2.1 What is Evolutionary Psychology: History of evolutionary psychology
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Who is referred to as the father of psychology and why
William James applied Darwin’s theory of evolution to psychology: the brain is the result of adaptation and natural selection in the same way as other parts of the body.
What was Francis Galton’s contribution to Evolutionary Psychology
Belief in personality and intelligence being inherited, recognition of traits that have been adapted for previous environments not necessarily being suitable for modern living, developed first intelligence tests
What is the difference between positive and negative eugenics
Positive eugenics (poineered by Galton) pushes more reproduction from people with desired traits , e.g. healthy people. Negative eugenics reduces reproduction of people with less desired traits, e.g. holocaust
After WW2, what was presented as an alternative to biology being the source of individual variation
Culture
What did Franz Boas pioneer
Cultural relativism (people’s actions should be understood from the perspective of their own culture, not that of others), ethnography (understanding other cultures by integrating into it) and ethnology (comparing cultures)
What did Margaret Mead (Boas’s student) believe about culture and why were her research methods flawed
She believed human nature is entirely dependent on culture and can be changed infinitely. She asked Samoan girls about their culture and they lied to her so her findings portrayed their culture inaccurately - a consequence of not being enculturated
What is biophobia
The fear of using biological explanations for behaviour - a consequence of historical events like the holocaust
What did Edward O. Wilson argue in his 1975 book Sociobiology, and why was this not accepted by the public
He argued that social behaviour is linked to biological functions of the brain, and that if behaviour predictively affects reproductive success and some behaviours are affected by genes, then natural selection would have somewhat shaped behaviour. This was seen as justifying eugenics and met with criticism
Who were the founders of evolutionary psychology
Tooby and Cosmides
Why was evolutionary psychology harder to ignore than sociobiology
It uses cognitive methods to explain behaviour, and sociobiology is more focused on non-human species.
What is the Standard Social Science Model (SSSM), as described by Tooby and Cosmides
The prevailing paradigm at the time that the brain starts as a blank slate and all behaviour is infinitely malleable, has no biological constraints, and created by learning, socialisation or indoctrination. The same learning process underlies learning regardless of what is being learnt.
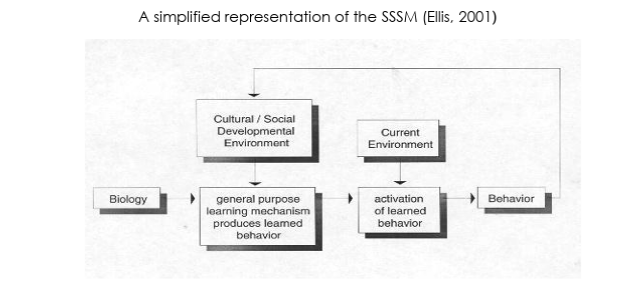
Why did the the founders of evolutionary psych disagree with the SSSM
There seem to be some innate factors to human learning and biological constraints to behaviour e.g. learning from human speech rather than dogs barking. Learning processes are different for learning different things
Why did the SSSM flourish before evolutionary psych was introduced
Historical baggage, biophobia, evolutionary thinking not necessary to explain how most traditional psych focuses work.Established thought
What did the evolutionary psychology model to replace SSSM include
Genes influence the development of mental mechanisms, which are activated by use in the environment. The menta mechanisms influence behaviour and behaviour in turn also influences the environment (e.g. influencing others). Behaviour also produces a net reproduction effect - if negative then people with that behaviour less likely to mate and population with that trait decreases. If positive, these people reproduce and the existence of the gene that codes for that behaviour is passed on to future generations.
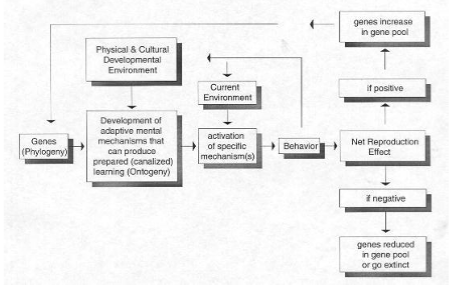
What did the Santa Barbara School outline as the principles of evolutionary psychology to combat the SSSM
Brain functions like a computer with a physical system generating environmentally appropriate behaviour (cognitive)
Neural circuits the result of natural selection (sociobiology)
Specialised neural circuits to solve different adaptive problems - modular mind (cognitive)
Modern skull houses ‘stone-age mind’, adapted in an environment of evolutionary adaptedness (EEA) (uniquely evolutionary psych)
3 and 4 have been controversial
Why was principle 3 (the brain having specialised neural circuits to solve adaptive problems) controversial?
Tooby & Cosmides claimed the mind should be very modular as natural selection would favour the quick thinking of a modular mind. The degree of modularity that the mind has is controversial
How have misunderstandings surrounding the EEA (environment of evolutionary adaptedness) caused controversy surrounding principle 4?
Some people misinterpret the EEA to mean the time that modern humans evolved, but the EEA is different for each adaptation of the brain - the modern brain is a combination of the results of many EEAs. Though natural selection will still be having an effect on us so saying our skulls are stone-ages is a bit misleading
Do the principles of the Santa Barbara school have an effect on modern day evolutionary psychology
They’re credited for establishing EP and their ideas are still popular and controversial, but many modern researchers don’t care about the modularity debate and place more importance on the main idea of applying evolution to psychology