Science Study Guide
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Predator
an animal that hunts and kills other animals for food
What are two main things that color can do for an organism in nature
it can help it camouflage to stay safe and it can also help it hunt because it will camoflauge
prey
an animal that is hunted or killed by another animal for food
population
a group of the same type of organism living in the same area
trait
a specific characteristic of an individual organism
generation
a group of individual organisms born and living at about the same time
variation
any difference in traits between individual organisms
On a histogram, what would variation look like? Describe it.
Variation is the amount of bars on the histogram. This would mean the different types of traits for an organism
distribution
The number of individuals with each trait in a population
On a histogram, what would distribution look like? Describe it.
Distribution is the number of organisms for each trait, this means how high the bar goes on the histogram
What is a non-adaptive trait? Also, give an example
A non-adaptive trait is any trait that does not make it more likely an individual will survive, an example would be a human hair color or eye color
What is an adaptive trait? Also, give an example
An adaptive trait is a trait that makes it more likely that an individual will survive in a specific environment
species
a group of organisms of the same kind ( in one or more populations ) that do not reproduce with organisms from any other group
environment
Everything abiotic and biotic interacting in a particular area
gene
An instruction for making a protein molecule
how are traits formed
Genes lead to proteins, proteins lead to traits
protein molecule
A type of large molecule that performs important functions inside organisms
What’s the difference between a gene and a chromosome?
Genes are found on chromosomes and chromosomes come in pairs
Why do chromosomes come in pairs
Because each chromosome, one from dad and one from mom, genes found in chromosomes and they help code for traits
Why do we have 2 copies of each gene?
An organism has two of any given gene because there is one copy on each chromosome in a pair
what are alleles
an identified specific gene
What’s the definition of offspring
An organism produced as a result of reproduction
According natural selection, why is it important to survive?
It is important to survive so you can pass on your traits to the next generation
natural selection
The process by which the distribution of traits in a population naturally changes over many generations is what eventually leads to evolution.
cause
An event or process that leads to a result or change
effect
A result of change that happens because of an event or process
What are the names of the two scientists mainly credited with discovering natural selection?
Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace
What is the title of the first published book about natural selection?
On the Origin of Species by Charles Darwin
What is the purpose of the Wallace line?
It divides the places where Asian animal species live from the places where animals of the South Pacific and Australia live.
What does having less genetic variation in a population mean for their survival?
They would have a less chance of surviving because they will have a harder time adapting to their environment when it changes
most mutations have ______ effect on traits
a minor, or no
mutation
A random change to a gene that sometimes results in a new trait
Through natural selection, non-adaptive mutation becomes ____ common over time
less
How can mutations possibly help us in a changing environment?
Mutations introduce new traits, which increase the chance that one of those traits might help make a population better adapt to the environment
Can a non-adaptive trait turn into an adaptive trait? Or vice versa? Explain
Yes, this is because if the environment changes, the animals will change too. This is in the sense that if water cools down, the animals that have more fur will most likely survive, but if the water warms up, the animals with less fur will most likely survive.
What’s the difference between a trait and a feature?
A trait describes a feature
What are histograms specifically used to show? And why are they useful?
Histograms usually show how the organisms changed over time with their environment. They are useful because they show what happens in the environment.
How can a mutation that only affects one individual organism end up being the most common trait in a population?
Because the trait will be adaptive which means that the organism will live longer which causes them to reproduce more and have offspring similar to themselves.
What does having more genetic variation in a population mean for that population’s survival?
It means that there is more of a chance of survival because they will be able to adapt more to their changing environment
artificial selection
An evolutionary process in which humans consciously select for or against particular traits in a population.
give an example of artificial selection
An example of this is when humans wanted to domesticate wolves and they had only two that were domesticated. They would continuously reproduce them to create more domesticated wolves over time. The result of this was dogs.
What is genetic engineering?
Genetic engineering is an intentional modification of traits by altering genes.
example of genetic engineering
An example of this would be that scientists genetically engineered strawberries to make them bigger.
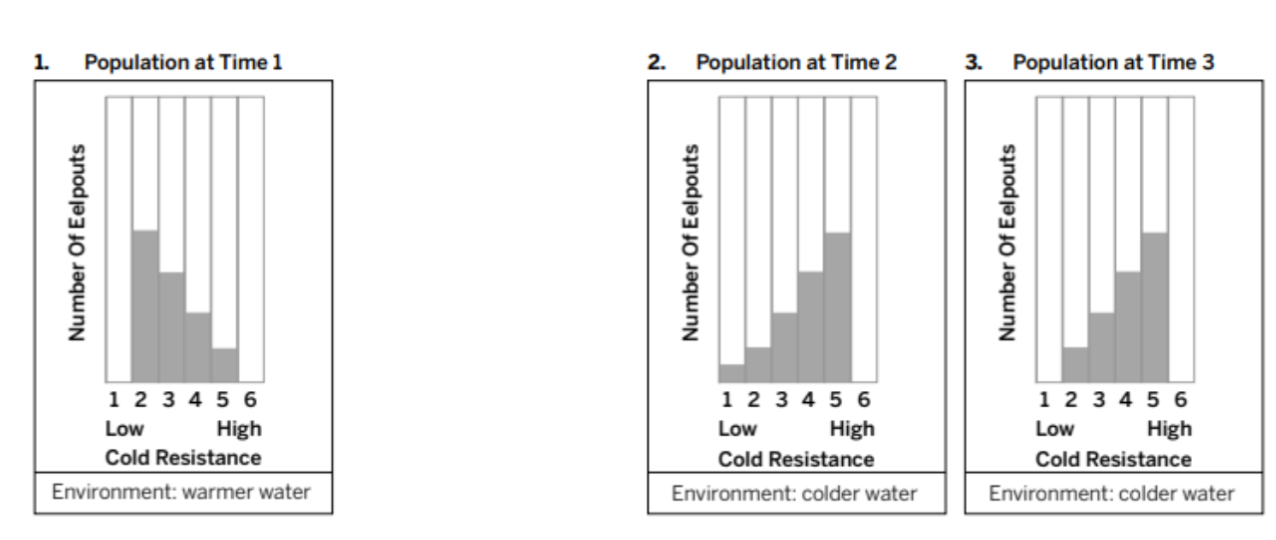
Was there a mutation in this population? If so, what was the mutation?
The mutation in the population is number 1 in low cold resistance
What was the adaptive trait? How do you know?
The adaptive trait is high cold resistance
How would you describe the change in distribution from Time 1 to Time 2?
The distribution went down for the low cold resistance and it went up for high cold resistance
When looking at the histograms for Time 1 and Time 3, how did the variation change?
The variation stayed the same because there were four bars in generations 1 and 3.
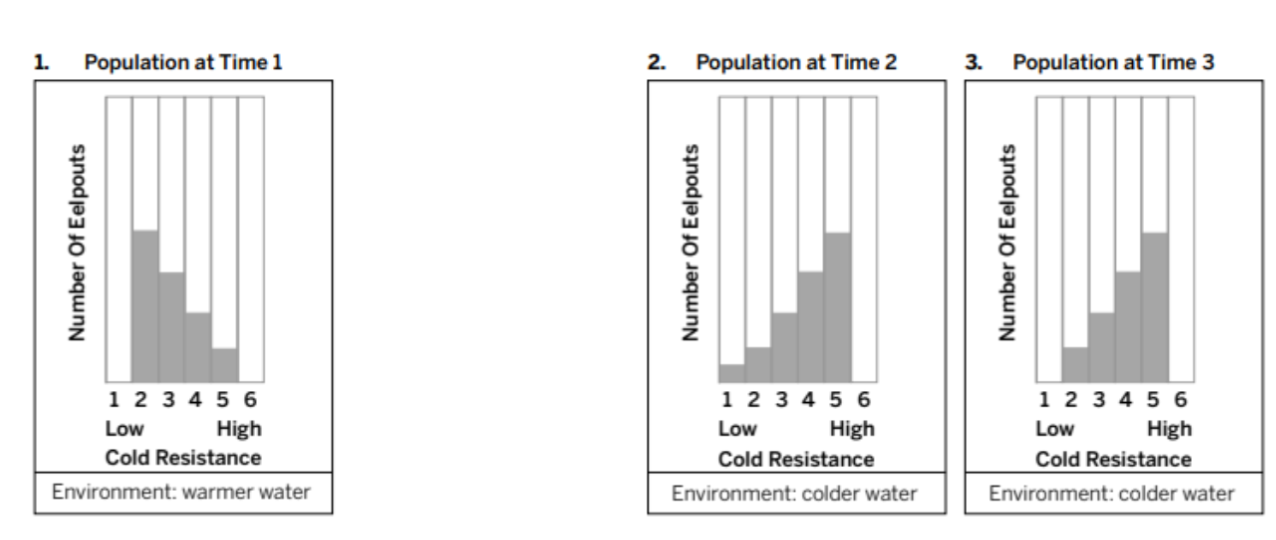
Between time 2 and time 3, other than the change in variation/distribution, what do we know FOR SURE happened to the population?
The population decreased because the water got too cold for some of the animals to live.