Psychology revision questions
1/356
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
357 Terms
What is the name of the temporary memory store with which people can remember a few items for several seconds?
Short-term memory (STM)
State 2 ways in which STM is limited.
Limited capacity and limited duration.
Name the types of memory demonstrated below:
A) Being able to ride a bike.
B) Remembering your first day of school.
C) Knowing that an MP is a type of politician.
A) Procedural
B) Episodic
C) Semantic
Is memory best described as an active or passive process?
An active process.
Which of the following is true?
A) Encoding new memories happens fairly automatically
B) Memories are retrieved in exactly the same form as they were remembered
C) Both encoding and retrieval often involve mental effort
D) Items always enter long-term memory even if the person is not paying attention
C) Both encoding and retrieval often involve mental effort
Which of the following is an input process to memory?
A) Encoding
B) Storage
C) Retrieval
D) Forgetting
A) Encoding
Murdock (1962) conducted an important experiment into memory. What is the name for the graph showing the effects found in this study?
Serial position curve
Explain how Murdock’s experiment can be used to evaluate the multi-store model. [3]
Murdock’s serial position curve supports the model [1]. The primacy effect is explained by items being rehearsed into LTM [1]. The recency effect is explained by a few items remaining within a limited capacity STM [1].
Is rehearsal a sufficient process to encode new information to LTM?
No - often rehearsal is not enough
Name 3 ways people might be in a different state when they try to retrieve a memory?
Different mood.
Drugs such as caffeine.
Consumption of alcohol.
(Also accept a different physical location)
Which of the following describes a schema?
A) A visual memory technique that can be used when revising
B) A mental concept, influenced by life experience and culture
C) the process of encoding things to LTM
D) A belief that people have about other cultures
B) A mental concept, influenced by life experience and culture
How long can items be held in the STM without making an effort to rehearse them?
Up to approx. 30 seconds
Is the STM best described as a permanent store or a temporary store?
A temporary store.
How much information can LTM hold?
Unlimited/ does not get full.
What is most important for encoding semantic long-term memories - understanding the meaning, or seeing the visual image?
Understanding the meaning (because it uses semantic encoding).
Name 2 things that can act as a cue to retrieving a memory.
Any 2 from:
The first letter
A questions
An image
An aspect of the learning context
Which of the following is another term for STM and emphasises that it is an active process?
A) LTM
B) Working memory
C) Free recall
D) Hard drive
B) Working memory
Which of the following is not true of STM?
A) Is it used for active processing of information in everyday tasks
B) People can use it to follow a series of instructions
C) It can rehearse items to store them for longer
D) It is simply used for storage
D) It is simply used for storage
Explain the role of attention in taking in new memories [2].
Information is only taken into memory if a person pays attention to it [1]. This typically happens when they find things interesting or emotional in some way/ if they don’t pay attention things will not enter STM and therefore will not be processed and encoded to LTM [1].
Explain the role of repetition in the process of encoding things to long-term [4].
It is important for memory, as more exposure increases the chances of encoding [1]. However, simply repeating things doesn’t always lead to encoding, particularly if information is hard to understand [1]. More important processes are active, such as linking new information to what is already known/ retrieving information from memory in a way that is spaced out over time helps to consolidate it [1]. Answers could also refer to the multi-store model of memory, which makes the over-simplistic claims that rehearsal is the only means of encoding items to LTM [1].
Draw (or describe?) a diagram of the multi-store memory.
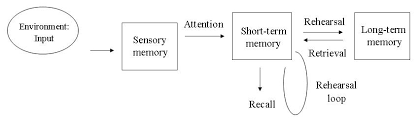
Name the researchers who devised the multi-story model of memory.
Atkinson and Shiffrin.
Name the 3 stores in the multi-story model of memory.
Sensory memory, STM and LTM.
What is the process by which information enters the STM? (Multi-story model of memory).
Attention.
What is the process by which information is kept in the STM for longer? (Multi-story model of memory).
Rehearsal.
What is the process by which information is encoded to the LTM? (Multi-story model of memory).
Rehearsal.
Briefly describe a possible experiment that could be run to demonstrate the primacy and recency effect. [3]
Reading out a list of random words to a group of participants [1]. Each participant would have to write down all of the words they could remember [1]. The researcher would count how many times each word was recalled, with the expectation that the words at the beginning and end of the list would be recalled more frequently on average [1].
How long does sensory memory last, and what it’s capacity? [3]
Visual memory is a very brief store [1]. The visual store was found by Sperling (1960) to have a large capacity but a duration of only 0.5 seconds [1]. The acoustic store is thought to last around 2 seconds [1].
What was the name of the British researcher who studied distortions in memory using folk stories?
Bartlett.
What 4 types of distortions did Bartlett find?
Additions, subtractions, transformations (to familiar) and preservation of detached detail.
Which of the following could result in a fake memory?
A) Being asked a leading question
B) Forgetting something
C) A blow to the head
D) Consuming caffeine or drugs
A) Being asked a leading question
Why was the story Bartlett used hard for the participants to understand and remember?
It came from a culture that was unfamiliar to the participants [1]. Therefore they lacked schema knowledge to connect it to [1].
What’s the technical name for a nerve cell?
A neuron.
Why can we perceive objects accurately even when it gets darker?
Due to light consistency. When people perceive objects, the brain makes allowances for lighting and therefore objects still appear the same to us.
What part of the brain processes visual information?
Visual cortex (or sensory cortex/ occipital lobe of the cerebral cortex).
Explain why depth perception is important to humans and other animals. [3]
Depth perception is essential for survival [1]. Accept two from the following:
Environmental risks for the species if they couldn’t tell how far away a threat was or how far they would fall if they jumped off something.
Predator species need to perceive how close a prey animal is before attacking.
Modern human examples such as sport and driving.
Do textures that are further away look sharper and more detailed?
No, they look blurry and less detailed.
Is the process of perception always accurate? Explain your answer.
No. There are illusions and distortions than can occur.
True or false? Some illusions occur because the stimulus is ambiguous.
True.
True or false? There is one basic explanation for all illusions.
False.
True or false? The Ponzo illusion is based on ambiguity.
False.
True or false? Illusions stop working when you know about them.
False.
What is the name of the researcher who is known for his work on the direct theory of perception?
James Gibson.
a) Which theory of perception states that inferences are a key aspect of perception?
b) Define inference and give an example. [2]
a) The constructivist theory
b) An inference involves working something out from incomplete information [1]. Accept any appropriate example, e.g. seeing a bus that is partially obscured by another object such as a building, and working out that it must be a whole bus [1].
What term means the group of emotions and other factors that lead to a tendency to perceive things in a particular way due to assumptions and emotions?
The perceptual set.
Give two examples of how people can sometimes fail to perceive the world accurately.
Illusions and hallucinations.
What general name is given to the cells that our senses use to gain information about the world, for example the rods and cones found in the retina?
Receptor cells.
Briefly explain the difference between sensation and perception. [2]
Answers must explain that sensation is the process of receiving information from the outside world to the sense e.g. vision, hearing [1]. While perception involves interpreting that information, automatically filtering it and making use of memories and assumptions [1].
Name 2 types of consistancy which are features of visual perceptions.
Any 2 from:
Colour constancy
Light constancy
Size constancy
Shape constancy
Is it easy to program a computer to perceive objects? Explain why or why not. [3]
No [1]. The perceptual system is very complex. The human brain automatically adjusts for things like lighting conditions and objects moving around - it is possible but difficult to program a computer to do this [1]. Also, human sensation relies on very complex network of receptor cells that help us to build up an image of the world/ could mention real-world examples, e.g. self-driving cars, facial recognition software [1].
Briefly explain what is meant by occlusion. [2]
Occlusion is a monocular depth cue [1]. Whereby one object partially covering another allows people to perceive that it must be closer [1].
Why do many predators have 2 forward-facing eyes?
Using binocular cues to depth gives more precise depth perception, and for predators this is very important for survival (more important than peripheral vision from side-facing eyes).
What would happen if a cheetah failed to judge the distance of a gazelle that it was trying to catch?
It would be less likely to hunt successfully, e.g. misjudging a pounce on the animal or running after it when it was too far away.
What term is given for the point that lines converge on as they get future away, helping to demonstrate the cue of linear perspective?
Vanishing point.
Why is it helpful to be able to use cues such as linear perspective in art?
It makes painting look more realistic, so that a 2D picture can give a sense of depth and distance.
Are illusions linked to perseption or to sensation?
Perception.
Describe the Necker cube illusion. [2]
It is a 2D shape that tends to be interpreted as a cube [1] but there are 2 ways it could be facing, making it possible for a person to mentally ‘flip’ the way they perceive the shape [1].
Explain the role of misinterpreted depth cues in illusions.
Depth cues guide us to distance but can be misinterpreted/ misleading. Various supporting points could be made, e.g. explanation of example(s) of illusions where depth cues are an issue e.g. Ponzo illusion, Muller Lyer.

Which illusion is shown here?
Rubin’s vase.
Name 2 researchers who have developed theories of perception, and name the theories with which they are associated.
James Gibson - direct theory
Richard Gregory - constructivist theory
Explain which theory of perception is supported by the idea that animals and humans perceive the the world in very similar ways. [2]
The direct theory (bottom-up processing) [1]. Animals have simpler thought processes than humans, so if they perceive the world in similar ways to us, then perception can’t be based to a large extent extent on cognitions such as memories, inferences, etc [1].
What term does the constructionist theory of perception give to the way that people try to make sense of incomplete sensory information?
A) Motion parallax
B) Inference
C) Bottom-up processing
D) A schema
B) Inference
What term does the direct theory of perception give to the effect that movement has on perception?
A) Visual cliff
B) Top-down processing
C) An illusion
D) Motion parallax
D) Motion parallax
Explain what is meant by an affordance and which theory it supports. [3]
It is a cue in the environment that allows a person or animal to perceive their surroundings [1]. The existence of affordances supports the direct (bottom-up) theory of perception [1]. Because it suggests that the environment provides enough information for organisms to perceive it without the need for using inference or schema knowledge (or could give examples of affordances such as depth cues) [1].
What general term do psychologists use to describe differences between people, including their age and culture?
Individual differences.
Which researchers conducted a study into expectations in perception, showing that the context (other letters or numbers) affected how an ambiguous figure was perceived?
A) Gilchrist and Nesberg
B) Atkinson and Shiffrin
C) Gibson and Walk
D) Bruner and Minturn
D) Bruner and Minturn
What term is used to describe the group of assumptions and emotions that affect and bias perception?
A) Light constancy
B) Perceptual set
C) Bottom-up processing
D) Motion parallax
B) Perceptual set
Briefly explain 2 classic research studies that demonstrated factors in the perceptual set. [4]
Gilchrist and Nesberg (1952) study [1] where people were asked to judge the brightness of food colours, such as the red of a tomato, and found it more vivid when they were hungry [1]. Burner and Minturn (1955) [1] where people were shown an ambiguous figure that could either be perceived as a ‘B’ or a ‘13’. The context )other numbers or letters) affected their expectations [1].
Name 2 parts of a neuron.
Any 2 from:
Axon
Cell body
Nucleus
Axon terminal
An unborn baby’s brain areas have developed by halfway through pregnancy. True or false?
True.
Define plasticity. [2]
The ability of the brain to respond to circumstances and modify its neural structure [1]. Even after childhood/ adolescent brain development processes are complete [1].
What’s the difference between the brain stem and a stem cell?
The brain stem is a region of the brain, responsible for autonomic functions whereas a stem cell is an individual cell that develops in early pregnancy and can later turn into a neuron.
Which side of the nature vs nurture debate states that genes play more of an important role in human development than the environment?
Nature.
Name a type of research study that can be done to help provide evidence about the role of genes in development.
A twin study.
True or false? Identical twins tend to be more similar in intelligence then non-identical twins.
True.
True or false? If one identical twin has a mental illness, then the other twin will definatly get it too.
False.
True or false? If a gene is expressed, this means that it causes a protein to be produced, affecting development.
True.
True or false? Cases where twins are raised by different families are rare and difficult to study.
True.
Explain the nurture side of the nature vs nurture. [4]
Nurture side puts more emphasis on parenting/ upbringing and life experiences rather than genetics when explaining personality, intelligence, mental health, etc [1]. Answer should include the role of parents/ environment/ social background (rather than genetics) e.g. in educational success [1]. Study of epigenetics suggests that life experiences can impact on gene expression, so the two are linked [1]. Could also mention the importance of an enriched rather than deprived environment, or the role of culture in behaviour [1].
What term means children can’t picture the world from another person’s point of view?
Egocentrism/ egocentric.
Explain the features of the concrete operational stage of development. [3]
The child starts to make logical operations [1], is less egocentric [1], and no longer shows centration/ can conserve volume in the ‘tall glass’ task [1].
What terms are sometimes used for learners who prefer to process new information verbally or visually?
Verbalisers and visulisers.
State one thing that can affect self-efficacy.
Any one from:
Praise
Success and failure
Feedback and messages from parents and teachers
Does Willingham think it is important to learn facts? Why, or why not?
Yes. Because learning facts provides essential schema knowledge to which new learning can be connected.
For what type of functions is the brain stem responsible? Give an example.
Autonomic functions. E.g. breathing, heartbeat.
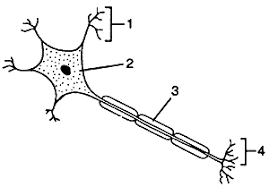
Label areas 2, 3 and 4.
2) Cell body with nucleus
3) Axon, which can send a message elsewhere in the body
4) Axon terminal, which can release neurotransmitters
True neurons begin to form on day 42 of a pregnancy. Why is it unlikely that the unborn child can think and remember before this point?
Because without neurons, the brain has not yet developed the structures that are required for sensory processing (thalamus and visual cortex), thinking, memory (cerebral cortex), etc.
The visual cortex is part of the cerebral cortex. Which part of the brain acts as a replay between the sense and the visual cortex?
The thalamus.
How many neurons are there in the human brain?
A) Fewer than 1 billion
B) Between 1-20 billion
C) Between 20-80 billion
D) Over 80 billion
D) Over 80 billion
Which area of the brain controls precise physical movement and helps to coordinate actions?
A) The cerebral cortex
B) The cerebellum
C) The brain stem
D) The thalamus
B) The cerebellum
Explain how a child’s brain develops after birth. Include the role of the environment. [4]
The child’s brain continues to develop through to adolescence and beyond [1] and this occurs mainly through the strengthening of connections and pruning of unnecessary ones [1]. It is important to have a stimulating environment that challenges the child and allows for creative play [1]. A deprived environment can set back brain development and take years to recover from, or even have permanent effects [1].
Which of the following explanations of personaility development is not associated with the nurture side of the debate?
A) Parenting
B) Education
C) Life experiences
D) Genetics
D) Genetics
Which of the following is not associated with biological development?
A) DNA
B) Education
C) Genes
D) Epigenetics
B) Education
Which side of the nature vs nurture debate states that intelligence is largely innate?
The nature side.
Describe how genes and the environment interact during development. [2]
Genes do not have a direct effect on development but instead are modified by life experience [1]. If a certain environmental condition is present then the gene will be expressed - if not, then it won’t be [1].
What process means linking new information to an existing schema?
Assimilation.
What is the name for the forth stage of Piaget’s theory?
The formal operarional stage.
What is the name of the developmental stage where the child focuses on interacting with physical objects?
A) Sensorimotor
B) Pre-operational
C) Concrete operational
D) Formal operational
A) Sensorimotor
What is the name of the developmental stage where the child becomes less egocentric?
A) Sensorimotor
B) Pre-operational
C) Concrete operational
D) Formal operational
C) Concrete operational
What is the name given to the controversial theory that everyone has their own most effective way of learning (verbal, visual or kinaesthetic)?
Learning styles.