DNA structure and function
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Define antiparallel
the two strands of the double helix run in opposite directions
Define base
A nitrogen-containing rings
Purine or pyrimidine
Chemically/physically distinguishable
CuT = pyrimidine
Au:Gold = purines
Define base pair
Purines CANNOT bind to other purines because of chemical structure
Keto group of one base binds to amino group of another
Define complementarity
one strand complements the other
Necessary because of base pairing requirements (hydrogen bond formation)
Define double helix
a pair of antiparallel helices intertwined about a common axis, especially that in the structure of the DNA molecule.
Define template
A pair of parallel helices intertwined about a common axis, especially that in the structure of the DNA molecule.
A DNA mold that codes for other DNA or proteins
Define intron
part of a sequence that is not used to make a protein structure
“unused” - but does have some unknown function
Define exon
part of a sequence that is used/transcribed into mRNA or eventually proteins
Spliced together to form a functional gene
What type of bond exists between bases/across DNA
Hydrogen bonds
contribute to double helix stability
What type of bonds are between sugar and phosphate in DNA backbone?
Covalent bonds
strong chemical bond with a sharing of electron pairs with a balance of attractive and repulsive forces
How many hydrogens bonds are between C-G and A-T
3 and 2
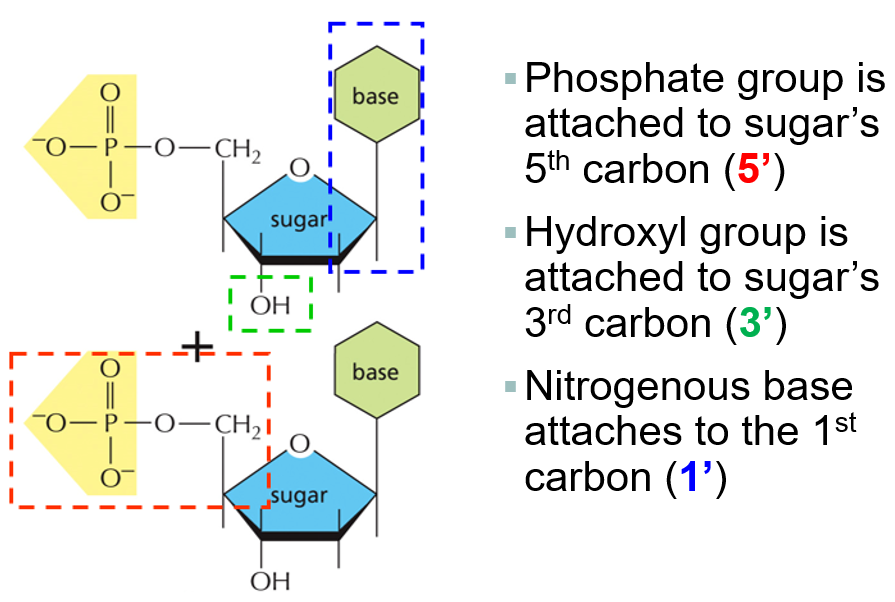
What makes up a nucleotide
nitrogenous base, five carbon sugar, and phosphate group
Sugar and phosphate form DNA back bone with covalent bonds
Where are phosphodiester bonds found
between the sugar and phosphate group in backbone
nucleotides are joined by the PO4 of one nucleotide attaching to the 3’ carbon of the next nucleotide to form a polynucleotide
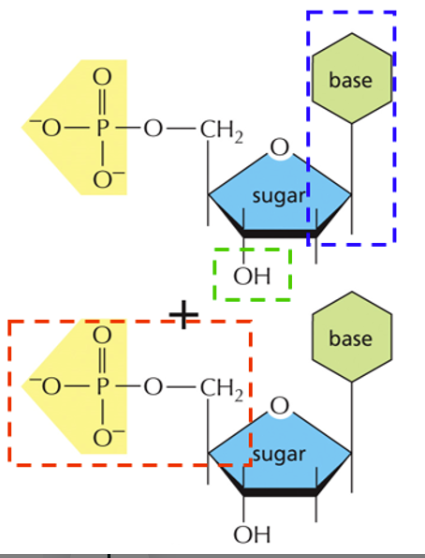
Identify the boxes and the bonds
See the image
What is the function of DNA in the overall physiology of the body
Purpose of DNA = to archive information
Not functional without it forming RNA
Is the blueprint for everything else
Protected in the nuclear membrane so it doesn’t get transported out or damaged
Only 1% of human genome is protein coding