Clotting Disorders
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
*starred stuff is from the slides. Italicized is from uptodate/openevidence/the book. I hate lazy people
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Vasoconstriction, platelet plug, coag cascade
*What is the normal body response to vessel injury?
PGI2 (inhibits aggregation), NO (vasodilator, inhibits aggregation)
*What are the mechanisms that prevent over clotting?
Immune Thrombocytopenia
*An autoimmune (IgG) mediated destruction of the platelet membrane protein GPIIb/IIIa that is either idiopathic or triggered by drugs, HIV, HEP C, SLE, H. Pylori, CLL or rhinovirus?
CBC, peripheral blood smear, retic count, TSH/T4, Coags, test for Hep C, HIV, and H. pylori
*6 y/o male presents to the ER for epistaxis. The mom says that this has been happening “ever since the boy had a cold.” On physical exam you note non-palpable petechiae and purpura. What diagnostics do you want?
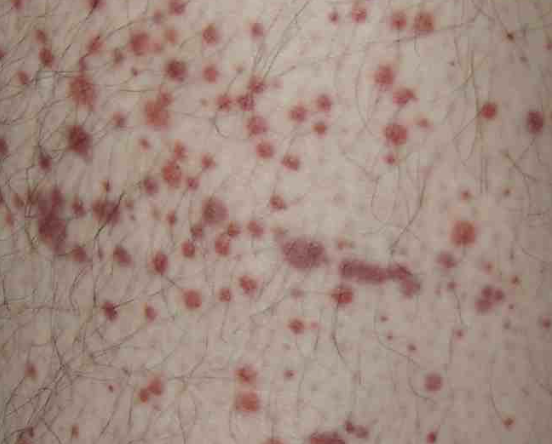
IV corticosteroids, IVIG, TPO (chronic/refractory - romiplostim, eltrombopag), splenectomy at 12 months (last resort), activity restriction, NO NSAIDS
*6 y/o male presents to the ER for epistaxis. The mom says that this has been happening “ever since the boy had a cold.” On physical exam you note non-palpable petechiae and purpura. Labs are as followed, normal white count, HgB, and coags, Platelets are under 30K, and on the peripheral blood smear you note enlarged platelets. What is your treatment plan (its severe so no observation)?
platelets (only under 30K), IVIG, steroids
*ER management of ITP for critical/severe bleeding
Kids (chronic = adult)
*Acute ITP is more common in
Wet purpura, hx of bleeding, under 20K platelets, high risk of stroke (prior bleeding, under 10K platelets, 60+ y/o)
Which ITP patients should be admitted?
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
*A severe life-threatening macroangiopathic hemolytic anemia caused by reduced activity of ADAMTS13 which normally cleaves VWF.
autoimmune antibodies, estrogen, HIV, Sepsis, cardiac surgery, pancreatitis, liver diseases
*Triggers for TTP
CBC, CMP, LDH, Peripheral blood smear, troponin, coags, haptoglobin, bilirubin ADAMST13 activity 🏆, DAT,
*45 y/o male presents to the ER for HA and fatigue. He also reports some mild SOB. Vitals are stable except for 92% on RA. On physical exam you note the abdomen is tender to palpation, splenomegaly, and widespread petechiae. What diagnostics you want?
NEURO (HA, focal deficits, seizures, confusions, vertigo)
*What symptoms dominate TTP?
Plasma exchange (stop if over 150K for 38 hours), high dose steroids, splenectomy, cyclosporin, rituximab, caplacizumab (anti-VWF)
*45 y/o male presents to the ER for HA and fatigue. He also reports some mild SOB. Vitals are stable except for 92% on RA. On physical exam you note the abdomen is tender to palpation, splenomegaly, and widespread petechiae. CBC reveals a low HgB, Hct, and RBCs, Platelets count is 10K, retics are elevated, Coags are normal, LDH and indirect bilirubin are elevated. Peripheral blood smear reveals schistocytes, helmet cells, and triangular cells. ADAMSTS13 activity is under 10%. What is your treatment plan
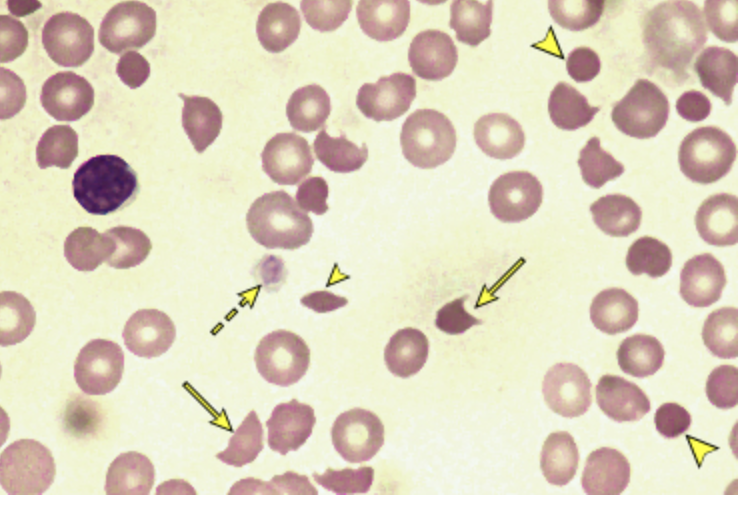
fever, thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, renal dysfunction, neuro deficits
*Pentad of TTP (That we haven’t seen since platelet exchange was invented 🙄 - GI manifestations are most common HOWEVER)
platelets under 30K, hemolysis (elevated retics, undetectable haptoglobin, elevated indirect bili), no active cancer, no transplant hx, MCV under 90, INR under 1.5, Creatinine under 2
Plasmic score parameters for TTP
Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
*What is the most common cause of acute renal failure in children characterized by a prodrome of abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloody diarrhea
Thrombocytopenia, AKI, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
*Triad of HUS
Fluids, anti-emetics, transfusion of RBCs or platelets, dialysis (if severe azotemia, fluid overload, or refractory electrolyte issues), NO ABX or ANTI-MOTILITY AGENTS (if caused by STEC), eculizumab (STEC - monoclonal antibody that blocks C5 cleavage)
*Treatment plan for HUS
Hgb under 8 + negative DAT + schistocytes and helmet cells
A Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia is characterized by
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
*What occurs when factor III is overreleased causing the deposition of fibrin clots (using clotting factors and platelets) which leads to bleeding?
Sepsis (most common), trauma (2x mortality), malignancy, OB events (obstruction, HELLP, elevated d-dimer, fibrin split), burns, snake bites, pancreatitis
*Triggers of DIC
High PT/INR/PTT, decreased fibrinogen, elevated D-dimer
*Lab findings in DIC
Treat the underlying, LMWH, Supportive care (transfusion, ventilation, aggressive rehydration)
*Treatment plan for DIC
Hemophilia A
*An X-linked recessive deficiency in factor 8 that occurs in 1/5000 live births
prolonged aPTT, normal PT and platelets (intrinsic path dysfunction)
*Lab findings in hemophilia A
Factor VIII 🥇, emicizumab (prophylaxis), DDAVP (if mild), bypassing agents, gene therapy
*treatment plan for hemophilia A
Hemophilia B (Christmas Disease)
*An X-linked recessive deficiency in factor 9 that occurs in 1/100,000 live male births
Hemophilia C (Rosenthal Syndrome)
*An autosomal recessive deficiency of Factor XI that predominantly affects those of Ashkenazi Jewish decent
Hemarthrosis
What is the most common finding in hemophilia?
Von Willebrand’s Disease (VWD)
*The most common inherited bleeding disorder caused by quant/qual deficits in VWF with three major types: type 1 (partial quantitative deficiency), type 2 (qualitative defects, further divided into 2A, 2B, 2M, and 2N), and type 3 (virtually complete deficiency)
CBC (normal platelets), Coags (APTT may be prolonged), VWF antigen, VWF activity
*Diagnostics for VWD
DDVAP (induces the release of VWF - effective in type 1 and 2), plasma-derived or recombinant VWF concentrates (if refractory), antifibrinolytics (TXA for mucosal bleeds)
*Treatment for VWD
Vitamin K deficiency
*What causes a reduction in the activity of the factors II, VII, IX, and X, as well as proteins C and S, leading to bleeding?
Fat malabsorption syndromes, liver disease, warfarin use, prolonged abx use, high levels of vitamin E
*What are the most common causes of Vitamin K deficiencies?
Prolonged PT (aPTT if really bad), Low II, VII, IX, XII; PIVKA (proteins induced by vitamin K absence - if vitamin K supplementation has already been started)
*Lab findings in Vitamin K deficiencies
Vitamin K supplementations (PO, SQ, IV)
*Treatment plan for Vitamin K deficiencies

pregnancy
*What is the most common hypercoagulable state?
Factor V leiden
What is the most common inherited hypercoagulable state?
Polycythemia Vera
*A chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm that is characterized by a JAK-2 mutation and uncontrolled RBC production
erythrocytosis (hemoglobin over 16.5 in men, 16 in women); maybe thrombocytosis or leukocytosis
*Lab findings in polycythemia vera
pruritus after bathing (aquagenic pruritus), splenomegaly, HA, visual disturbances, dizziness, claudication
*Clinical presentation of polycythemia vera
phlebotomy (target Hct of 45%), low dose ASA, increased fluid intake, myelosuppressive agents, If refractory use cytoreductive therapy
*Treatment plan for polycythemia vera