exam 3 pt 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Meiosis and sexual life cycles; each stage?
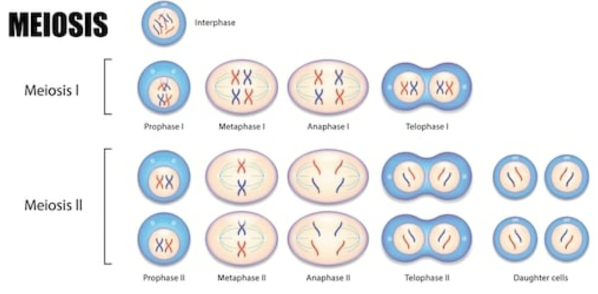
Sister chromatids
Half of a chromosome
23 pairs of chromosomes
Each half is identical and have the same genes
Homologous Chromosomes
Same trait, different allele.
Allele
Different versions of a gene
(brown vs green eye color allele)
Non-Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that carry different traits.
Locus
A gene’s location on a chromosome.
Haploid
Half of a set of chromosomes.
Diploid
One set of chromosomes.
Karyotype
Chromosomal makeup.
Human chromosome numbers
Humans contain 23 pairs of chromosomes (22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes)
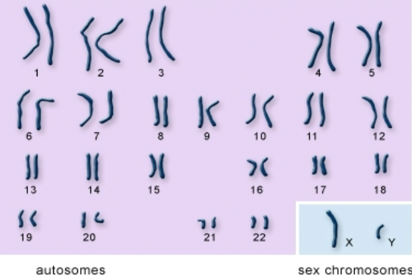
Sex Chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual.
X chromosome is….
Known as the female chromosome
X chromosome contains approximately 1,100 genes
Y chromosome is…
Known as the male chromosome
Y chromosome contains approximately 450 genes
Genetics
Study of heredity.
Heredity
Transmission of traits from one generation to the next.
Trait
A variant of a character.
Character
A heritable feature that varies among individuals.
hair color, eye color
Meiosis vs. Mitosis
Mitosis produces diploid cells (one division, somatic cells)
Meiosis produces haploid cells (two divisions, gametes)
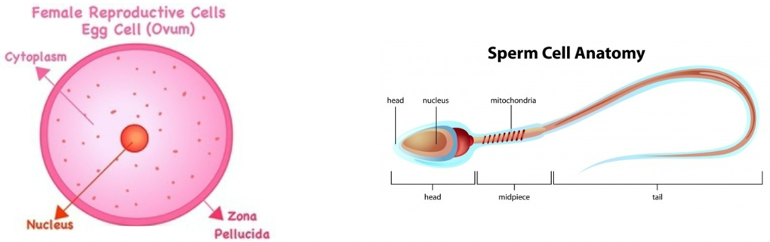
Sperm & Oocyte anatomy
Zona Pellucida egg membrane provides protection
Only head of
sperm penetrates membrane to form zygote.
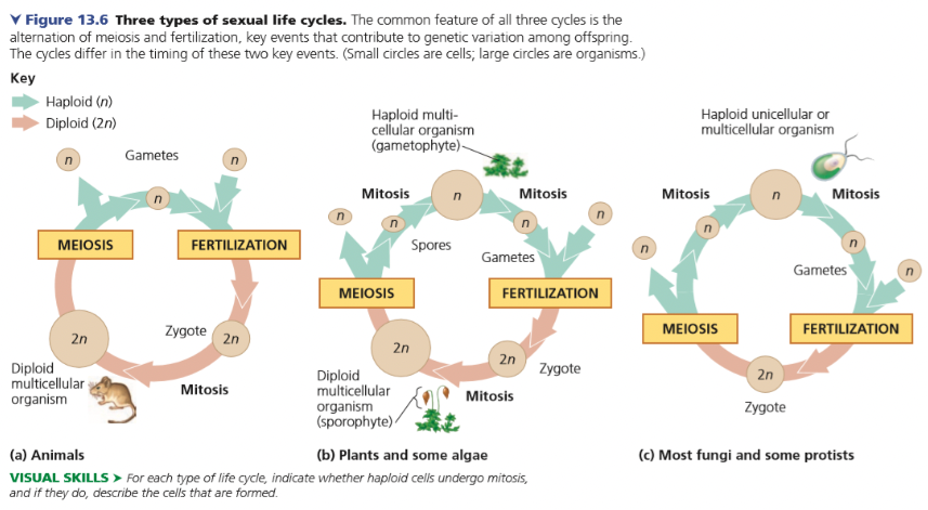
haploid; in animals, plants, fungi
Sexual Reproducing Organism
In animals only gametes are haploid.
Plants and some algae have haploid multicellular stage.
Fungi and some protist primarily have haploid unicellular stage.
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis (prophase 1)
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate properly during cell division.
Aneuploidy
When you have an abnormal number of chromosomes.
Trisomy 21
A condition caused when chromosome 21 fails to properly separate so there is an extra copy of chromosome 21.
leading to Down Syndrome
Have two chromosomes at telophase 2+cytokinesis 2, creating 3 instead of 2
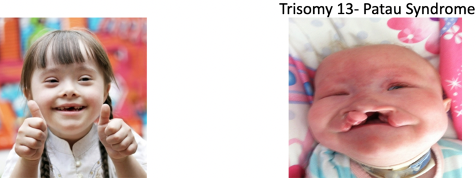
Trisomy 13
A condition associated with Patau Syndrome.
Turner Syndrome (X)
Condition where a female has only one X chromosome, resulting in being born with 45 chromosomes.
Webbed neck, don’t go through traditional puberty
Sterile

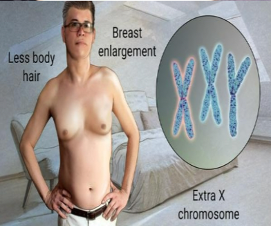
Klinefelter’s Syndrome (XXY)
Condition in males with two Xs and one Y
have less body hair and breast enlargement
Not sterile but tougher for reproduction
Jacob Syndrome (XYY)
Condition in males with an extra Y chromosome
has more masculine features
More testosterone
Taller, excess acne, more lean / tougher to put on muscle
Not much issue with reproduction
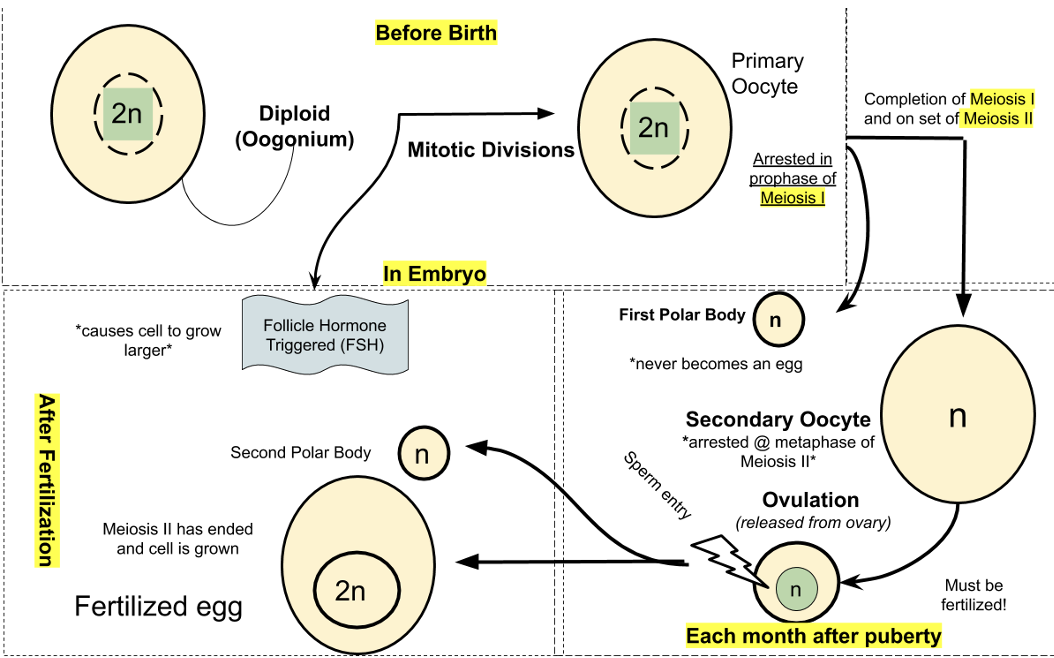
Egg meiosis
Egg completes meiosis and arrests (stops) in metaphase II after puberty.
Egg arrests ion prophase 1 after birth
After puberty egg completes meiosis and arrests in metaphase 2
After fertilization egg completes meiosis 2
Factors that create genetic variation
Besides mutations these three factors are required to maintain genetic variation within a population.
Crossing over
Independent Assortment
Random Fertilization
Random Fertilization
Creates different combinations of zygotes due to random fusion of gametes.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype
Physical makeup of the genotype.
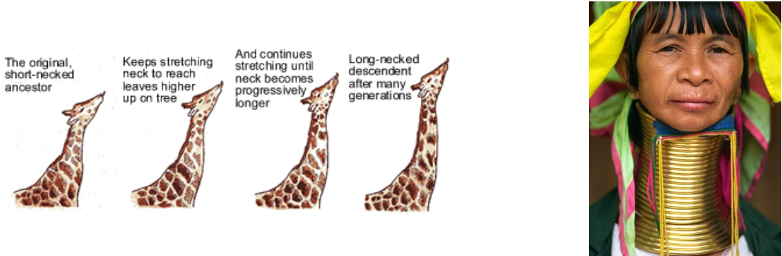
Lamarck inheritance theory
acquired traits can be inherited
Would say if their mother had the long neck phenotype then their kid will have the long neck characteristic but that is not the case since it is an acquired trait and you had to do something to acquire the long neck
His theory was proven to be wrong
Mendelian inheritance theory
Conducted pea plant experiments to gather evidence to show how
traits are inherited.
Determined dominant traits are expressed over recessive traits.
Additionally, determined organisms only inherit two copies of a gene.
His hypothesis was that a trait is passed down from one generation to the next
Proved Lamarck theory as wrong
Homozygous dominant
An organism with two identical dominant alleles for a particular trait, such as AA.
Heterozygous
An organism with two different alleles for a particular trait, such as Aa.
Homozygous recessive
An organism with two identical recessive alleles for a particular trait, such as aa.
True breeding
Homozygous for specific alleles (homozygous dominant or recessive)
Complete Dominance
Dominant alleles mask the effect of recessive alleles.
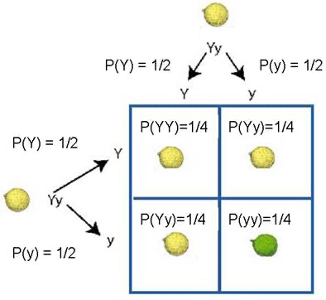
Law of Segregation
Alleles are present for each trait and segregate during division
Lowercase = recessive
Uppercase = dominant
Happens during meiosis?
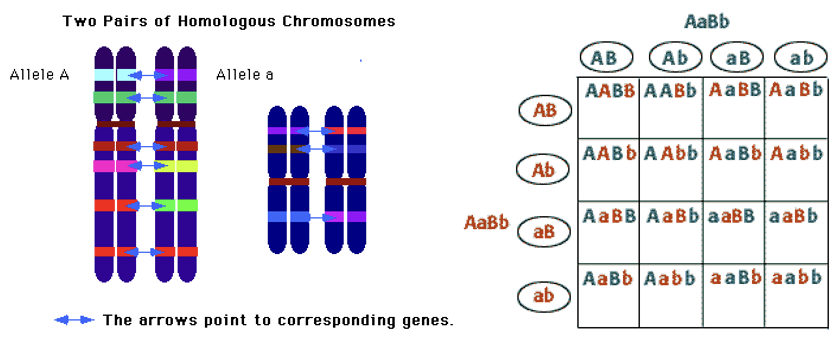
Law of Independent Assortment
Inheritance of one character gene does not affect the inheritance of another.
Recessive Disorders
Disorders that manifest if both alleles are recessive.
Sickle cell
Cystic Fibrosis
Tay-Sachs
Common complete dominance condition where only the recessive phenotype expressed when both alleles are present.
Dominant Disorders
Disorders that manifest if at least one allele is dominant.
Huntington’s disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Osteopetrosis
Common complete dominance condition where the dominant phenotype is expressed even when only one dominant allele is present.
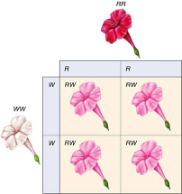
Incomplete Dominance
(partial dominance) (exception to Mendel’s rule)
Phenotype that is a mix of two different alleles.
Carl Correns (1864-1933)
Snap dragon experiment
The intermediate phenotype of two traits
Humans have a straight hair allele and curly hair allele. People who inherit both alleles have wavy hair.

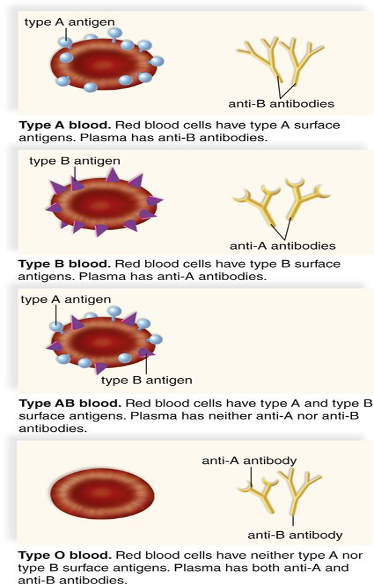
Codominance
Both alleles in a heterozygote are fully expressed.
Humans have three alleles for blood type A, B and O blood
A and B are codominant, and O is recessive to both.
Epistasis
An interaction between genes where one gene influences the phenotype produced by another gene.
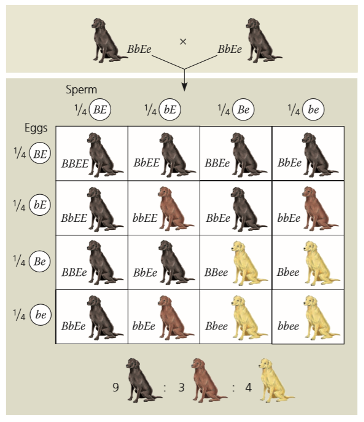
Labrador example shown below Black is dominant to brown. However, pigment only deposited if pigment localization protein present. If it is not, the dog is yellow.
B= black
b= brown
E= pigment
e= no pigment
Exception:
A allele —> directly affects B allele —> expression which then affects the phenotype
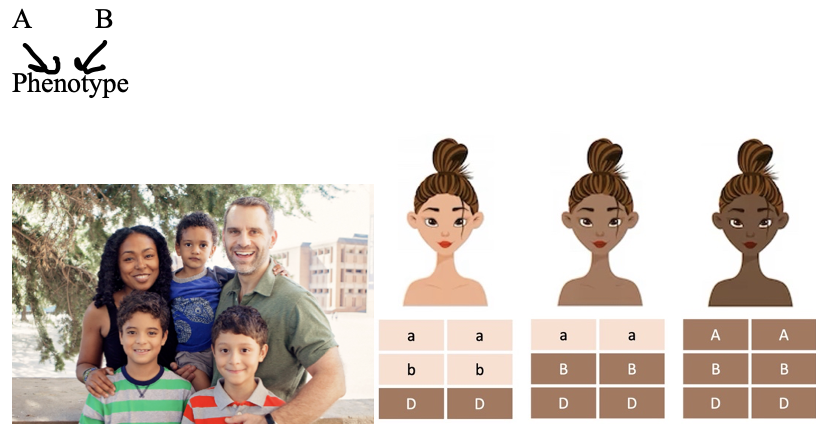
Polygenic Inheritance
Traits controlled by two or more genes.
(An exception to Mendel’s theory)
such as skin color and height in humans.
A and B allele both affect phenotype

Epigenetic Inheritance
Traits and DNA influenced by environmental factors over time
= sunlight / radiation , food & medicine you consume
Challenges ideal genetic makeup is 100% a mixture of parent's DNA
Variations in identical twins is a common example

Sex-linked traits
Traits associated with genes located on sex chromosomes.
X chromosome is known as the female chromosome
Y chromosome is known as the male chromosome
X chromosome contains approximately 1,100 genes
Y chromosome contains approximately 450 genes
Sex linked conditions
Men primary inherit sex linked traits
Men lack extra X to mask recessive traits
Examples:
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Hemophilia
Color Blindness
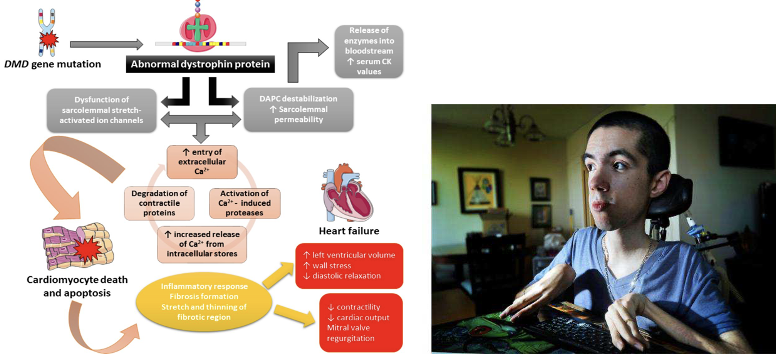
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Condition causing muscles to deteriorate because of a defective protein
DMD gene is mutated over time that causes muscles to break down leading to heart failure and death around 15 years old
Hemophilia
Condition where the blood cannot form clots due to platelet defects = even a minor cut can cause bleed out and death
H= no hemophilia
h= hemophilia
XHY = make without hemophilia
XhY = male with hemophilia
XHXH = female without hemophilia
XHXh = female without but is a carrier