AP Psychology - Memory Mini Unit
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Memory
The persistence of learning over time through the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information.
Recall
Retrieving information that is not currently in your conscious awareness but that was learned at an earlier time.
Recognition
Identifying items previously learned
Relearning
Learning something more quickly when you learn it a second or later time.
Encoding
The process of getting information into the memory system
Storage
The process of retaining information over time.
Retrieval
The process of getting information out of memory storage.
Sensory Memory
The immediate very brief recording of sensely information in the memory system.
Short-Term Memory
Activated memory that holds a few (5-9) items briefly (10-30 seconds) before information stored or forgotten
Long-Term Memory
The relatively permanent and limitless store house of the memory system.
Central Executive
A memory component that directs our selective attention.
Phonological Loop
A memory component that briefly holds auditory information.
Visuospatial Sketchpad
A memory component that briefly holds information about subjects’ appearance and location in a space.
Long-Term Potentiation
A persistent increase in the strength of Synapses between neurons in the brain, and is the neural basis for learning and memory.
Explicit or Declorative Memory
The retention of facts and experiences that one can consciously know
Semanic
Episodic
Implicit or Nondeclarative Memory
Retention of learned skills / procedural memory, such as riding a bike
Classically conditioned associations
Effortful Processing
We encode explicit memories through effort full processing, which requires attention and conscious effort.
Automatic Processing
We encode implicit memories through automatic processing, which is the unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time and frequency.
Ionic Memory
Momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli
Echoic Memory
Momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
Chunking
Organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically
Phone numbers
Mnemonics
Memory aids, especially these techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
Method of loci - placing things into catogories
Sematic Networks
Represented in a dense network of hierarchical association. Those at the top are quickly retrieved.
Spacing Effect
The tendency for distributed study/practice to yield better long-term retention than achieved through massed practice
Shallow Encoding
Encodes on a basic level, such as a word’s letters (structural) or, at a more intermediate level, a word’s sound (phonemic)
Deep Encoding
Encodes semantically, based on the meaning of the words. The deeper more meaningful the processing, the better our retention.
Elaborative Rehearsal
Helps commit information to long-term memory. Contextualizes information for better storage and retrieval.
Maintenance Rehearsal
Use to commit information to short term memory. Uses repetition without contextualization.
Autobiographical Memories
Events and skills from long ago in a persons life can be retrieved.
Hippocampus
Brain region that initially processes explicit memories
Memory Consolidation
neural storage of long-term memory in the cortex as memories migrate away from the hippocampus.
Cerebellum & Basal Ganglia
Coordinated movements
Procedural memory
Amygdala
Emotional memories
Flash Bulb Memories
Clear sustained memories of emotionally significant moments or events.
Ex: 9/11
Retrospective
From the Past
Prospective
Intended future actions
Retrieval Clues
Stimuli that help retrieve information from LTM - The more the better
Priming
Procedure of providing cues that stimulate memories without awareness of the connection between the clue and the retrieved memory.
Encoding Specificity Principle
The idea that clues and context its specific to a particular memory will be most effective in helping us recall it.
Context - Dependent Memory
The activation of memory when returning to the setting of the original encoding
Forgetting when you came to the kitchen for, returning to your room and remembering you needed to add an item to a grocery list
State dependent memory
The tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with the state in which a person what at a time of encoding
Mood-congruent memory
The tendency to recall experiences that one consistent with one’s current good to bad mood.
Serial Position Effect
Our tendency to best remember to items at the beginning and end of a list
Recency Effect
Only remembering the end of the list
Primary Efffect
Only remembering the beginning of the list
Metacognition
Thinking about thinking; in this case monitoring and evaluating your own learning.
Testing Effect
Repeated self-testing and rehearsal improves memory & learning
Interleaving
Switching between topics of study and/or studying different, but related concepts; boosts retention, protects against overconfidence, and allows for extra retrieval practice.
Method of loci
Placing things into categories
Episodic Memory
Experienced Events
Procedural Memory
Retention of learned skills
Working Memory
Conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory.
Sensory Memory
The immediate very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
Levels of Processing
Shallow processing / encoding
Deep processing / encoding
Structual Processing
Shallow processing based on the words letters.
Phonemic Processing
Shallow Processing based on the words sound.
Semantic Processing
Deep Processing based on the words meaning
Categories
Placing items into catagories can help enhance encoding and retrieval.
Heirarchies
Hierarchies in the information were trying to remember can help aid retrieval.
Massed Practice
“cramming” or a large amount of information trying to be remembered in a short period of time.
Distributed Practice
Yields better long-term retention, such as studying a little each night.
Duration vs. Capacity
Short-Term - 18-30 sec and 5 to 9 items
Long-Term - Unlimited in Duration and Capacity
Memory Retention
Explicit memory involves the retention of facts and experiences that one can consistently know.
Highly Superior Autobiographical Memory
People who can remember everything about their past.
Retrograde Amnesia
An inability to recall past memories.
Anterograde Amnesia
An inability to form new memories
Alzheimer’s Disease
A progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss, confusion, and other cognitive decline.
Infantile Amnesia
The inability to remember things from early childhood, typically before age 3.
Forgetting Curve
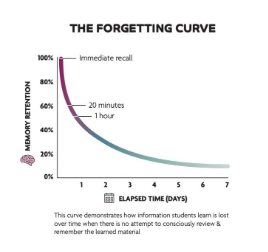
Encoding Failure
Sometimes, forgetting happens because we didn’t properly encode the information in the first place.
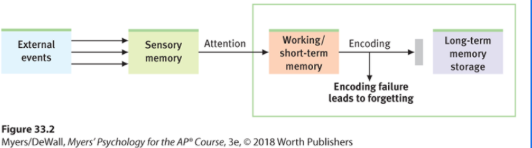
Proactive Interference
Prior learning interferes with recall of new information.
Retroactive Interference
New learning disrupts recall of old information.
Tip-of-the-tongue Phenomenon
Sometimes information is encoded and stored, but cannot be retrieved.
Ego Defence Mechanism
Banishes anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories from consciousness.
Repression
The basic ego defense mechanism that banishes anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories from consciousness.
Misinformation Effect
A phenomenon that occurs when misleading information has distorted one’s memory of an event.
Source Amnesia
Impaired memory for how, where, or when information was learned despite good memory for the information itself.
Imagination Inflation
Repeatedly imagining an event and increasing your confidence, despite its distortion or invention.
Constructive Memory
Repeatedly imagining an event and increasing your confidence, despite its distortion or invention.
Memory Consolidation
The neural storage of long term memory in the cortex as memories migrate away from the hippocampus.