OROFACIAL W1: Oral Cavity + Mucosa
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
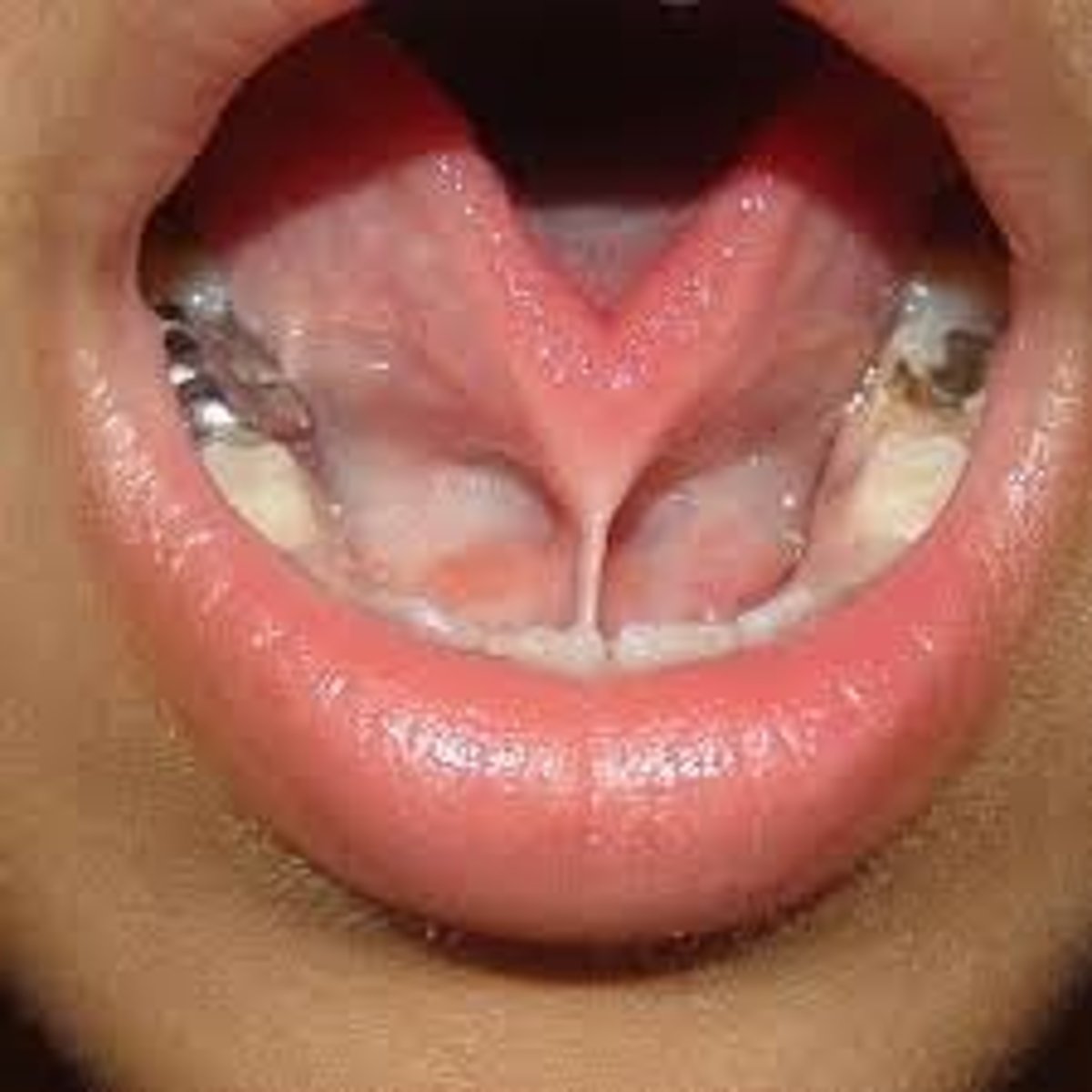
What are tonsillar pillars?
2 folds of tissue on each side of the throat
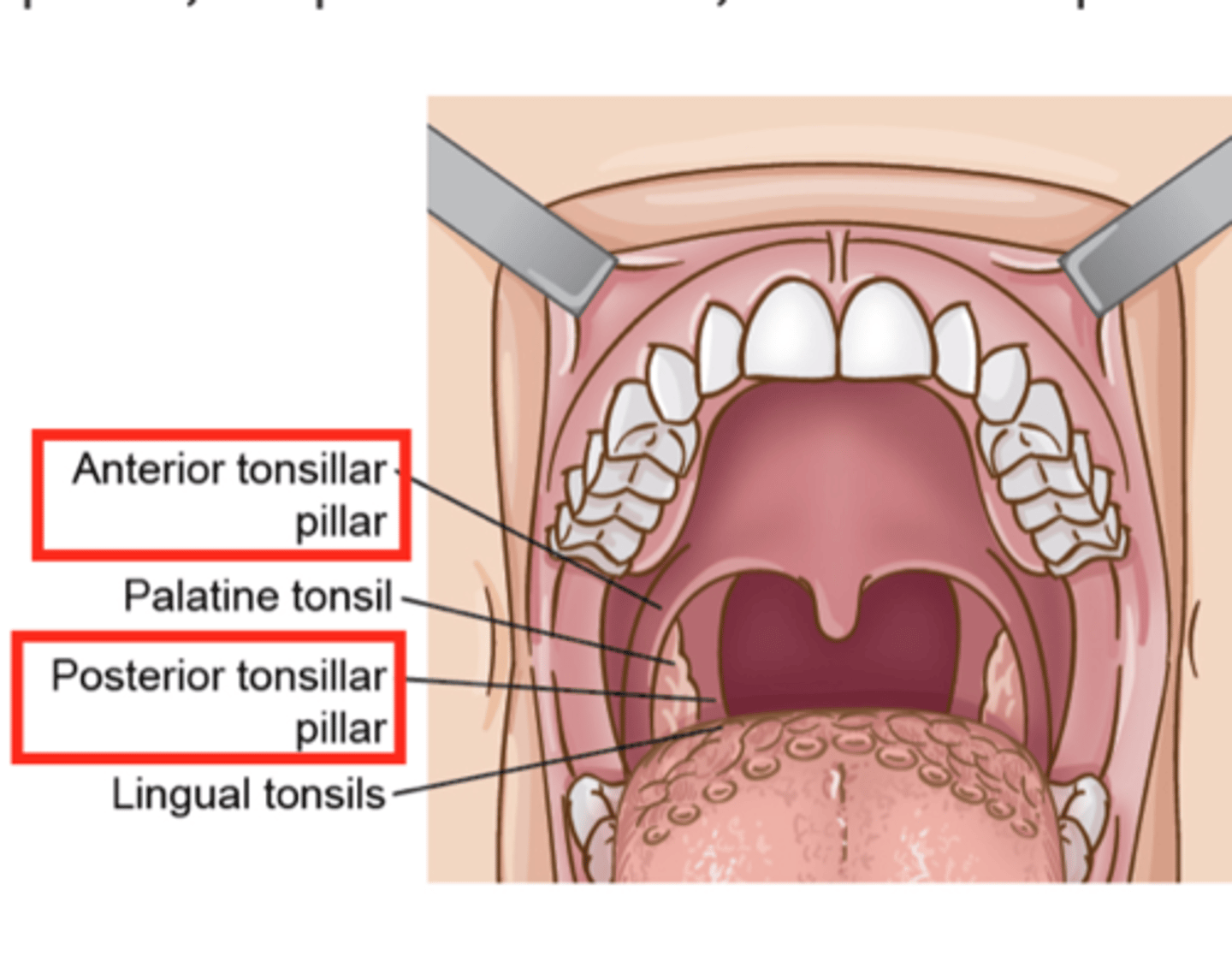
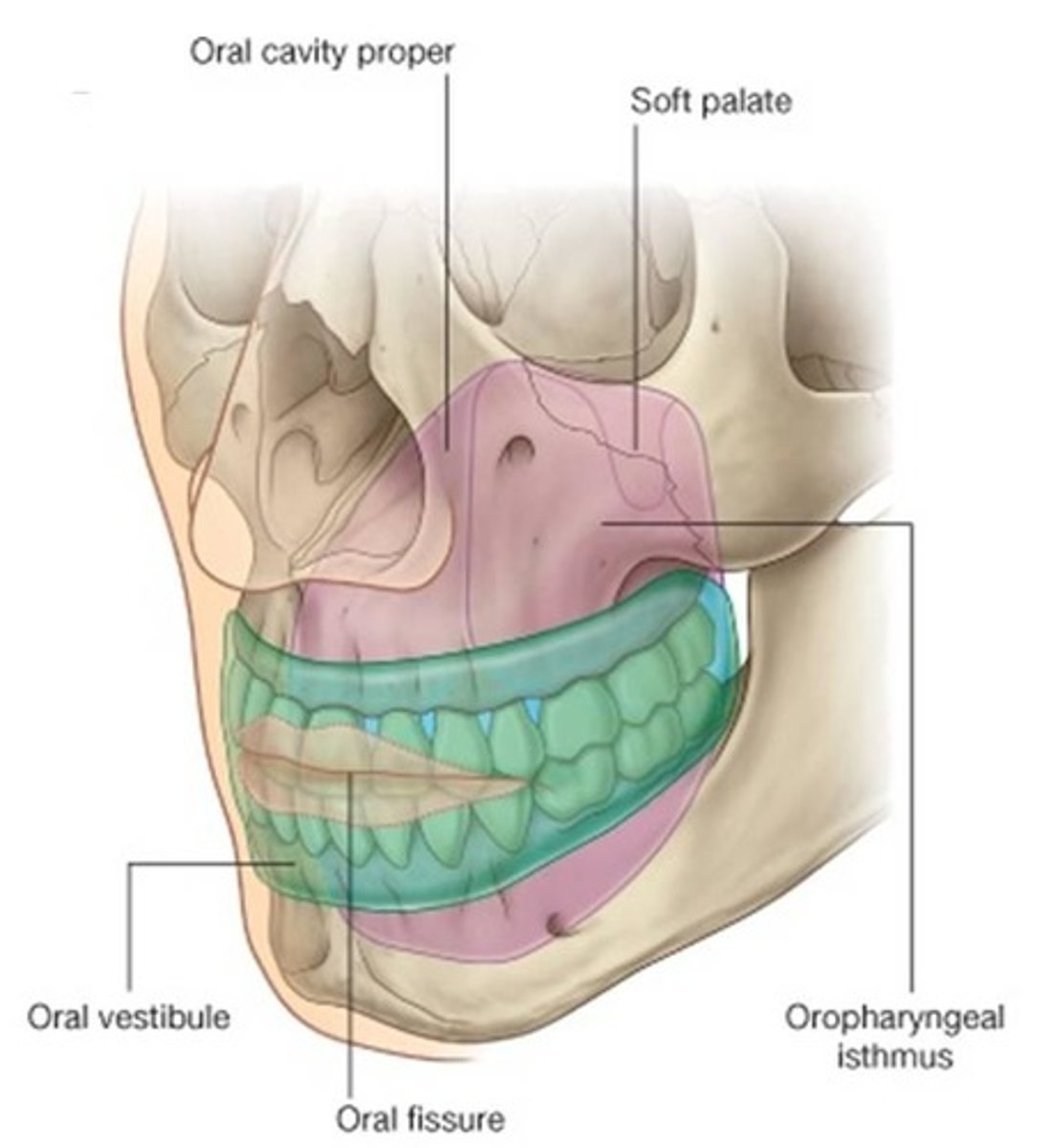
What are the 2 divisions of the oral cavity?
1. Oral Vestibule - space that exists between the lips/cheeks and the teeth
2. Oral Cavity Proper - area surrounded by the teeth back to the palatine tonsils
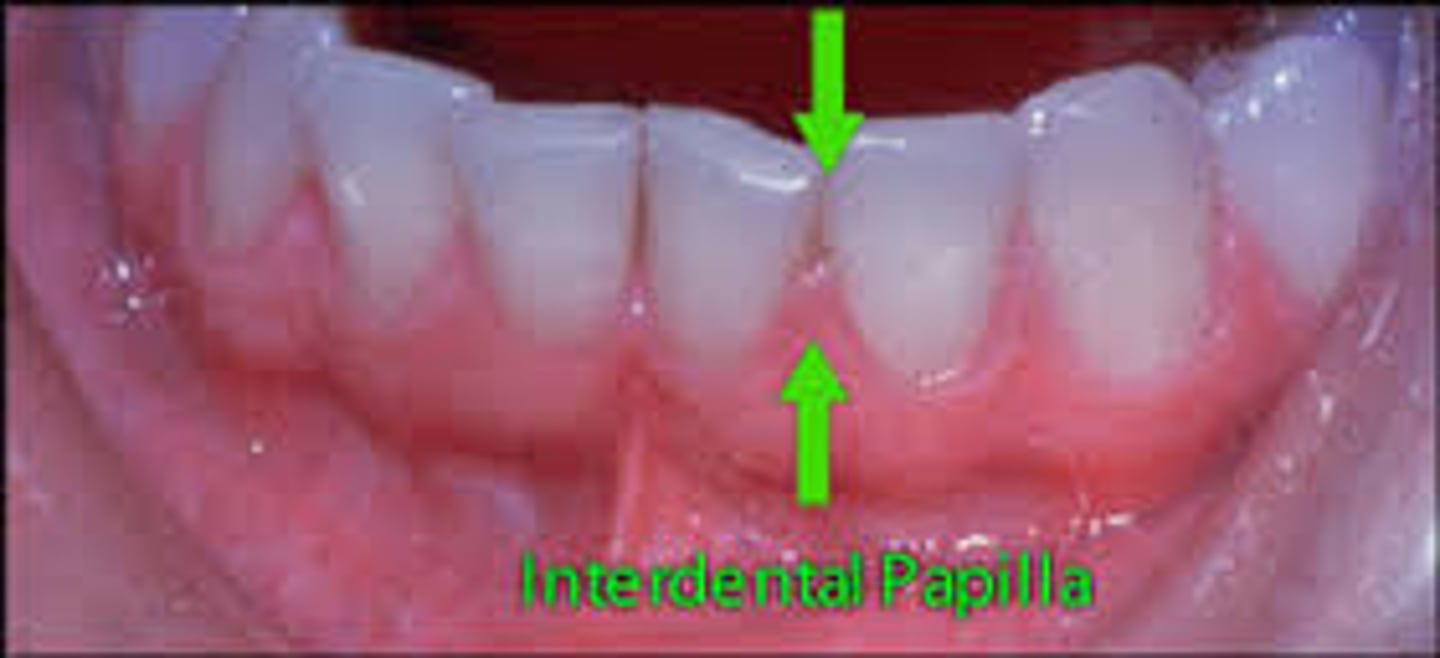
Define interdental papilla - what is another name we use for it?
interdental gingiva - projection of gingiva (gum tissue) between the teeth
What is the vermilion zone of the lips?
Transitional zone of reddish tissue between the dry skin of the face and the moist mucosa of the oral cavity (lips)
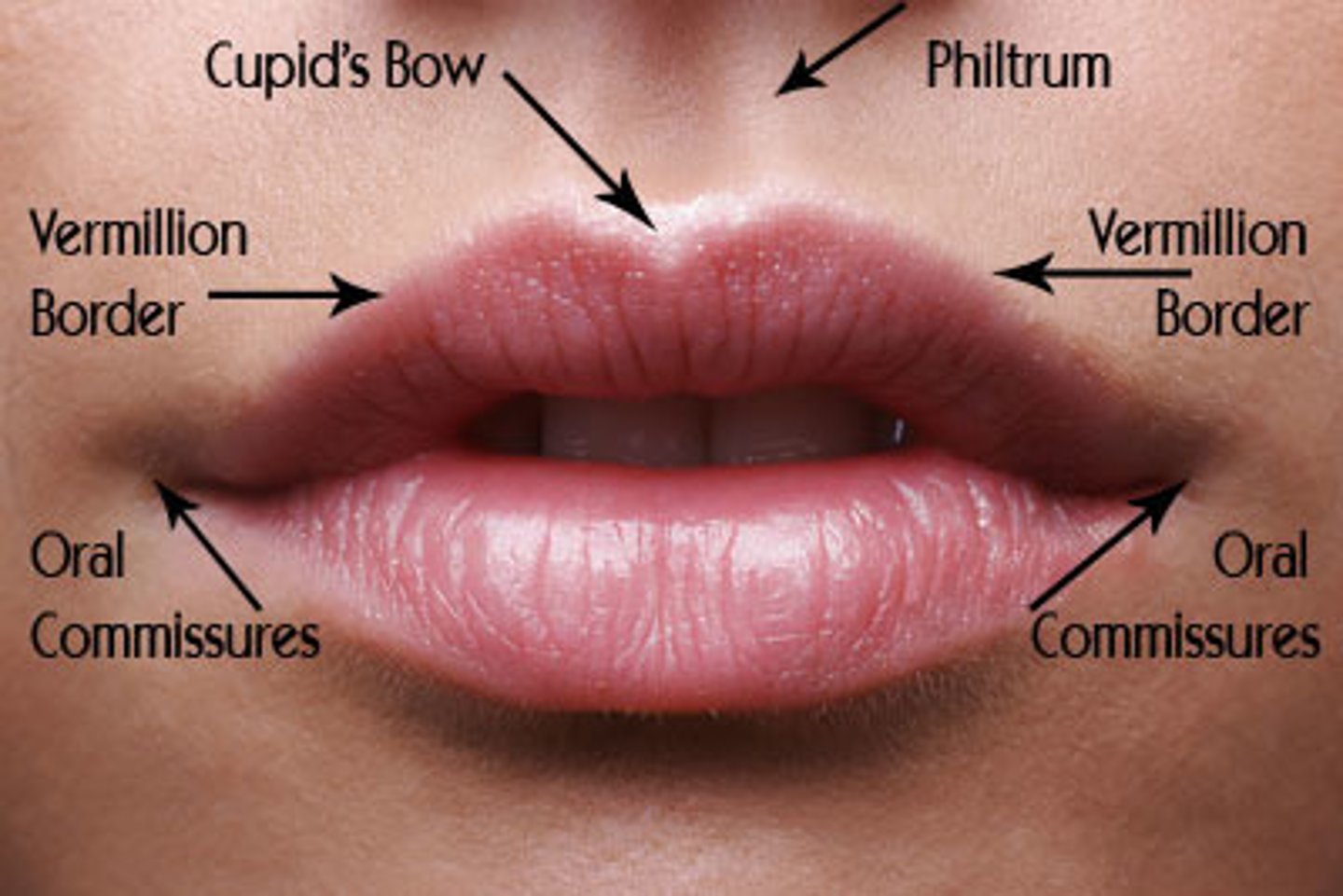
What is the vermillion border of the lips?
Outlines the vermillion zone
- area where cold sores commonly appear here
What is the Philtrum?
Small depression at the midline of the upper lip (above cupids bow)
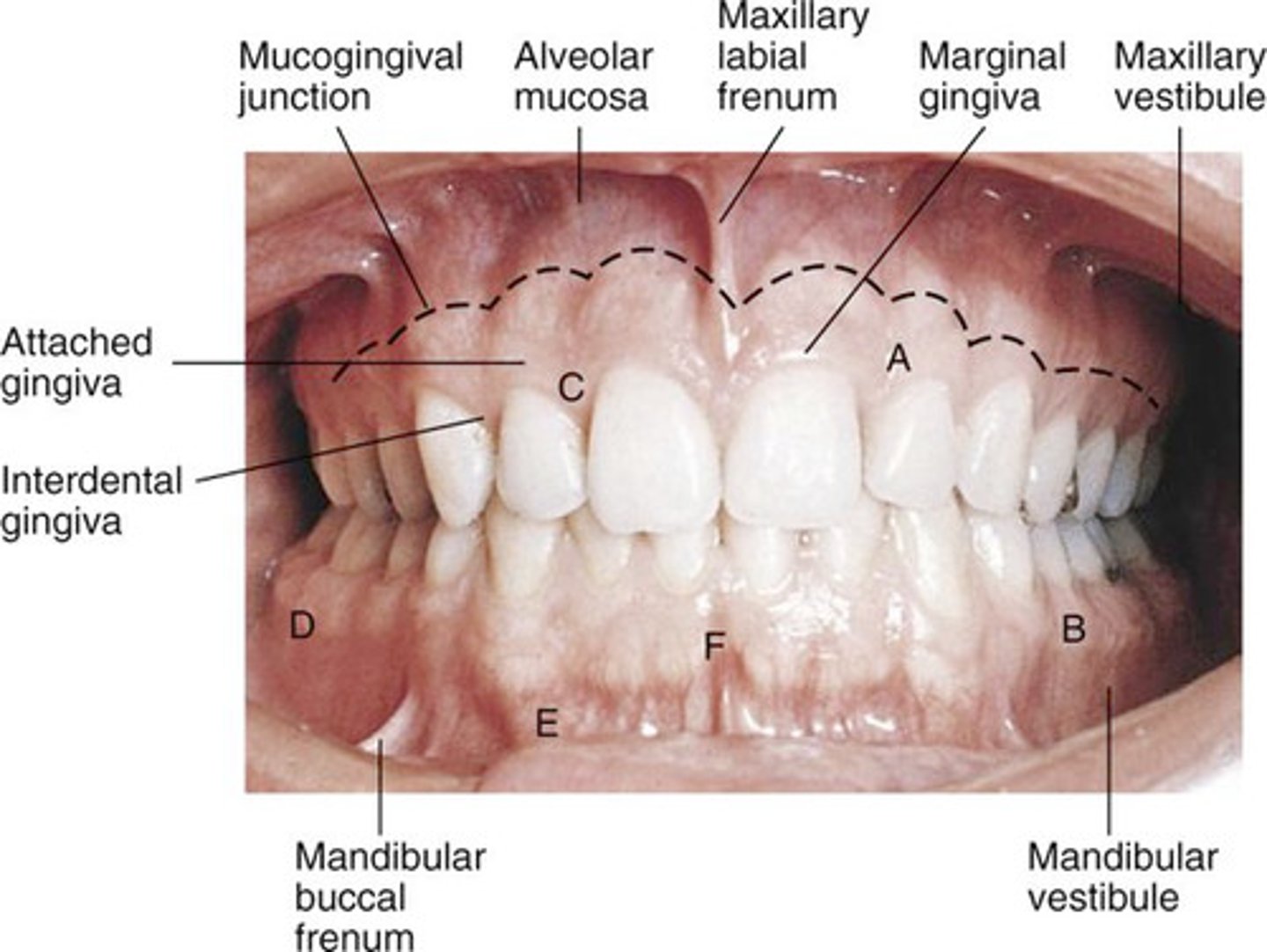
What is the mucobuccal fold?
The point where the lips/cheeks turns to go towards the gingival tissue
What is the alveolar mucosa?
The mucosa lying against the alveolar bone, loosely attached and moveable. It is reddish due to the many blood vessels
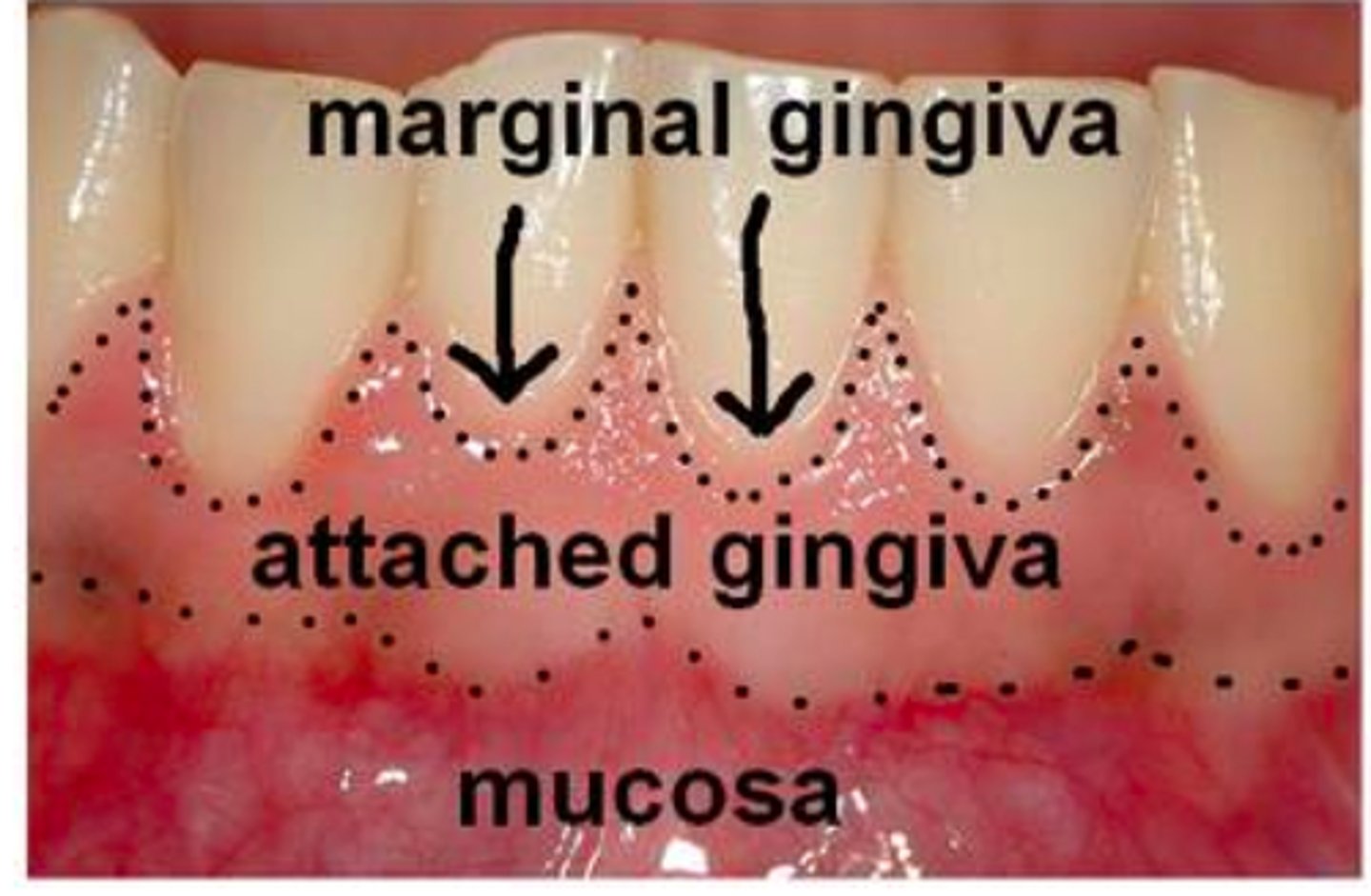
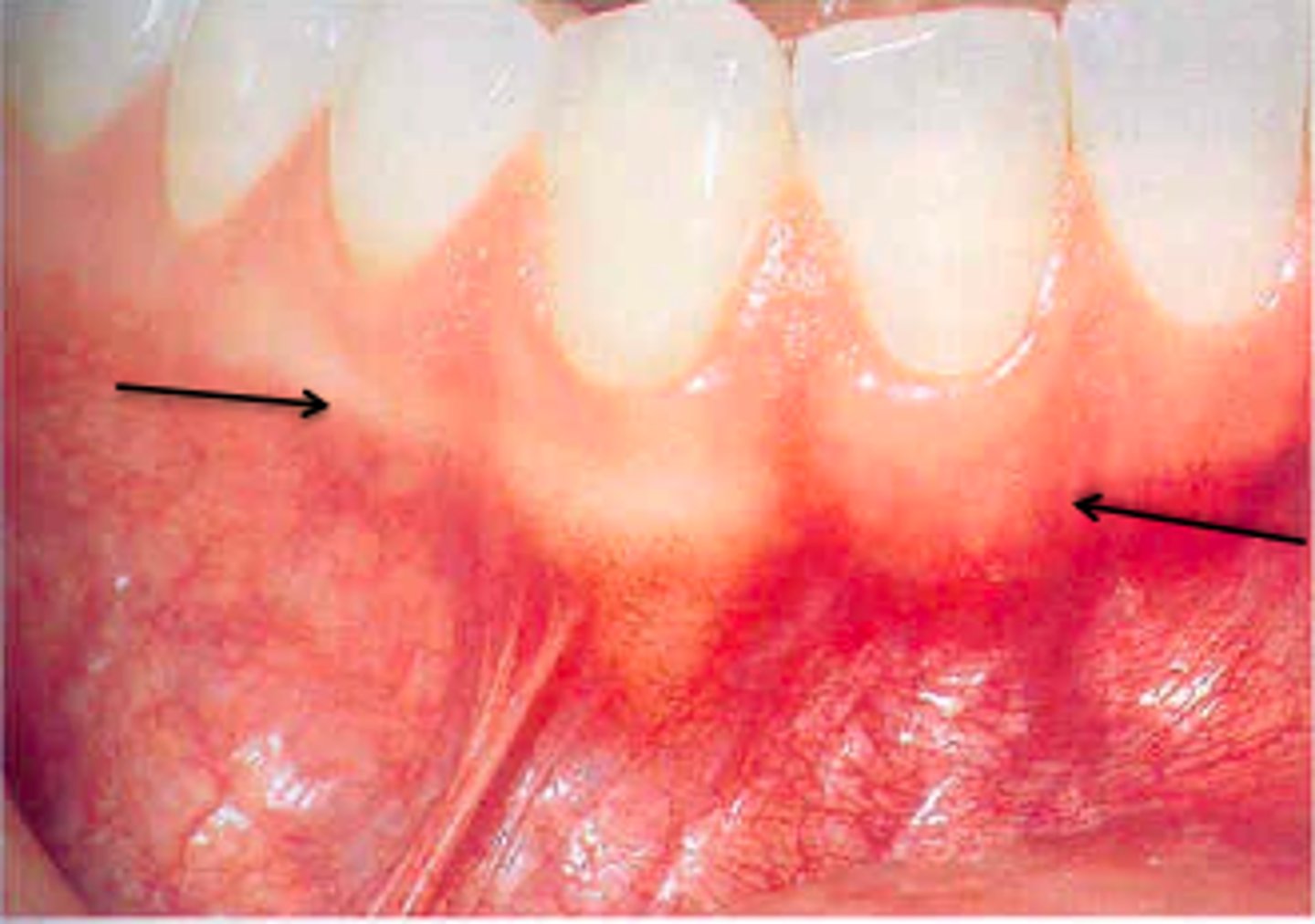
What is the mucogingival junction?
The point where the gingiva becomes tightly attached to the bone.
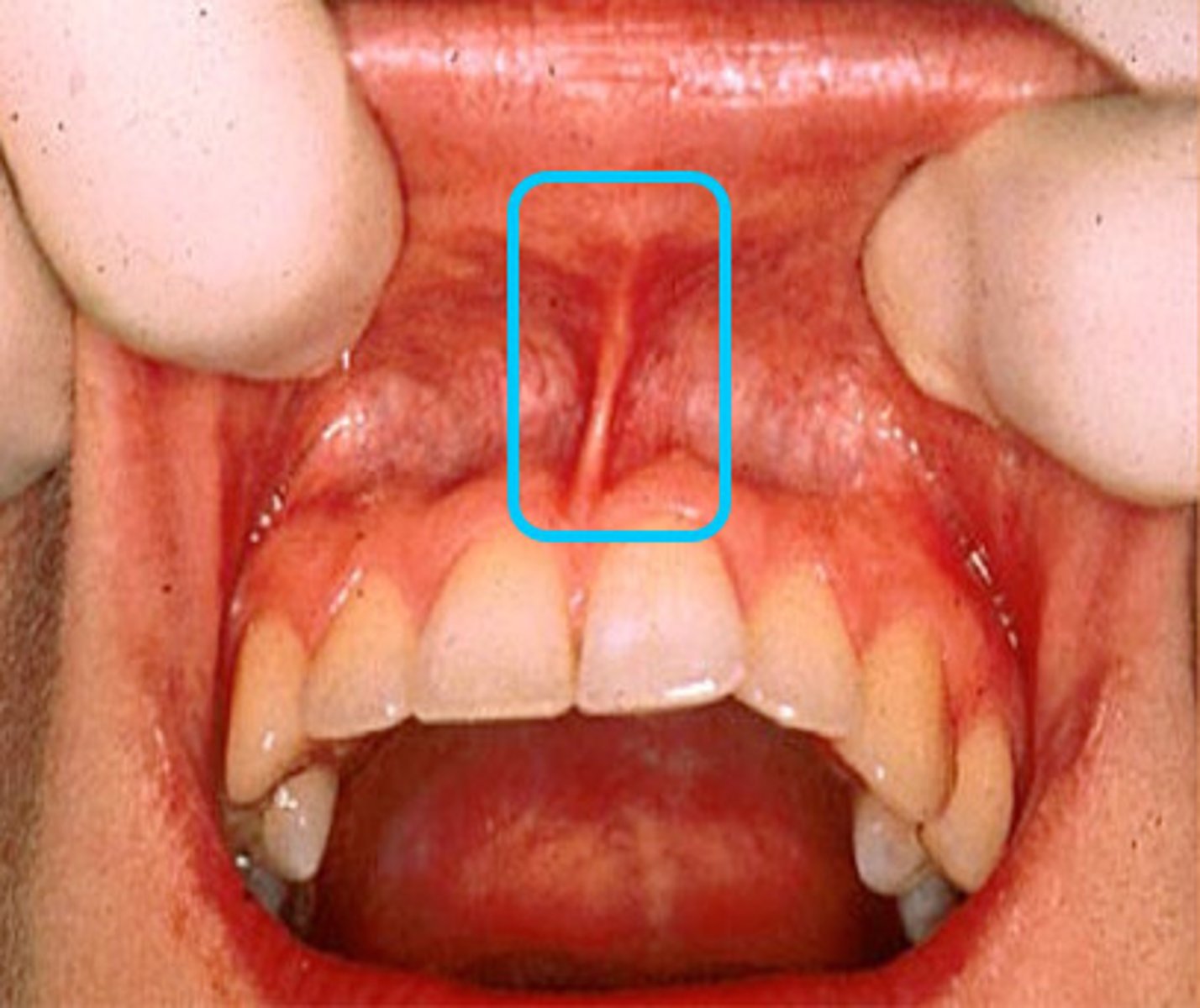
What is the maxillary labial frenum? How is the mandibular labial frenum different?
A fold of connective tissue attached to the upper alveolar mucosa. It is more pronounced than the lower frenum.
*fun fact: if the maxillary frenum is very firm or low, it may cause the central incisors to be pushed aside as it cannot penetrate it. There will be a gap between teeth (classic tooth gap look)
*if the mand. frenum extends too close to the gingiva, it can contribute to gingival recession as it pulls down on the gingiva.
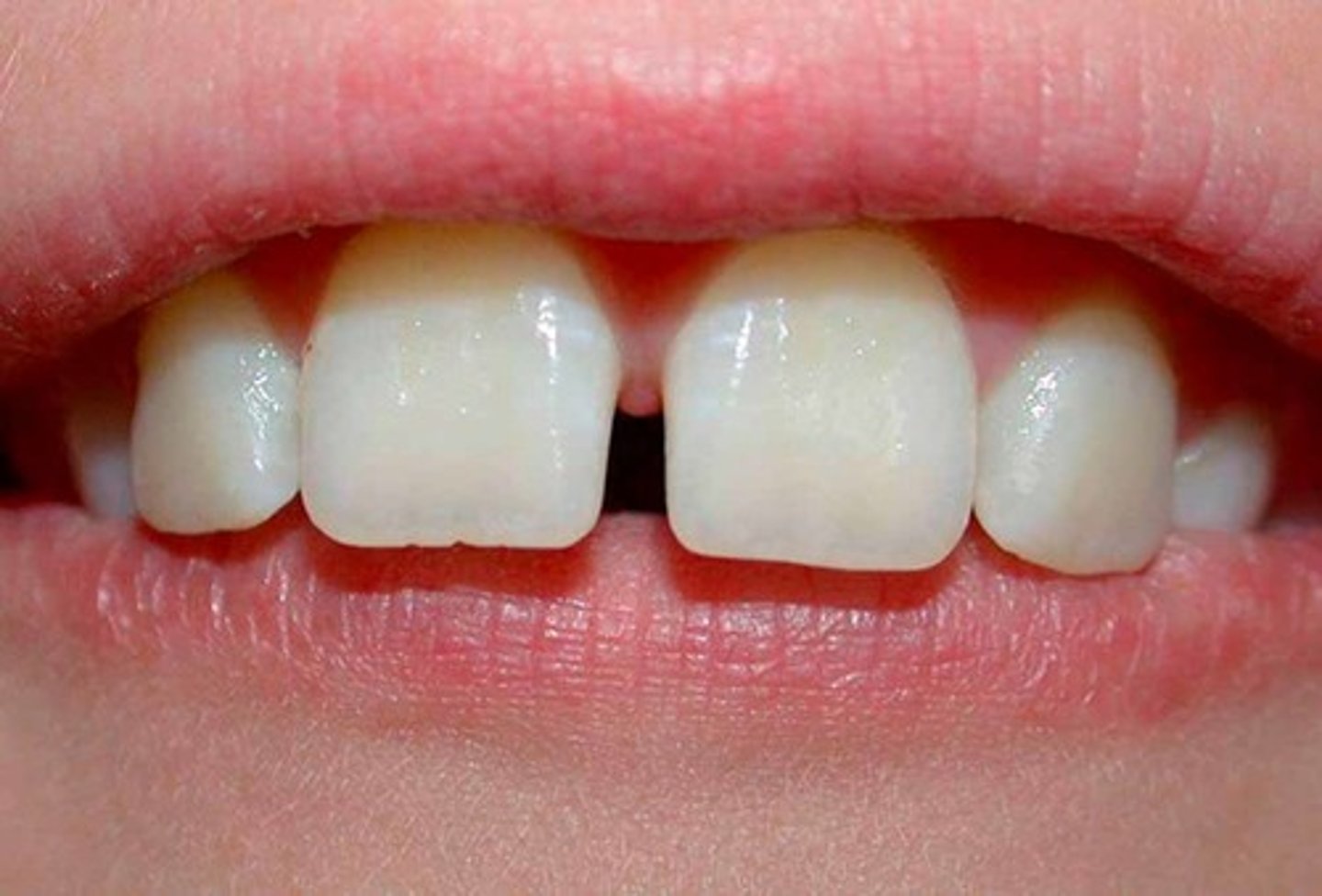
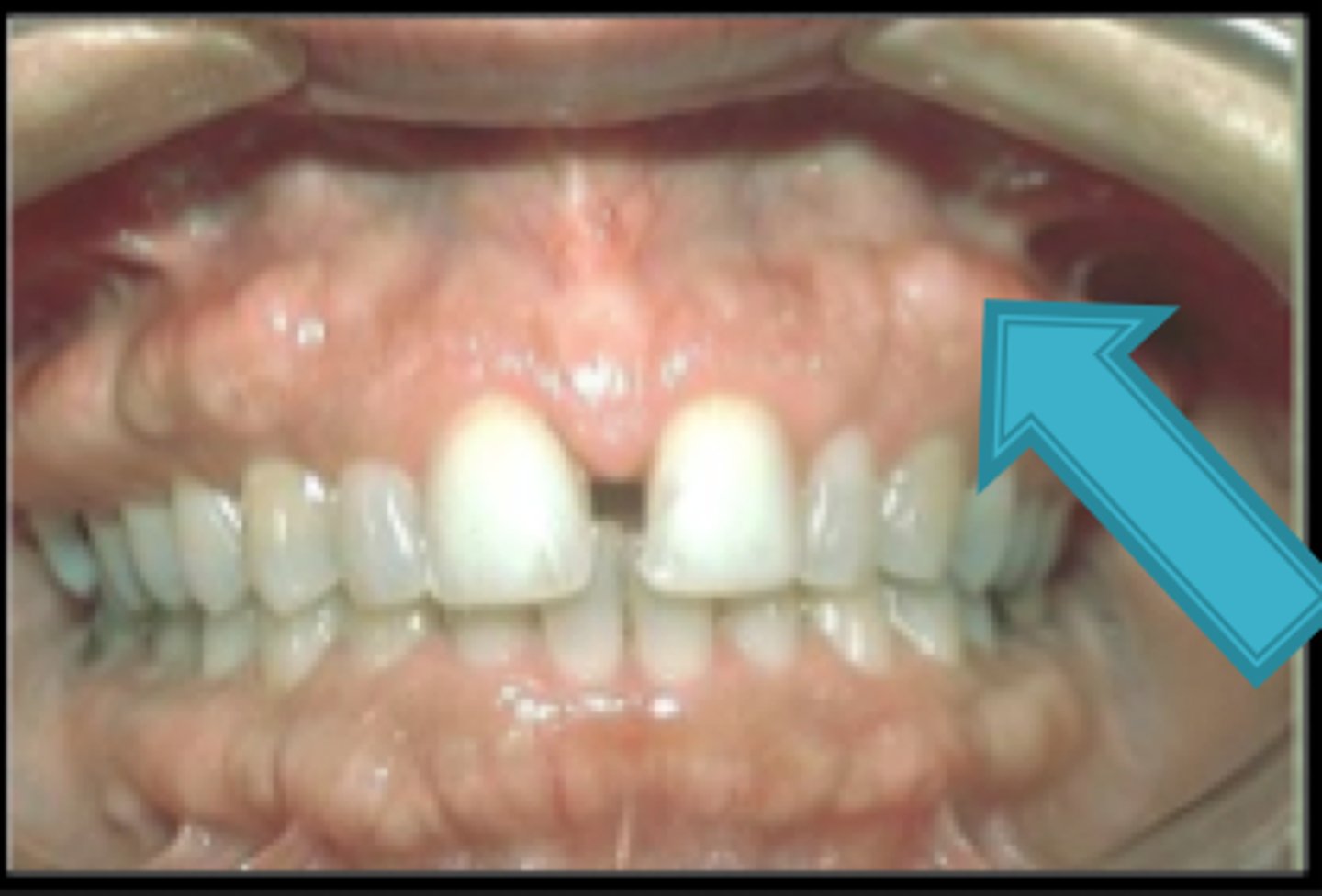
What is the Diastema?
space between teeth (may be caused by maxillary labial frenum)
Draw and label all the structures of the oral vestibule.
Vermillion zone, vermillion border, philtrum, mucobuccal fold, alveolar mucosa, mucogingival junction, maxillary and mandibular labial frenum, diastema, attached gingiva
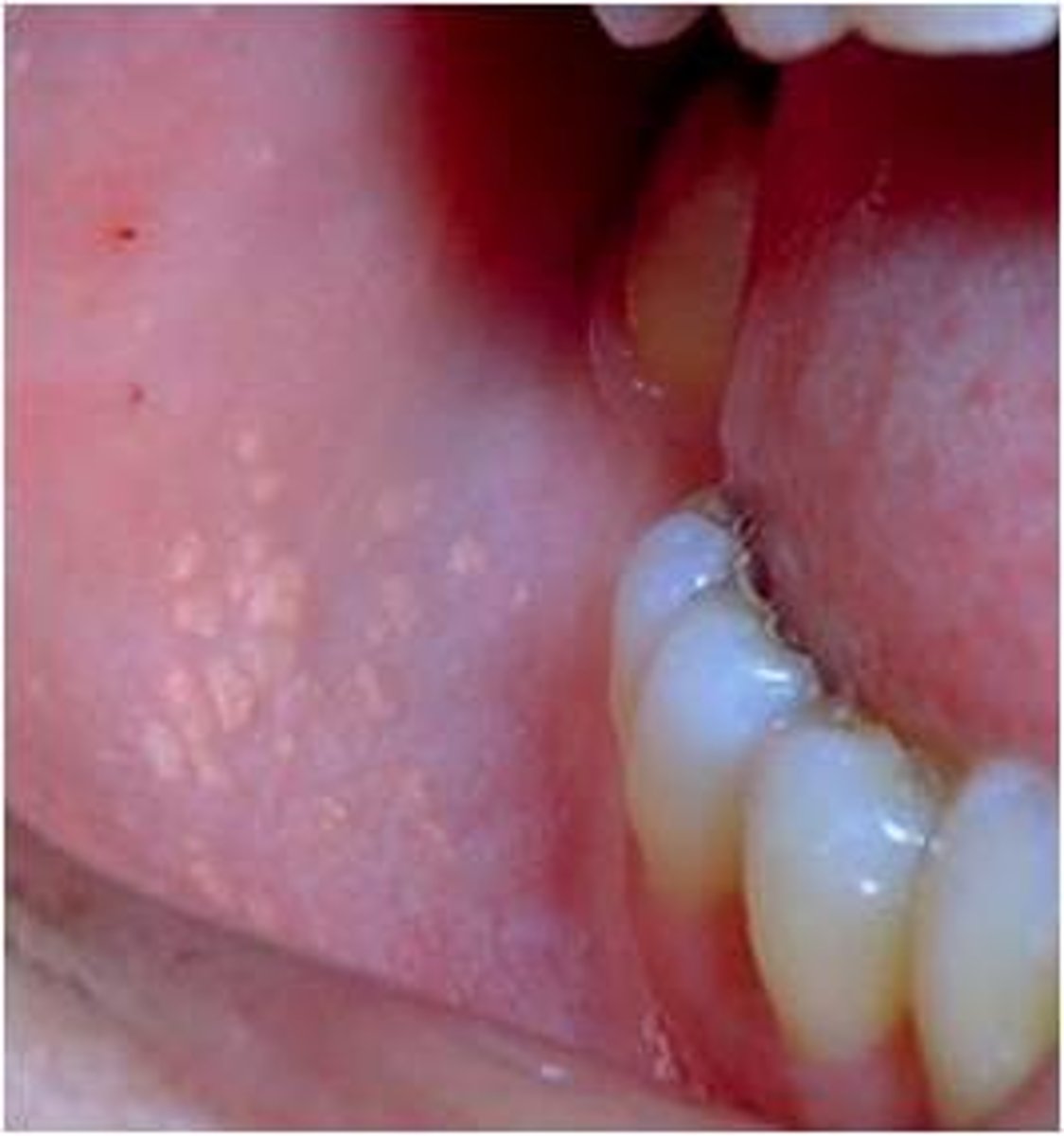
What are Fordyce granules?
Misplaced sebaceous glands in the mucosa of lips, cheeks, and retromolar pad area
*appear as yellowishh granular structures embedded in the mucosa. they are benign.
What is exostosis?
bony growths on the buccal cortical plate of the mandible and maxilla
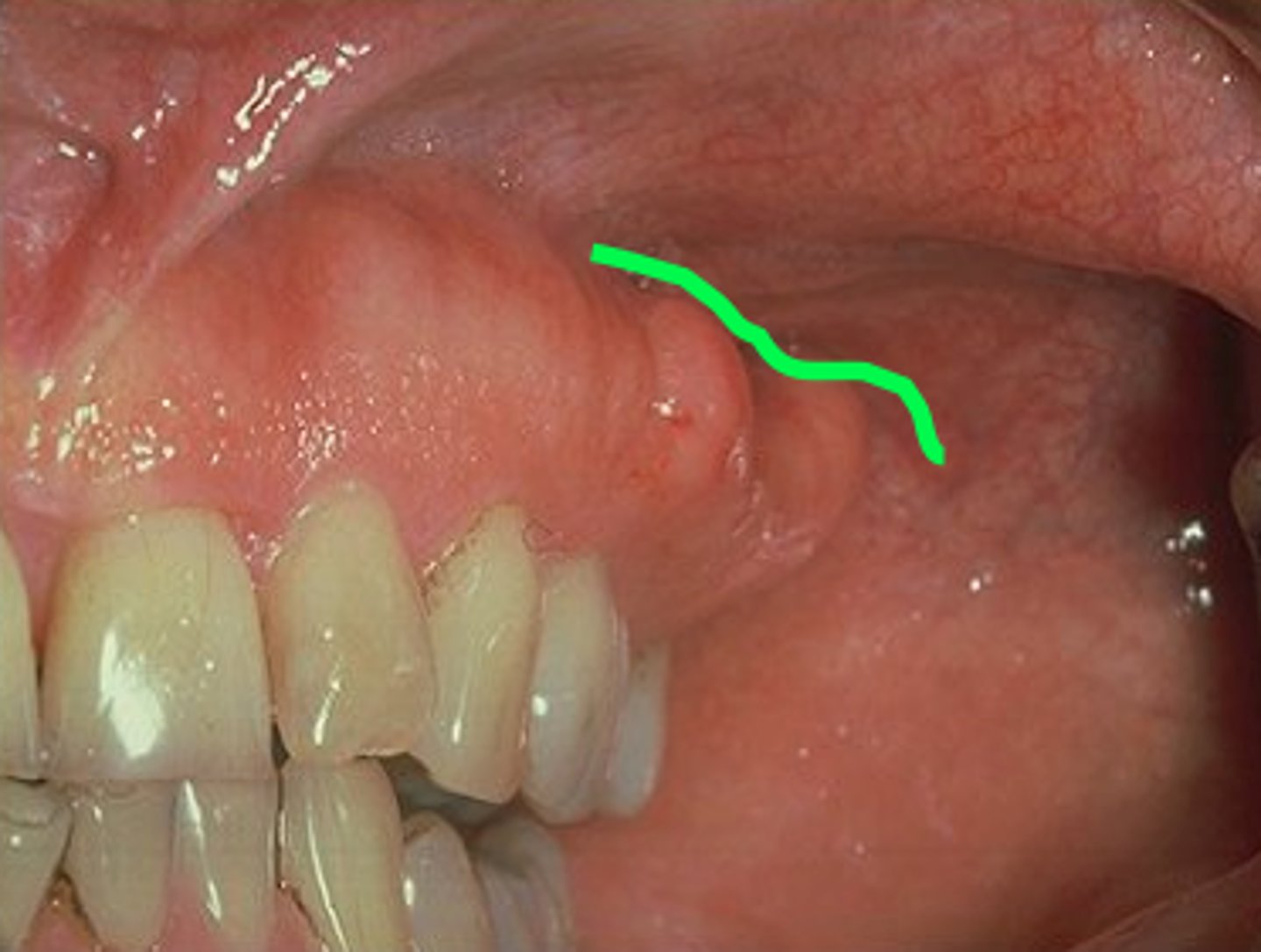
What are rugae of the oral cavity?
Oral rugae are ridges of epithelial tissue and connective tissue found on the anterior portion of the hard palate. It is covered by keratinized epithelium.
*green arrow in picture
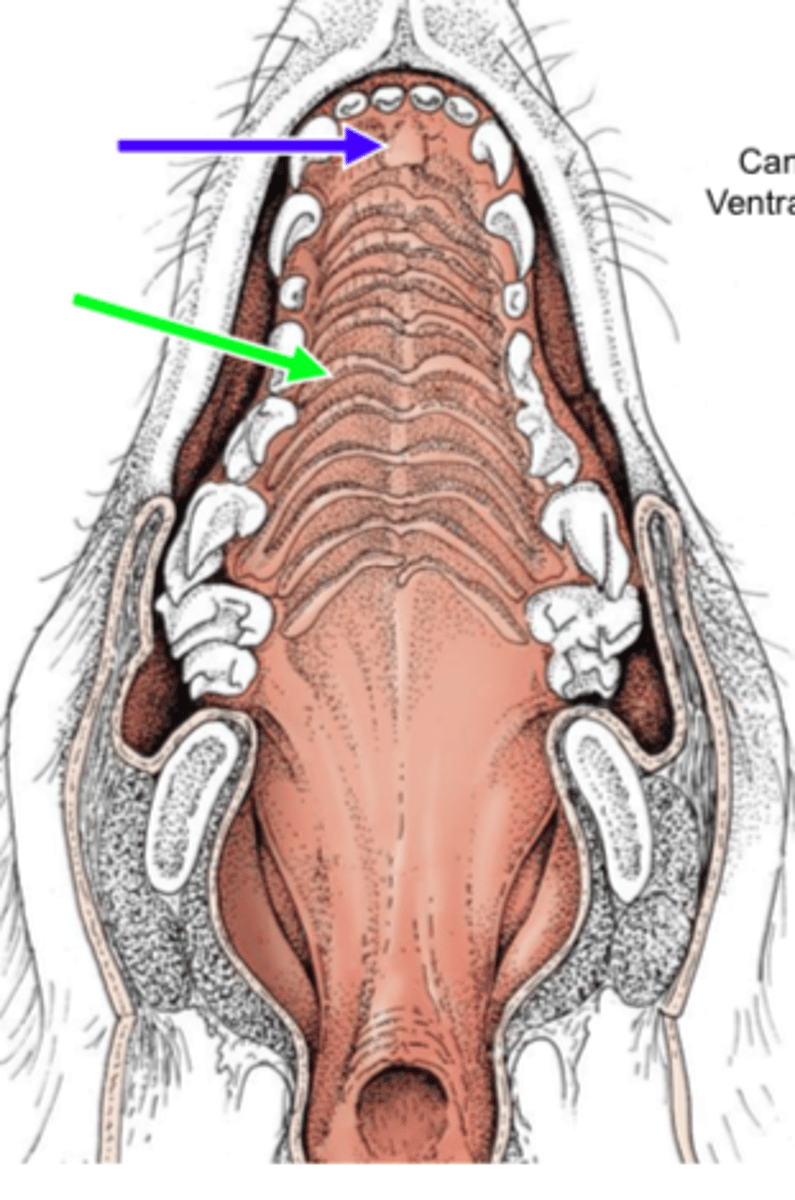
What are incisive papilla?
Bulge of tissue at the midline behind the maxillary central incisors.
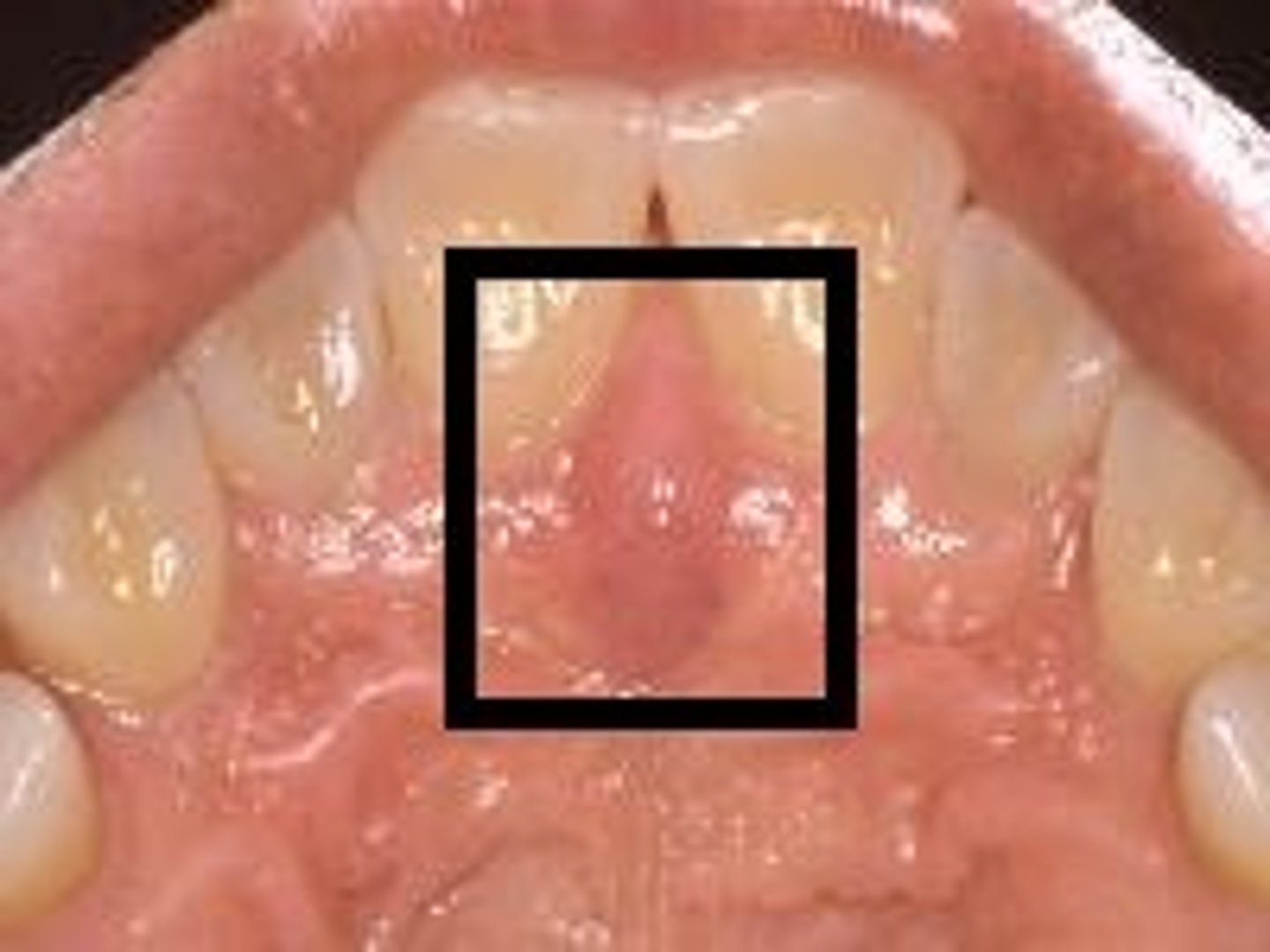
What is the function of the uvula?
The uvula aids in speech and swallowing.
What structures confines the lateral borders of the oral cavity proper?
teeth and mucosa
What is the palatoglossal arch?
anterior boundary between oral cavity and pharynx
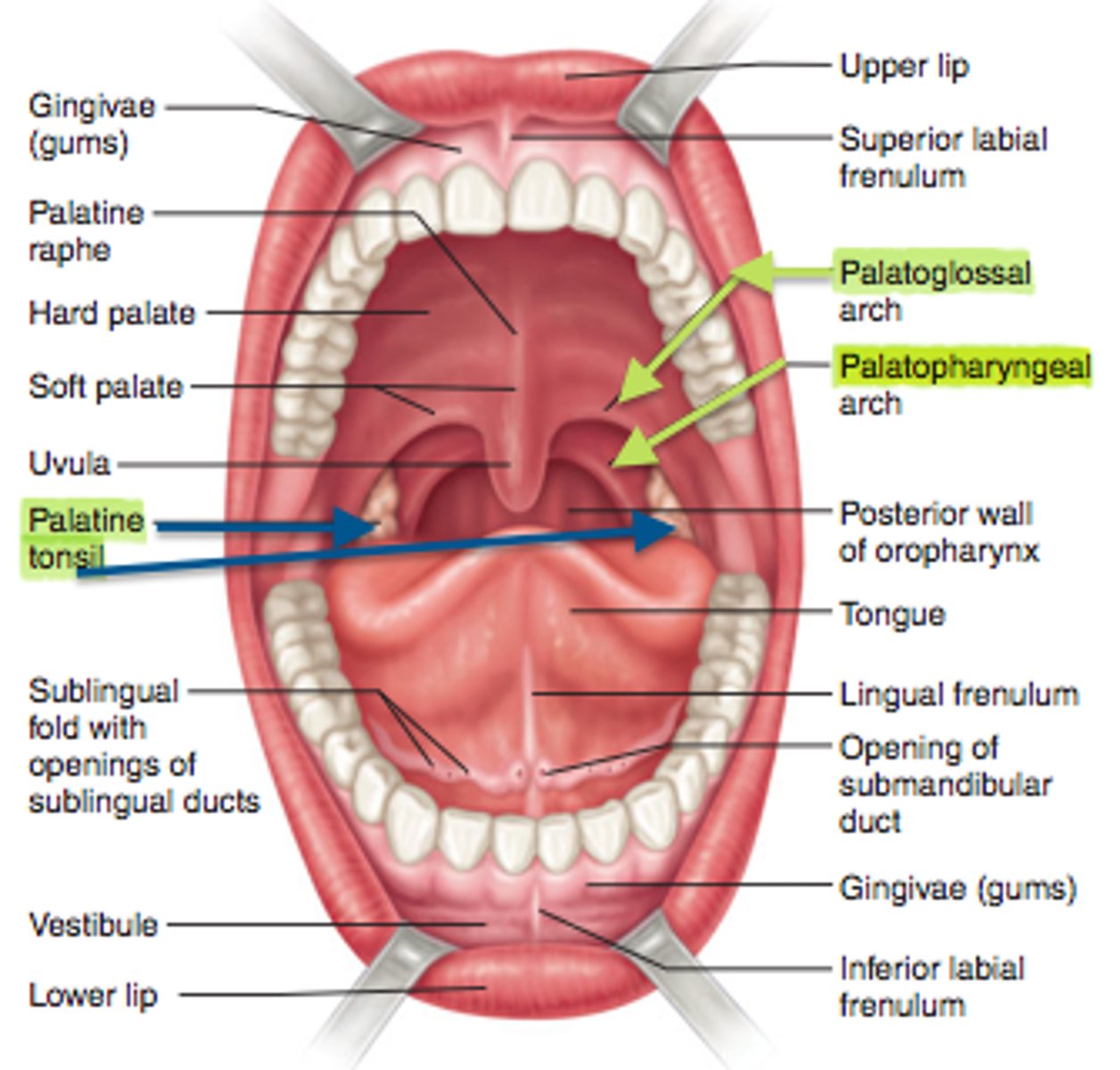
What is the palatopharyngeal arch?
posterior boundary - muscular arch from palate to pharynx
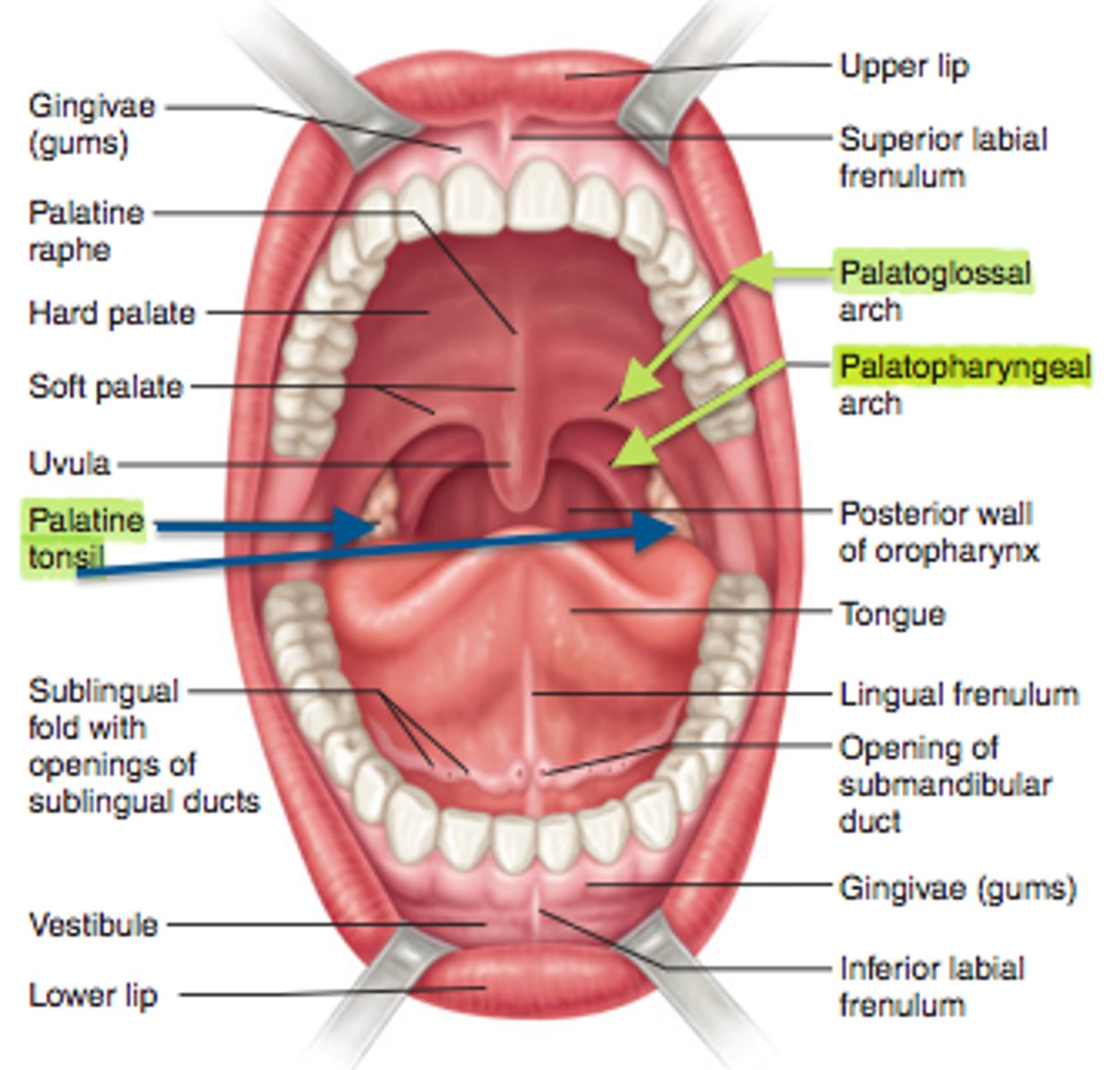
What is a retromolar pad?
Small elevations of tissue posterior to the mandibular third molars
What are the fauces?
Spaces between left and right tonsils
Which side is the dorsal/ventral side of the tongue?
Doral side is the "top" of the tongue that touches the hard palate.
Ventral side is the underside of the tongue that shows many blood vessels.
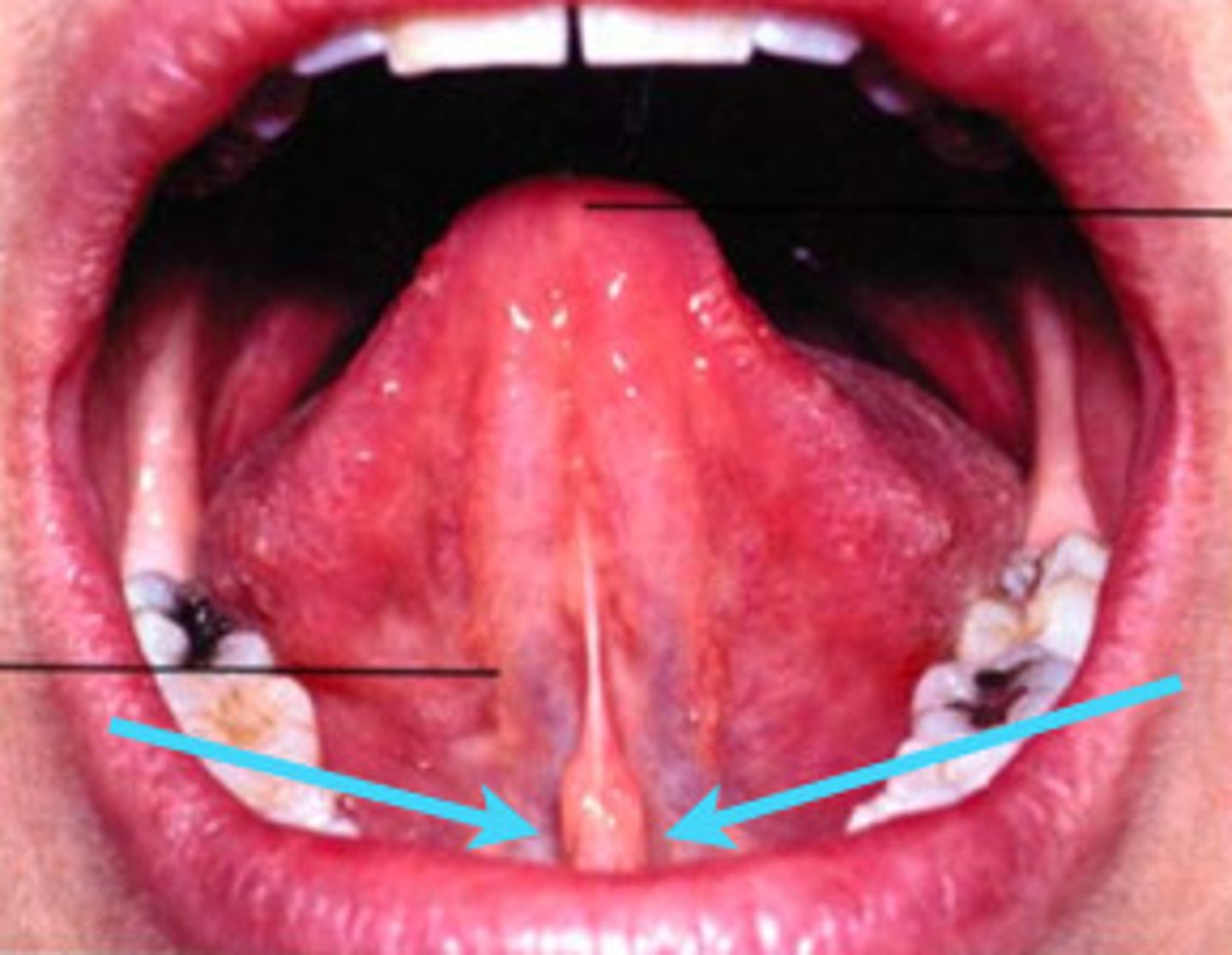
What is the lingual frenum?
midline fold of tissue between the ventral surface of the tongue and the floor of the mouth
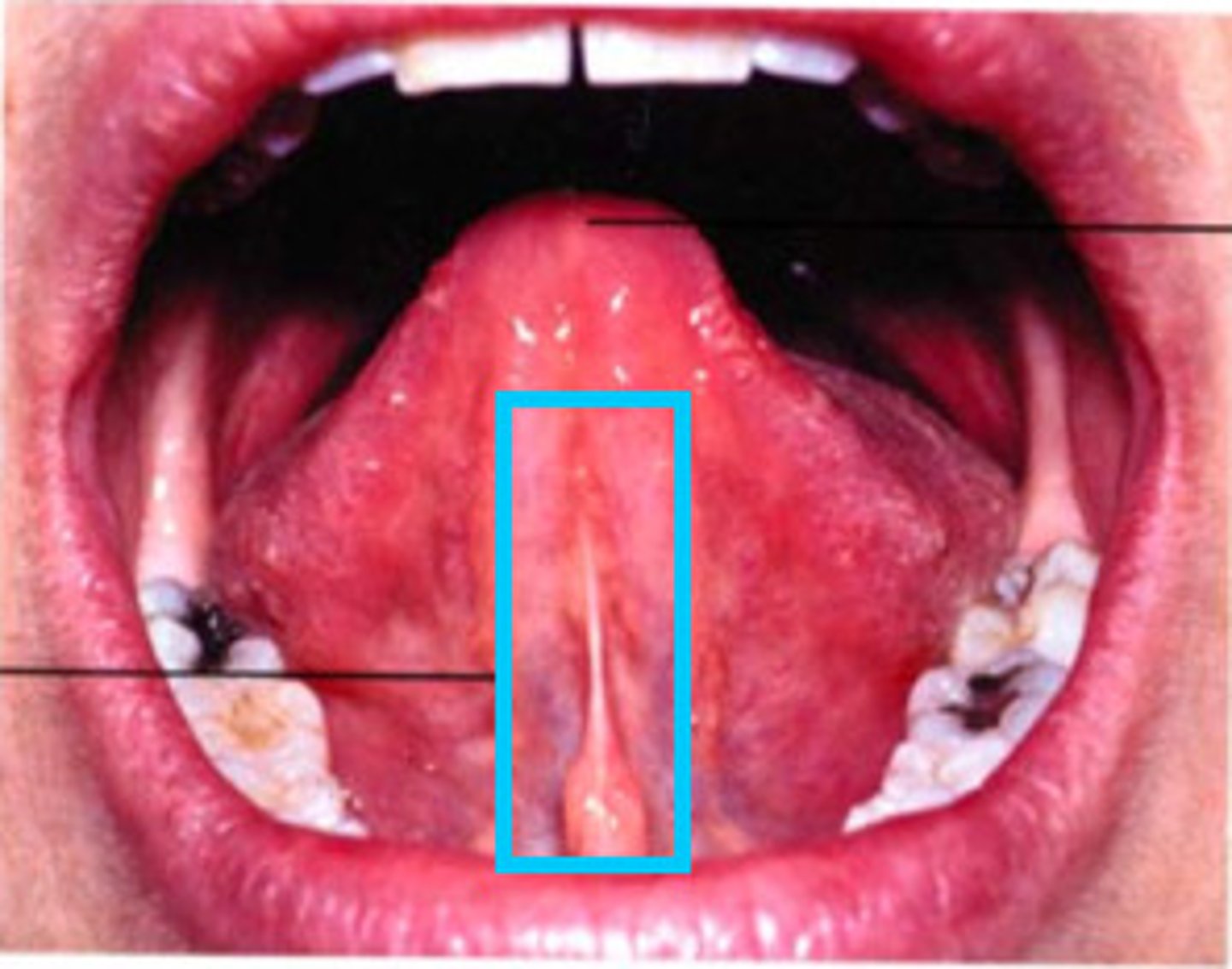
What is the sublingual caruncles?
Small elevation on each side of the base of the lingual frenum. It is the opening for the ducts of 2 major salivary glands, submandibular and sublingual glands.
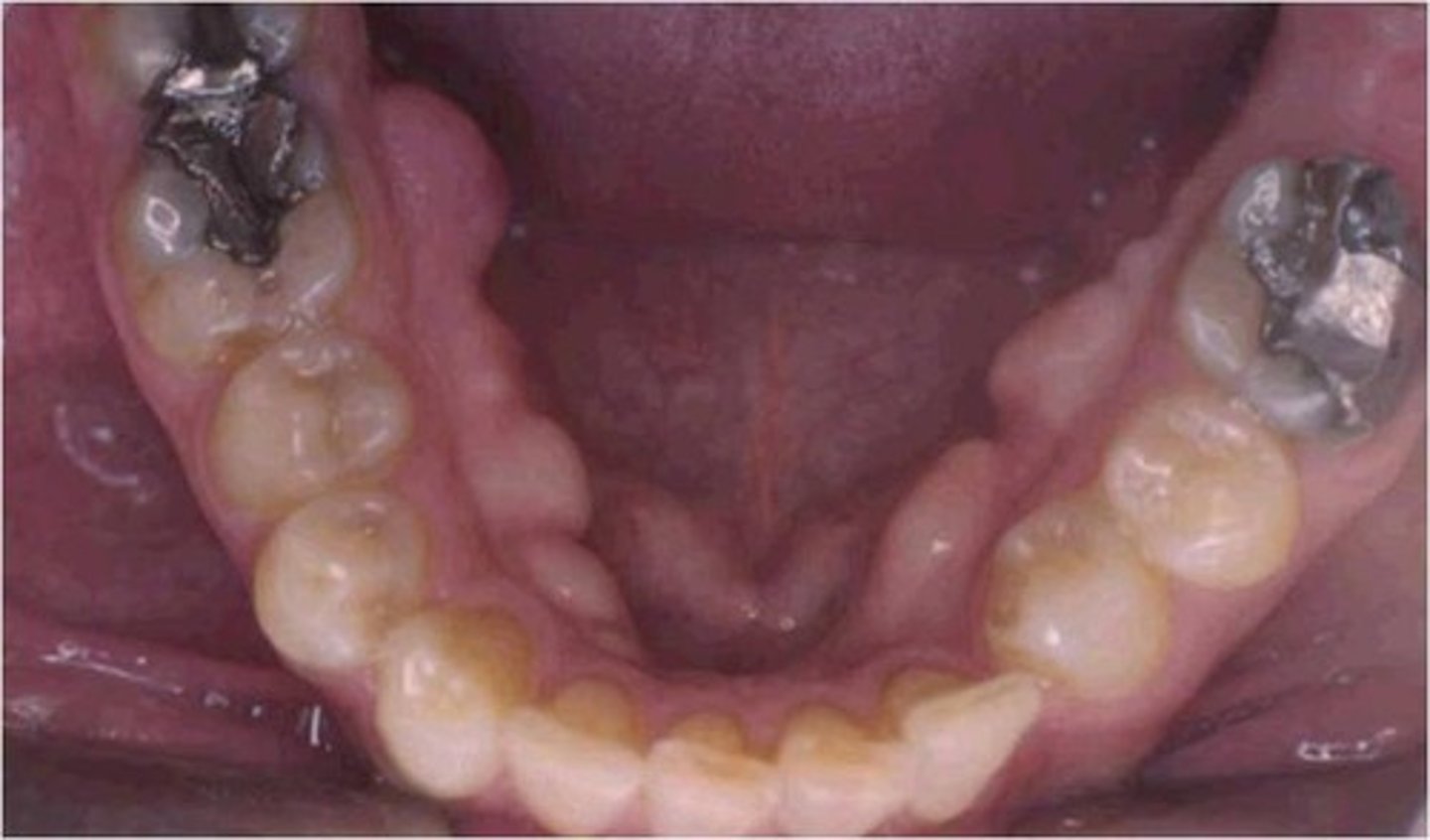
What are mandibular tori?
Bony growths along the lingual aspect of the mandible
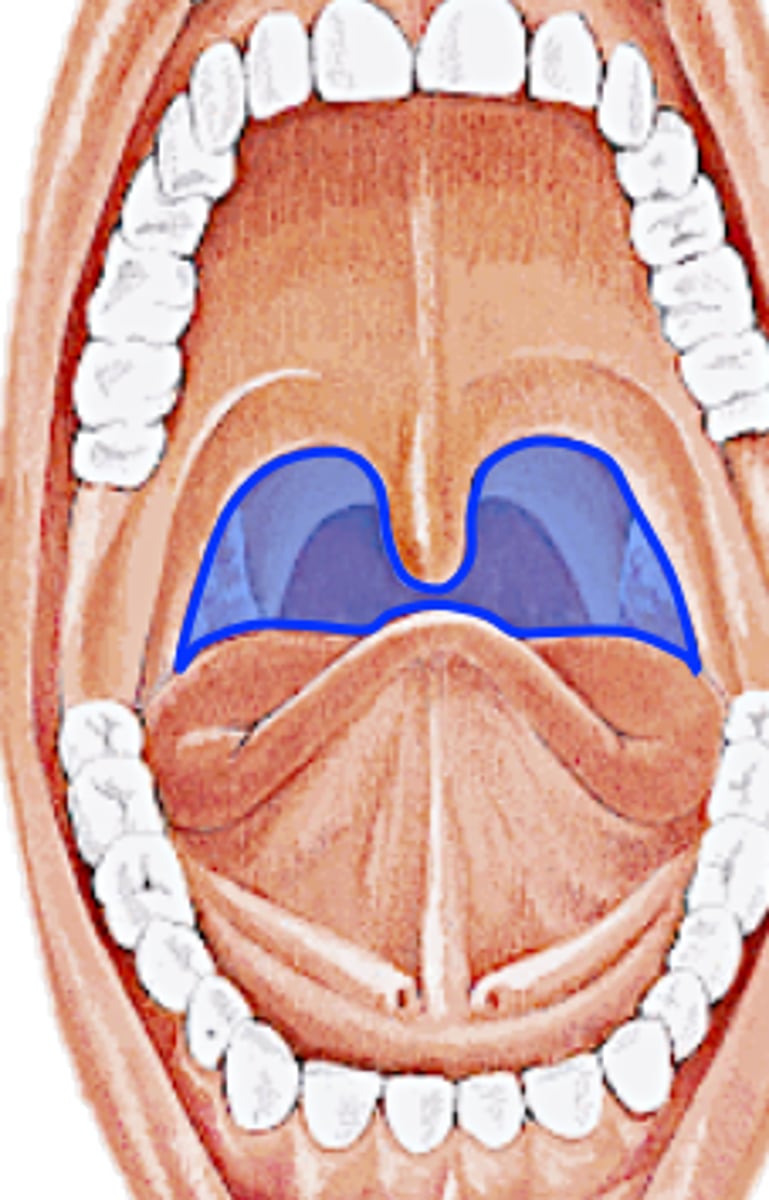
What are the 3 divisions of oral mucosa?
1. Specialized mucosa - on the upper surface of the tongue
2. Masticatory mucosa- on the gingiva and hard palatal tissue
3. Lining mucosa - all other areas of the oral mucosa
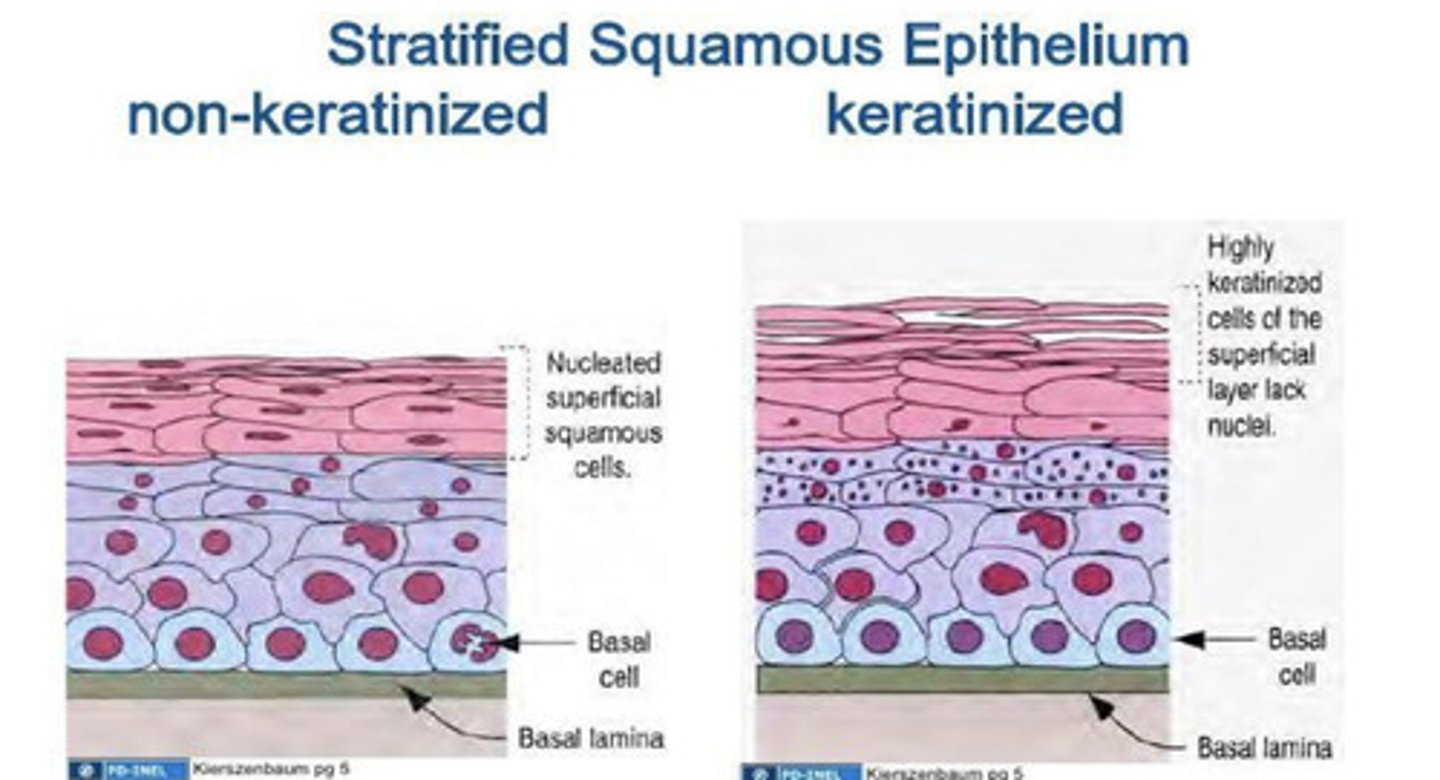
Oral mucosa is composed of _____? What are the 3 variations of its surface?
Stratified squamous epithelium
It can be:
1. Keratinized - having a layer of dead cells with no nuclei
2. Parakeratinized - dead and dying cells with no nuclei
3. Nonkeratinized - cells that are alive (has nuclei)
What are the 3 main functions of oral mucosa?
1. Protect oral surfaces
2. Secretes moisture to maintain the surface texture and to keep tissues moist
3. Absorb nutrients
Where can you find specialized mucosa in the oral cavity?
Upper surface of the tongue
Where can you find masticatory mucosa?
Tissue of the gingiva and hard palate.
- Any surface that undergoes trauma or compression during mastication
What 4 areas can you find lining mucosa?
1. Labial/buccal mucosa (cheek) - lines cheek and inside of lips
2. Alveolar Mucosa - from attached gingiva to mucobuccal fold
3. Soft apalte
4. Ventral surface of tongue/floor of mouth
Which category of oral mucosa has keratinized epithelium?
Masticatory mucosa - it is firm, thick and immovable
What is the term for the condition known as tongue-tied?
Ankyloglossia