Animal Biology test 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/240
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
1
New cards
characteristics of the phylum cnidaria
1\.Entirely aquatic, some in fresh water but mostly marine
2\.Radial Symmetry or biradial symmetry around a longitudinal axis with oral and aboral ends; no definite head
3\.Two basic types of individuals: polyps and medusae
4\.Exoskeleton or endoskeleton of chitinous, calcareous or protein components in some
5\.Body with two layers, epidermis and gastrodermis with mesoglea; mesoglea with cells and connective tissue in some
6\.Gastrovascular cavity with a single opening that serves as both mouth and anus; extensible tentacles usually encircling the mouth or oral region
7\.Special stinging cell organelles called nematocysts in either epidermis or gastrodermis or both, nematocysts abundant on tentacles, where they form batteries or rings
8\.Nerve Net with symmetrical and assymetrical synapses; with some sensory organs; diffuse conduction
9\. Muscular system of an outer layer of longitudinal fibers at the base of the epidermis and an inner one of circular fibers at the base of the gastrodermis
10\. Asexual reproduction by budding (in Polyps) or sexual reproduction by gametes; sexual forms monoecious or dioecious, planula larvae
11\. No excretory or respiratory system
12\. No coelomic cavity
\
2\.Radial Symmetry or biradial symmetry around a longitudinal axis with oral and aboral ends; no definite head
3\.Two basic types of individuals: polyps and medusae
4\.Exoskeleton or endoskeleton of chitinous, calcareous or protein components in some
5\.Body with two layers, epidermis and gastrodermis with mesoglea; mesoglea with cells and connective tissue in some
6\.Gastrovascular cavity with a single opening that serves as both mouth and anus; extensible tentacles usually encircling the mouth or oral region
7\.Special stinging cell organelles called nematocysts in either epidermis or gastrodermis or both, nematocysts abundant on tentacles, where they form batteries or rings
8\.Nerve Net with symmetrical and assymetrical synapses; with some sensory organs; diffuse conduction
9\. Muscular system of an outer layer of longitudinal fibers at the base of the epidermis and an inner one of circular fibers at the base of the gastrodermis
10\. Asexual reproduction by budding (in Polyps) or sexual reproduction by gametes; sexual forms monoecious or dioecious, planula larvae
11\. No excretory or respiratory system
12\. No coelomic cavity
\
2
New cards
structure of an Anemone
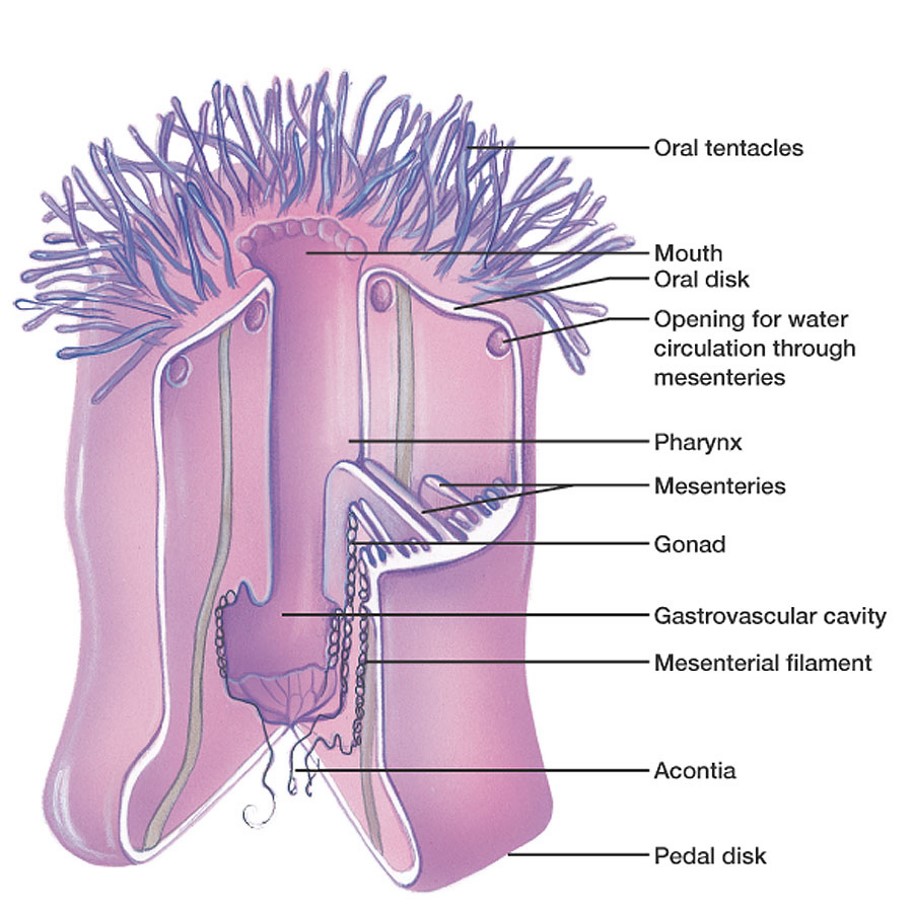
3
New cards
what are Cnidarians
an ancient phylum of Eumetazoans; one of the oldest groups in this clade
4
New cards
All animals except ________ belong to the clade Eumetazoa, animals with true tissues
sponges and a few other groups
5
New cards
Cnidarians have diversified into a wide range pf both sessile and motile forms including…
jellies, corals and hydras
6
New cards
what do Cnidarians exhibit?
a relatively simple diploblastic, radial body plan
7
New cards
the basic body plan of a cnidarian is…
a sac with a central digestive compartment, the gastrovascular cavity; a single opening functions as mouth and anus
8
New cards
what are the two variations for cnidarians body plan?
the sessile polyp and motile medusa
9
New cards
picture of a polp and a medusa
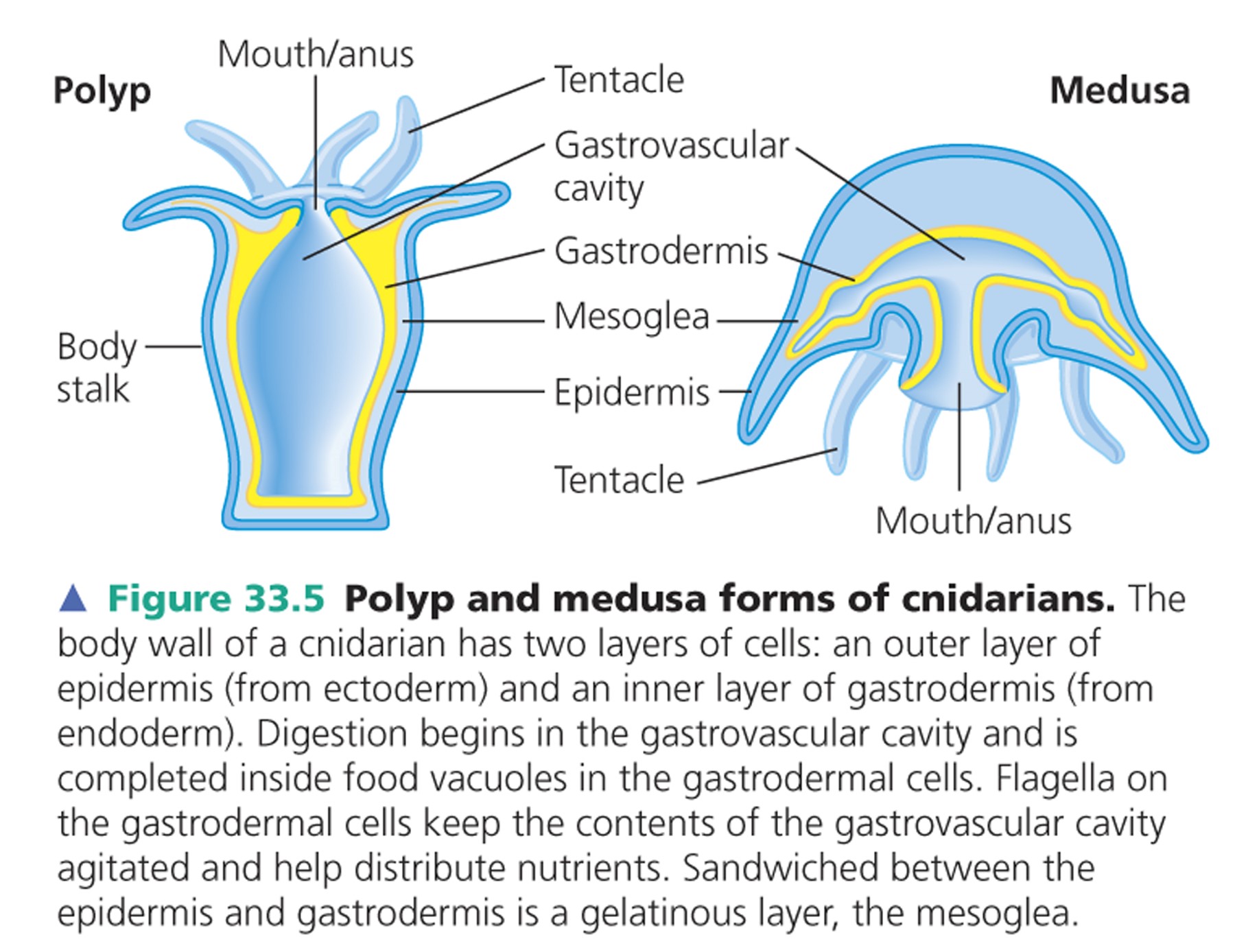
10
New cards
cnidarians are carnivores that use…
tentacles to capture prey
11
New cards
what are cnidarians tentacles armed with?
cnidocytes- unique cells that function in defense and capture of prey
12
New cards
what are nematocysts?
specialized organelles within cnidocytes that eject a stinging thread
13
New cards
a cnidocyte that contains a stringing capsule, a nematocyst, which contains a coiled thread
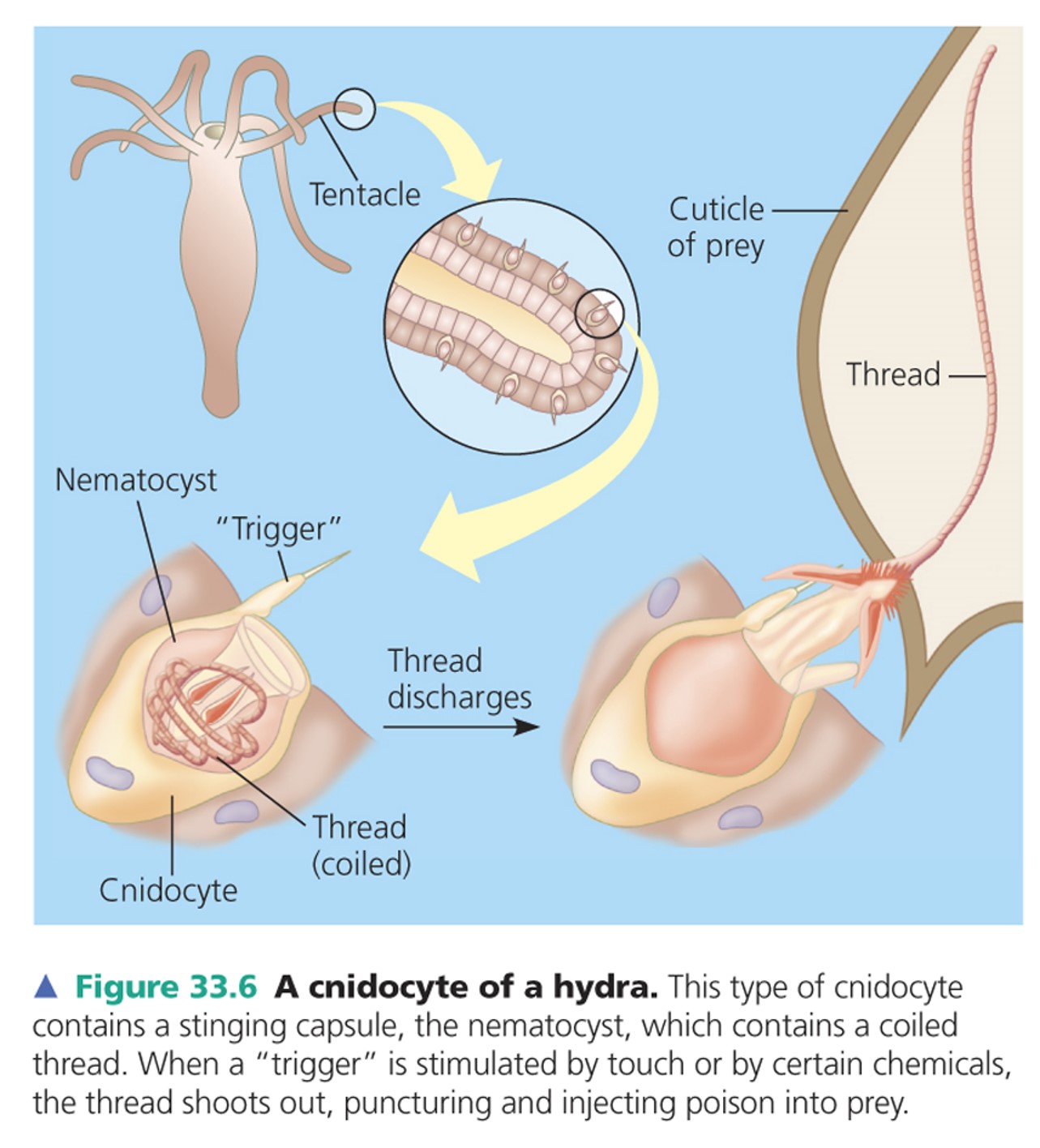
14
New cards
name the four major classes of the Phylum Cnidaria
Hydrozoa, Scyphozoan, Cubozoan, and Anthozoa
15
New cards
main characteristics of Hydrozoa (Portuguese man of war, hydras, Obelia, some corals)
most marine, a few freshwater; both poly and medusa stages in most species; polyp stage often colonial
16
New cards
Scyphozoan ( Jellies, sea nettles)
all marine; polyp stge absent or reduced free swimming medusae up to 2M in diameter
17
New cards
cubozoan( box jellies, sea wasps)
all marine; box-shaped medusae; complex eyes; potent venom
18
New cards
anthozoa( sea anemones, most corals, sea fans)
all marine; medusa stage completely absent; most sessile; many colonial
19
New cards
life cycle of the hydrozoan Obelia
\
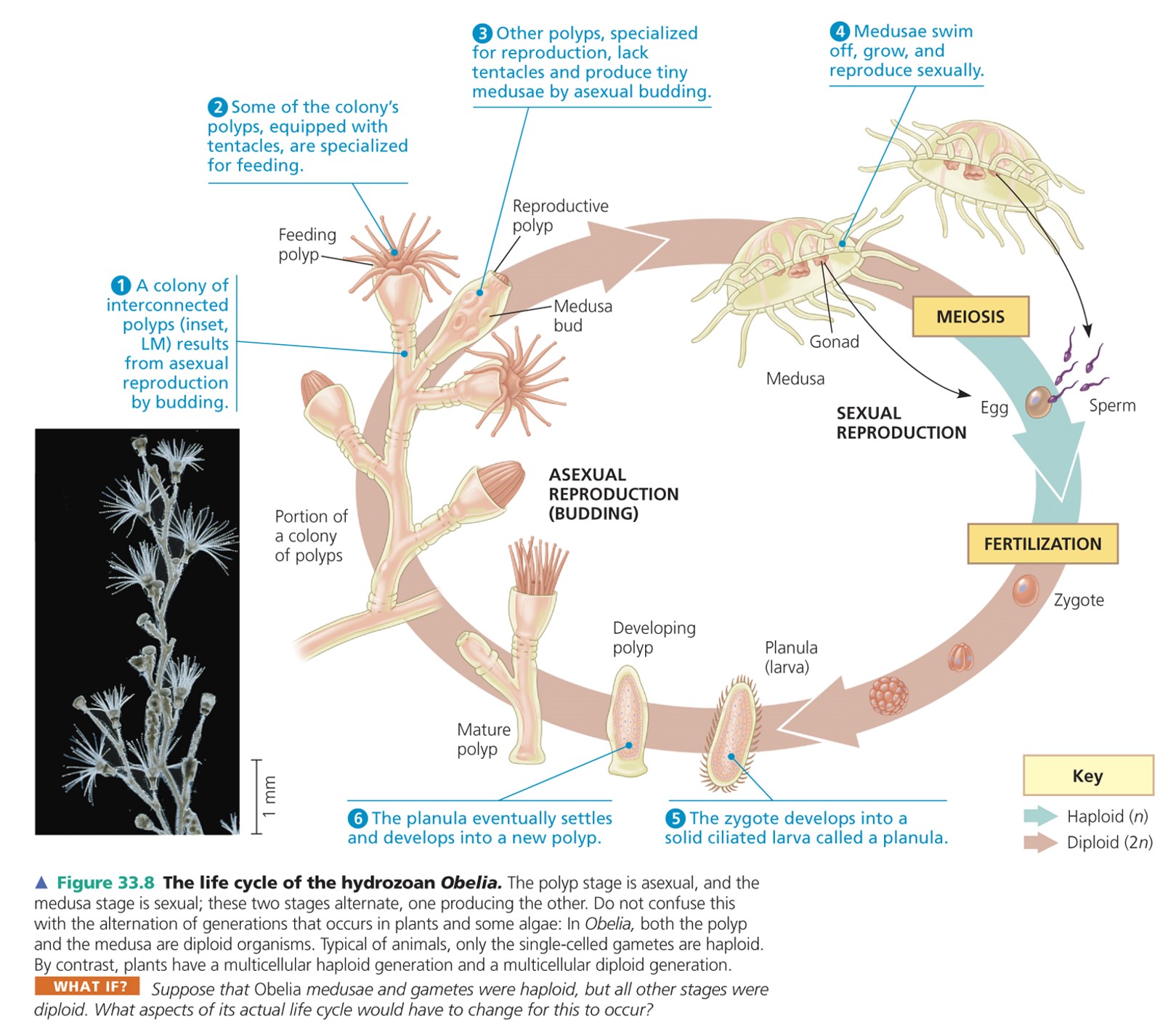
20
New cards
Cnidarian body wall
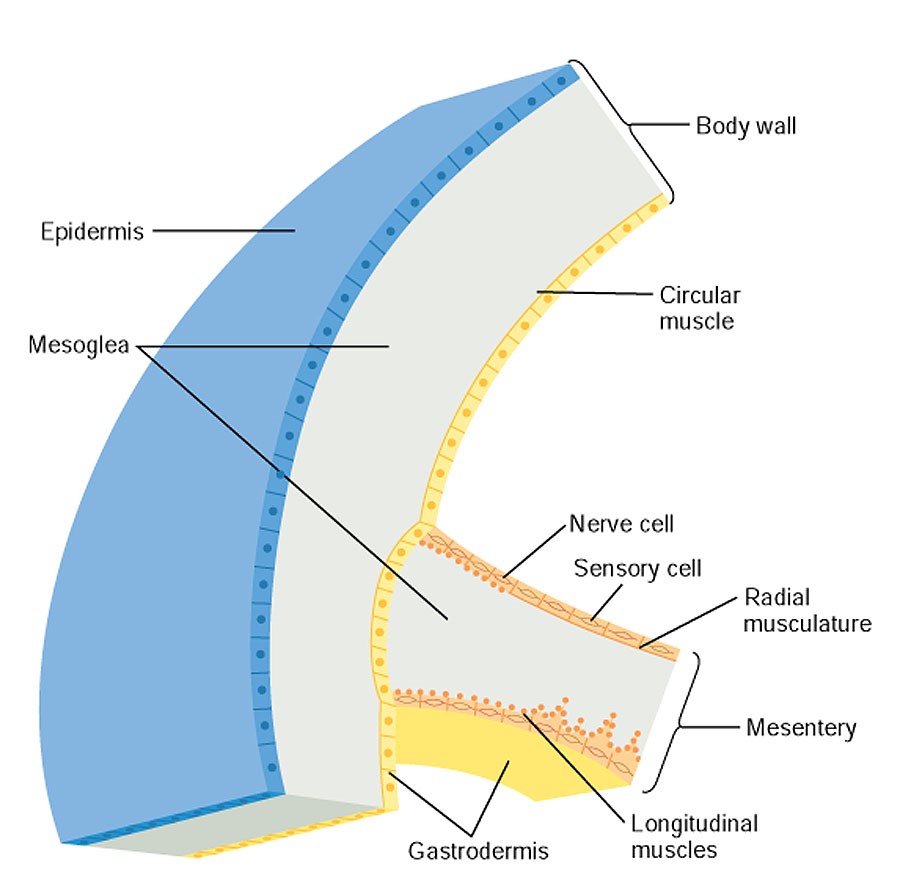
21
New cards
integument Cnidaria
tentacles lined with nematocysts

22
New cards
skeleton Cnidaria
hydrostatic skeleton- water or body fluids confined in a cavity of the body and against which elements of the body wall act
23
New cards
movement(muscularity) Cnidaria
depends on the stage of the life cycle, polpys-sessile, medusae-free swimming
24
New cards
digestion Cnidaria
Nematocysts lining the tentacles bring in foods to the gastrovascular cavity where digestion occurs
25
New cards
nervous(control) Cnidaria
nerve net
26
New cards
protection Cnidaria
stringing cells that line the tentacles
27
New cards
generalized Cnidarian life cycle
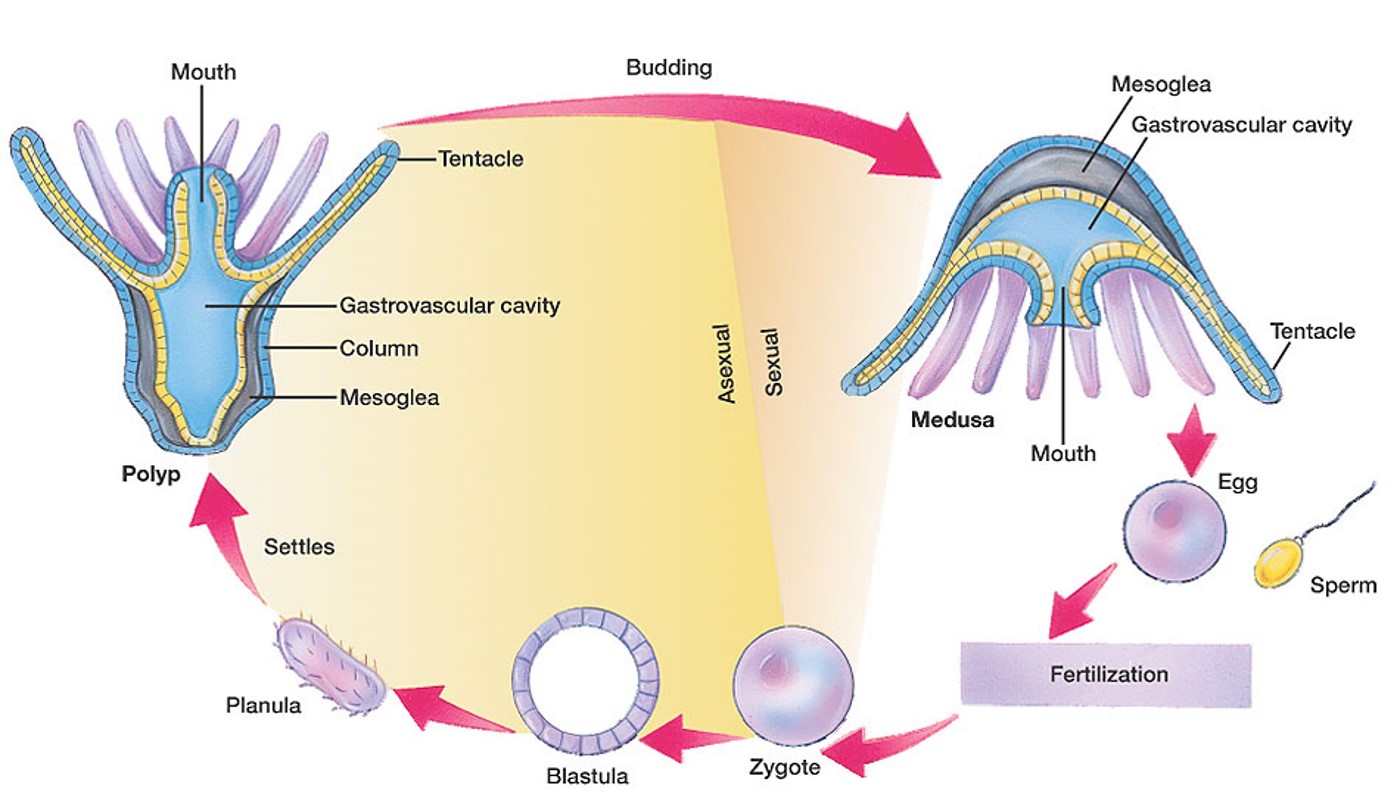
28
New cards
Obelia structure and life cycle
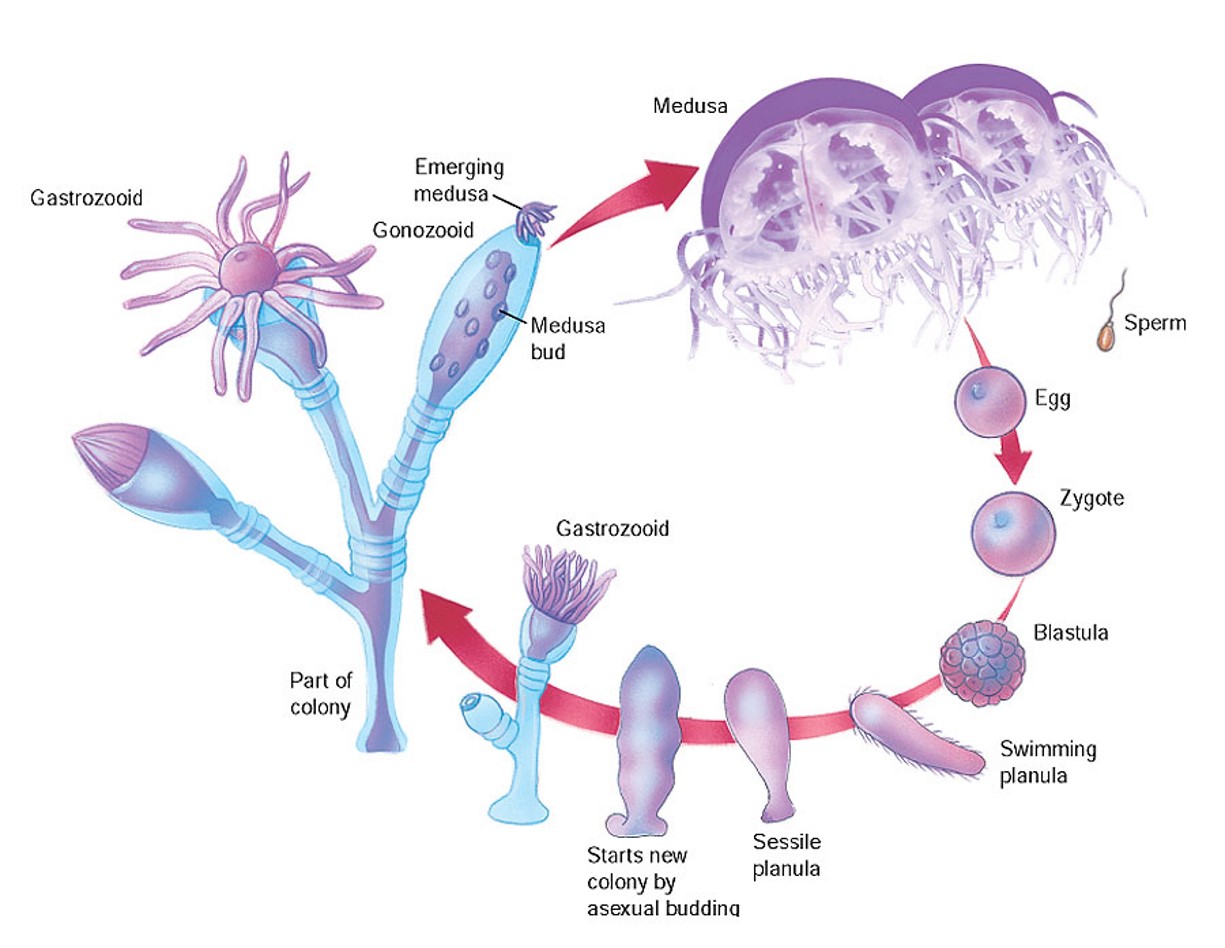
29
New cards
structure of gonionemus medusa
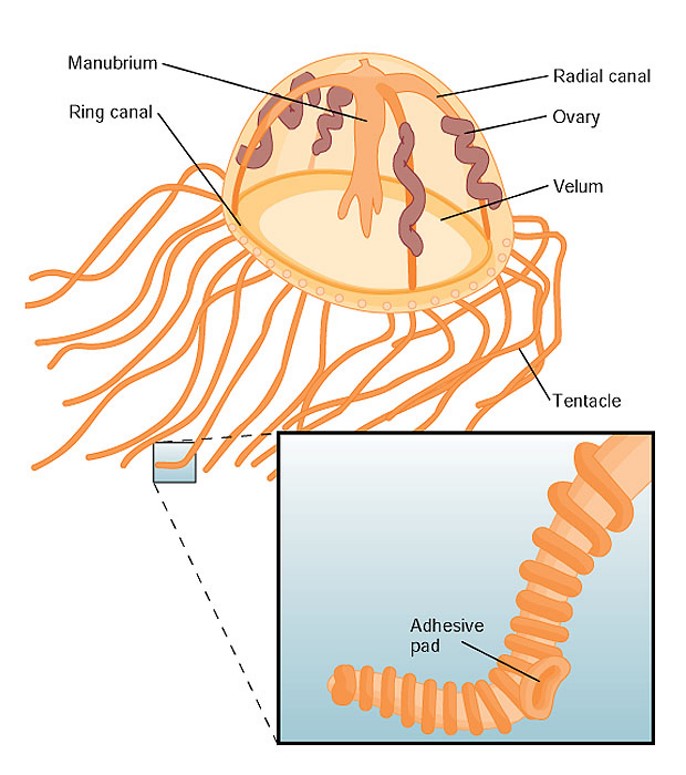
30
New cards
structure of scyphozoan medusa
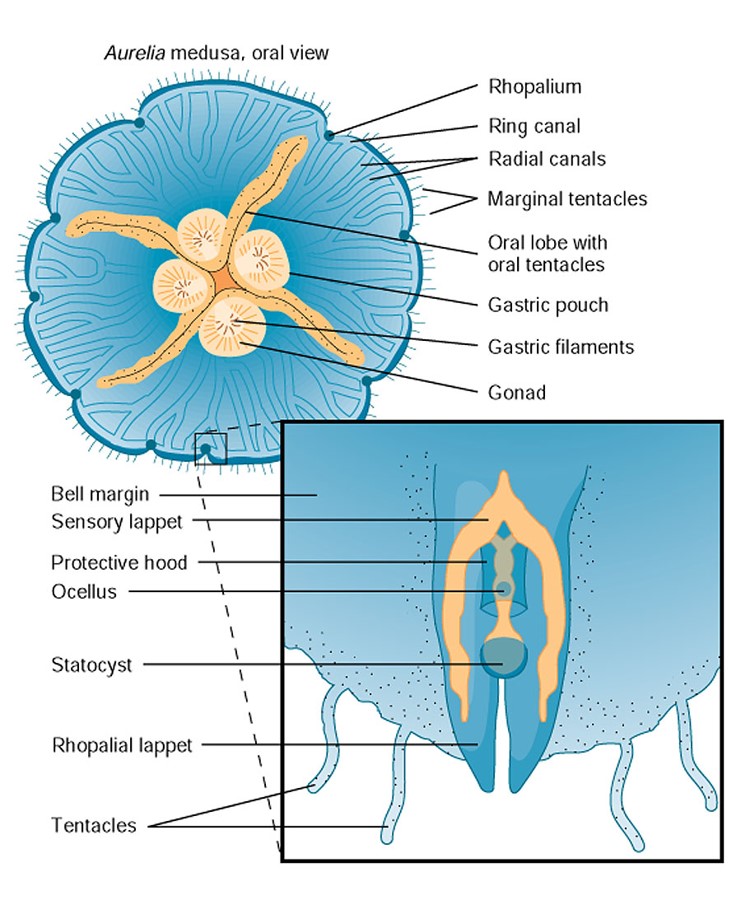
31
New cards
aurelia life history
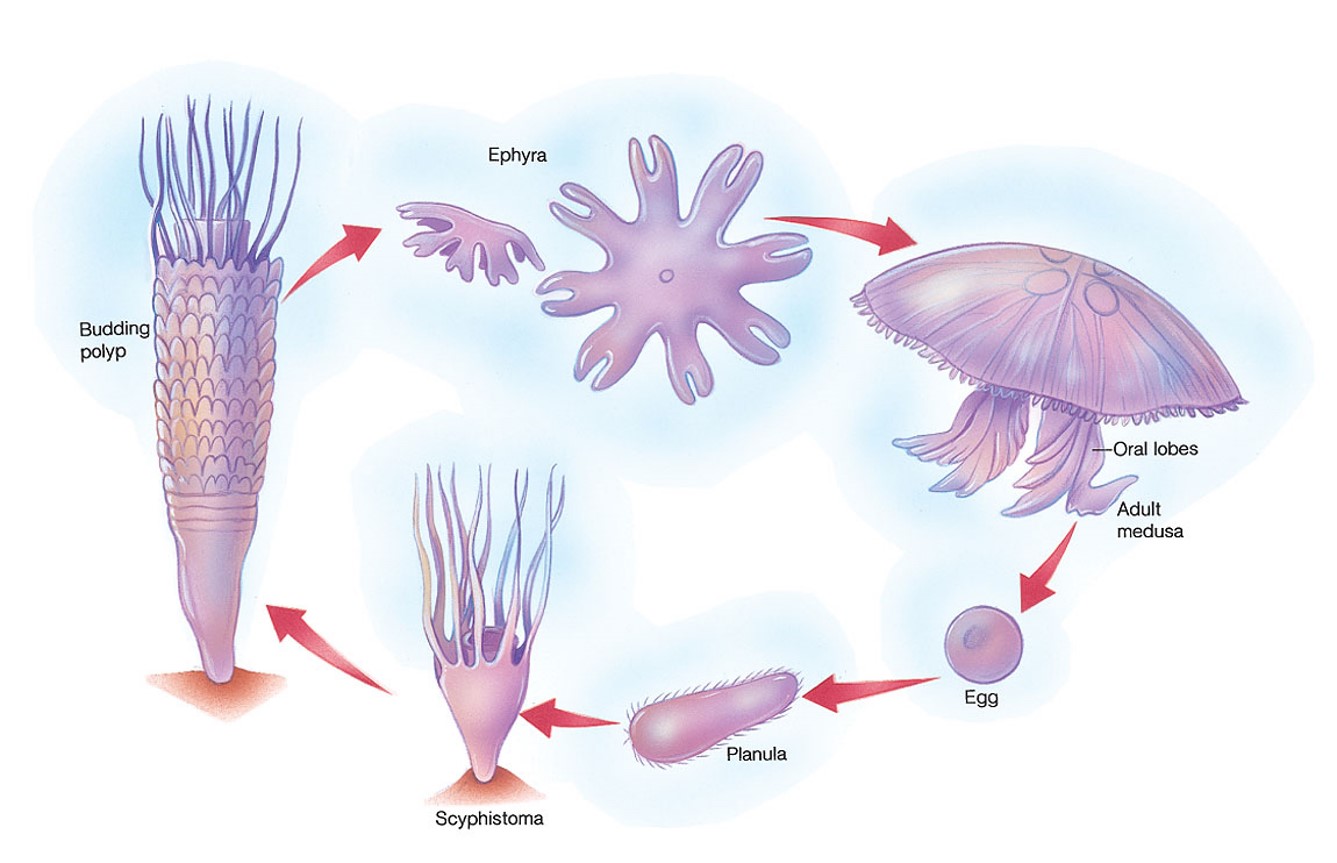
32
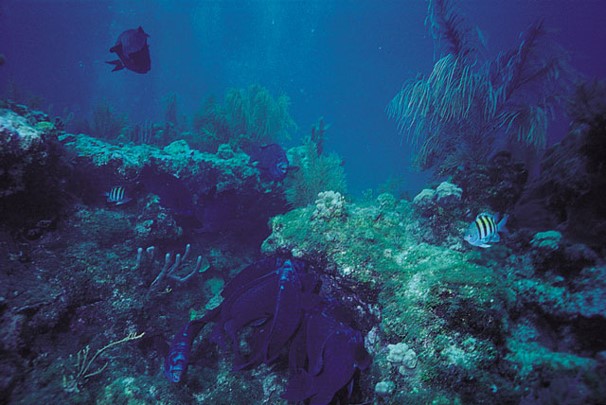
New cards
coral reef ecosystem

33
New cards
coral bleaching
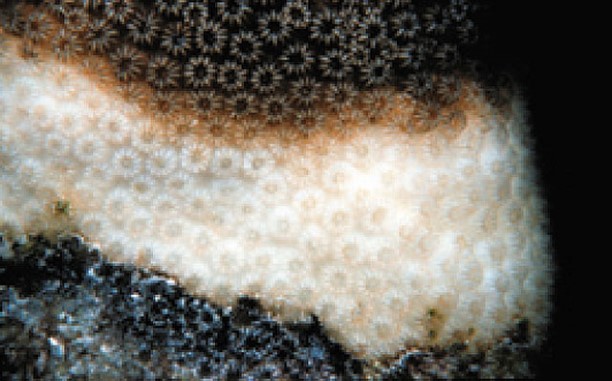
34
New cards
platyhelminthes characteristics
1\.Triploblastic – (3 germ layers)
2\.Bilaterally symmetrical; definite polarity of anterior and posterior ends; Somewhat Cephalized
3\.Body flattened dorsoventrally; oral and genital apertures mostly on ventral surface
4\.Body with multiple reproductive units in one class
5\.Epidermis may be cellular or synctial (a mass of protoplasm containing many nuclei and not divided into cells)
6\.Muscular system in the form of a sheath of circular, longitudinal and oblique layers beneath the epidermis or tegument 7. No internal body space other than digestive tube; spaces filled with parenchyma (Cestodes lack digestive tube) 8. Digestive system incomplete (gastrovascular type); absent in some
Nervous system with a pair of anterior ganglia with longitudinal nerve cords connected by transverse nerves
10\. Simple sense organs; eyespots in some
11\. Excretory system of two lateral canals with branches bearing flame cells (Protonephridia as excretory/osmoregulatory structures); lacking in some forms
12\. Respiratory, circulatory and skeletal systems lacking, lymph channels with free cells in some nematodes. Most forms monoecious; complex reproductive system with well developed gonads, ducts and accessory organs; internal fertilization; life cycle variable
14\. Class Turbellaria mostly free- living; Classes Monogenea, Trematoda, and Cestoda entirely parasitic
2\.Bilaterally symmetrical; definite polarity of anterior and posterior ends; Somewhat Cephalized
3\.Body flattened dorsoventrally; oral and genital apertures mostly on ventral surface
4\.Body with multiple reproductive units in one class
5\.Epidermis may be cellular or synctial (a mass of protoplasm containing many nuclei and not divided into cells)
6\.Muscular system in the form of a sheath of circular, longitudinal and oblique layers beneath the epidermis or tegument 7. No internal body space other than digestive tube; spaces filled with parenchyma (Cestodes lack digestive tube) 8. Digestive system incomplete (gastrovascular type); absent in some
Nervous system with a pair of anterior ganglia with longitudinal nerve cords connected by transverse nerves
10\. Simple sense organs; eyespots in some
11\. Excretory system of two lateral canals with branches bearing flame cells (Protonephridia as excretory/osmoregulatory structures); lacking in some forms
12\. Respiratory, circulatory and skeletal systems lacking, lymph channels with free cells in some nematodes. Most forms monoecious; complex reproductive system with well developed gonads, ducts and accessory organs; internal fertilization; life cycle variable
14\. Class Turbellaria mostly free- living; Classes Monogenea, Trematoda, and Cestoda entirely parasitic
35
New cards
flatworms
\*Members of phylum Platyhelminthes live in marine, freshwater, and damp terrestrial habitats
\*Although flatworms undergo triploblastic development, they are acoelomates
\*They are flattened dorsoventrally and have a gastrovascular cavity
\*Gas exchange takes place across the surface, and protonephridia regulate the osmotic balance
\*Although flatworms undergo triploblastic development, they are acoelomates
\*They are flattened dorsoventrally and have a gastrovascular cavity
\*Gas exchange takes place across the surface, and protonephridia regulate the osmotic balance
36
New cards
what are the four classes of flatworms?
\*Turbellaria (mostly free-living flatworms)
\*Monogenea (monogeneans)
\*Trematoda (trematodes, or flukes)
\*Cestoda (tapeworms)
\*Monogenea (monogeneans)
\*Trematoda (trematodes, or flukes)
\*Cestoda (tapeworms)
37
New cards
turbellarians
\*are nearly all free-living and mostly marine
\*The best-known turbellarians are commonly called planarians
\*The best-known turbellarians are commonly called planarians
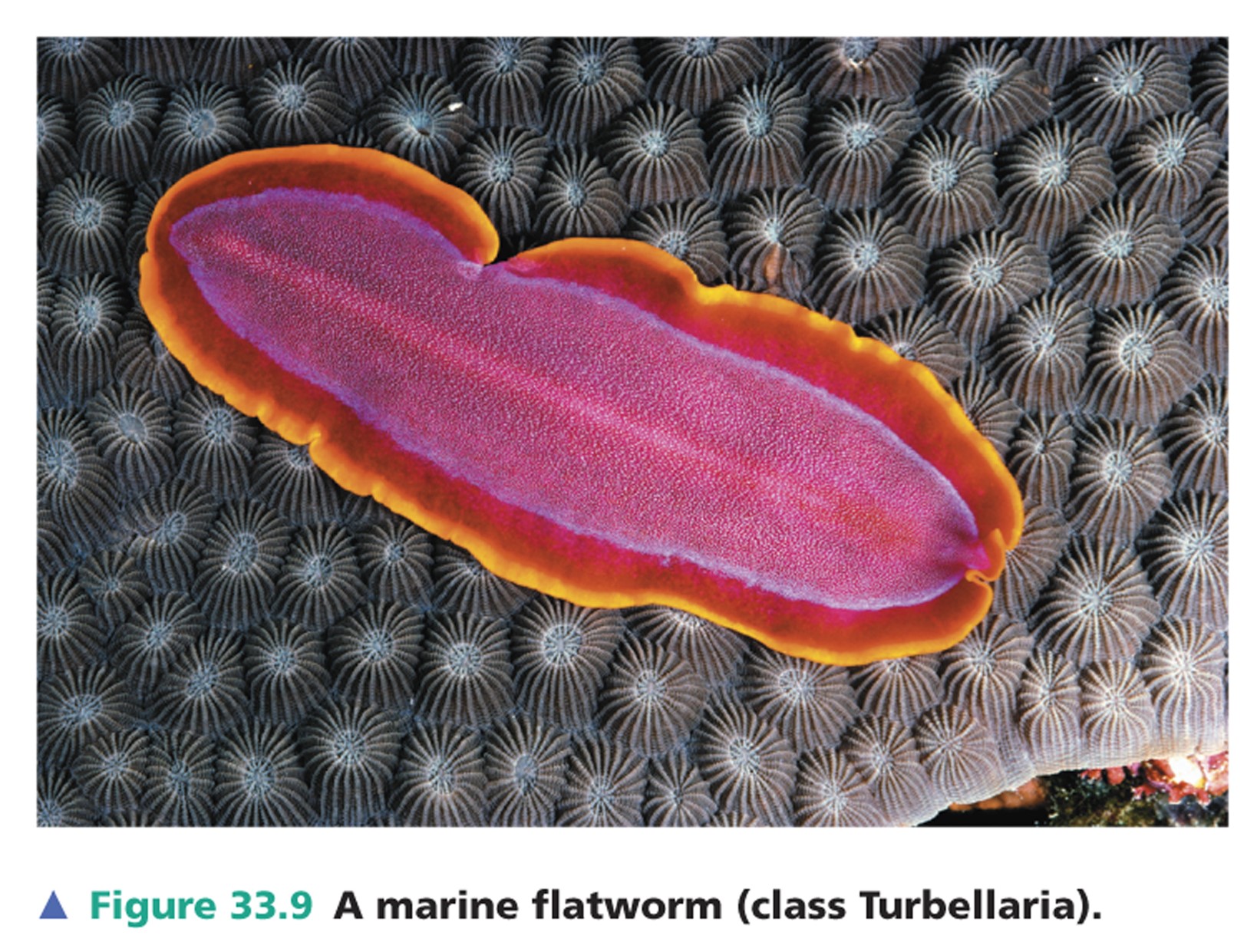

38
New cards
planarians characteristics
\*Planarians have light-sensitive eyespots and centralised nerve nets
\*The planarian nervous system is more complex and centralised than the nerve nets of cnidarians
\*Planarians are hermaphrodites and can reproduce sexually, or asexually through fission
\*The planarian nervous system is more complex and centralised than the nerve nets of cnidarians
\*Planarians are hermaphrodites and can reproduce sexually, or asexually through fission
39
New cards
monogeneans and trematodes
\*live as parasites in or on other animals
\*They parasitise a wide range of hosts, and most have complex life cycles with alternating sexual and asexual stages
\*Trematodes that parasitise humans spend part of their lives in snail hosts
Most monogeneans are parasites of fish
\*They parasitise a wide range of hosts, and most have complex life cycles with alternating sexual and asexual stages
\*Trematodes that parasitise humans spend part of their lives in snail hosts
Most monogeneans are parasites of fish
40
New cards
life cycle of a blood fluke
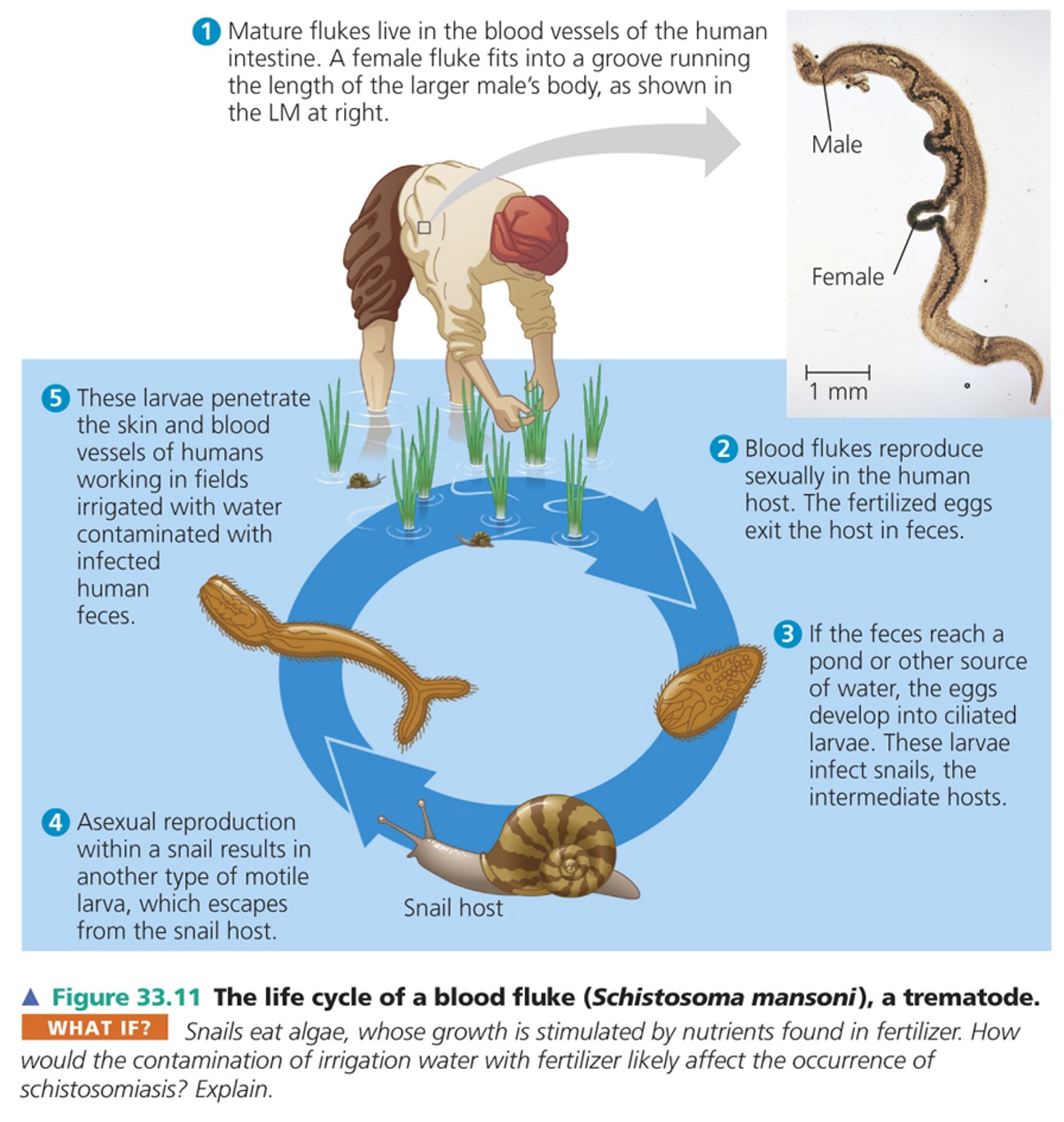
41
New cards
tapeworms
\*parasites of vertebrates and lack a digestive system
\*Tapeworms absorb nutrients from the host’s intestine
\*Fertilised eggs, produced by sexual reproduction, leave the host’s body in faeces
\*Tapeworms absorb nutrients from the host’s intestine
\*Fertilised eggs, produced by sexual reproduction, leave the host’s body in faeces
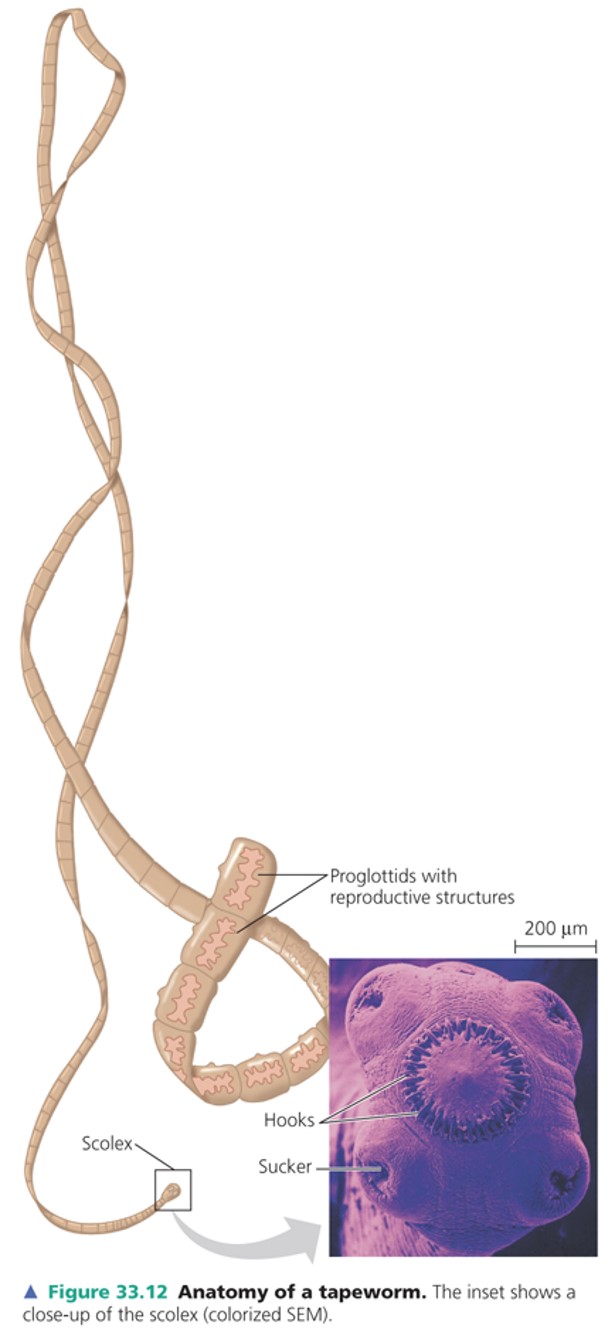
42
New cards
integument Platyhelminthes
\*Epidermis in contact with the environment
\*Tegument is highly efficient at absorbing nutrients and is effective for protection
\*Tegument is highly efficient at absorbing nutrients and is effective for protection
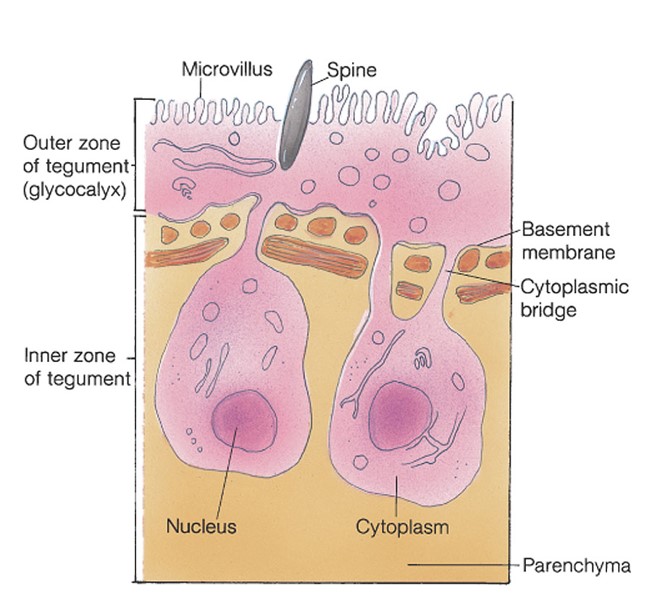
43
New cards
skeleton Platyhelminthes
none to speak of, a few have structures for holding on
44
New cards
movement(muscularity) Platyhelminthes
well developed muscularity
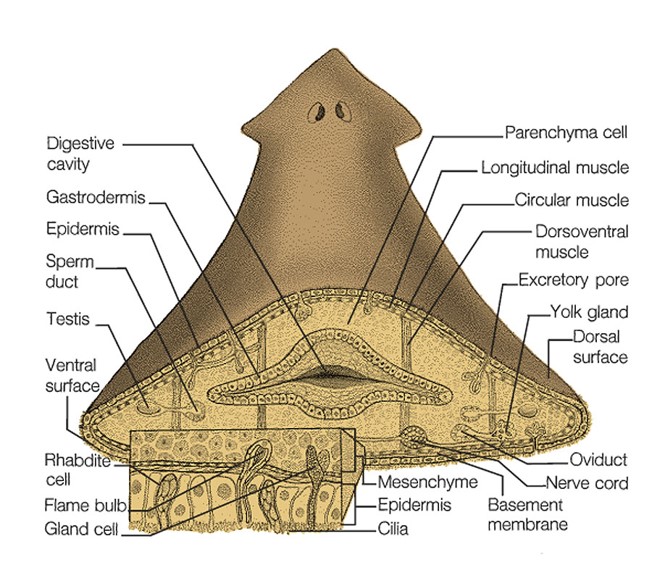
45
New cards
digestion Platyhelminthes
\*Digestion is variable
\*Pharynx of turballarian serve as mouth and anus
\*Digestive tracts are of varying complexities
\*Pharynx of turballarian serve as mouth and anus
\*Digestive tracts are of varying complexities
46
New cards
nervous (control) Platyhelminthes
\*Variable
\*Relatively well developed with a cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord in planaria
\*Relatively well developed with a cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord in planaria
47
New cards
nervous system in turbellarians
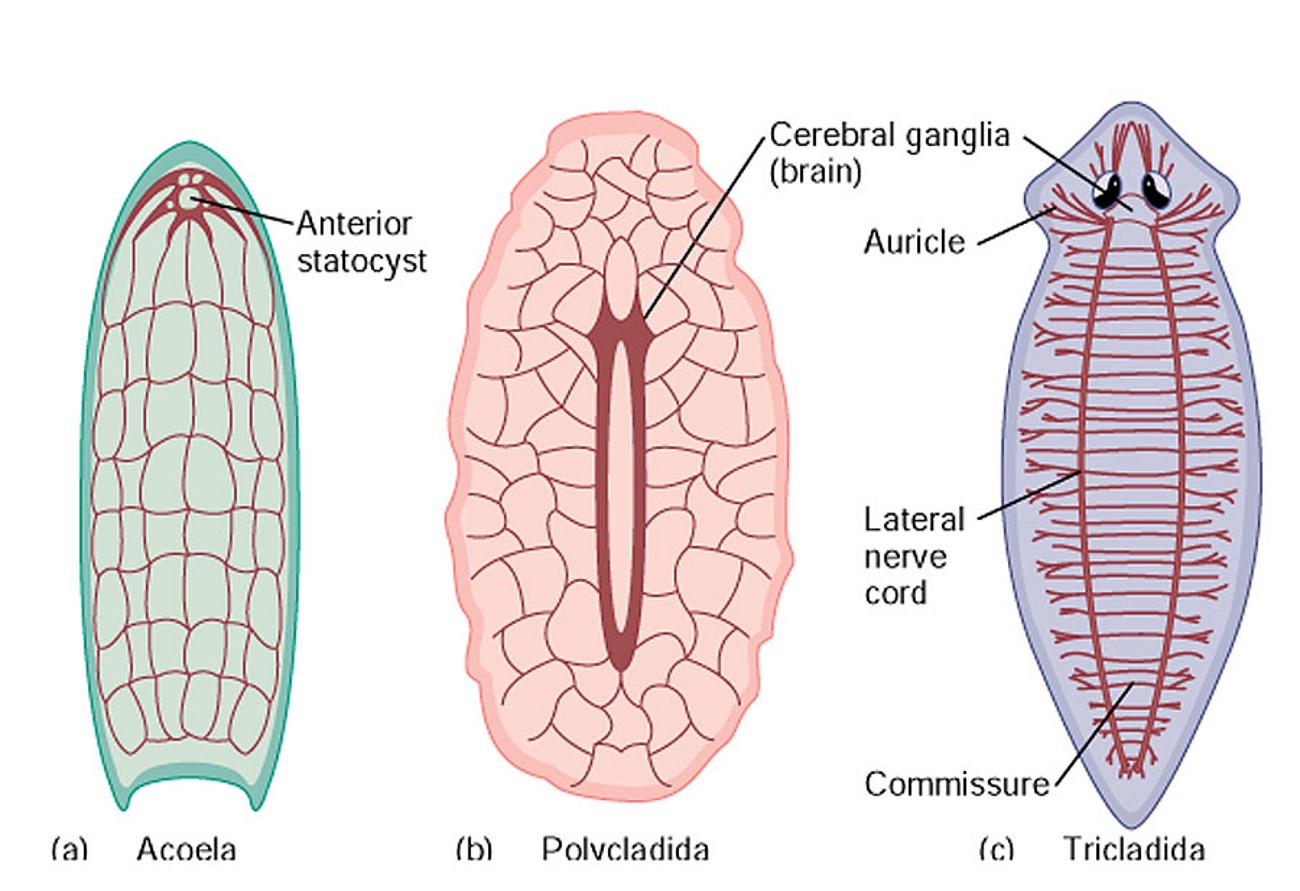
48
New cards
circulation Platyhelminthes
highly centralized digestive system in contact with cells that diffuse nutrients
49
New cards
protection platyhelminthes
some have a scolex for holding on, photoreceptors in free-living platyhelminths
50
New cards
respiration platyhelminthes
diffusion through the tegument
51
New cards
waste removal Platyhelminthes
protonephridia, flame cells
52
New cards
reproduction Platyhelminthes
\*Highly variable, but possibly the most interesting system in the Entire Phylum
\*Hermaphroditic
\*Hermaphroditic
53
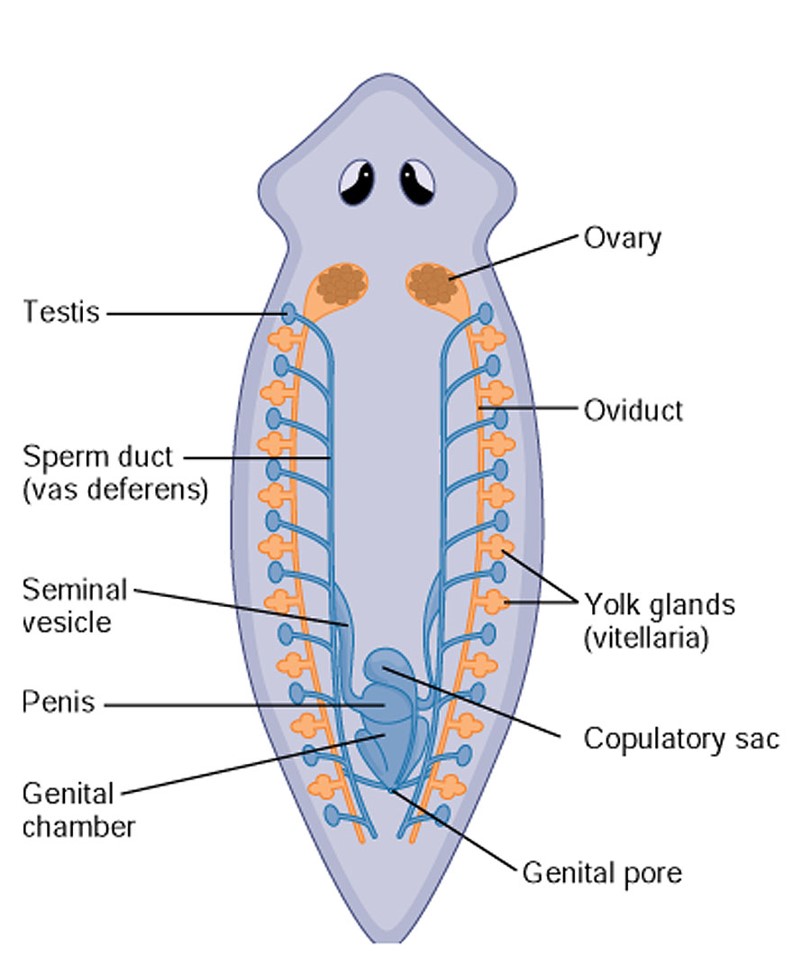
New cards
turbellarian reproductive system
54
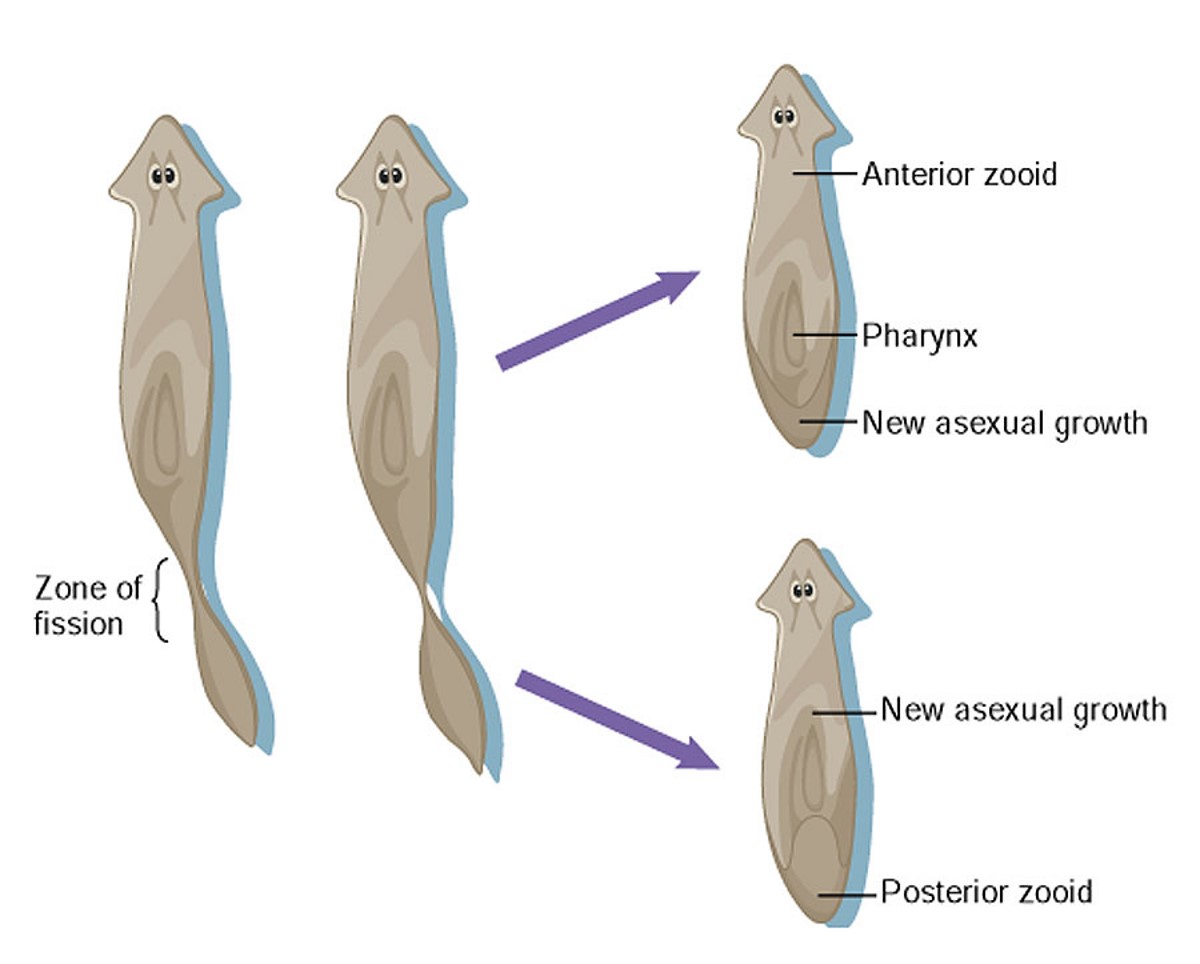
New cards
asexual reproduction in turbellarians
55
New cards
pseudocoelomate body plan
rotifera, kinorhncha, nematoda, nematomorpha, acanthomorpha, lricifera, priapulida
56
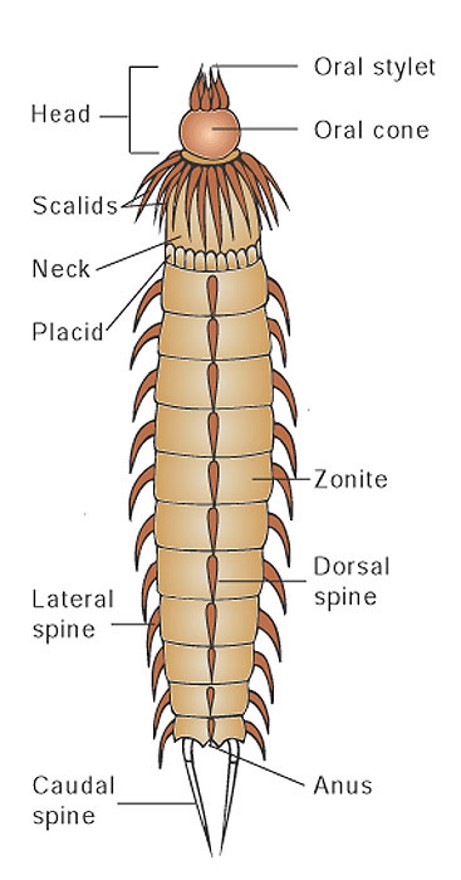
New cards
external anatomy of a an adult kinorhynch
57
New cards
what is the highest percent of nematoda species
arthropoda
58
New cards
nematoda characteristics
Triploblastic, bilateral, vermiform (resembling a worm in shape; long and slender), unsegmented, pseudocoelomate
2\. Body round in cross section and covered by a lateral cuticle; molting usually accompanies growth in juveniles
3\. Complete digestive tract; mouth usually surrounded by lips bearing some sense organs
4\. Most with unique excretory system comprised of one or two rennete cells or a set of collecting tubules
5\. Body wall has only longitudinal muscles
2\. Body round in cross section and covered by a lateral cuticle; molting usually accompanies growth in juveniles
3\. Complete digestive tract; mouth usually surrounded by lips bearing some sense organs
4\. Most with unique excretory system comprised of one or two rennete cells or a set of collecting tubules
5\. Body wall has only longitudinal muscles
59
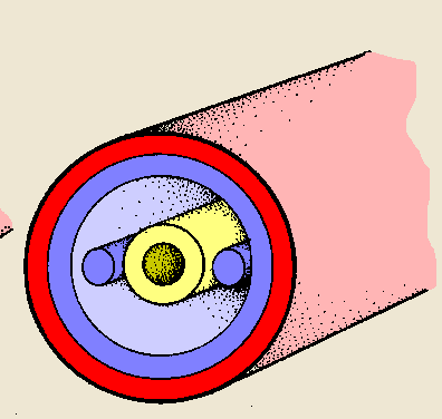
New cards
pseudocoelomate structure
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
60
New cards
two major classes of pseudocoelomate
secernentea(phasmidea)- phasmids in the tail
adenophorea(aphasmidia)- phasmids absent
adenophorea(aphasmidia)- phasmids absent
61
New cards
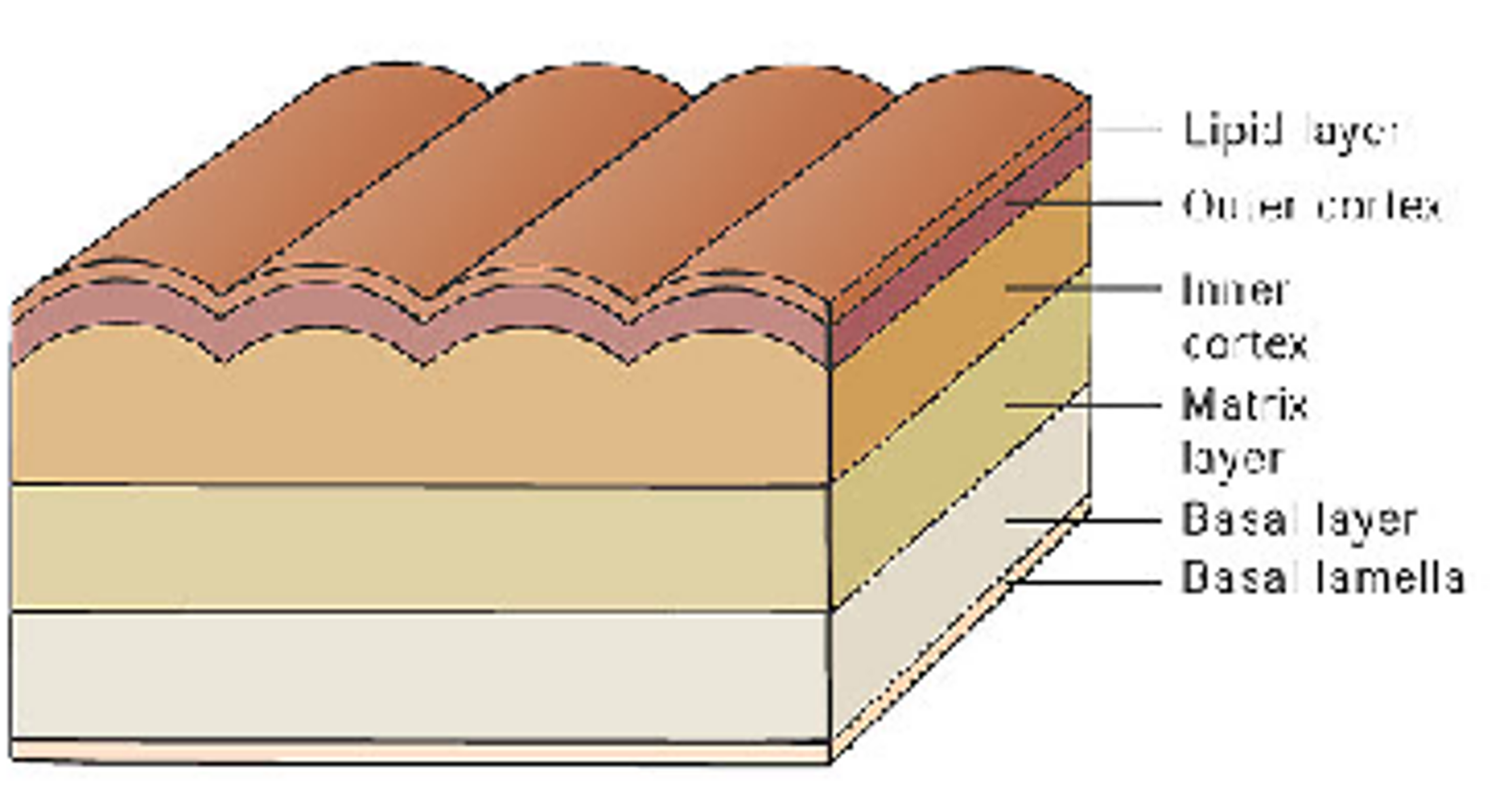
integument nematoda
Collagenous cuticle, three layers cortex, matrix, and basal layer
Molt four times before maturation
Molt four times before maturation
62
New cards
skeleton nematoda
hydrostatic skeleton consisting of an internal fluid filled pseudocoel
63
New cards
movement(muscularity) nematoda
bLongitudinal muscles and circular muscles to allow for characteristic undulating movement
64
New cards
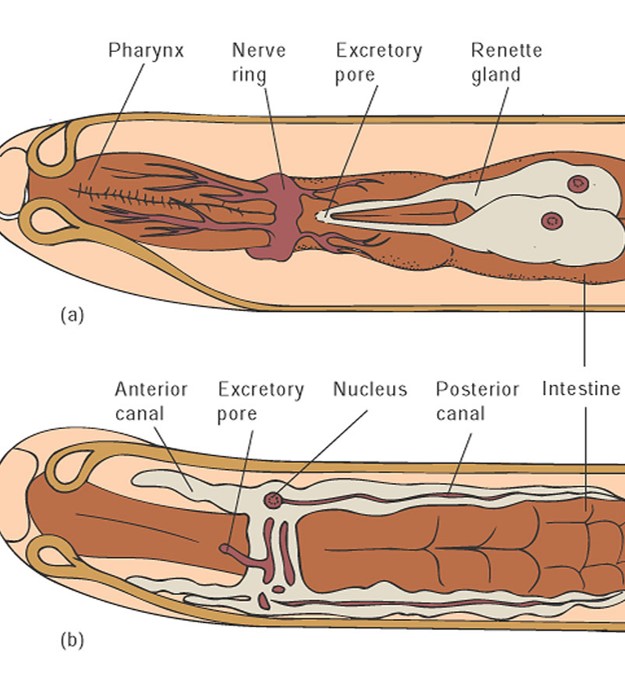
nervous(control) nematoda
relatively complex nerve ring
65
New cards
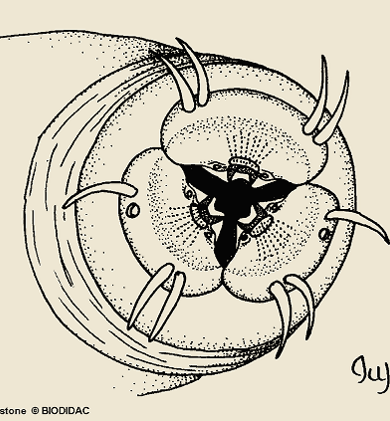
protection Nematoda
Movement, teeth in some, and sheer numbers in reproduction help to protect perpetuation
66
New cards
nematoda mouth
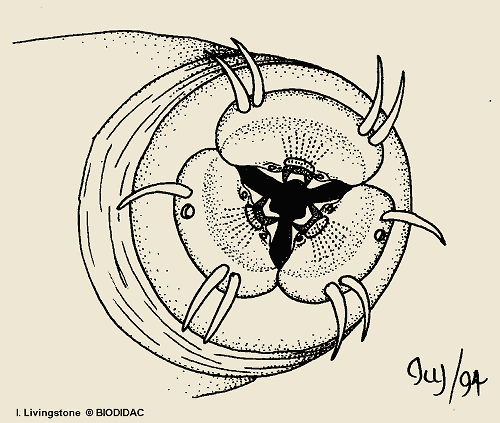
67
New cards
respiration nematoda
diffusion from the cuticle
68
New cards
waste removal Nematoda
renette cells responsible for osmoregulation
69
New cards
renette cells
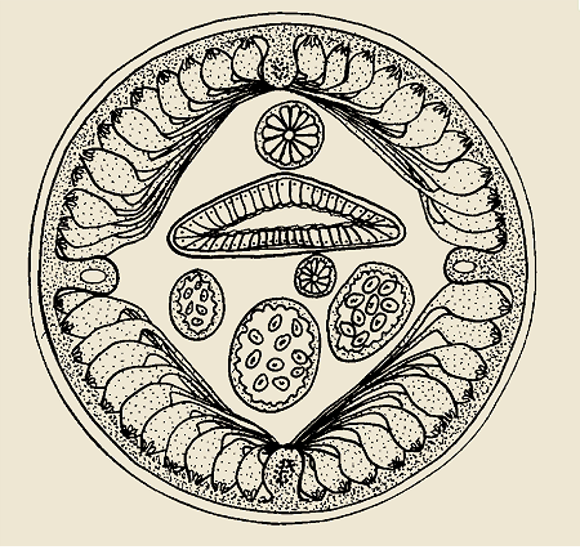

70
New cards
reproduction Nematoda
Definitely dioecious
Internally much different and externally males with “curl”
Usually females larger than males, but not always
Internally much different and externally males with “curl”
Usually females larger than males, but not always
71
New cards
Phylum Mollusca
soft bodied, shelled-some without, cephalization- sensory organs, mouths, body divisions- visceral mass, head-foot, mantle, complete digestive tract, digestive glands, specialized feeding structures, circulatory system-heart (2 chambers), open system in most groups, closed in cephalopods, coelom restricted to pericardium in most cases
72
New cards
banana slug
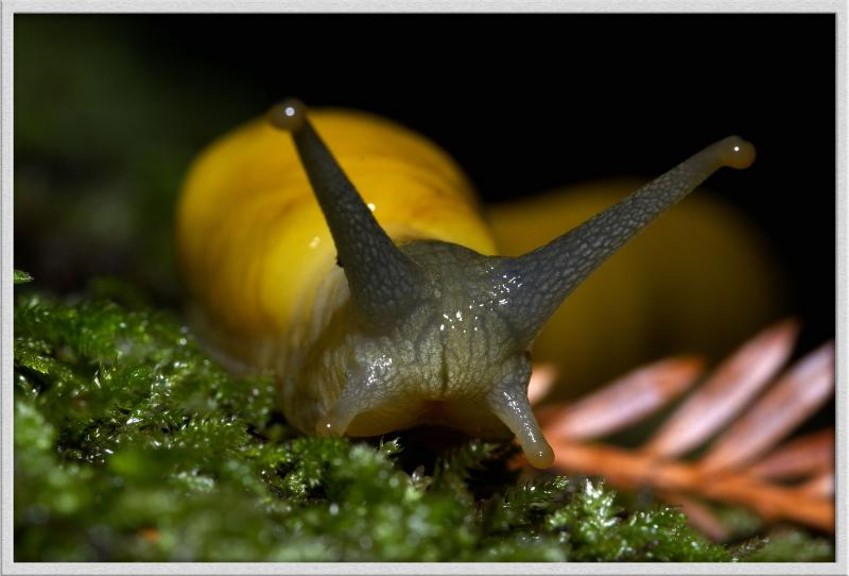

73
New cards
scallops
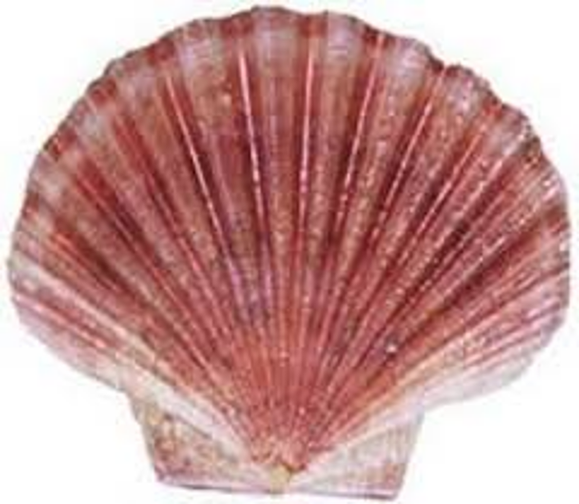

74
New cards
integument bivlaves
soft bodied, hard 2 part shell
75
New cards
integument gastropods
soft bodied, often a shell with torsion
76
New cards
integument cephalopods
soft bodied with tentacles and feet, some with a hard shell
77
New cards
mussels
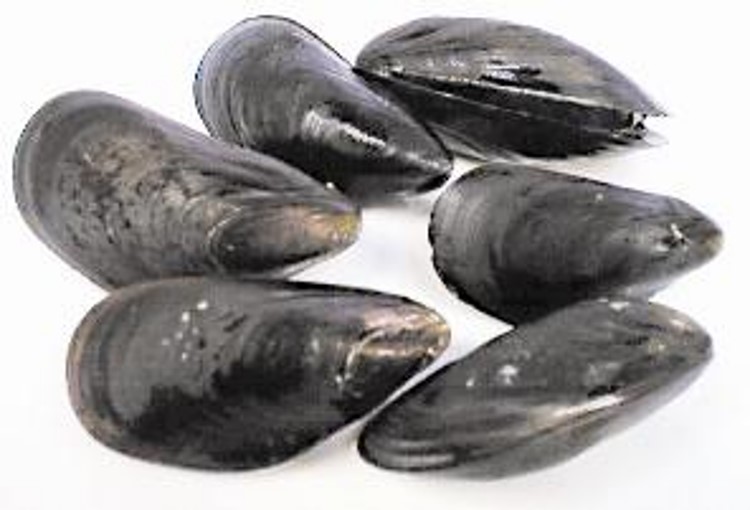

78
New cards
skeleton bivalves
hydrostatic skeleton inside a two part shell
79
New cards
skeleton gastropods
hydrostatic skeleton inside a one part shell usually
80
New cards
skeleton cephalopods
hydrodtatic dskeleton inside a one part shell(if any), some skeletal elements( beak, pen)
81
New cards
generalized mollusc anatomy
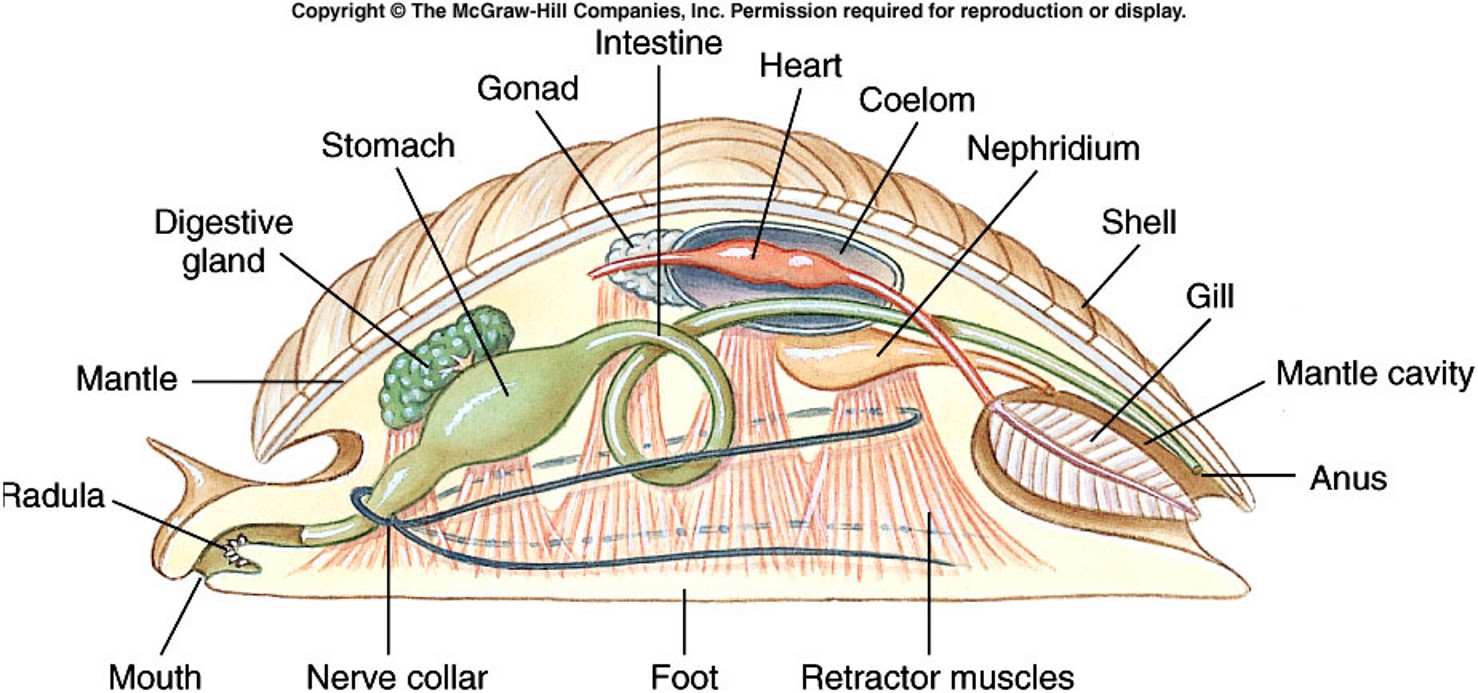
82
New cards
respiration mollusc
gills
83
New cards
mollusc reproduction and development
indirect development- larval stages, trochophore larva-free swimming, ciliated, shell formation begins, veliger larva- free swimming, ciliated velium forms, shell/body torsion occurs, spat- metamorphic form between veliger and juvenile, shell elaborates
84
New cards
marine gastropods
cowries

85
New cards
pulmonata
the mantle cavity serves as a lung, glandular epidermis-secrete mucus upon which gastropod glides
86
New cards
metabolism(digestion) bivalves
complete digestive system coordinating with the circulatory system; typically filter feeders
87
New cards
metabolism(digestion) gastropods
complete digestive system also with unusual anal opening leading to fouling
88
New cards
metabolism(digestion) cephalopods
complete digestive system with ceca that are accessory as well as highly developed digestive glands
89
New cards
largest cephalopods?
squid
90
New cards
nervous(control) system bivalves
relatively well developed in some many sensory eyes around the fringe of the mantle
91
New cards
nervous(control) system gastropods
well developed nervous system with stalked eyes that can move in all directions
92
New cards
nervous(control) system cephalopods
very well developed nervous system, problem solving brains
93
New cards
cephalopod eye
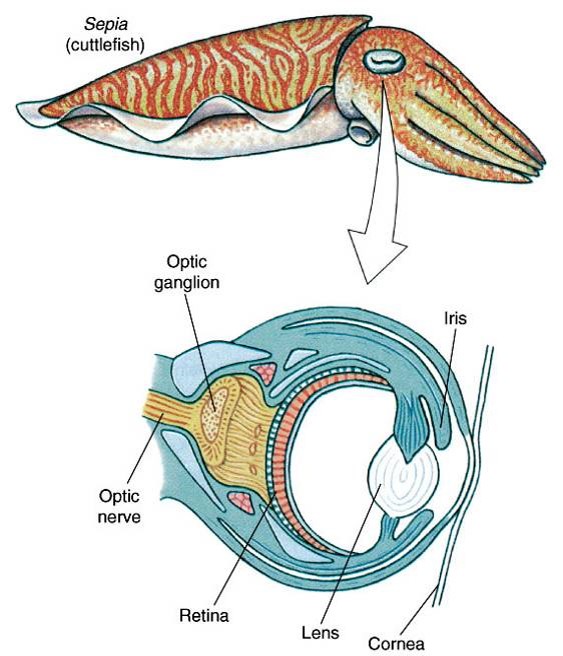
94
New cards
circulation bivalves
open circulation with blood connected to pools or sinuses for movement of materials
95
New cards
circulation gastropods
open circulatory system
96
New cards
circulation cephalopods
open circulatory system with hearts for directing blood from gills and throughout the body to sinuses
97
New cards
protection bivalves
hard shell, varied styles of locomotion, glochidia larvae
98
New cards
protection gastropods
hard shell often with an operculum, many poisonous
99
New cards
protection cephalopods
some with a shell, hard, bird-like beak, suckers, ink sac for diversionary tactics
100
New cards
reproduction bivalves
•Entirely aquatic with sexual reproduction, gametes are released into the water for external fertilization