Exchange rates
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
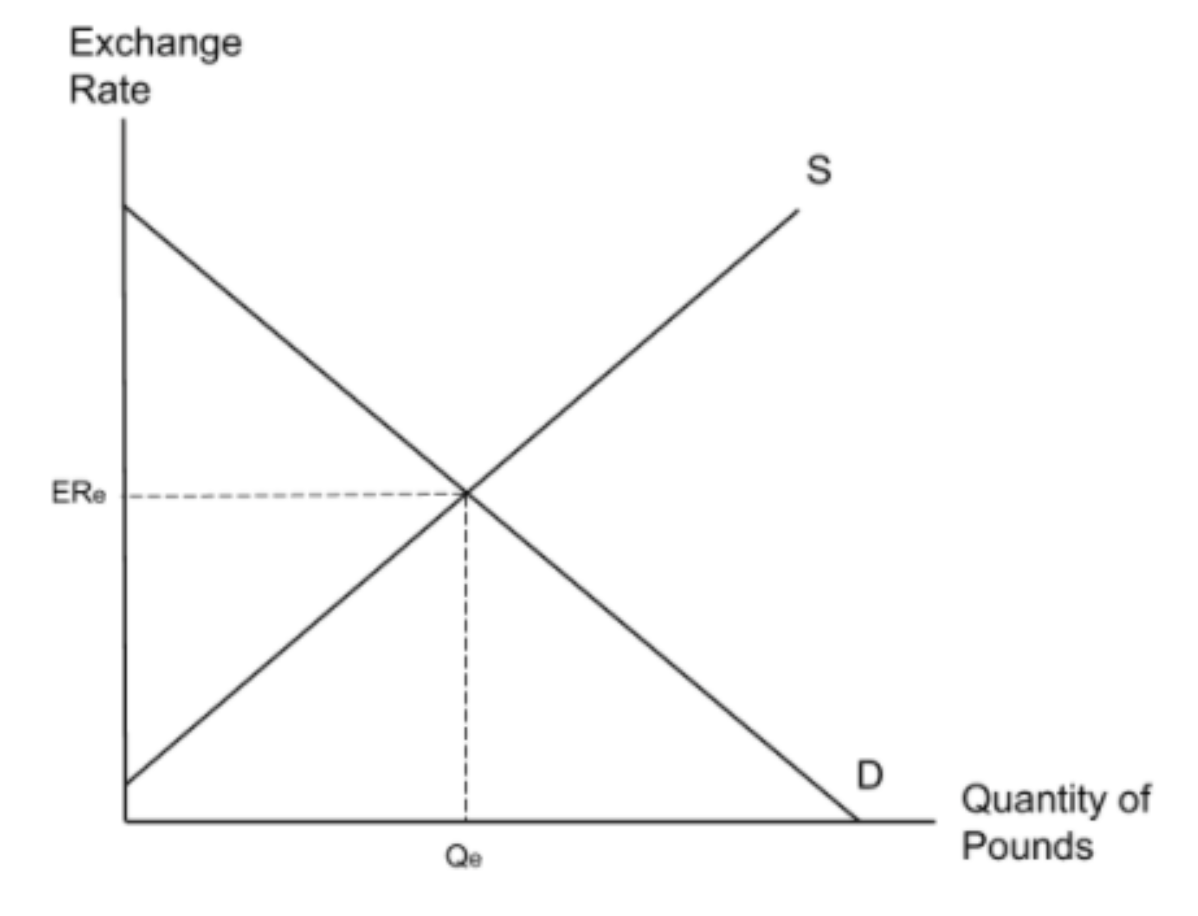
What is the diagram to show the supply and demand of a currency?
The diagram below shows how exchange rates are determined by market forces. The vertical axis denotes the price of the currency (also known as its exchange rate), while the horizontal axis denotes the quantity of the currency. We now have a standard supply and demand graph which demonstrates how exchange rates depend on the supply and demand of a currency.
What is the impact of a decrease in the value of the pound on British Imports and Exports?
A weaker pound leads to the the opposite of SPICEE - a weak pound leads to more expensive imports and cheaper exports.
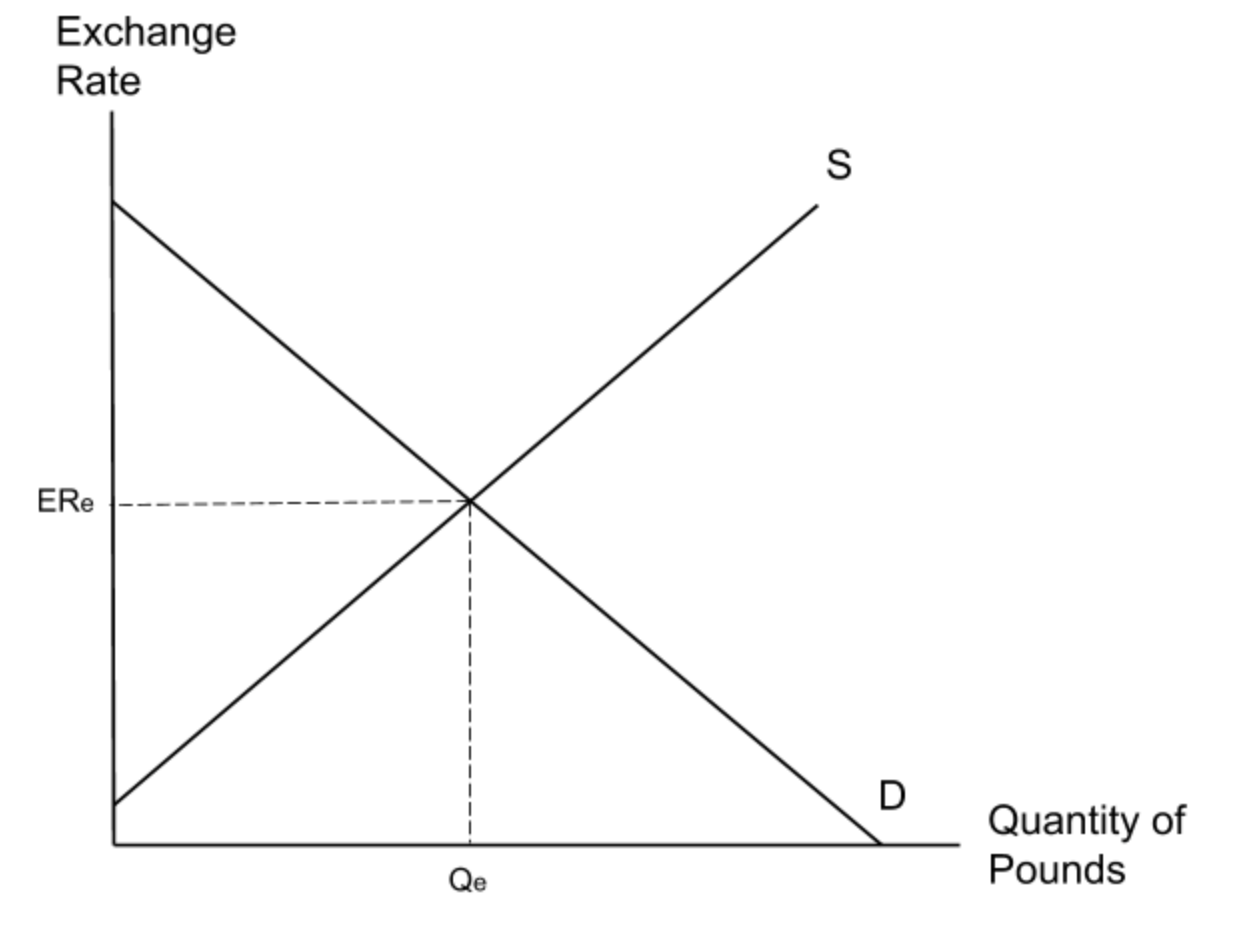
What is a diagram to show the impact of a decrease in the supply of pounds on the exchange rate?
A decrease in the supply of pounds will shift the supply curve to the left. This will cause an appreciation in the exchange rate as the pound increases in value.
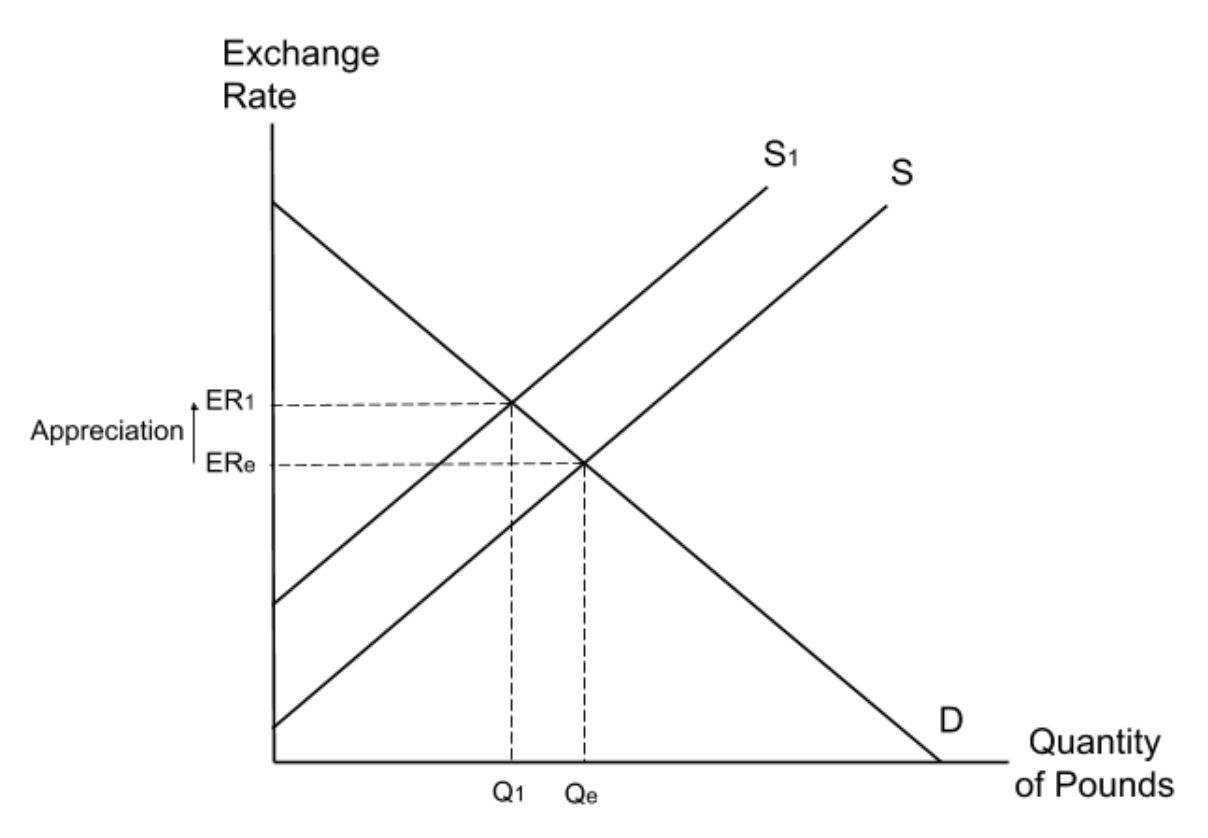
What is a diagram to show the impact of an increase in the demand for pounds on the exchange rate.
An increase in demand for pounds will shift the demand curve to the right. This will cause an appreciation in the exchange rate as the pound increases in value.
What does a weaker pound mean?
that imports become more expensive for domestic consumers and exports become cheaper for foreign consumers.
Factors influencing exchange rates
imports and exports
speculation
relative interest rates
relative inflation rates
FDI
QE
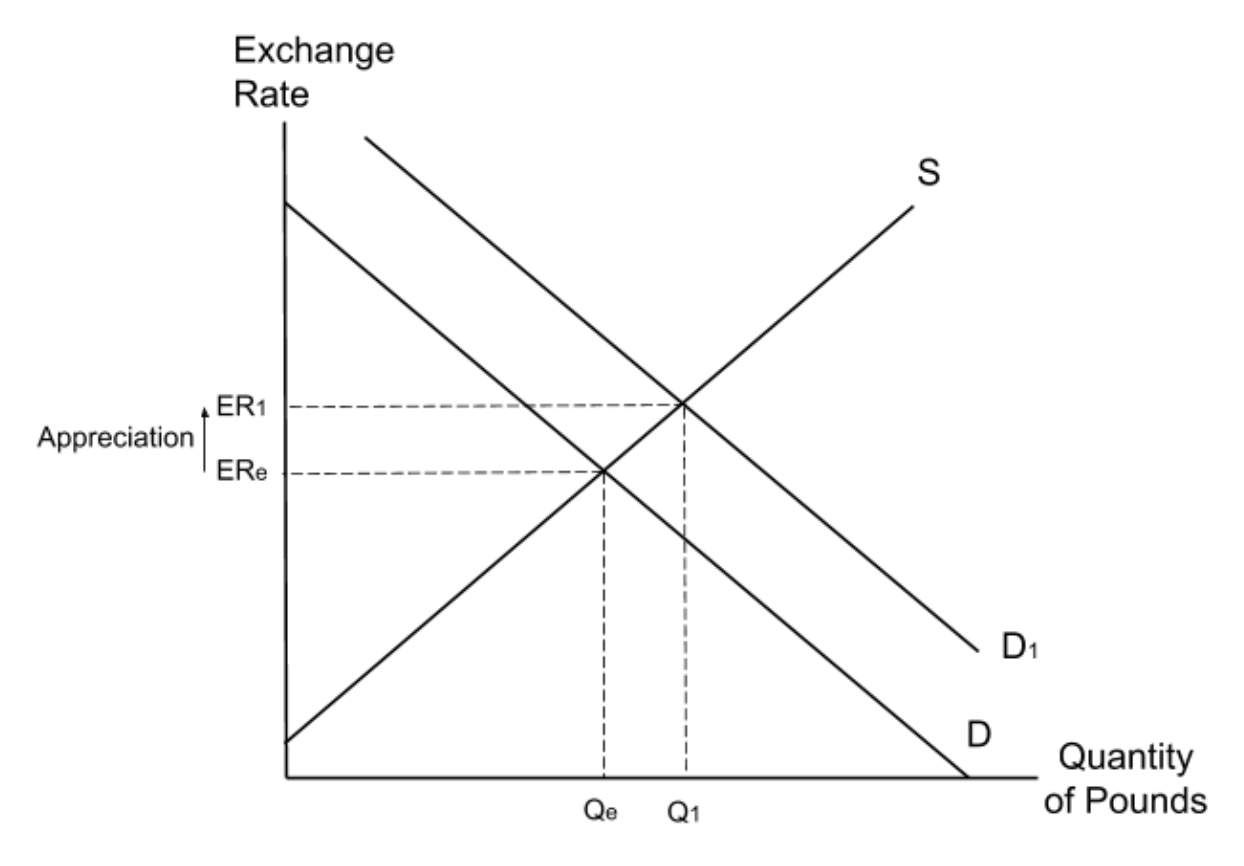
UK consumers stop purchasing pork from several countries following a swine flu scare. Which of the following shows a possible impact of this?
Pork purchased from other countries is an import. When imports fall, UK consumers supply fewer pounds as they purchase less of the foreign currencies needed to buy the imports. A reduction in the supply of pounds will lead to an increase (appreciation) in the exchange rate.
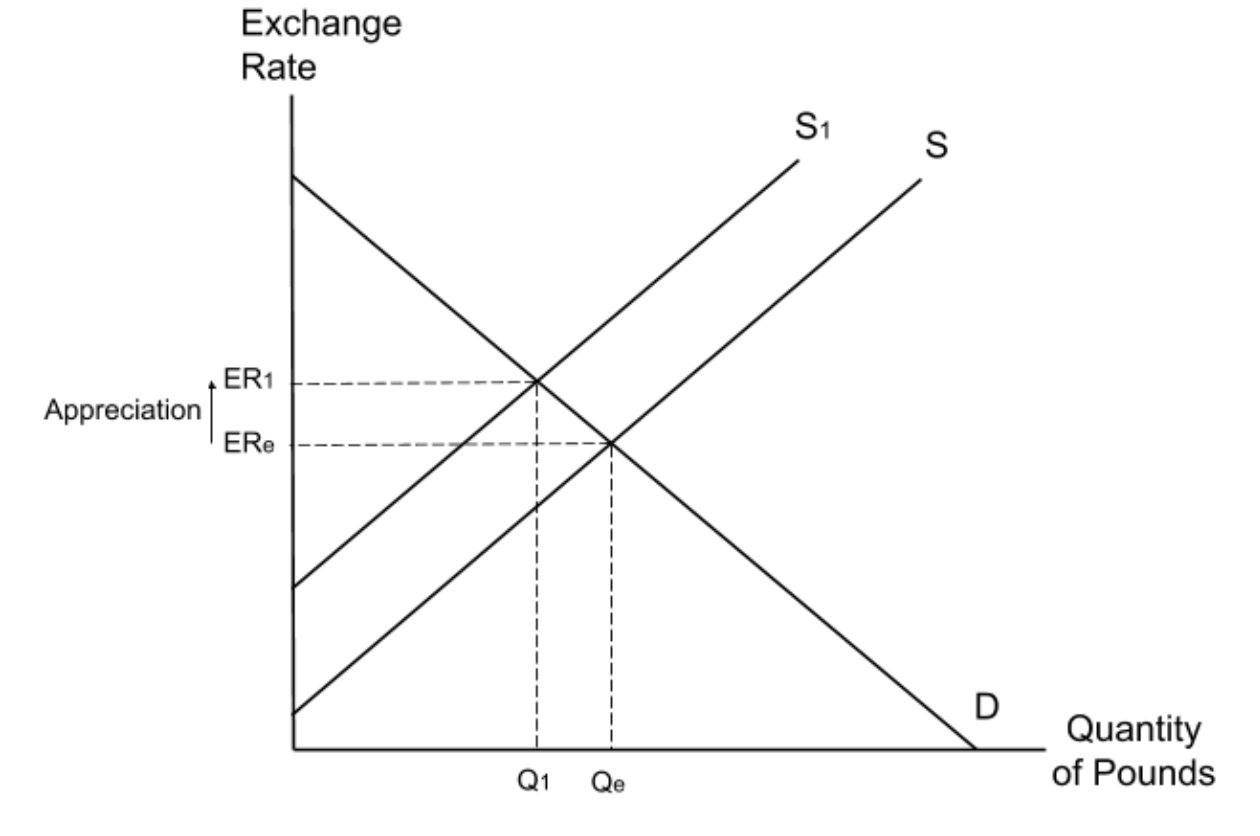
The UK government imposes regulations to stop UK arms producers from selling guns and fighter jets abroad. Which of the following shows a possible impact of this?
The regulations will reduce the number of UK exports. This means that fewer foreign consumers will need to buy UK pounds and so the demand for pounds will fall. This will in turn decrease the exchange rate.
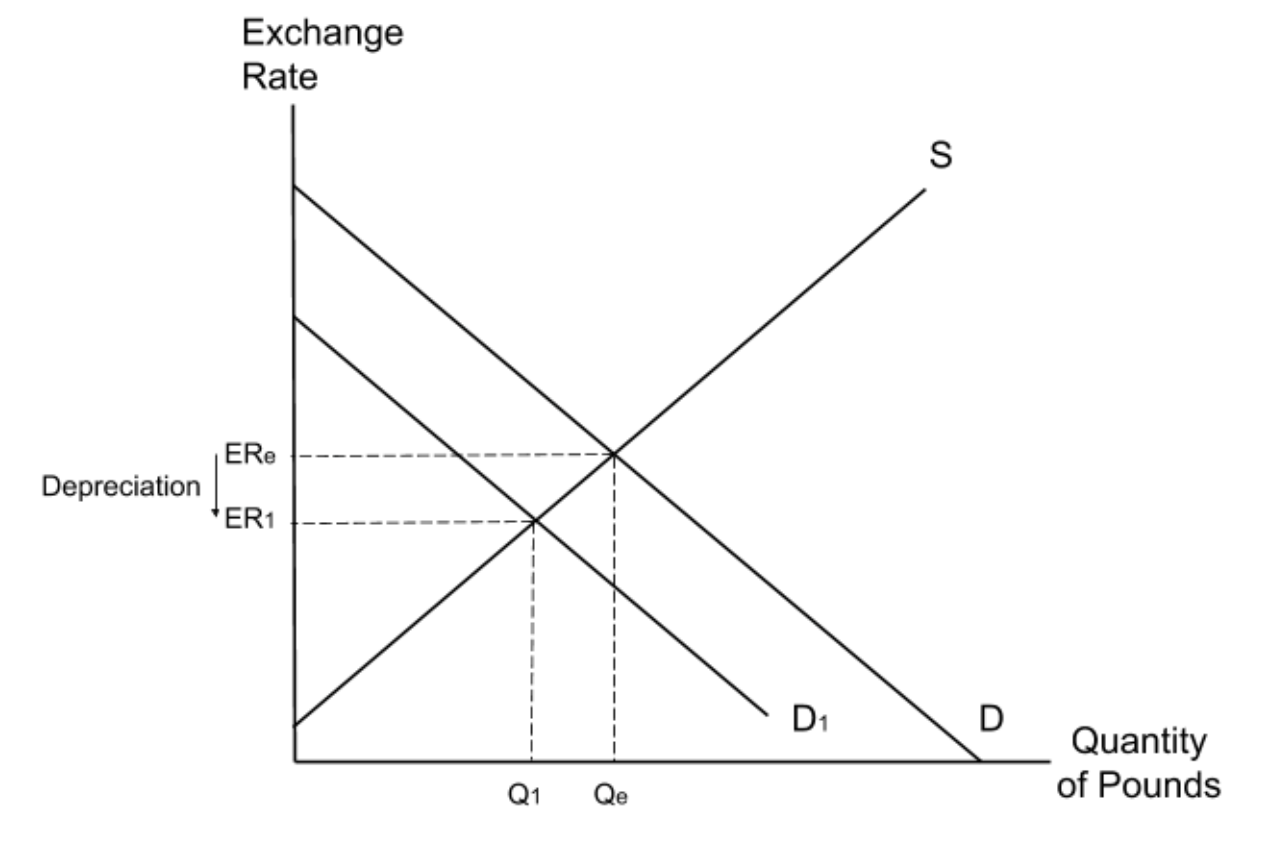
What will happen to the exchange rate as a result of an increase in the number of UK consumers travelling abroad in the summer?
When UK consumers travel abroad they will need to purchase a foreign currency. In order to do this they will need to sell (or supply) their pounds. This means that an increase in foreign travel by UK consumers will lead to an increase in the supply of pounds. An increase in the supply of pounds will in turn lead to a decrease in the exchange rate, causing a depreciation
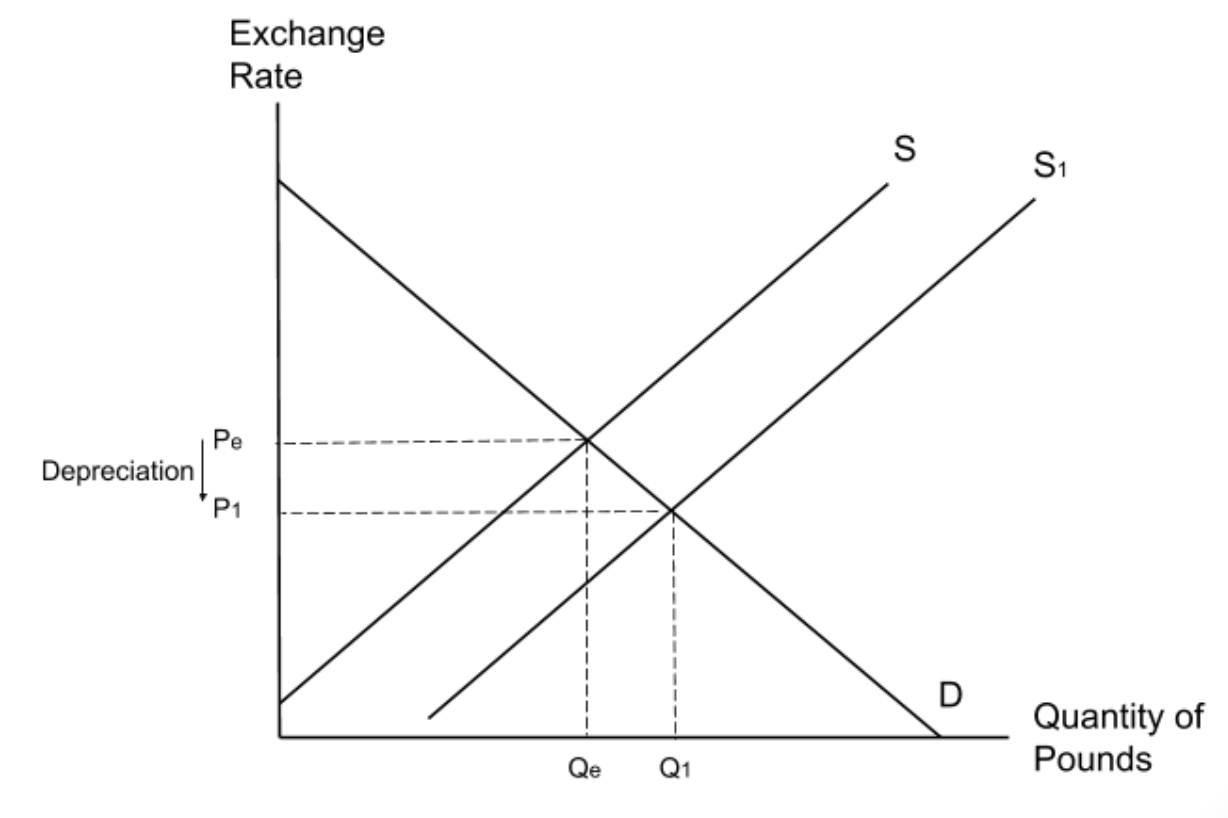
What will happen to the exchange rate as a result of an increase in the number of Chinese consumers travelling to the UK?
When Chinese consumers travel to the UK they will need to purchase poundsmeaning that the demand for pounds will increase. This will lead to an increase in the value of the exchange rate, also known as an appreciation.
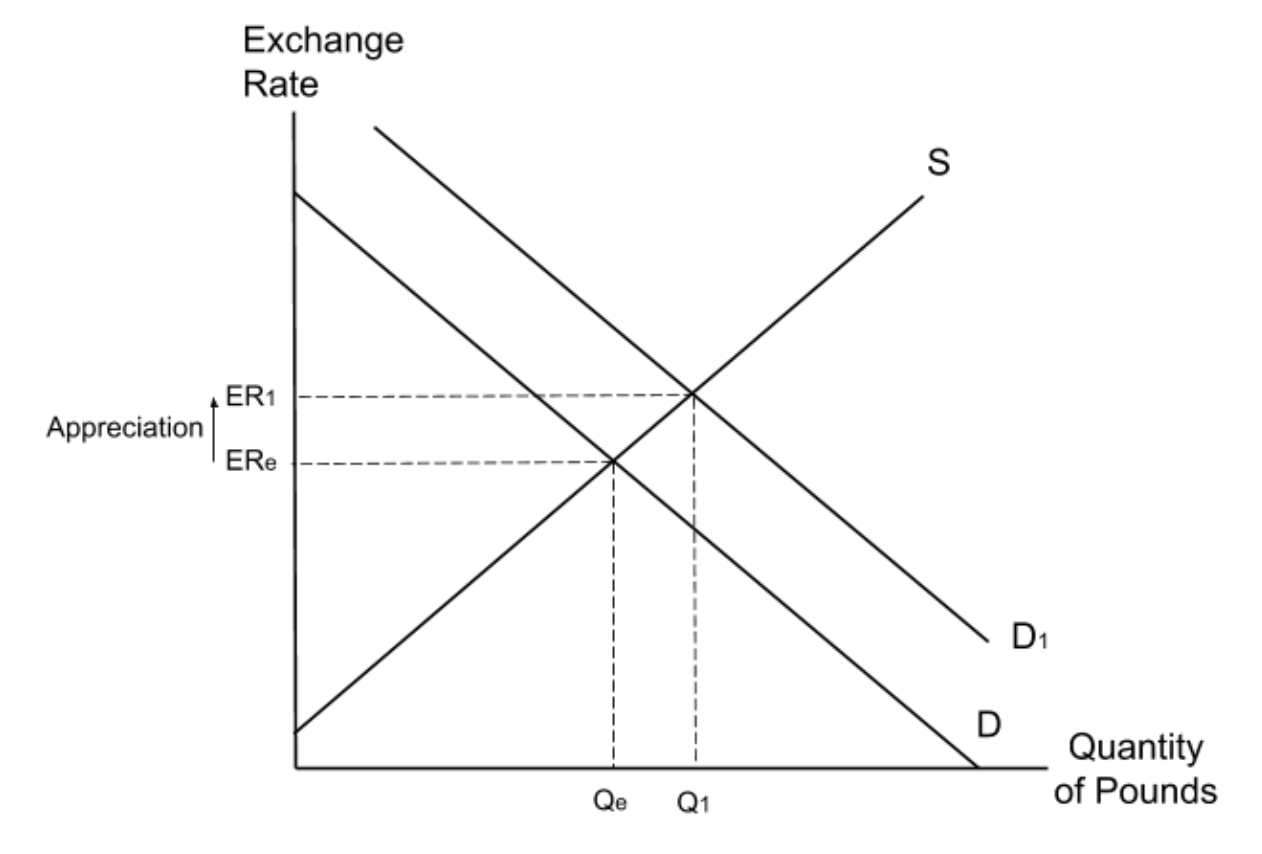
How does a decrease in the demand for a country’s imports impact the exchange rate?
decrease the supply of that country’s currency causing its exchange rate to appreciate.
How does a decrease in the demand for a country’s exports impact the exchange rate?
decrease the demand for that country’s currency causing its exchange rate to depreciate.
What is the best strategy for a speculating currency investor?
Currency speculators want to buy a currency when it is cheap and sell it when it is expensive. This allows them to make a profit.
A currency speculator predicts that the pound will appreciate in four months time. What can this currency speculator do in order to make a profit?
In order to make a profit, the investor should buy pounds when they are cheaperand sell them in 4 months when they are more expensive.
A currency speculator predicts that the pound will depreciate in seven months time. What should the currency speculator do in order to make a profit?
To make a profit, the investor should sell pounds when they are more expensiveand buy them in 7 months when they are cheaper.
A currency speculator has predicted a depreciation of the pound. However, by the time he goes to sell his pounds it is likely that…
t is likely that lots of investors will predict the depreciation which will lead them to sell (supply) their pounds. This will increase the supply of pounds which and lead to an immediate depreciation.
What is the likely impact of a decrease in the Australian interest rate?
The supply of Australian dollars will increase as investors buy currencies with a higher interest rate
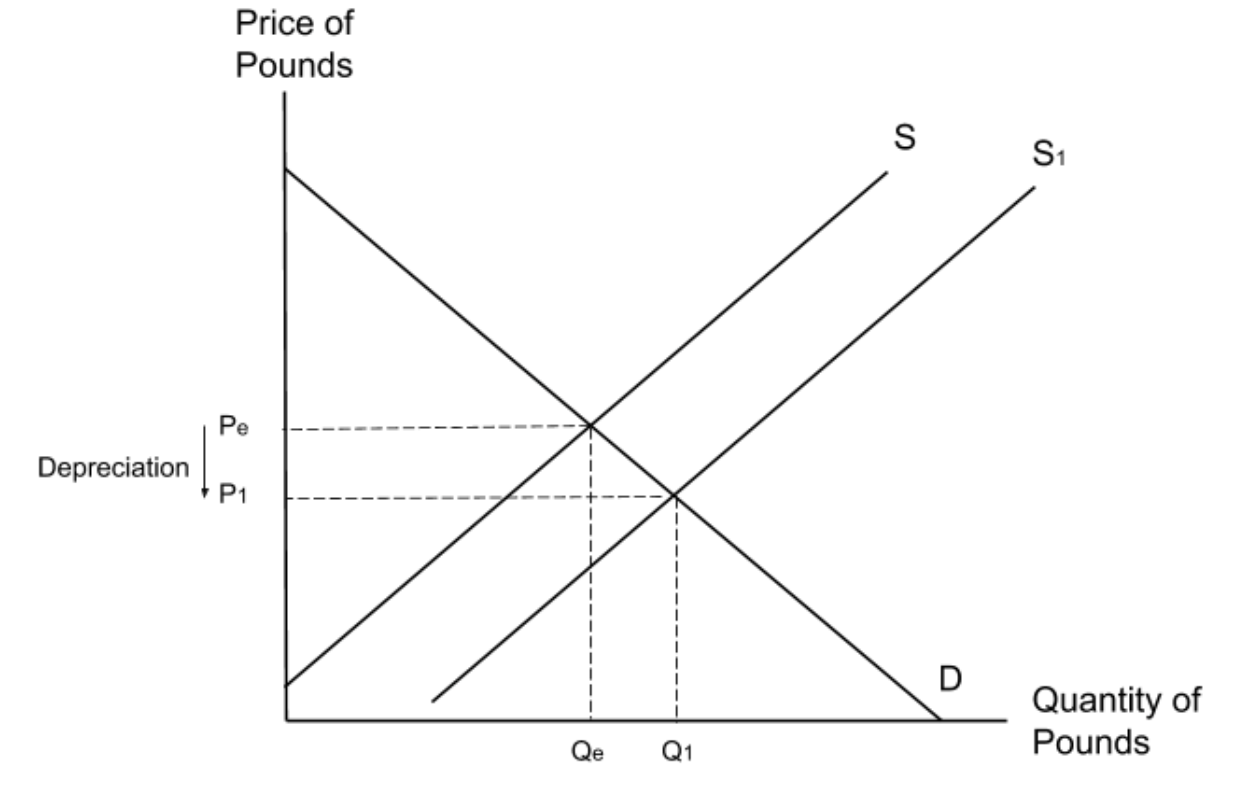
What is the impact of countries having high interest rates?
If a country’s interest rate is high relative to other countries, hot money will flow into that country. This will increase the demand for that country’s currency and cause its value to appreciate
How is the exchange rate for pounds determined?
In the UK, the exchange rate is determined by the equilibrium between the supply and demand for pounds as shown below.
France’s inflation rate is 9% and Australia’s inflation rate is 2%.
What is likely to happen to France’s exchange rate?
It will depreciate because consumers are decreasing their demand for French exports
What does a country with a lower inflation rate do to the exchange rate?
If a country’s inflation rate is low relative to its competitors, its prices will go up by less than its competitors. This means that the country’s exports will become relatively cheaper which in turn means that the demand for exports will increase. This will then increase the demand for the country’s currency, leading to an appreciation of its exchange rate
What will an increase in FDI going into a country do to the exchange rate?
An increase in FDI going into a country will increase the demand for its currency which in turn means that its exchange rate will appreciate.
What is quantitative easing an extreme type of?
Quantitative easing is an extreme type of monetary policy. It is used when the central bank wants to grow the economy but can’t decrease the interest rate further as it is already very low.
How does quantitative easing affect the exchange rate?
The supply of a currency increases causing it to depreciate
Impacts of changes in exchange rates
growth and employment
impact on inflation
FDI flows
What is the impact of the exchange rate appreciating?
imports get cheaper and exports get more expensive. This leads to an increase in import expenditure and a decrease in export revenue. As a result, aggregate demand decreases which in turn causes a decrease in growth and employment.
What is the impact of the exchange rate depreciating?
exports get cheaper and imports get more expensive. This leads to decrease in import expenditure and an increase in export revenue. As a result, aggregate demand rises which in turn causes an increase in growth and employment.
What is the impact of depreciation on inflation?
will increase aggregate demand, leading to demand-pull inflation. It will also decrease aggregate supply leading to cost-push inflation.
What is the impact of appreciation on growth and employment?
imports get cheaper and exports get more expensive. This leads to an increase in import expenditure and a decrease in export revenue. As a result, aggregate demand decreases which in turn causes a decrease in growth and employment.
how can a decrease in the price of imports improve growth?
decreases the cost of production for businesses shifting the SRAS supply yo the right
What is the impact of an appreciation of the pound on FDI?
will fall
What is the impact of an appreciation of the exchange rate on the current account'?
When the pound appreciates, import expenditure will increase and export revenue will decrease. This will lead to a decrease in the UK current account.
Import expenditure increases because the stronger pound makes imports cheaper for UK consumers, increasing their demand. This means that more money is leaving the UK economy.
Export revenue decreases because the stronger pound makes them more expensive for foreign consumers, decreasing their demand. This means that less money is entering the UK economy.
Outflows will increase and inflows will decrease which means that the current account will decrease.
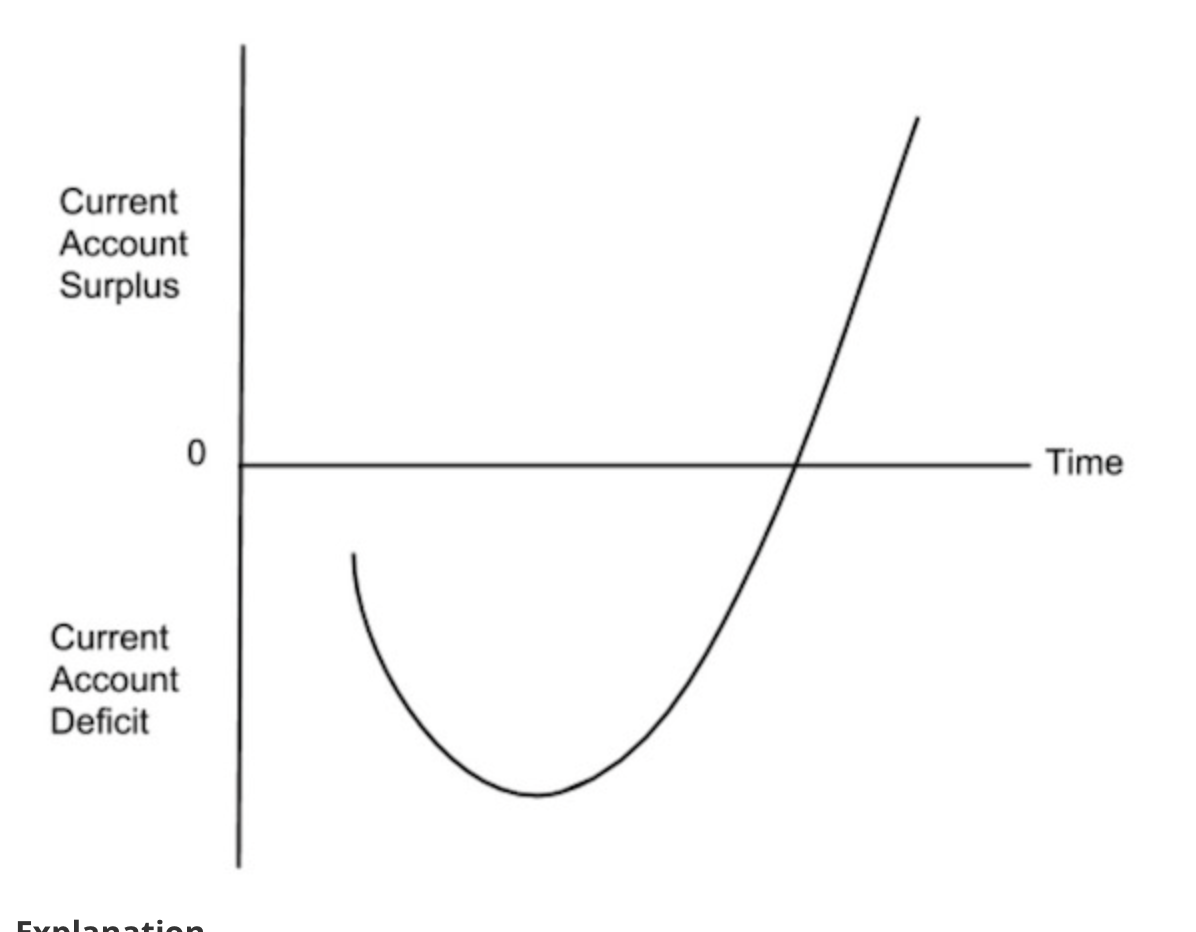
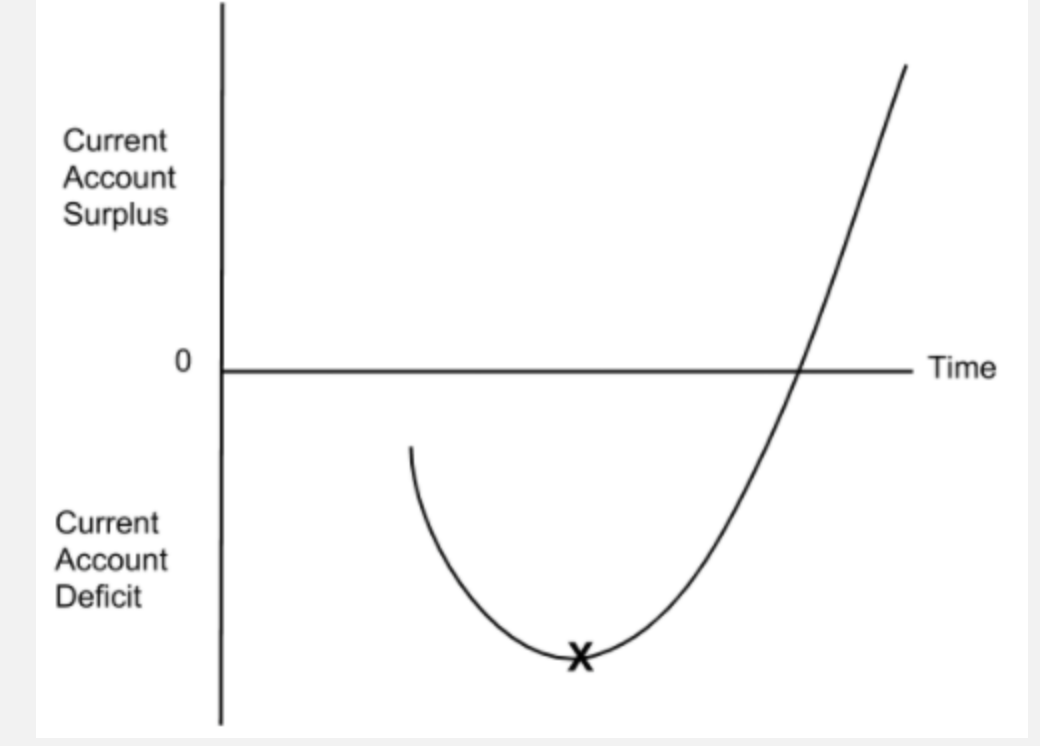
Explain the J curve
In the short run, demand for imports is inelastic meaning a depreciation will increase import expenditure and worsen the Current Account. As demand becomes more elastic over time (like when companies finish their contracts), the demand for imports decreases leading to a decrease in import expenditure. This will then improve the Current Account.
The graph should to show the Current Account starting in a deficit. It should then get even worse before eventually improving.
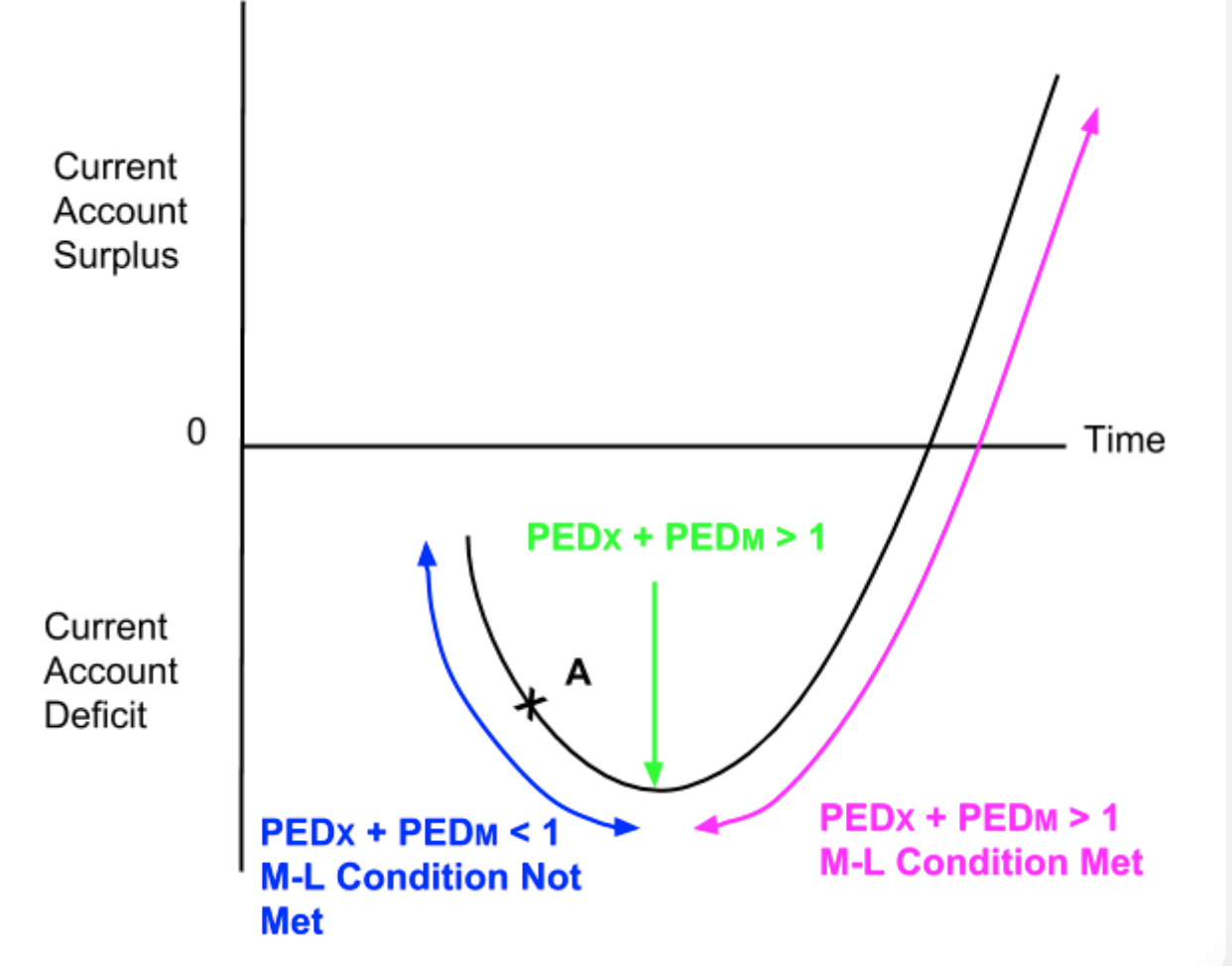
What is the equation for the short run?
In the short run, demand for imports and exports is inelastic. This means that it will be a low number and so the sum of the price elasticity of demand for imports and the price elasticity of demand for exports will be less than one.
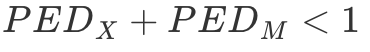
What is the equation for the long run?
In the long run, demand for imports and exports is more elastic. This means that it will be a higher number and so the sum of the price elasticity of demand for imports and the price elasticity of demand for exports will be more than one. This means that the Marshall-Lerner condition has been satisfied and the Current Account will start to improve.
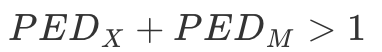
Write the definition of: J-Curve
Following a depreciation of the exchange rate, the J-curve effect shows a worsening of the Current Account in the short run and then an improvement in the long run.
Write the definition of: Marshall-Lerner Condition
Following a depreciation of the exchange rate, the Current Account will only improve if the sum of the elasticity of demand for exports and the elasticity of demand for imports is greater than one (i.e.) PEDx + PEDm > 1).
What does the x mean?
The Marshall-Lerner condition is met
Factors to manage exchange rates
interest rates
foreign currency transactions
lower interest rates
supply side
What does a decrease of the interest rate?
hot money will flow out of the country decreasing the demand for its currency leading to a depreciation of the exchange rate
What are infant industries?
industries are industries which are too young to benefit from economies of scale as they are producing a low level of outpu
What happens if a country sells its own currency on the currency market?
it will increase the supply of that currency and cause an exchange rate depreciation
If a country sells another country’s currency in exchange for its own, what is the effect of the exchange rate?
demand for its own currency will increase causing its exchange rate to appreciate
What is a currency war?
When countries depreciate their exchange rate to make exports more competitive
Write the definition of: Competitive Depreciation
When a country depreciates their own currency to keep their exports cheap and competitive.
What are the two types of expenditure switching policies
trade barriers
low interest rates
What is the impact of a fall in interest rates?
Hot money will flow into other countries, increasing the supply of the £ and therefore depreciating the pound
How is a decrease in the UK price level (relative to trading partners) likely to affect the UK’s net exports?
A decrease in the UK price level (relative to trading partners) will make British exports cheaper and should increase competitiveness. This will increase the demand for UK exports which in turn will increase export revenue. At the same time, domestic goods will be cheaper relative to imports. This this will incentivise consumers to switch to domestic goods which will lead to a decrease import expenditure.
Write the definition of: Expenditure Switching Policies
Policies which aim to switch expenditure from imported goods to domestic goods. They include trade barriers and low interest rates.