ESS SL Semester 2 Term 3 (3.2, 3.3, 8.2, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3
1/263
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
264 Terms
Population Pyramids
Structures which show any measurable characteristics of the population; like sex, age, language, religion and occupation.
What does a wide base indicate?
It indicates high birth rate
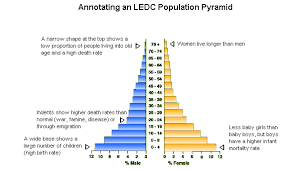
What does a narrow base indicate?
Falling birth rate
What does a straight or near vertical sides indicate?
Low death rate
What does a bulge in the slope indicate?
Immigration or in-migration
What does deficits in the slope indicate?
Emigration or out-migration or age-specific or sex-specific deaths (epidemics, war)
What causes birth rates to decline?
Children are costly
The government looks after people through pensions and health services
More women widespread use of family planning
As the infant mortality rate decreases there is no need of child replacement.
Why do people want children? (High birth rates)
For labour
To look after them in old age
To continue family name
Prestige
To replace children who have died
What causes death rate to decline?
Clean water
Reliable food supply
Lower population densities
Better vaccination and healthcare
rising standards of living
What causes High death rates?
Lack of clean water
Lack of food
Poor hygiene and sanitation
Overcrowding
Contagious disease
Poverty
Crude Birth Rate
The number of births per 1000 of the population.
Whats the formula for “Crude Birth Rate”? (CBR)
Total no of births/ Total population x 1000
What are the key influences of CBR?
Age structure of population
Sex structure of population
Customs & family size expectations
Adopted population policies
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
It is the number of deaths/ 1000 people in a population
Formula for Crude Death Rate (CDR)
Total no. of deaths/ total population x 1000
What influences CDR? (10)
Age structure
Access to food/ water
Social Class
Income
IMR
Literacy
Child mortality
Occupation
Place of residence
Healthcare
Whats a poor indicator of mortality trends?
CDR
Doubling Time
Number of years it will take a population growing at a constant rate to double 70% natural increase.
Natural Rate of Increase
Rate (%) at which the population changes (CBR - CDR) / 10
The difference between CBR and CDR and accounts for how fast populations grow.
Epidemiological Transition
The pattern of change in mortality factors during a population’s development which represents one element of the demographic transition.
Fertility Transition
the decline of fertility from high levels
Phase 1
Primitive stability resulting from a high CBR being offset by an equally high CDR
Basic stability is achieved when a high birth rate is balanced by an equally high death rate. Despite a life expectancy at birth of less than 30 years, the population doesn't decline because cultural factors, such as religious teachings and social pressure, encourage large families for practical benefits, power, and prestige. As a result, population growth remains close to zero.
Phase 2
Marked by a declining CDR — the epidemiological transition. Additionally, as the fertility rate is high this results in rapid population growth.
Death rates begin to fall, because of improved living conditions better food supplies and better health practices (eg. immunisation). The birth rate remains high and may even increase because women are healthier. Population growth is a consequence and as it takes time for social attitudes (eg. high value attached to having children) to change, birth rates remain high.
Phase 3
Marked by declining CBR resulting in declining fertility rate, but population growth is still significant.
Birth rates fall due to better education, family planning more career options for women and reduced infant mortality and will eventually catch up with the death rate. Population growth remains high at the beginning of this phase but eventually approaches zero.
Demographics
The study of the dynamics of population change (how populations change over time)
What are the demographic tools used for quantifying human population?
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
Doubling Time (DT)
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
Crude
Considers births to the total population without regard to the age or sex structure of the population.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman has during her lifetime.
Where can we find high fertility rates?
Poor countries, because they have lack of access to contraceptives and generally lower levels of female education.
What factors affect fertility rates? (9)
Urbanization
Importance of children in the workforce
Children are costly
Education/ Employment for women
The average age of marriage
Availability of abortion
Availability of birth control
Religious beliefs, traditions, and culture
Government policies
DT (years) =
70% growth rate
Development and Transition
The total size of the world population depends on when and how much fertility declines in MEDCs.
This will be more readily achieved by improving the educational levels of women and making contraceptives more readily available.
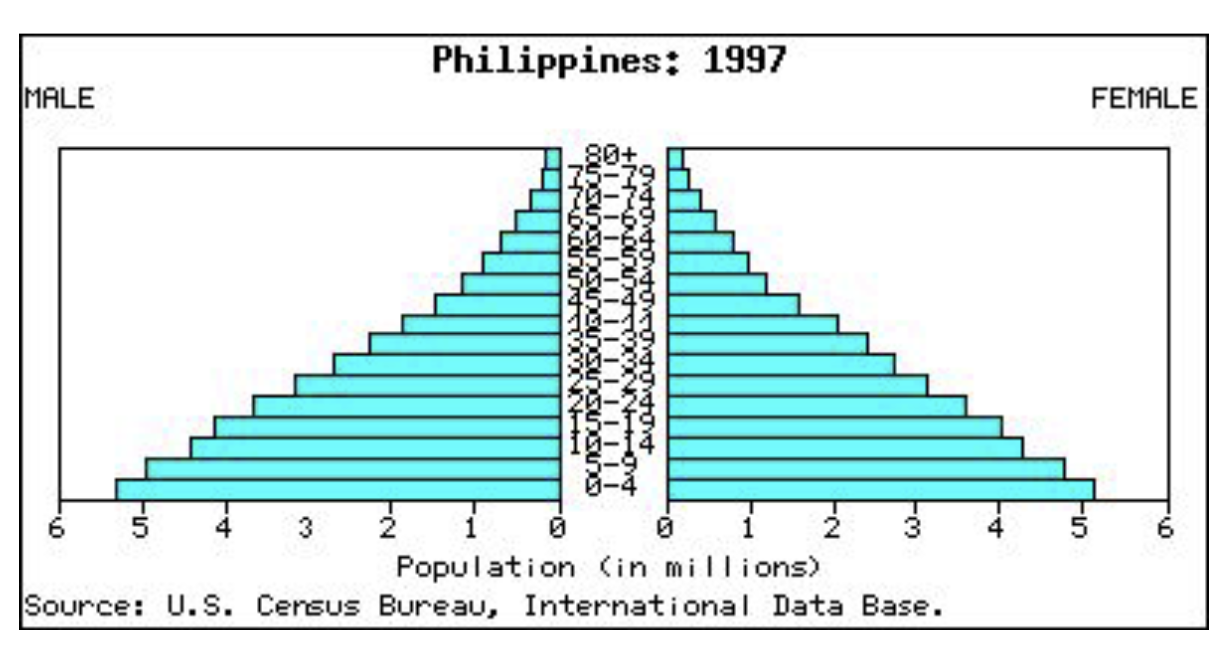
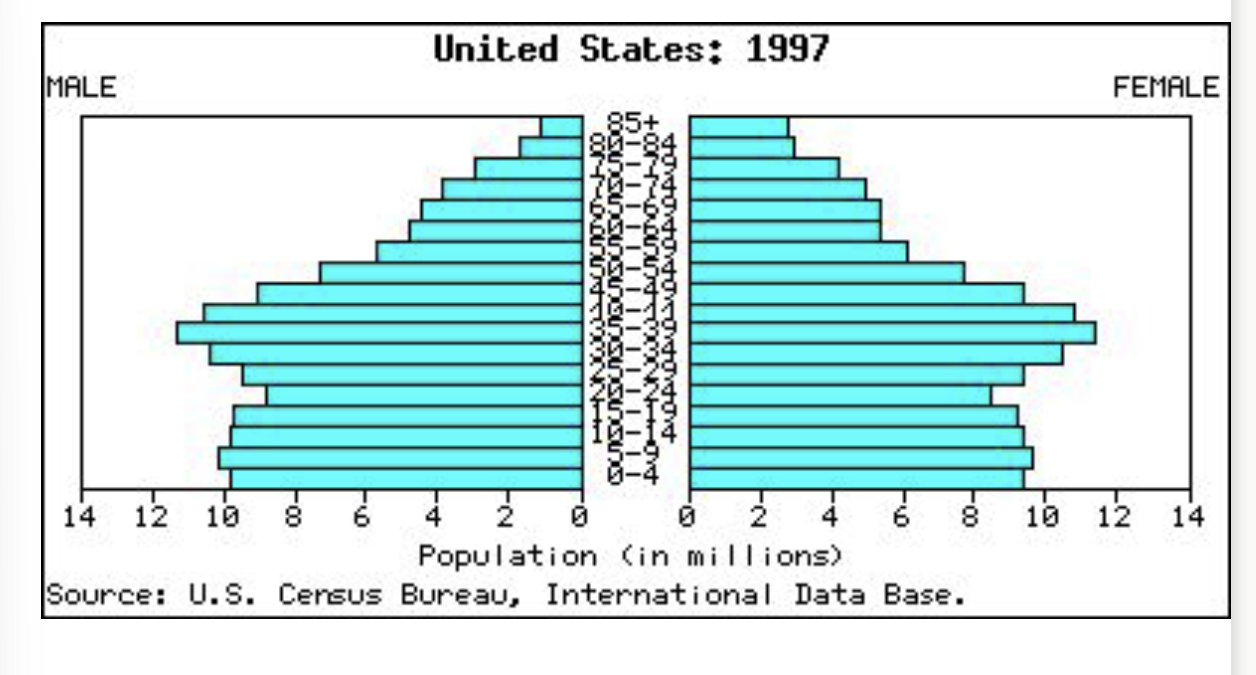
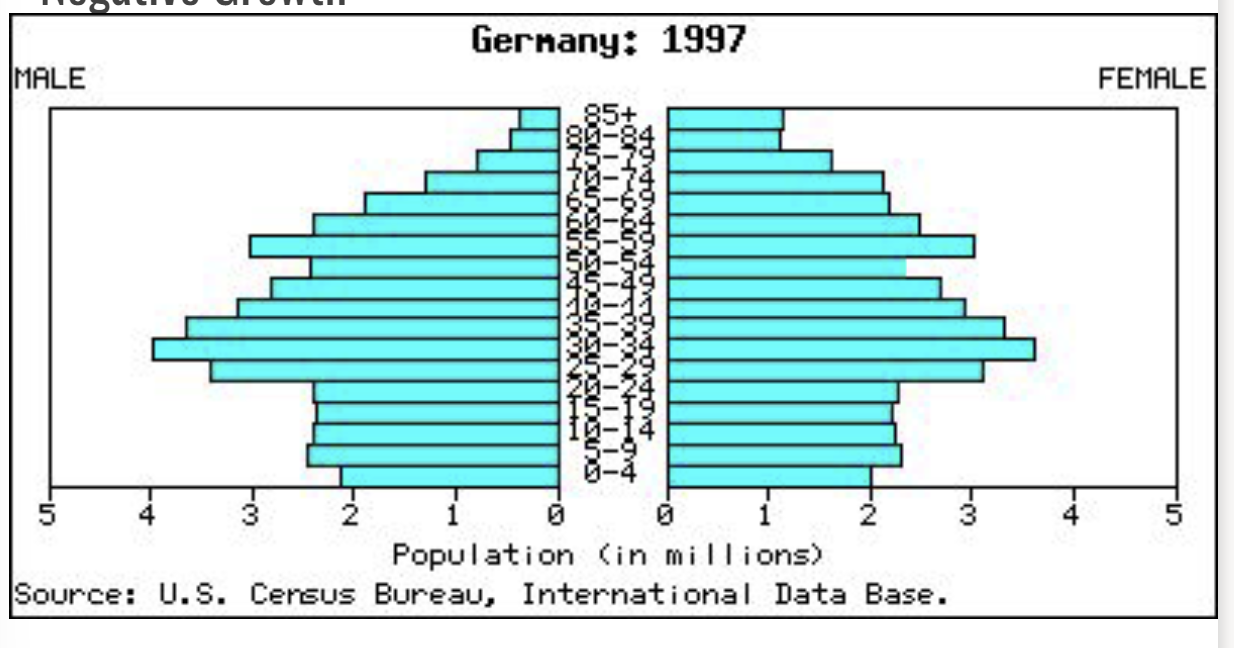
Population Profiles
Bar graph showing the number of people (sex separated) at each age for a given population.
How does population profile data get collected?
A questionnaire given to households
Demography
Collection, compilation, and presentation.
Rapid Growth
Slow Growth
Negative Growth
What’s the purpose of population profiles (age/ sex pyramids)?
Estimate future population growth or decline but they are not “clever”
What are the limits of population profiles?
Do not take into account socio-economic factors
Simply move the bars up for the necessary number of years.
Predictions can be based on what?
The natural rate of increase and not taking any developmental factors into account
Predictions are rough and show what would happen if the current doubling time continued unabated.
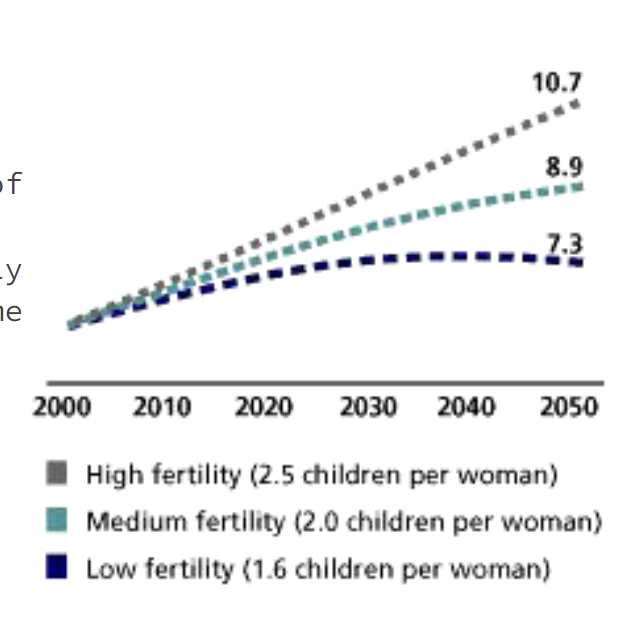
UN Predictions
High, medium, and low fertility
Does not rely upon DT as the projections assume that the growth rate will drop slightly by 20202 and continue declining as the century progresses.
What drives conservation efforts?
Losing biodiversity
3 Direct Values for Habitat Preservation
Food sources
Natural Products
Economic
Indirect Values for Habitat Preservation (6)
Scientific and educational value
Aesthetic — Beauty and inspiration derived from looking at diverse species and habitats.
Ethical — Biorights, and obligations to future generations.
Genetic — Diversity of the gene pool ensures a future variety of life. Needed for stable ecosystems.
Social — Habitats provide homes, work, resources, and social cohesion for indigenous people.
Ecological — Nutrient cycling, pollination, CO2 removal, and etc.
Utilitarianism
Taking the best moral action that maximizes happiness/minimizes suffering to organisms.
Intrinsic Value
The value a species has within its own right.
IGO & GO (Media)
Statements written by officers & clerks
Works alongside official media outlets
Publish scientific reports
NGO (Media)
Graphic footage to gain media attention.
Mobilize public protests to attract attention.
Effective use of social media to spread messages.
Sabotage events with high media coverage.
Publish scientific reports
IGO & GO (Speed of response)
Considered and slow (bureaucratic)
May go against public opinion so many views need to be considered.
NGO (Speed of Response)
Can be rapid
Member only join if they share opinions, so little deliberation.
Little consideration of the status quo.
IGO & GO (Diplomatic constraints)
Considerable — Often hindered by political disagreement (different cultural opinions and motives)
Decisions can be politically driven rather than by best conservation strategy.
NGO (Diplomatic Constraints)
Generally unaffected by political constraints
Can even include illegal activity
Driven by what is best for conservation — can lead to extreme actions.
IGO & GO (Enforcement)
International agreements and national or regional laws can lead to prosecution.
NGO (Enforcement)
No legal power — use of persuasion and public opinion to pressure governments.
IGO & GO (Public Image)
Organized as businesses with concrete allocation of duties
Cultivate an upright image based on scientific/business-like approaches.
Lead and encourage partnerships between nations and organizations.
NGO (Public Image)
Can be a confrontational/ radical approach to an environmental issue.
Lead and encourage partnerships between nations and organizations to conserve and restore ecosystems and biodiversity.
IGO & GO (Political Influence)
Enforce their decision through legislation
Seek to ensure that decisions are applied
NGO (Political Influence)
Serve as watchdogs (suing gov agencies and businesses who violate environmental law).
Seek to ensure that decisions are applied
IGO & GO (Agenda)
Provide guidelines and implement national treaties
IGO, GO & NGO may collaborate in global, transactional scientific research projects, both may provide a forum for discussion.
NGO (Agenda)
Use public pressure to influence national gov/ lobby gov over policies and legislation.
Buy and manage land to protect habitat, wildlife, etc.
IGO, GO & NGO may collaborate in global, transactional scientific research projects, both may provide a forum for discussion.
IGO & GO (Funding)
Potentially very large budgets
Funded by national budgets
NGO (Funding)
Manage publicly owned lands.
Private donations
Can be funded by companies, governments ot political parties.
IGO & GO (Extent of influence geographically)
Global or national in extent
Countries can be fined/ shunned for breaking international rules
NGO (Extent of influence geographically)
Focus more on local and/ or national information, aiming at education, producing learning materials and opportunities for schools and public
Often relies on disruptive/ embarrassment techniques to cause change.
CITES
Convention on the International Trade of Endangered Species
WCC (World Conservation Strategy)
Commissioned by the UNEP and WWF provided the funds for its preparation and contributed to the evolution of its basic themes and structure.
CBD (Convention of Biological Diversity)
Focused on reversing trends in loss of biodiversity.
Main Approaches of Conservation
Species based
Habitat Based
Combination of both
How to make a conservation more successful?
Research
Adequate funding
Support of the local community
What’s ‘Species Based’ Conservation?
Focuses on keystone species. Includes efforts such as captive breeding, zoos, and reintroduction.
What’s ‘Habitat Based’ Conservation?
Focus on habitats, and protect all species. Generally on-site conservation.
What’s ‘Combined’ Conservation?
Apply species-based strategies within the boundaries of habitat-based protected areas or nature reserves.
Corridors
Strips of land that link reserves together
Ecotone
Where two habitats meet near a boundary.
Lots of species can be found in an ecotone.
Edge effect
the effect of a sudden transition between two different adjoining ecological communities on the numbers and kinds of organisms in the marginal habitat.
This occurs at ecotones because more species are present from the two habitats (increased resources)
Protected areas
Islands within the surrounding landscape. The success and effectiveness of protected areas depend on several factors.
Criterias for consideration when designing protected areas: (5)
Size
Shape
Edge Effect
Corridors
Proximity to potential human influence
(SLOSS) Single Large or Several Small — Large is better than small.
More habitats
More species
More niches
More varied
Supports larger populations
Ideal for large mammals and apex predators
Less edge effect
Wildlife corridor
Link of wildlife habitat, generally native vegetation, which joins two or more larger areas of similar wildlife habitat.
Corridors are critical for?
The maintenance of ecological processes including allowing for the movement of animals and the continuation of viable populations.
What are the advantages of ‘Corridor in Wildlife Reserve’?
Gene flow — emigration, and immigration
Seasonal movement
Reduces collisions between cars and animals
Reducing roads that act as barriers
What are the disadvantages of ‘Corridor in Wildlife Reserve’?
Invasion of exotic pests or diseases
Poachers can easily move from one reserve to another could become barriers to some species
Could have increased edge effects
Buffer Zone
Areas around conservation areas. They contain habitats that may be managed or undisturbed.
Minimize disturbance from outside like people, agriculture, or invasion.
In situ
Conservation of species in their natural habitat
Natural parks, natural reserves
Ex situ
Conserving species in isolation of their natural habitat
Zoos, botanical gardens
Alternative approaches to the development of protected areas and species-based conservation such as: (7)
CITES (Conservation of International Trade in Endangered Species), captive breeding, botanical gardens, seed banks, reintroduction, flagship species, keystone species,
Captive Breeding
the process of keeping plants or animals in controlled environments, such as wildlife reserves, zoos, and botanic gardens.
Ex situ strategy
Cost-intensive so mostly MEDCs
Seed banks
Where seeds are stored, frozen and dry, for many years.
Flagship Species
a species selected to act as an ambassador, icon, or symbol for a defined habitat, issue, campaign, or environmental cause.
cute, cuddly, and iconic
Often large mammals at or near top trophic levels
Useful for media and fundraising
Project integrity of the food web
Fulfill essential niches
not necessarily top trophic levels
Keystone species
a species on which other species in an ecosystem largely depend, because when it is removed, the ecosystem would change and cause other species to disappear.
for conservation to be successful these species must be identified.
Often engineers (e.g. beavers) create habitats.
Examples of Keystone species
California Sea Otters
Pisaster Starfish
“Mangrove” trees
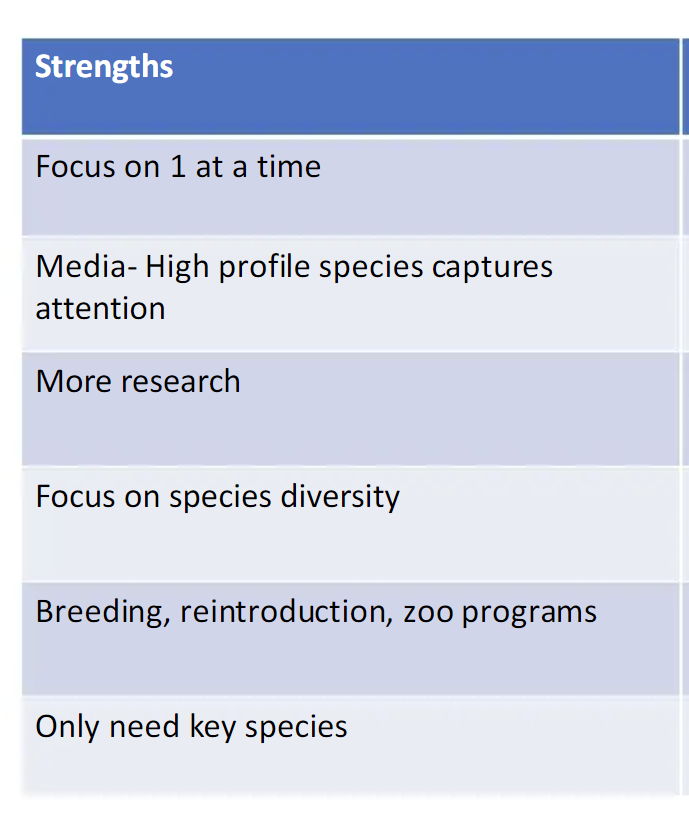
Strengths of species-based conservation strategies (1)
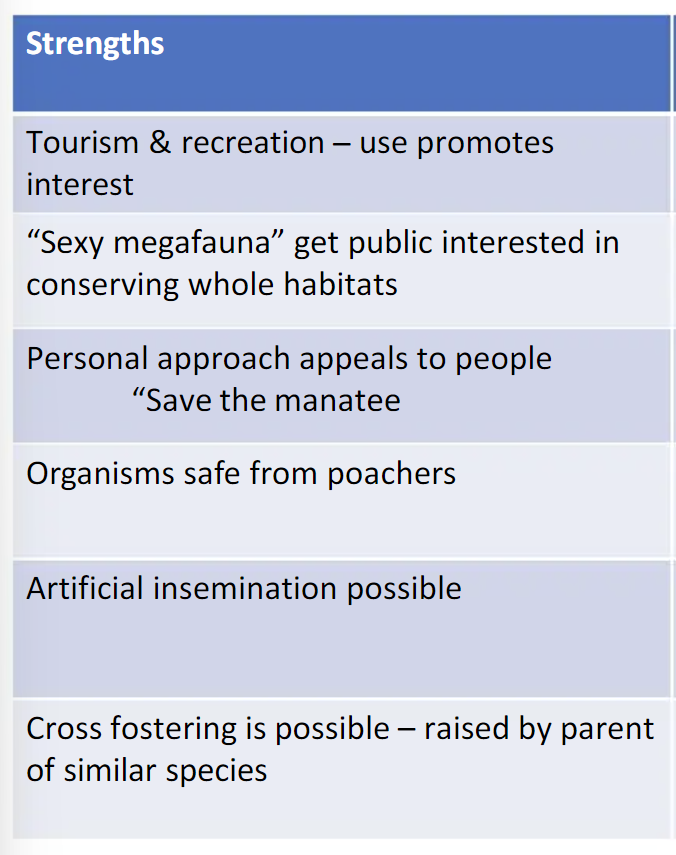
Strengths of species-based conservation strategies (2)
Weaknesses of species-based conservation strategies (1)

Weaknesses of species-based conservation strategies (2)

The Species Approach (Goal)
Protect species from premature extinction
The Species Approach (Strategies)
Identify endangered species
Protect their critical
The Species Approach (Tactics)
legally protect endangered species
Manage habitat
Propagate endangered species in captivity
Reintroduce species into suitable habit
The Ecosystem Approach (Goal)
Protect populations of species in their natural habitats