Chapter 19 - Blood
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is Blood
specialized fluid of connective tissue containing cells suspended in fluid matrix
Physical Characteristics of Blood
Normal Temp: 38oC (100.4oF)
High viscosity
Slightly alkaline pH (7.35-7.45)
Major Functions of Blood
transport system
O2, CO2, nutrients, hormones, waste, cells
regulation of pH & ion concentration
restriction of fluid loss at injury sits (hemostasis)
defense against toxins & pathogens
stabilizing body temp
Make Up of Whole Blood
Plasma
water, plasma proteins (made by liver), other solutes
55%
Formed Elements
RBC, WBC, platelets (pieces of cells), other solids
45%
Plasma Make Up
Plasma Proteins (7%)
albumins
globulins
firbrinogen
Other Solutes (1%)
specialized plasma proteins
i.e. antibodies, complement proteins
quantities vary
Water (92%)
Albumins
60%
produced in liver
transport fatty acids & hormones
Globulins
35%
antibodies (aka immunoglobulins)
transport globulins for hormones & steriods
Fibrinogen
4%
involved in blood clotting process, forming insoluble strands of fibrin from dissolved fibrinogen in serum
serum is plasma w/o antibodies
Other Plasma Proteins
1%
specialized proteins present at varying levels
ex: peptide hormones (insulin, follicle-stimulating hormone)
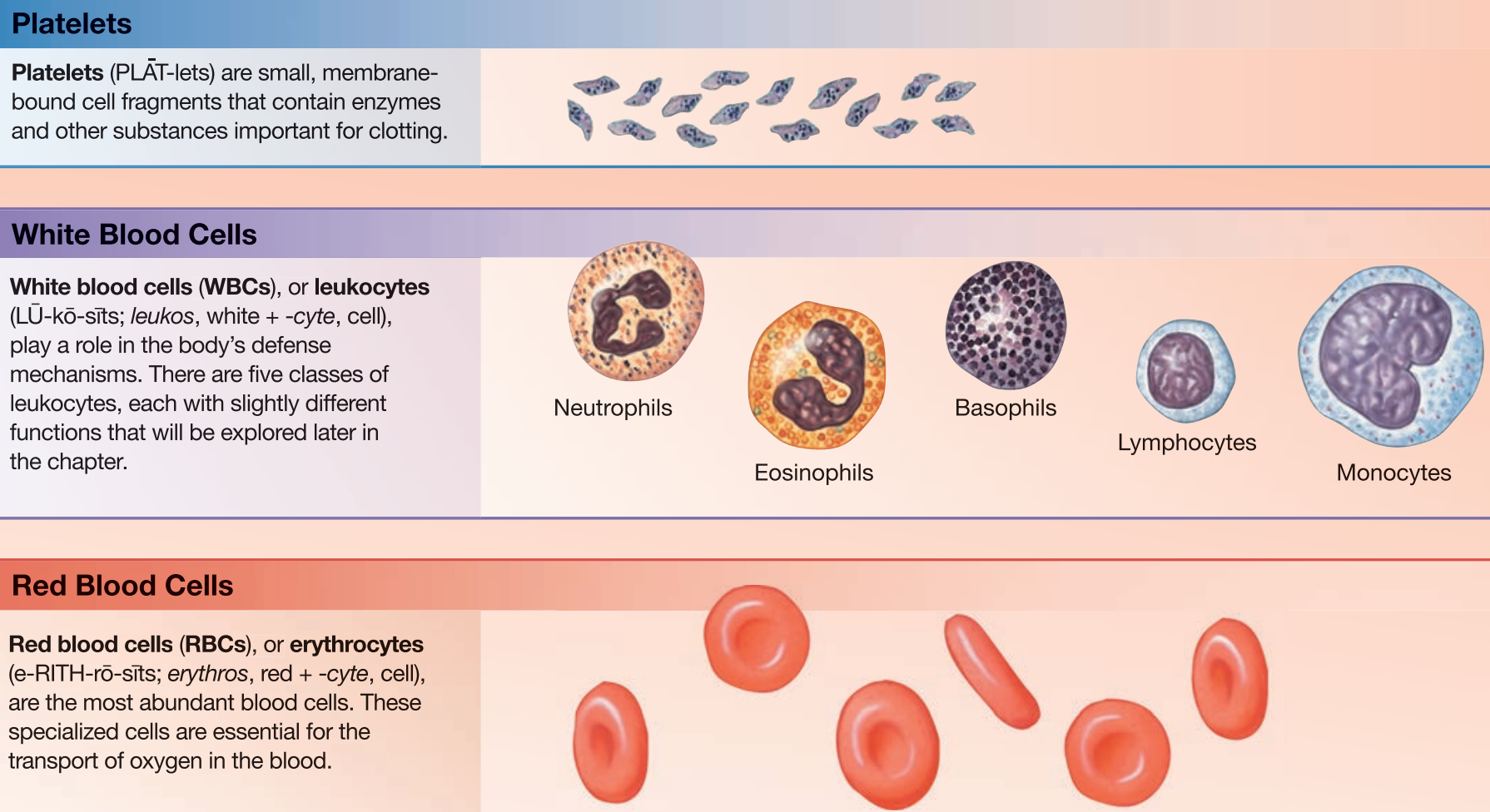
Types of Formed Elements
Red Blood Cells / Erythrocytes
transports ocygen
White Blood Cells / Leukocytes
component of immune system
Platelets
cell fragments involved in clotting
Hemopoiesis
process of producing formed elements stimulated by erythropoietin (EOP)
EOP released by kidney
produced from hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow
generates ~3 mil new RBCs per sec
Red Blood Cells
small, highly specialized discs comprising 99.9% of formed elements
contains hemoglobin, which transports O2 & CO2
provides red color
1% die out per day
Red Blood Cell Count
# of RBCs in 1microliter of whole blood
Males — 4.5-6.3 million
Females — 4.2-5.5 million
Packed Cell Volume (PCV)
% of formed elements in centrifuged whole blood
Hematocrit
% of RBC in centrifuged whole blood
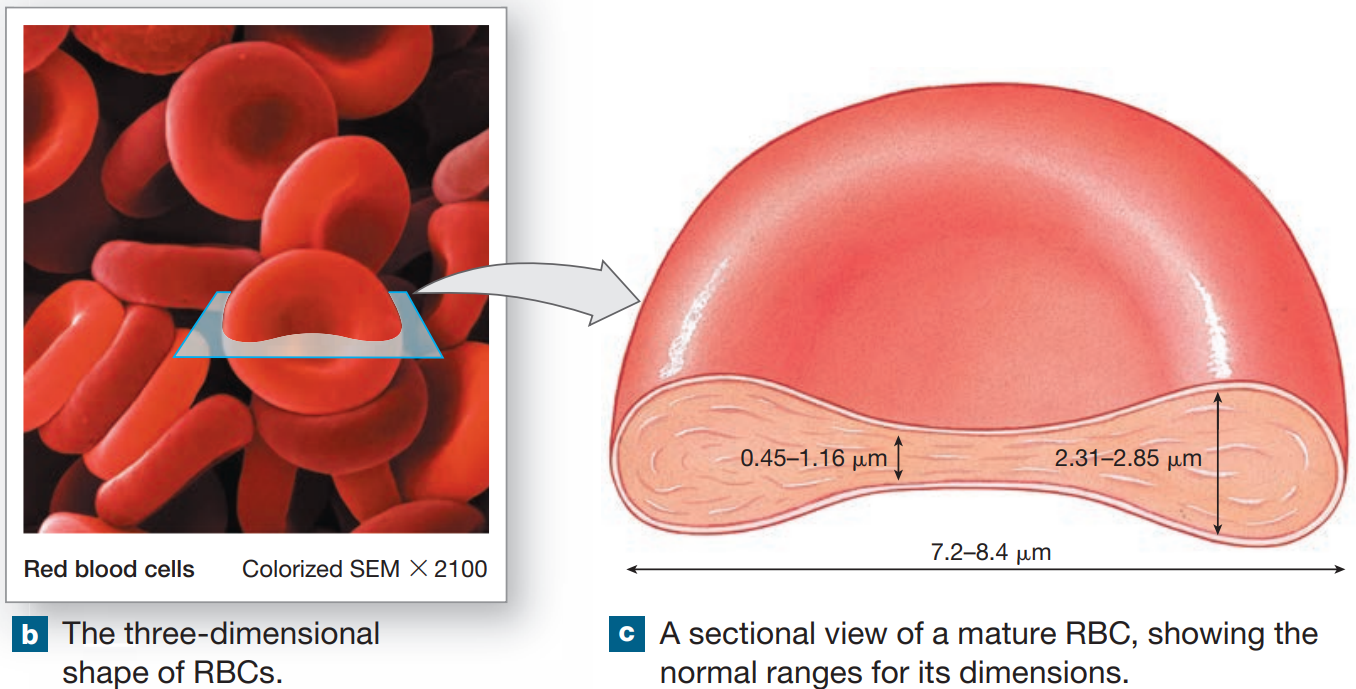
Structure & Function of RBCs
high surface-to-volume ratio to exchange O2 rapidly
flexbility to transverse small capillaries
Life Span of RBCs
lack nuclei, mitochondria, ribosomes
unable to divide for synthesis of proteins
no repair mechanisms
only anaerobic metabolism
120 days
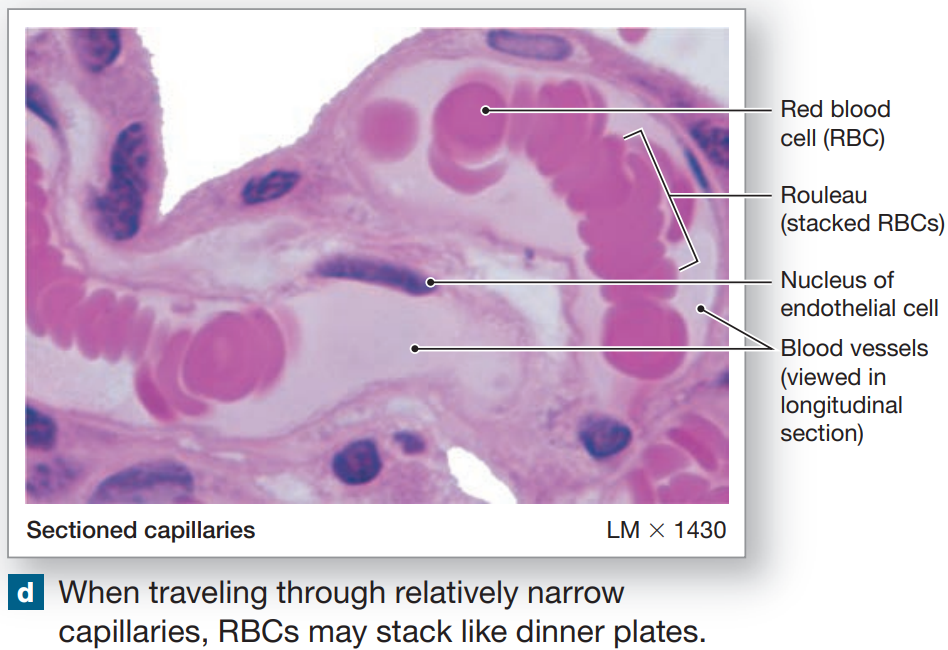
Rouleaux
stacks formed by discs
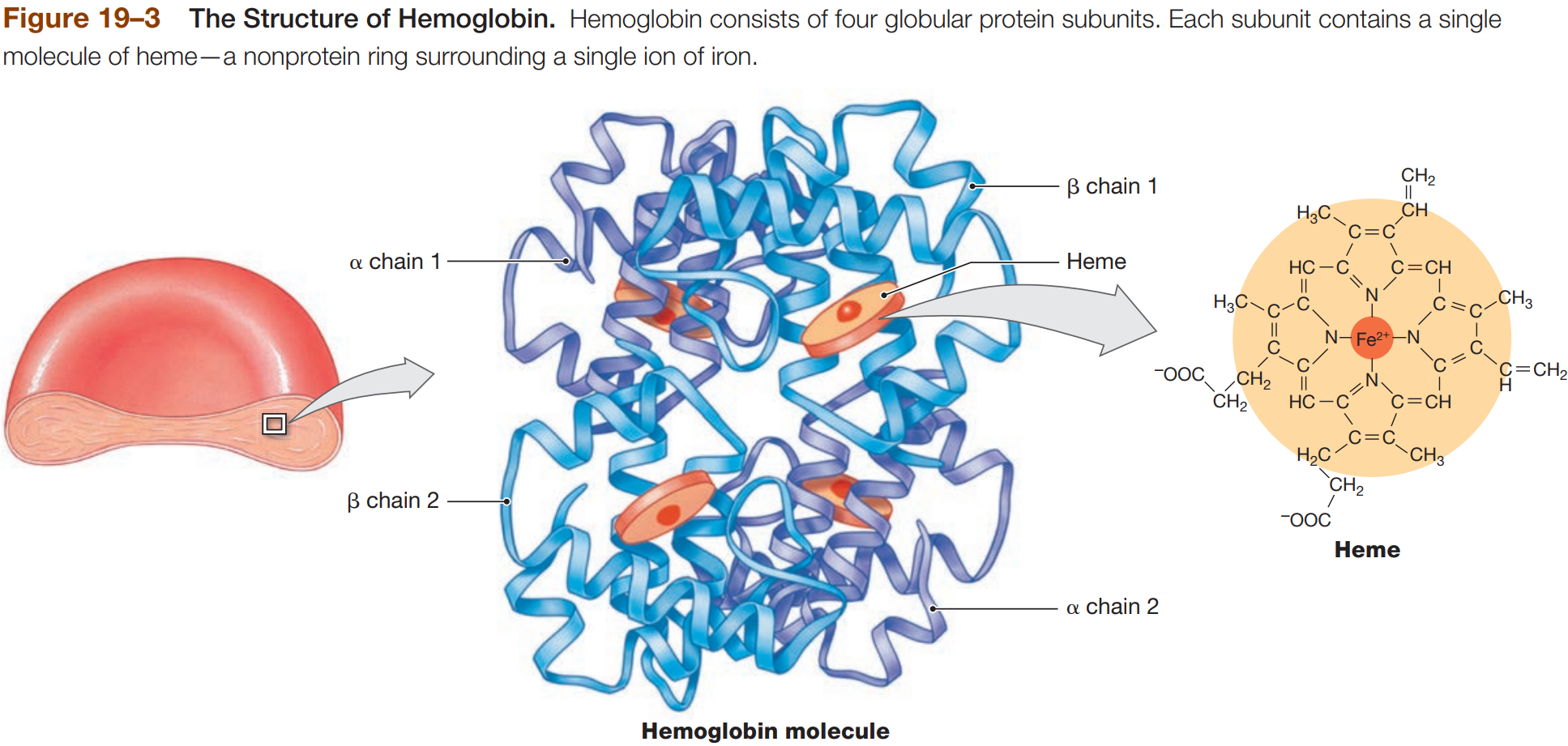
Hemoglobin (Hb)
molecule with 4 globular protein subunits that transport respiratory gases
each subunit contain one molecule of heme
each heme contains free Fe2+ ion (contributes to red color) that binds O2
Hb + O2 = HbO2 (Oxyhenoglobin)
HbO2 - O2 = Deoxyhemoglobin
each subunit carries O2
Fetal Hemoglobin
potent form of Hb present in developing fetus
can take O2 from mother’s Hb
Carbaminohemoglobin
Hemoglobin containing CO2
low O2 state (e.g. at peripheral capillaries), Hb releases O2 & binds CO2
carries CO2 to lungs
CO2 doesn’t bind to heme
RBC Turnover
macrophages of liver, spleen, bone marrow monitor RBC population & engulfs RBCs before membrane ruptures or hemolyzes
phagocytes break down Hb complex
proteins converted to AA
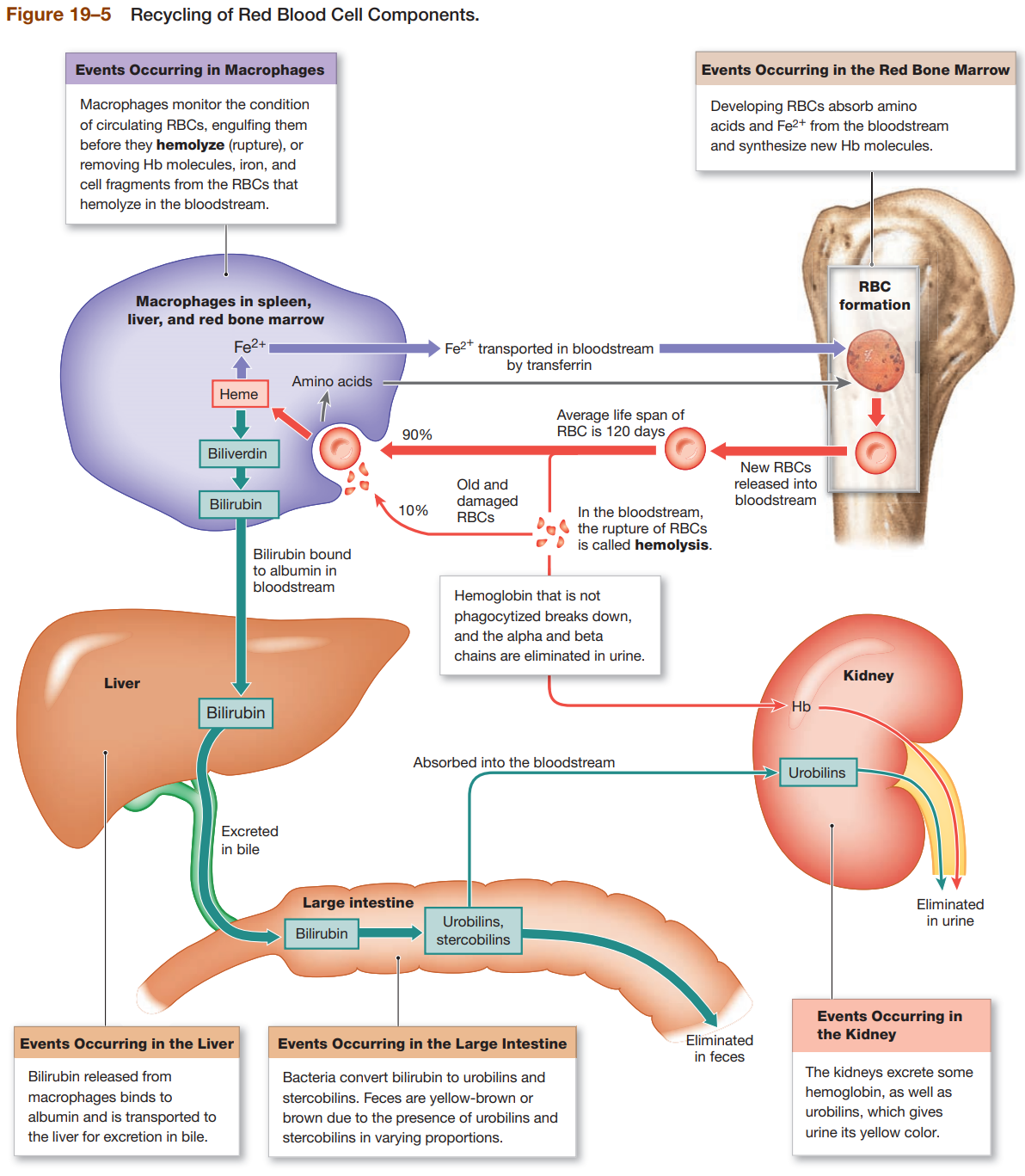
Hemoglobinuria
hemoglobin in urine due to excess hemolysis in bloodstream
Hematuria
whole RBCs found in urine due to kidney or tissue damage
Breakdown Of Heme
heme is metabolized into biliverdin by removal of iron
biliverdin (green) is quickly metabolized to bilirubin
bilirubin (yellowish-orange) is excreted by liver through bile
buildup of bilirubin causes jaundice
bilirubin is converted to urobilins & stercobilins by intestinal bacteria
Fe2+ Recycling
Fe2+ is released by metabolism of heme
Fe2+ is either transported or stored
transported by transferrin
stored by forming complex with ferritin or hemosiderin
Erythropoiesis
in adults, erythropoiesis occurs only in myeloid tissue (red bone marrow)
generation of RBCs requires amino acids, Fe2+, Vit B12, Vit B6, folic acid
EPO secreted from kidney when O2 in peripheral tissues is low
Hemocytoblasts
stem cells
erythroid stem cells → RBCs
myeloid stem cells → WBCs
lymphoid stem cells → Lymphocytes
Hypoxia
low O2
Anemia
condition resulting from low hematocrit or Hb content
Pernicious Anemia
low RBC production due to lack of Vit B12
Blood Doping
dangerous practice by athletes to elevate hematocrit
Erythropoiesis: Stages of RBC Maturation
Myeloid Stem Cell
Proerythroblast
Erythroblast
Reticulocyte
Mature RBC
Blood Typing
determined by presence or absence of surface antigen on RBCs
blood type genetically determined by A, B, Rh antigens
surface-expressed antigens are “screened” by immune system
circulating anti-antigen antibodies bind “forgein” antigens
Type A Blood
Surface Antigen: Antigen A
Anti-Antigen Antibodies: Anti-Antigen B Antibodies
Type B Blood
Surface Antigen: Antigen B
Anti-Antigen Antibodies: Anti-Antigen A Antibodies
Type AB Blood
Surface Antigen: Antigen A & B
Anti-Antigen Antibodies: NO Anti-Antigen A or B Antibodies
Type O Blood
Surface Antigen: NO Antigen A or B
Anti-Antigen Antibodies: BOTH Anti-Antigen A & B Antibodies
Rh Factor (Antigen D)
Rh+ → antigen D
Rh-- → no antigen D
Agglutination
binding causes clumping of foreign antigens
Agglutinogens
RBC surface antigen antibodies
Rh Factor & Pregnancy
humans are either Rh+ or Rh-
only sensitized Rh- blood has anti-Rh antibodies
since fetal blood does not typically mix with maternal circulation, mother is not exposed to Rh factor
Rh- mother’s blood does not express anti-Rh antibodies
Hemolytic Disease of Newborns
next time mother is pregnant, anti-Rh antibodies from maternal blood can enter fetal circulation
anti-Rh antibodies will bind to Rh+ fetal RBC & cause hemolysis
treat mother with anti-Rh antibodies (RhoGAM) to prevent sensitization
Blood Transfusion
blood must be tested for compatibility
is transfused blood is not compatible, plasma antibodies will recognize its specific antigen
blood cells will agglutinate
results in hemolysis of RBCs
Transfusion Reaction
plasma antibodies recognize specific surface antigen
Cross-Matching
critical to check compatibility of donor & recipient
Type O-
universal donor
no surface antigen on RBCs (type O)
no Rh factor (negative)
Type AB-
universal recipient
both surface antigens on RBCs (type AB)
no Rh factor (negative)
Proerythroblast
large cells with large nucleus surrounded by small amount of cytoplasm
Megakaryocyte
precursors of platelets
found in bone marrow
Platelets
aka thrombocytes
cell fragments involved in clotting system
circulate for 9-12 days
removed by phagocytes in spleen
Thrombocytopenia
low platelet count
Thrombocytosis
high platelet count
Functions of Platelets
release clotting chemicals
temporarily patch damaged vessel wall
reduced size of break in vessel wall
Thrombocytepoeisis
formation of platelets from cytoplasm of megakaryocytes in bone marrow
Hormones Involved in Platelet Production
thrombopoietin
interleikin-6 (IL-6)
multi-colony stimulating factor (Multi-CSF)
Hemostasis
cessation of bleeding
Phase 1 of Hemostasis
Vascular Phase
cut triggers vascular spasm that lasts 30 min
endothelial cells release factors in response
tissue factor, prostacyclin, ADP
Endothelins
stimulate smooth muscle contraction & endothelial division
cells become sticky & act to seal off blood flow
Phase 2 of Hemostasis
Platelet Phase
begins within 15 sec of injury
platelets stick to endothelial cells, basement membranes, exposed collagen fibers
aggregate to plug break
release clotting compounds
ADP - platelet aggregation
thromboxane A2
serotonin - vascular spasm
clotting factors
PDGF - vessel repair
calcium - clotting factor
Factors that Limit Platelet Plug Size
Prostacyclin & Nitric Oxide - inhibit aggregation
inhibitory factors are released by other WBCs
ADP breakdown inhibits platelet aggregation
negative serotonergic feedback to reduce release of serotonin
clot isolates injured area
Phase 3 of Hemostasis
Coagulation Phase
blood clotting begins in less than 30 sec after injury
enzymatic chain reactions convert circulating fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin
Ca2+ & Vit K
all pathway require Ca2+
Vit K needed for synthesis of 4 clotting factors
Extrinsic Pathway
begins in vessel wall, outside bloodstream
damaged cells release tissue factor (TF)
TF & other factors form enzyme complex activates Factor X
Intrinsic Pathway
begins with circulating proenzymes, within bloodstream
enzymes form prothrombin activator complex that converts prothrombin → thrombin
thrombin converts fibrinogen → fibrin
Regulation of Clotting
pathways regulated by positive & negative feedback loops
to accelerate clotting, increase production of TF or Platelet Factor-3 (PF-3)
to inhibit clotting, increase production of anticoagulants
Examples of Anticoagulants
Antithrombin-III - inhibits thrombin
Heparin - released by mast cells
activates antithrombin-III
Aspirin
Protein C - activated by thrombomodulin
stimulates formation of plasmin
Prostacyclin - vasodilator
opposes thrombin activity
Hemophilia
inherited bleeding disorder
Thrombophilia
increased clot formation
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) - clots form in venous system
Pulmonary Embolism - moving clot blocks one of vessels of lung
Phase 4 of Hemostasis
Clot Retraction
pulls torn edges of vessel closer together
reduces residual bleeding
stabilized injury site
reduces size of damaged area
fibrinolysis - slow dissolving clot
thrombonin & tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) convert plasminogen to plasmin
plasmin digests fibrin strands & dissolves clot