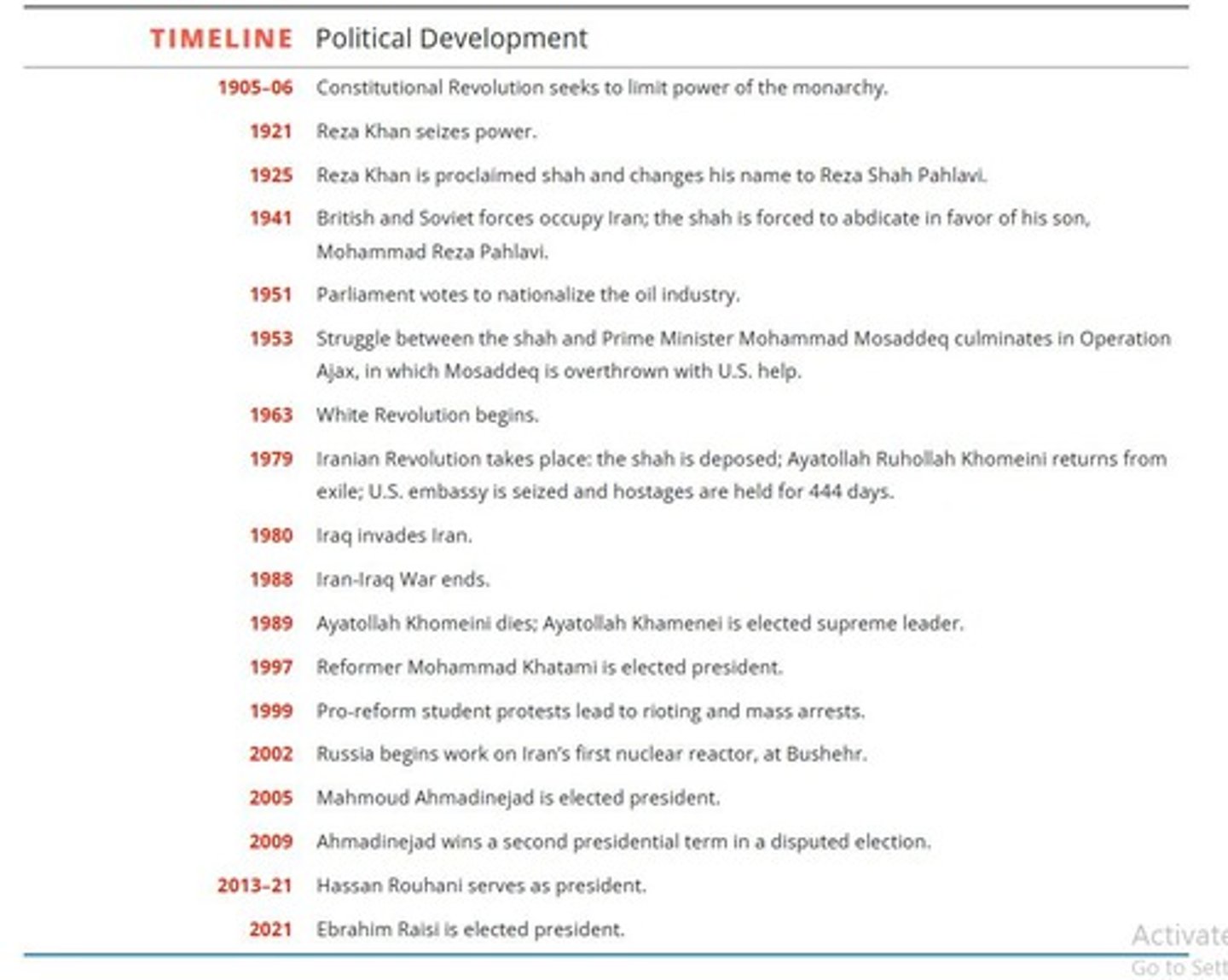
Constitutional Revolution
1906 protest for limits on Qajar monarchy's power.
Majlis
First elected assembly and legislative body in Iran.
Republicanism
Iran's first attempt at democracy, akin to American Revolution.
Secularists
Conflict with ayatollahs over future regime direction.
Women's Rights
Shah's modernization included education access for women.
Hijab and Chador
Symbols of modesty, later banned in public schools.
Operation Ajax
CIA-backed coup restoring the shah's power in Iran.
National Front
Political party advocating for reduced monarchy power.
White Revolution
Shah's modernization policies including land reform and literacy.
Military Expansion
Iran built military to assert regional power and influence.
Oil Revenue
Billions flowed into Iran, creating a middle class.
Khomeini
Leader who capitalized on turmoil to establish Islamic regime.
Islamic Republic
New political system established after the revolution.
Charismatic Authority
Khomeini's influence undermined the secular provisional government.
Lavish Lifestyle
Wealth concentrated among shah's family and supporters.
Protests in Tehran
Massive demonstrations called for monarchy's end in September.
Political Turmoil
Uncertainty about the type of regime post-revolution.
Violent Birth
The Islamic Republic established amidst significant conflict.
Cultural Differences
Persian and Arab cultures retained distinct characteristics post-Islam.
Modernization Policies
Included privatization and enfranchisement under the shah.
Islamic Republic
Government form guiding people towards Islamic principles.
Supreme Leader
Highest authority controlling military and judiciary.
Guardian Council
Body ensuring legislation aligns with Islamic criteria.
Majlis
Iran's parliament with limited legislative authority.
Revolutionary Guard
Paramilitary force supporting the supreme leader's power.
Constitution
Document mandating laws based on Islamic criteria.
Democratic Participation
Elections exist but choices are heavily constrained.
Voter Turnout
70% of eligible voters participated in 2017 election.
Civic Organizations
Most are state-controlled or banned in Iran.
Reformists
Political faction advocating for changes within the system.
Conservatives
Political faction maintaining traditional power structures.
Expediency Council
Advisory body mediating disputes between councils.
Elected Offices
Candidates must be approved by the Guardian Council.
Public Sphere
Area of civic activity increasingly repressed in Iran.
Civil Society
Flourished in the 1990s but faced government attacks.
Press Restrictions
2000 law limited press operations, closing many outlets.
Electronic Communication
Area of civic activity thriving despite state control.
Islamic Revolution
Khomeini's movement aimed at spreading Islamic governance.
Judicial Influence
Supreme leader appoints chief justice, affecting judiciary.
Legislative Veto
Guardian Council vetoes reformist legislation frequently.
Political Repression
Opposition faced suppression under the new government.
Nuclear Program
Revolutionary Guard's unclear role in development.
Direct Elections
Held for Majlis, Assembly of Experts, and presidency.
Internet Activism
Protests against government restrictions online in Iran.
Headscarves
Traditional attire for women in Iran, often enforced.
Ethnic Identity
Sense of belonging to a specific ethnic group.
Azeris
Largest ethnic minority in Iran, connected to Azerbaijan.
Kurds
Ethnic group in Iran, facing discrimination and protests.
Baluchis
Ethnic minority in Iran, located near Pakistan.
Arab Population
Ethnic group along the Persian Gulf in Iran.
Centralized Political System
Government structure limiting power distribution to regions.