3.8 Investment appraisal
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Investment
Capital expenditure or the purchase of assets with the potential to yield future financial benefits
Eg upgrading computer equipment / purchase of a building
Investment appraisal
A financial decision-making tool
Helps managers determine whether certain investment projects should be undertaken based mainly on quantitative techniques
Evaluates costs + benefits of an investment decision
Qualitative investment appraisal
Judging whether an investment project is worthwhile thru non-numerical techniques
Eg determining whether the investment is consistent with the corporate culture
Quantitative investment appraisal
Judging whether an investment project is worthwhile based on numerical (financial) interpretations
PBP, ARR and NPV methods
3 methods of investment appraisal
Payback period- PBP
Average rate of return- ARR
Net present value- NPV
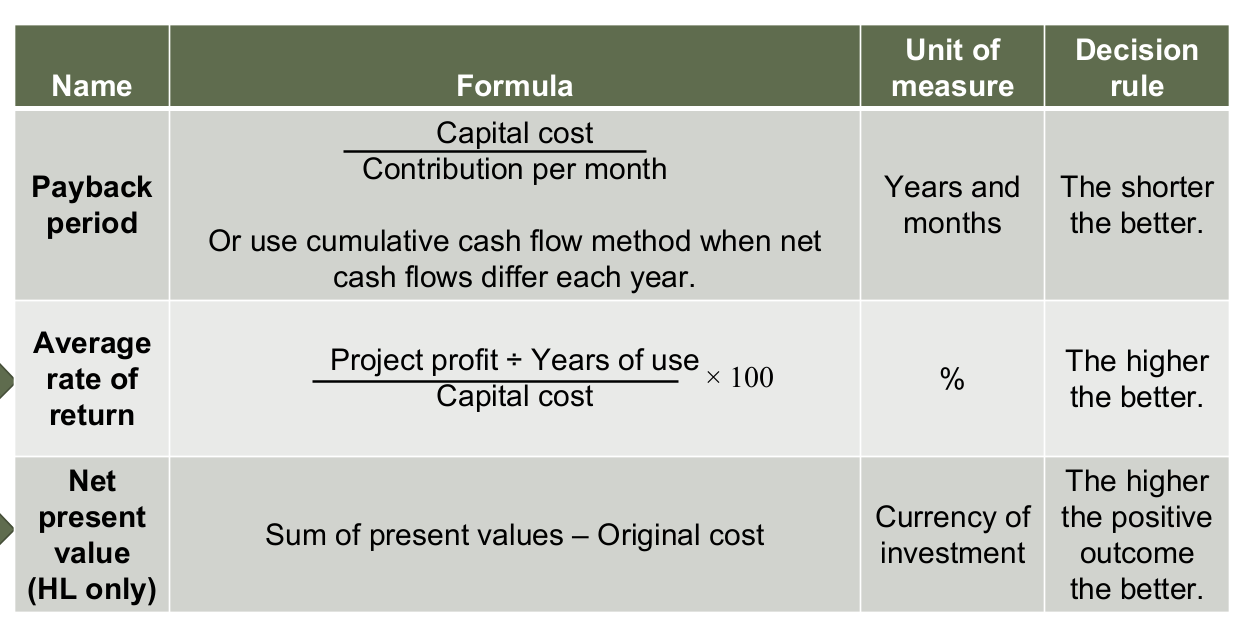
Payback period PBP
An investment appraisal technique that calculates the length of time it takes to recoup (earn back) the initial expenditure on an investment project
Amt of time needed for an investment project to earn enough profits to repay the initial cost of the investment
2 methods to calculate payback period- PBP
PBP formula
Cumulative cash flow method
PBP equation
Initial investment cost / contribution per month

Cumulative net cash flow
Sum of an investment project's NCFs for a particular year plus the NCFs of all previous years
Betw the 2 methods to calculate PBP, which is more accurate + why?
Cumulative cash flow method
Bc income from investment differs each year
Cumulative cash flow method to calculate PBP
Make table with year, NCF, cumulative NCF (include Y0)
Identify betw which years the cost of investment will be paid back
Cost of investment - cumulative NCF for calendar year b4 the investment will be paid back
no need to do this if year 0 is included in the table
Calc avg monthly CF for calendar year in which the cost of investment is paid back
Amt left / monthly CF
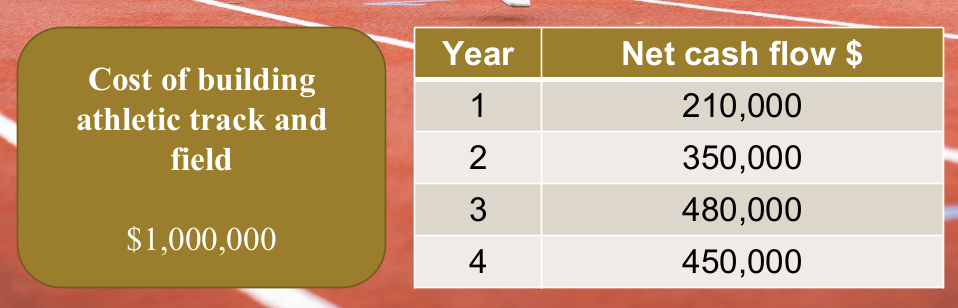
Calculate PBP using cumulative CF method
PBP = (amt left / cash inflow) x 12
2 years 11 months
Calculate PBP using PBP formula:
Firm will purchase asset, cost = $10,000
Anticipated financial gain = $6,000 of revenue per year after maintenance costs are paid for
(10,000 / (6000/12)) = 20 months
Pros of using PBP
Simplest + quickest method
Useful for firms with CF problems → see how fast can recoup cash
Can see if business will break even on the purchase b4 it needs to be replaced
Can use tocompare diff investment projects
Assesses only ST → less prone to errors
Managers assess projects which yield a quick return for shareholders
Cons of using PBP
Not constant contribution per month → longer PBP
Focuses on time, not profit
ST approach to investment
PBP calculations prone to errors
PBP not suitable for some business
Why is contribution per month unlikely to be constant?
Bc demand is prone to seasonal fluctuations → PBP might take longer
The longer the PBP…
The more risky the investment is
Exam tip: just bc something is high risk, does it mean a business should avoid it?
No
Need to know if benefits of the risks are likely to outweigh the costs
Exam tip: when using PBP should you reject a project just bc it isn’t expected to pay off quickly + why?
No
Bc it may be v profitable in the LT
Consider context
Average rate of return- ARR
Calculates the average annual profit of an investment project as a percentage of the initial amt of money invested
ARR equation
(((total returns - capital cost) / years of use) / capital cost)
x 100
aka (AAP / COI) x100

How to calculate ARR
Calc total net CF over years of project
Calc expected profit from the project
Project profit = total returns - capital cost
Basically total NCF - COI
Div by no. of years
Div by COI
x 100
Project profit equation
Total returns - capital cost
Or total NCF - COI
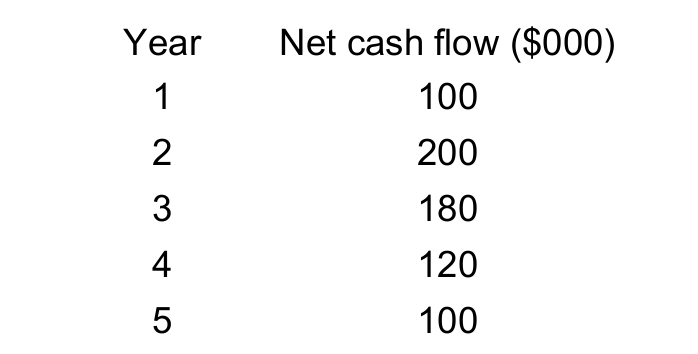
Calculate ARR practice question
Cost of investment = $400,000
15%
700 - 400 = 300
300 / 5 = 60
60 / 400 = 0.15
0.15 × 100 = 15%
What does ARR measure?
Profitability
Not cash flow
As a basic benchmark, what can ARR be compared with?
Base interest rate in the economy
So can assess rewards + risks involved in the investment
Pros of ARR
Easy to understand, calc, compare→ aids decision making
Focuses on profitability
Cons of ARR
Ignores NCF → prone to forecasting errors
Focuses on profit instead of cash flow
Figures are only estimates bc based on projects useful life (maybe pure guess)
Longer time = more errors
Net present value- NPV
Calculates the total discounted NCFs minus the initial cost of an investment project
Works out the present value of the return on an investment
What does it mean if NPV is positive?
Project is viable on financial grounds
Discounting
Reverse of calculating compound interest
Discount factor
The number used to reduce the value of a sum of money received in the future to determine its present (current) value
Used to convert the future NCF to its
present value today
Based on inflation / interest rates
Discounted cash flow
Uses a discount factor to reduce the value of money received in future years bc money loses its value over time
NPV equation
Sum of present values - original cost
Aka sum of all discounted cash flows - cost of investment
How to calculate NPV
Find NCF for each year
NCF x discount factor = present value
Add tog all present values
Sum of present values - og cost = NPV
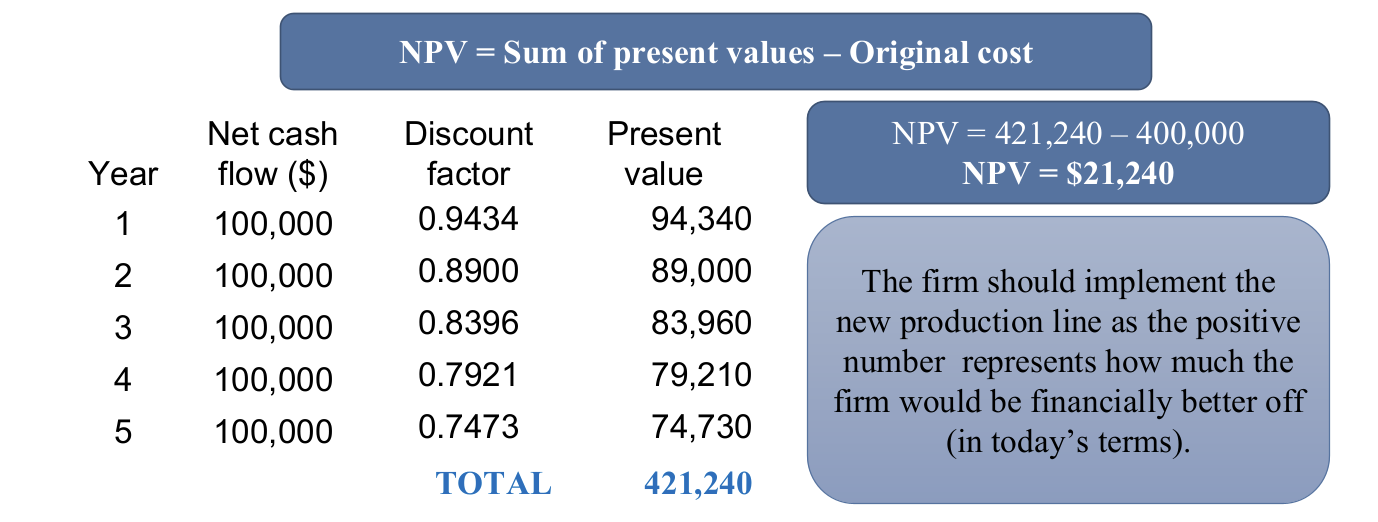
Calculate the NPV for this investment project
Cost of investment = $400,000
$21,240
Pros of NPV
Cons of NPV
NPV value would be reduced if interest rates increase
NPV calculations are complex
NPV results are only comparable if the initial investment cost is the same between competing projects
Good value for NPV
Must be positive
Higher the better
Summary of quantitative investment appraisal methods
PBP- risk + time
ARR- profitability
The longer the time period of the project considered…
… the lower the present value of that future amt of money
Bc money received in the future is worth less than if it were received today
Principal (capital outlay)
The og amount spent on an investment project
What does it mean if NPV is positive + what does this mean?
It is greater than the principal
The value of the discounted (future) net CFs are enough to justify the initial cost of the investment
What does it mean if NPV is negative?
The investment project is not worth pursuing on financial grounds
Why is cash received in the future not the same value as if it were received today?
Bc:
The money could have been invested to generate financial returns
Inflation reduces the value of money in the future
How are PBP, ARR, NPV expressed?
PBP- time (years, months)
ARR- %
NPV- monetary value
Qualitative investment appraisal methods that affect investment decisions
PORSCHE
Projections
Objectives
Risk profiles
State of the economy
Corporate image
Human relations
External shocks