Drugs Impacting the Brain and Nervous System: Overview
1/371
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
372 Terms
Pain
Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience from tissue damage.
Pain Threshold
Stimulus level needed to perceive pain.
Pain Tolerance
Maximum pain one can endure without dysfunction.
Acute Pain
Sudden pain that subsides with treatment.
Persistent Pain
Chronic pain lasting 3-6 months or longer.
Nociceptors
Sensory nerve fibers transmitting pain signals.
Somatic Pain
Pain from skeletal muscles, ligaments, or joints.
Visceral Pain
Pain from internal organs or smooth muscles.
Analgesics
Medications relieving pain without loss of consciousness.
Opioid Analgesics
Drugs for moderate to severe pain relief.
Adjuvant Analgesic Drugs
Non-opioid drugs enhancing opioid pain relief.
Non-Opioid Analgesics
Pain relievers not classified as opioids.
WHO Analgesic Ladder
Three-step approach for pain management.
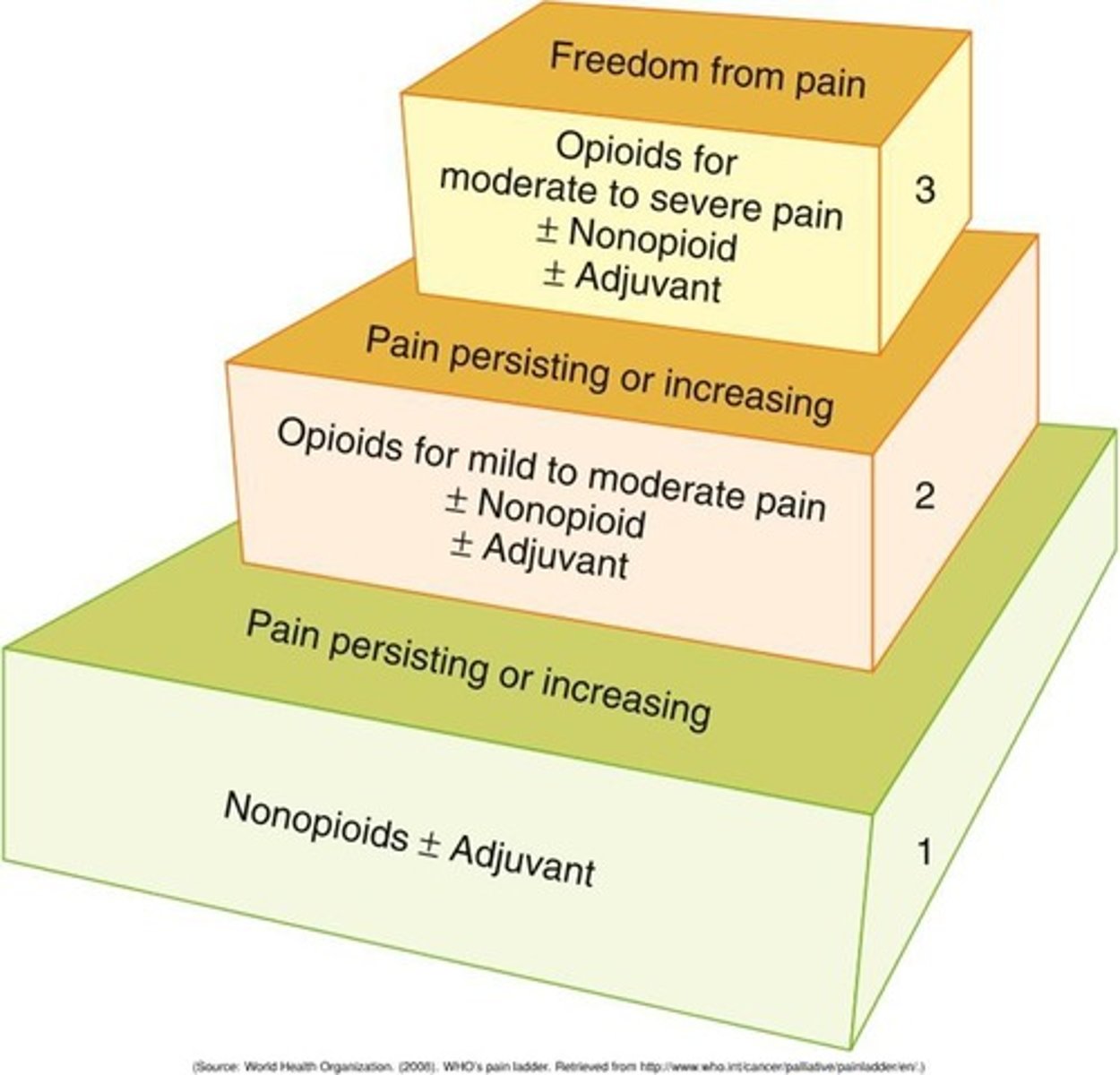
Step 1 (WHO Ladder)
Nonopioids with or without adjuvants for mild pain.
Step 2 (WHO Ladder)
Opioids with or without nonopioids for moderate pain.
Step 3 (WHO Ladder)
Strong opioids for severe pain management.
Opioid Drugs
Synthetic drugs binding to opiate receptors for pain relief.
Mild Agonists
Opioids like codeine and hydrocodone for pain.
Strong Agonists
Opioids like morphine and fentanyl for severe pain.
Meperidine
Opioid not recommended for long-term use.
Neurotoxic Metabolite
Substance causing seizures from meperidine accumulation.
Opioid Ceiling Effect
Maximum analgesic effect reached, no improvement with higher doses.
Agonists
Bind to opioid receptors, causing pain relief.
Agonists-antagonists
Bind to receptors, causing weaker pain response.
Antagonists
Reverse opioid effects without causing pain relief.
Analgesic response
Reduction of pain sensation through receptor binding.
Opioid indications
Used for moderate to severe pain relief.
Adjuvant analgesics
Assist primary drugs in enhancing pain relief.
Opioid contraindications
Known allergies and severe asthma limit use.
Opioid tolerance
Need for larger doses over time for effect.
Physical dependence
Body adapts to opioid presence, requiring dosage.
Psychological dependence
Compulsive drug use beyond pain relief.
Naloxone hydrochloride
Opioid antagonist used in overdose situations.
Naltrexone
Long-acting opioid antagonist for addiction treatment.
Opioid withdrawal syndrome
Symptoms occurring after stopping opioids abruptly.
Morphine Sulphate
Prototype opioid, high abuse potential, severe pain.
Toxic metabolites
Morphine 6-glucuronide accumulates in kidney insufficiency.
Hydromorphone
Opioid 5-8 times more potent than morphine.
Codeine Sulphate
Natural opiate alkaloid used for pain relief.

Fentanyl
Synthetic opioid for severe pain management.
Parenteral Injections
Administered via injection for rapid effect.
Transdermal Patches
Fentanyl delivery method for sustained pain relief.
Dilaudid
Brand name for hydromorphone, an opioid analgesic.
Methadone Hydrochloride
Synthetic opioid for detoxification in addiction treatment.

Acetaminophen
OTC analgesic with antipyretic properties.
Prostaglandin Synthesis
Process inhibited by acetaminophen to relieve pain.
Hepatotoxicity
Liver damage caused by excessive acetaminophen.
Acetylcysteine Regimen
Antidote for acetaminophen overdose, effective within 10 hours.
Feverfew
Herbal product with anti-inflammatory properties.
Fifth Vital Sign
Pain level measurement alongside other vital signs.
Pain Control
Administer medication before pain escalates.
Antitussive Drug
Used to suppress cough, e.g., codeine.
Ceiling Effect
Maximum effect beyond which no further response occurs.
Pharmacological approaches
Use of medications to alleviate pain.
Nonpharmacological approaches
Techniques like therapy, relaxation, and physical methods.
Oral analgesics administration
Take with food to reduce gastric upset.
Safety measures
Implement precautions to prevent patient injury.
Vital signs monitoring
Check for abnormalities, especially respiratory rate.
Respiratory rate threshold
Withhold analgesics if less than 10 breaths/min.
IM injections guidelines
Follow site rotation and proper administration techniques.
IV administration guidelines
Include dilution and rate of administration protocols.
Constipation prevention
Encourage fluid and fiber intake with analgesics.
Patient instructions
Record pain experiences and treatment responses.
Orthostatic hypotension
Change positions slowly to avoid dizziness.
Normal sleep
Cyclic and repetitive state of reduced consciousness.
Sedative-hypnotic drugs
Affect different stages of the sleep pattern.
REM sleep
Rapid eye movement stage associated with dreaming.
Non-REM sleep
Stages of sleep without rapid eye movement.
REM rebound
Increased REM sleep after discontinuing sedative drugs.
Melatonin
Hormone regulating sleep cycles, used as a supplement.
Circadian rhythm
Body's natural cycle of sleep and wakefulness.
Melatonin adverse effects
Includes daytime fatigue, drowsiness, and headaches.
Melatonin contraindications
Avoid in patients on anticoagulants or immunosuppressants.
CNS Depressants
Drugs that inhibit central nervous system activity.
Sedatives
Drugs reducing nervousness, excitability, and irritability.
Hypnotics
Drugs inducing sleep with potent CNS effects.
Sedative-hypnotics
Drugs calming CNS, inducing sleep at high doses.
Barbiturates
A group of CNS depressants used as sedatives.
Benzodiazepines
Commonly prescribed sedative-hypnotics with favorable profiles.
Non-benzodiazepine sedatives
Sedatives like Zopiclone, distinct from benzodiazepines.
Long acting benzodiazepines
Include clonazepam, diazepam, and flurazepam.
Intermediate acting benzodiazepines
Include alprazolam, bromazepam, and lorazepam.
Short acting benzodiazepines
Include midazolam, triazolam, and zolpidem.
Benzodiazepine mechanism
Depress CNS activity affecting limbic and thalamic systems.
GABA
Neurotransmitter involved in benzodiazepine action.
CNS depressant interactions
Azole antifungals and grapefruit juice prolong effects.
Indications for benzodiazepines
Used for sedation, anxiety relief, and muscle relaxation.
Adverse effects of benzodiazepines
Include headache, drowsiness, and cognitive impairment.
Benzodiazepine toxicity
Symptoms include confusion, coma, and diminished reflexes.
Flumazenil
Antidote for benzodiazepine overdose.
Zopiclone
Short-acting non-benzodiazepine for insomnia treatment.
Temazepam
Intermediate-acting benzodiazepine for sleep induction.
Diazepam
Commonly used benzodiazepine for anxiety and sedation.
Midazolam
Used preoperatively for sedation and amnesia.
Hangover effect
Daytime sleepiness following benzodiazepine use.
Fall hazard
Increased risk for older adults using benzodiazepines.
Cognitive impairment
Reduced mental function due to benzodiazepine use.
Zolpidem tartrate
Short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic for sleep.
Daytime sleepiness
Lower incidence with zolpidem compared to benzodiazepines.
Onset of action
Zolpidem acts within approximately 30 minutes.