L5_Introduction to Helicopters
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
helicopter
is an aircraft that is lifted and propelled by one or more horizontal rotors, each rotor consisting of two or more rotor blades.
rotorcraft or rotary-wing
Helicopters are classified as _____ aircraft to distinguish them from fixed-wing aircraft because the helicopter derives its source of lift from the rotor blades rotating around a mast.
move forward
vertically
The primary advantages of the helicopter are due to the rotor blades that revolve through the air, providing lift without requiring the aircraft to _____.
This creates the ability of the helicopter to take off and land _____ without the need for runways.
congested or isolated
Helicopters are often used in _____ areas where fixed-wing aircraft are not able to take off or land.
The lift from the rotor also allows the helicopter to hover in one area and to do so more efficiently than other forms of vertical takeoff and landing aircraft, allowing it to accomplish tasks that fixed wing aircraft are unable to perform.
vertical flight
The earliest references for _____ came from China.
400 BC
bamboo flying toys (or Chinese top)
Since around _____. Chinese children have played with _____.
bamboo-copter
is spun by rolling a stick attached to a rotor.
The spinning creates lift, and the toy flies when released.
1480s
aerial screw
It was not until the early _____, when Italian polymath Leonardo da Vinci created a design for a machine that could be described as an "_____", that any recorded advancement was made towards vertical flight.
Leonardo da Vinci
It was not until the early 1480s, when Italian polymath _____ created a design for a machine that could be described as an "aerial screw", that any recorded advancement was made towards vertical flight.
1939
Vought-Sikorsky VS-300
In _____, Igor Sikorsky designed and flew the _____, the first viable American helicopter, which pioneered the rotor configuration used by most helicopters today.
Igor Sikorsky
In 1939, _____ designed and flew the Vought-Sikorsky VS-300, the first viable American helicopter, which pioneered the rotor configuration used by most helicopters today.

Sikorsky R-4
Igor Sikorsky modified the design into the _____, which became the world's first mass-produced helicopter in 1942.
Igor Sikorsky
designed the first successful helicopter incorporating the tail rotor into the design, upon which further designs were based.
1951
K-225 helicopter
In _____, at the urging of his contacts at the Department of the Navy, Charles H. Kaman modified his _____ with a new kind of engine, the turbo-shaft engine.
Charles H. Kaman
turbo-shaft
horsepower
In 1951, at the urging of his contacts at the Department of the Navy, _____ modified his K-225 helicopter with a new kind of engine, the _____ engine.
This adaptation of the turbine engine provided a large amount of _____ to the helicopter with a lower weight penalty than piston engines, heavy engine blocks, and auxiliary components.

K-225
On December 11, 1951, the _____ became the first turbine-powered helicopter in the world.
hover
low airspeed
time or work-intensive
Due to the unique operating characteristics of the helicopter its ability to take off and land vertically, to _____ for extended periods of time, and the aircraft’s handling properties under _____ conditions, it has been chosen to conduct tasks that were previously not possible with other aircraft or were too _____ or _____ to accomplish on the ground.
Helicopters are used for transportation, construction, firefighting, search and rescue, and a variety of other jobs that require its special capabilities.
helicopter rotor system
is the rotating part of a helicopter that generates lift.
main rotors
tail rotor
Rotor system may be mounted horizontally, as _____ are, providing lift vertically; it may be mounted vertically, such as a _____, to provide lift horizontally as thrust to counteract torque effect.
tilt rotors
horizontal
vertical
In the case of _____, the rotor is mounted on a nacelle that rotates at the edge of the wing to transition the rotor from a _____ mounted position, providing lift horizontally as thrust, to a _____ mounted position providing lift exactly as a helicopter.
nacelle
lift horizontally
lift exactly as a helicopter
In the case of tilt rotors, the rotor is mounted on a _____ that rotates at the edge of the wing to transition the rotor from a horizontal mounted position, providing _____ as thrust, to a vertical mounted position providing _____.
tail rotor
is a smaller rotor mounted vertically or near vertically on the tail of a traditional single-rotor helicopter.
tail rotor
either pushes or pulls against the tail to counter the torque.
main transmission
tail boom
The tail rotor drive system consists of a drive shaft powered from the _____ and a gearbox mounted at the end of the _____.
tail rotor
is powered by the helicopter's main power plant, and rotates at a speed proportional to that of the main rotor.
Hover
Forward Flight
2 Flight Conditions
Hover
means that it is in flight at a constant altitude, with no forward, aft, or sideways movement.
main rotor blades
In order to hover, a helicopter must be producing enough lift in its _____ to equal the weight of the aircraft.
Forward flight
a helicopter's flight controls behave more like those in a fixed-wing aircraft.
down
altitude
airspeed.
Forward Flight
Moving the cyclic forward makes the nose pitch _____, thus losing _____ and increasing _____.
up
Forward Flight
Moving the cyclic back makes the nose pitch _____, slowing the helicopter and making it climb.

collective pitch control
cyclic pitch control
antitorque pedals or tail rotor control
3 Major controls in a helicopter that the pilot must use during flight.
throttle control
In addition to these 3 major controls, the pilot must also use the _____, which is usually mounted directly to the collective pitch control in order to fly the helicopter.
collective pitch control (or simply “collective” or “thrust lever”)
is located on the left side of the pilot’s seat and is operated with the left hand.
collective pitch control (or simply “collective” or “thrust lever”)
is used to make changes to the pitch angle of the main rotor blades.

pitch angle
As the collective pitch control is raised, there is a simultaneous and equal increase in _____ of all main rotor blades; as it is lowered, there is a simultaneous and equal decrease in _____.
collective pitch control
The pilot uses _____ to rise vertically.
pitch angle
angle of incidence
Changing the _____ on the blades changes the _____ on each blade.
angle of incidence
With a change in _____ comes a change in drag, which affects the speed or revolutions per minute (rpm) of the main rotor.
increases
increases
increases
decreases
Decreasing pitch angle decreases both angle of incidence and drag, while rotor rpm increases.
As the pitch angle ____, angle of incidence _____, drag _____, and rotor rpm _____.
proportionate
throttle control or governor
In order to maintain a constant rotor rpm, which is essential in helicopter operations, a _____ change in power is required to compensate for the change in drag.
This is accomplished with the _____, which automatically adjusts engine power.
throttle
The function of the _____ is to regulate engine rpm.
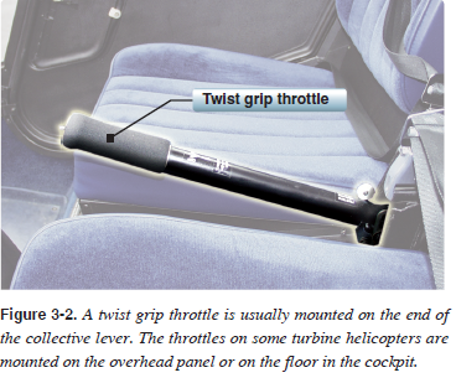
twist grip
If the correlator or governor system does not maintain the desired rpm when the collective is raised or lowered, or if those systems are not installed, the throttle must be moved manually with the _____ in order to maintain rpm.
collective
If the correlator or governor system does not maintain the desired rpm when the _____ is raised or lowered, or if those systems are not installed, the throttle must be moved manually with the twist grip in order to maintain rpm.
throttle control
The _____ is much like a motorcycle throttle, and works in virtually the same way.
increases
decreases
Twisting the throttle control to the left _____ rpm; twisting the throttle to the right _____ rpm.
governor
is a sensing device that senses rotor and engine rpm and makes the necessary adjustments in order to keep rotor rpm constant.
throttle
In normal operations, once the rotor rpm is set, the governor keeps the rpm constant, and there is no need to make any _____ adjustments.
Governors
are common on all turbine helicopters and used on some piston powered helicopters.
correlator
is a mechanical connection between the collective lever and the engine throttle.
collective lever
When the _____ is raised, power is automatically increased; when lowered, power is decreased.
Correlator
this system maintains rpm close to the desired value, but still requires adjustment of the throttle for fine tuning.
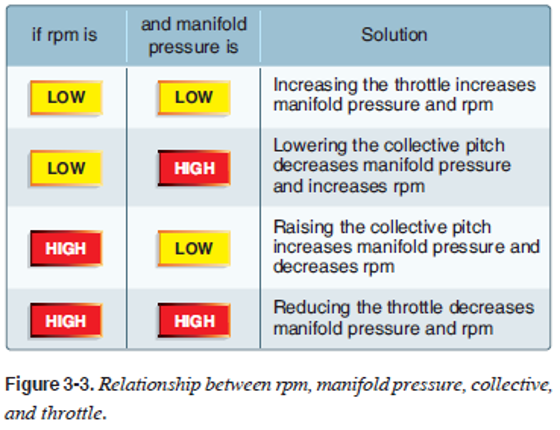
collective pitch
throttle
In piston helicopters, the _____ is the primary control for manifold pressure, and the _____ is the primary control for rpm.
secondary control
However, the collective pitch control also influences rpm, and the throttle also influences manifold pressure; therefore, each is considered to be a _____ of the other’s function.
tachometer (rpm indicator) and the manifold pressure gauge
Both the _____ and the _____ must be analyzed to determine which control to use.
cyclic pitch control
is usually projected upward from the cockpit floor, between the pilot’s legs or between the two pilot seats in some models.
cyclic pitch control
This primary flight control allows the pilot to fly the helicopter in any direction of travel: forward, rearward, left, and right.
total lift force
is always perpendicular to the tip-path plane of the main rotor.
tip-path plane
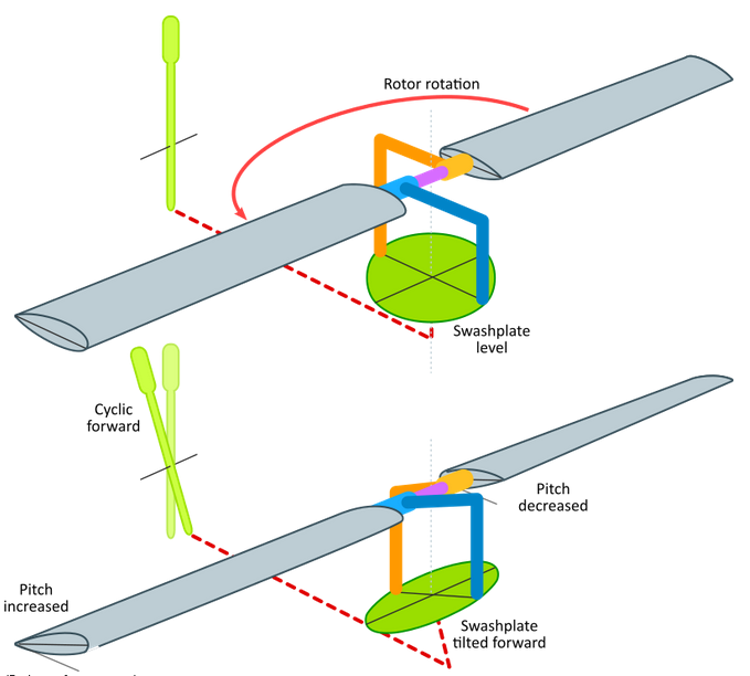
The purpose of the cyclic pitch control is to tilt the _____ in the direction of the desired horizontal direction.

rotor disk
The cyclic controls the _____ tilt versus the horizon, which directs the rotor disk thrust to enable the pilot to control the direction of travel of the helicopter.
rotor disk
If the cyclic is moved forward, the rotor disk tilts forward; if the cyclic is moved aft, the disk tilts aft, and so on.
tilts in the same direction the cyclic pitch control is moved.
gyro
rigged
Because the rotor disk acts like a _____, the mechanical linkages for the cyclic control rods are _____.
increase
increases
decrease
decreases
An _____ in pitch angle _____ AOA; a _____ in pitch angle ____ AOA.
AOA
downward
upward
If the cyclic is moved forward, the _____ decreases as the rotor blade passes the right side of the helicopter and increases on the left side.
This results in maximum _____ deflection of the rotor blade in front of the helicopter and maximum ____ deflection behind it, causing the rotor disk to tilt forward.

antitorque pedals
located on the cabin floor by the pilot’s feet, control the pitch and therefore the thrust of the tail rotor blades or other antitorque system.
fuselage
Newton’s Third Law “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction”.
This law applies to the helicopter _____ and its rotation in the opposite direction of the main rotor blades unless counteracted and controlled.
antitorque rotor or tail rotor
To make flight possible and to compensate for this torque, most helicopter designs incorporate an _____.
antitorque pedals
allow the pilot to control the pitch angle of the tail rotor blades.
antitorque pedals
are connected to the pitch change mechanism on the tail rotor gearbox and allow the pitch angle on the tail rotor blades to be increased or decreased.
tail rotor
is used to control the heading of the helicopter while hovering or when making hovering turns, as well as counteracting the torque of the main rotor.
Hovering turns
are commonly referred to as “pedal turns.”
tail rotor
tail rotor blades
The thrust of the _____ depends on the pitch angle of the _____.
This pitch angle can be positive, negative, or zero.
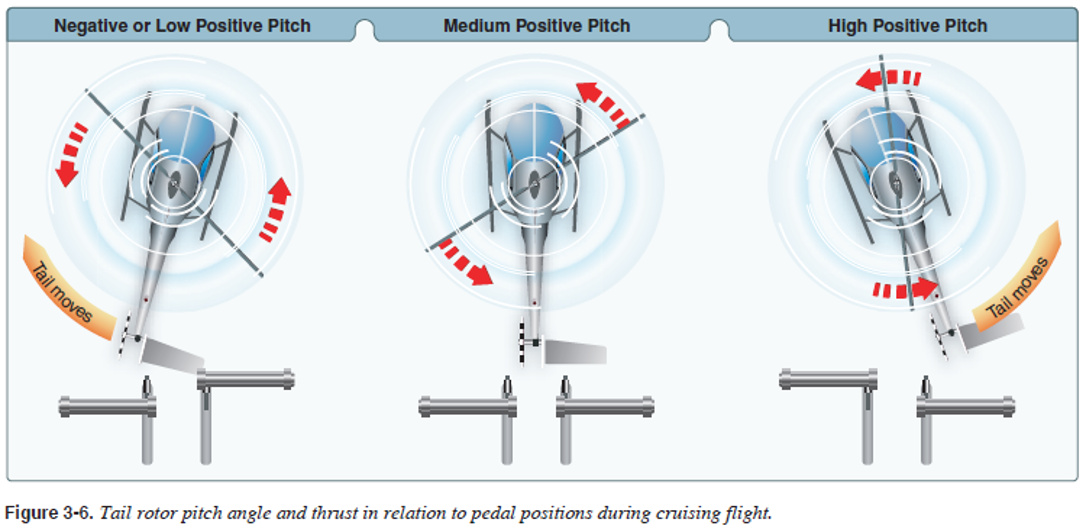
positive pitch angle
tends to move the tail to the right.
negative pitch angle
moves the tail to the left, while no thrust is produced with a zero pitch angle.
positive
negative
The maximum _____ pitch angle of the tail rotor is generally greater than the maximum _____ pitch angle available.
This is because the primary purpose of the tail rotor is to counteract the torque of the main rotor.
right
left
From the neutral position, applying right pedal causes the nose of the helicopter to yaw _____ and the tail to swing to the _____.
nose
tail
Pressing on the left pedal has the opposite effect: the ____ of the helicopter yaws to the left and the _____ swings right.
medium positive
With the antitorque pedals in the neutral position, the tail rotor has a _____ pitch angle.
tail rotor thrust
torque of the main rotor
In medium positive pitch, the _____ approximately equals the _____ during cruise flight, so the helicopter maintains a constant heading in level flight.
vertical fin or stabilizer
is used in many single-rotor helicopters to help aid in heading control.
vertical fin or stabilizer
is designed to optimize directional stability in flight with a zero tail rotor thrust setting.
A
A