1.3 Structure and function: Brain Structure
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What are the planes of dissection?
Horizontal, Sagittal, Coronal
Medial/Lateral
Toward Middle / Toward Side
Ipsilateral / Contralateral
Same / Opposite Side
Proximal / Distal
Near / Far
Superior / Inferior
Up / Down
Anterior / Posterior
Front / Back
Rostral / Caudal
Beak / Tail
Dorsal / Ventral
Back / Belly
Cerebral Cortex
Outermost layer of the brain; has gyri and sulci
Gyri
In the cerebral cortex, ridged or raised portions
Sulci
In the cerebral cortex, furrows
Lobes in Cerebral Cortex
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal
Frontal Lobe
Attention, planning, motor
Parietal Lobe
Touch, other
Occipital Lobe
Visual processing
Temporal Lobe
Auditory Processing, memory
List of Boundaries between lobes
Longitudinal fissure, sulvian fissure, central sulcus
Longitudinal Fissure
Separates Left/Right Hemispheres
Sylvian Fissure
Boundary of temporal lobe
Central Sulcus
Divides frontal/parietal lobes
Precentral Gyrus
In frontal lobe, for motor control
Postcentral gyrus,
In parietal lobe, for touch
Gray Matter
Cell bodies and dendrites (lack myelin), Nuclei (collections of neurons)
White matter
Axons with white myelin sheaths (fatty), tracts (bundles of axons)
Tracts
Bundles of axons
Embryonic Development
Begins with neural tube; divided by into forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain
What does the forebrain develop into?
Telencephalon and diencephalon
What does the midbrain develop into?
Remains as midbrain
What does the hindbrian develop into?
Cerebellum, pons, and medulla
List of inside the telencephalon
Cerebral Cortex, Basal Ganglia, Hippocampus Amygdala, Cingulate Gyrus, Olfactory bulb
Cerebral Cortex
Sensory, motor, associative, cognitive, six layers, pyramidal cells
Basal Ganglia
Control of movement and actions
Hippocampus and Fornix
Learning
Amygdala
Emotional Regulation and Perception of Odor
Cingulate Gyrus
Attention
Olfactory bulb
Sense of Smell
List inside the Diencephalon
Thalamus, Hypothalamus
Thalamus
Cluster of Nuclei that relay all sensory information to cortex
Hypothalamus
Motivated behavior, homeostasis, regulating autonomic nervous system, control pituitary gland
List inside the Midbrain
Tectum, Tegmentum, Reticular Formation, Periaqueductal Gray
Tectum
Superior colliculi (visual) and Inferior colliculi (auditory)
Tegmentum
Sustantia nigra (source of dopamine to basal ganglia)
Periaqueductal Gray
Pain Perception
Reticular Formation
Sleep and arousal
List of Structures in Hindbrain
Pons, Medulla, Cerebellum
Pons
Sensory and motor nuclei
Medulla
Transition from brain to spinal cord; essential process such as respiration and heart rate
Cerebellum
Attached to brain stem, function in motor cooridination/control
Meninges
Protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord; Dura mater, arachnoid membrane, pia mater
Dura mater
tough outermost layer
Arachnoid membrane
between other two, filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Pia Mater
Delicate innermost layer
Ventricular system
Series of chambers filled with CSF
Lateral Ventricle
Extend into all four lobes and lined with choroid plexus
Choroid Plexus
Membrane that produces CSF
How does the CSF flow?
From the lateral ventricles, into third ventricle at midline, into fourth ventricle, exits to circulate over the brain and spinal cord
What does CSF provide?
Buoyancy, protection, exchange of nutrients/waste between blood and brain
What does the brain depend on besides CSF?
Oxygenated blood from the cerebral arteries
Cerebral Arteries
Branch from the carotid and vertebral arteries
Stroke
Caused by the rupture of blockage of blood vessels
Blood Brain Barrier
Filters blood before it enters brain tissue; selectively permeable
Structural Imaging
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT or CT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Diffusion Tensor Imaging
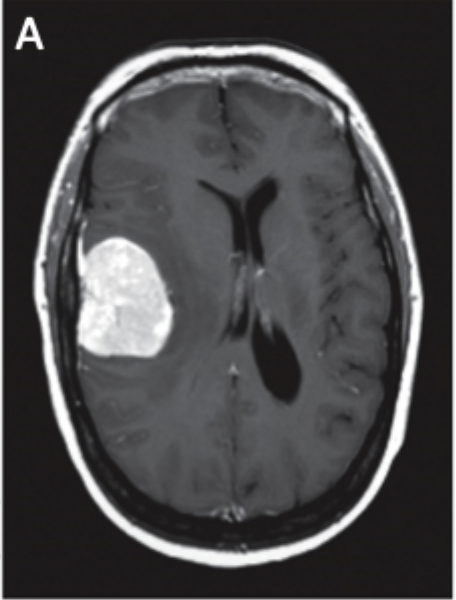
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT or CT)
Map based on tissue density and X-ray absorption, best for strokes and tumors
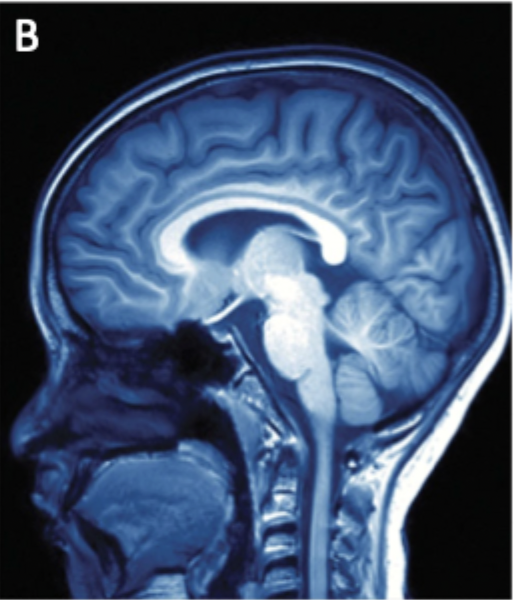
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic fields and radio waves to map tissue density, best for high resolution images
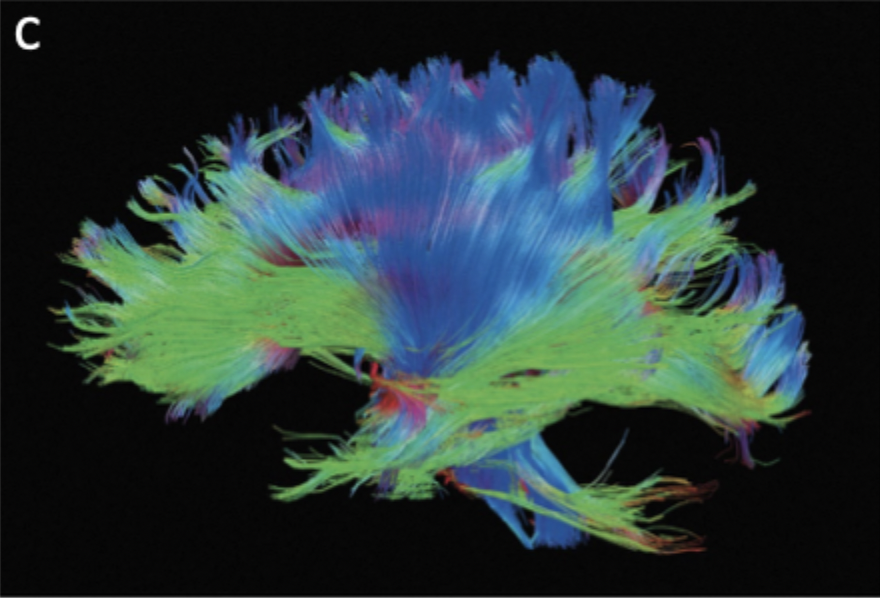
Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Visualize axon fiber tracts
Functional Brain Imaging
Functional MRI (fMRI), Positron Emission Tomography (PET), Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
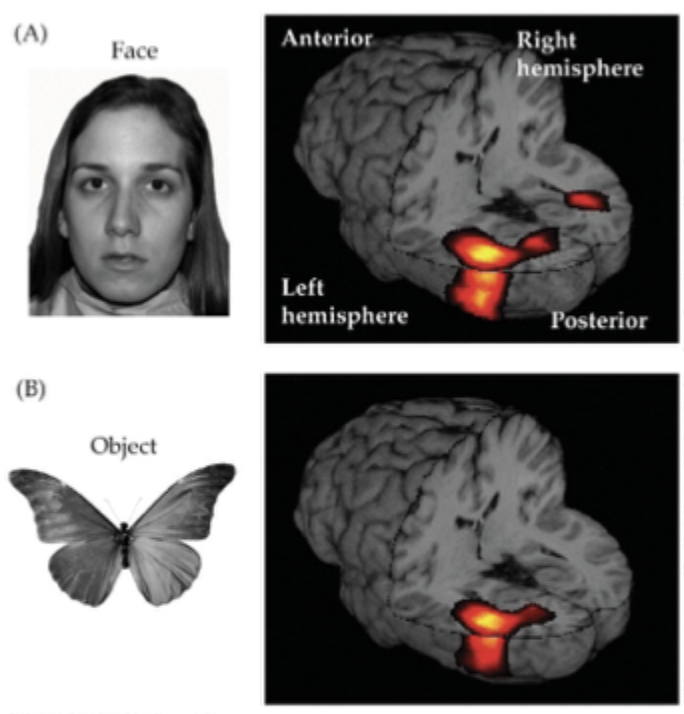
Functional MRI (fMRI)
detect small changes in brain metabolism (ex. oxygen use)
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
gives images of brain activity using radioactive chemicals in blood stream
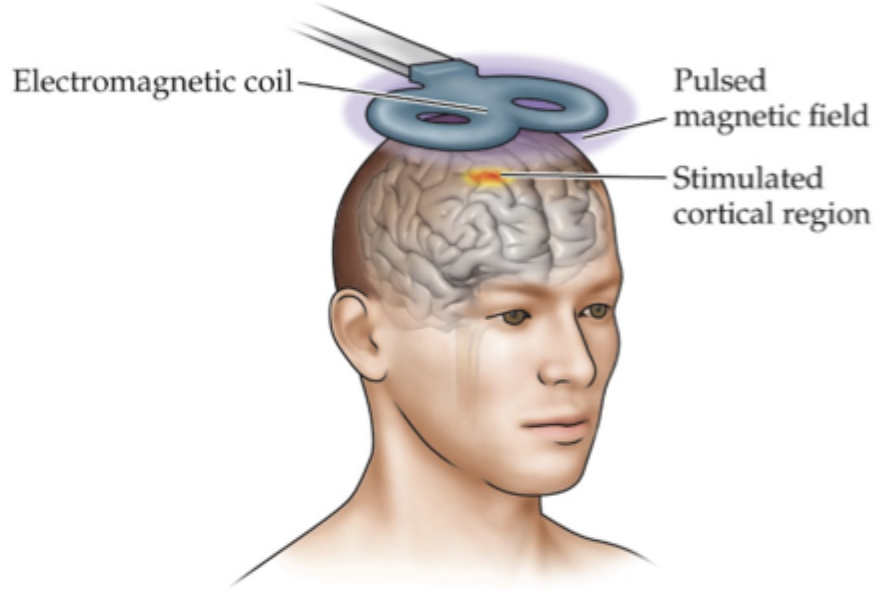
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Stimulates discrete cortical regions through magnetism
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Measures tiny magnetic fields given off by active neurons through magnetism