Microbio Ch: 8.2 - 8.4, Operons, Mutations, and Gene Transfer
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
As a group
In bacteria, genes encoding enzymes are regulated -
Operon
Set of operator and promoter sites and the structural genes they control
Promoter
Segment of DNA where RNA polymerase initiate transcription of structural genes
Operator
Segment of DNA that controls transcription of structural genes
Operon
“A” is the -
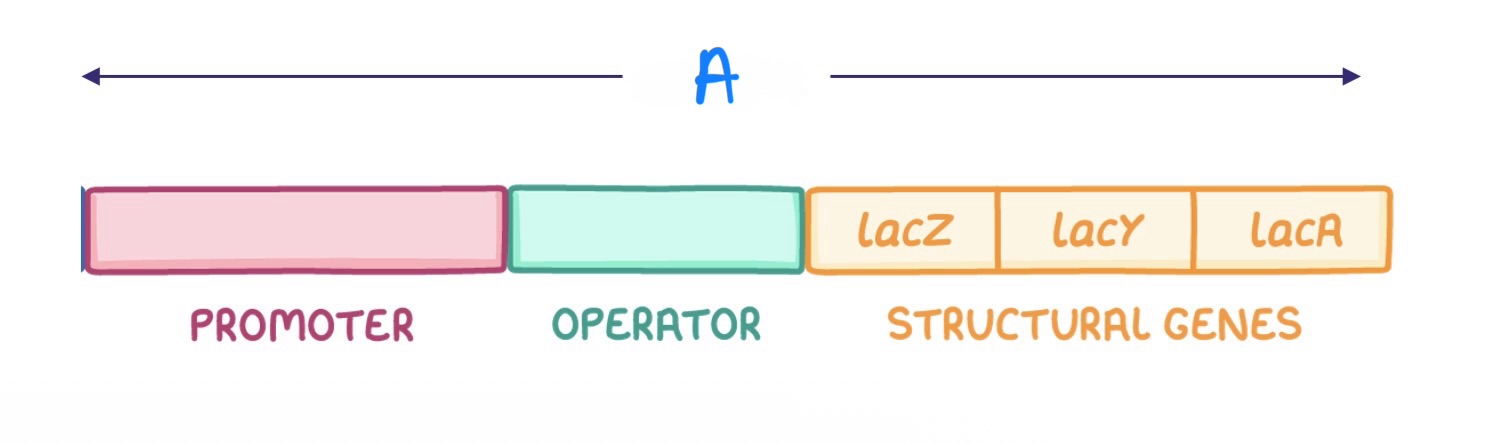
Promoter
“B” is the -

Operator
“C” is the -
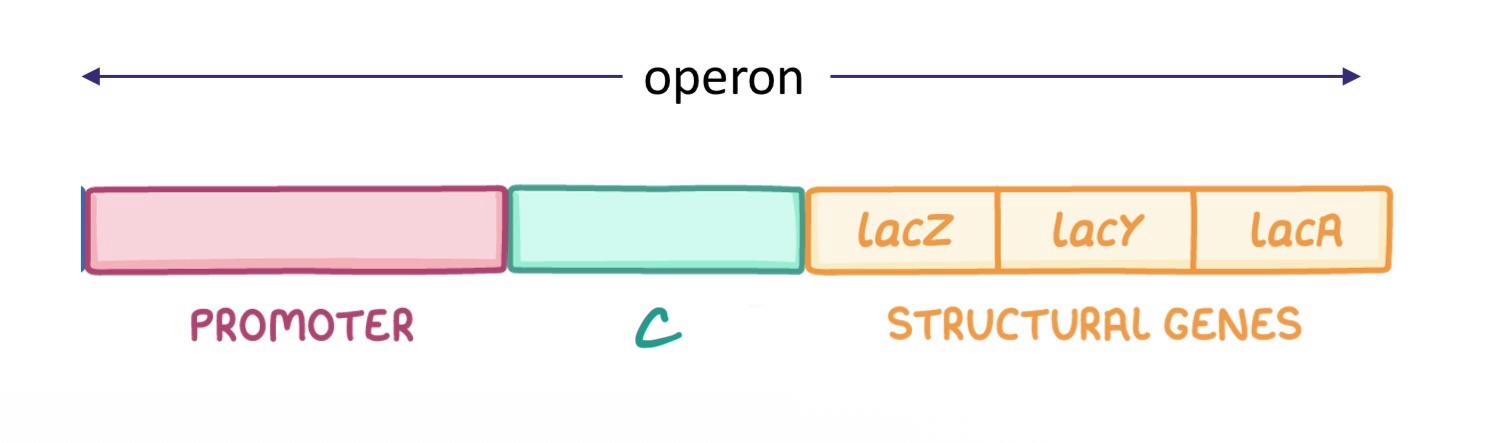
Structural genes
“D” is the -
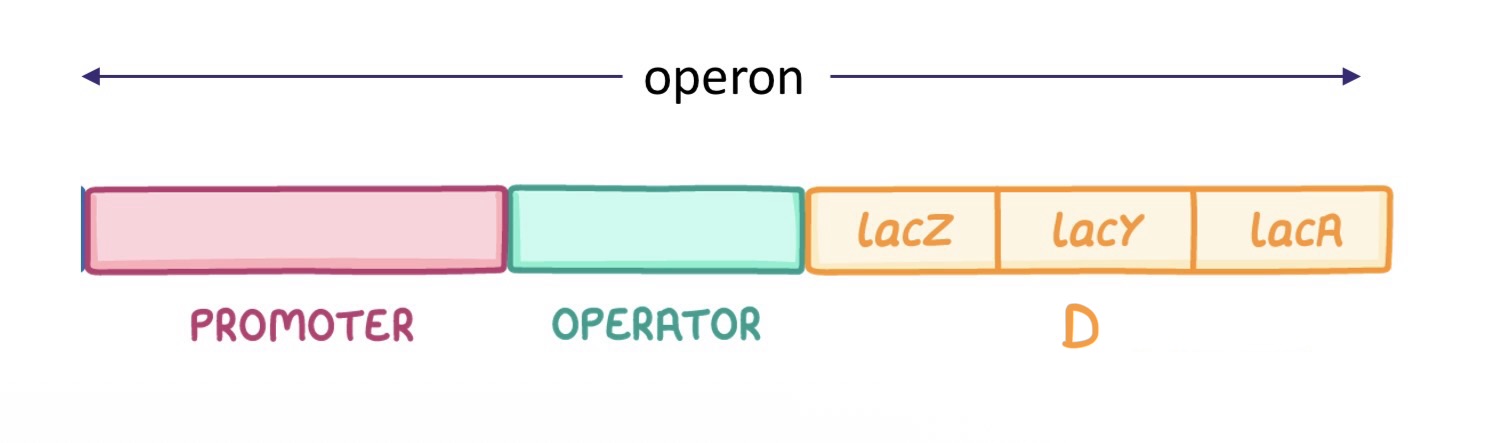
Operon
What helps bacteria in mRNA efficiency by bunching up genes together and saving resources
Repression genes
Inhibit gene expression and decreases enzyme synthesis
mediated by repressors (proteins that block transcription)
Default position is “on”
Induction gene
Will turn on gene expression
Initiated by an inducer
Default position is “off”
Inducer
Inducible operon will not have its structural genes transcribed unless an - is present
Lac operon
Example of an inducible operon
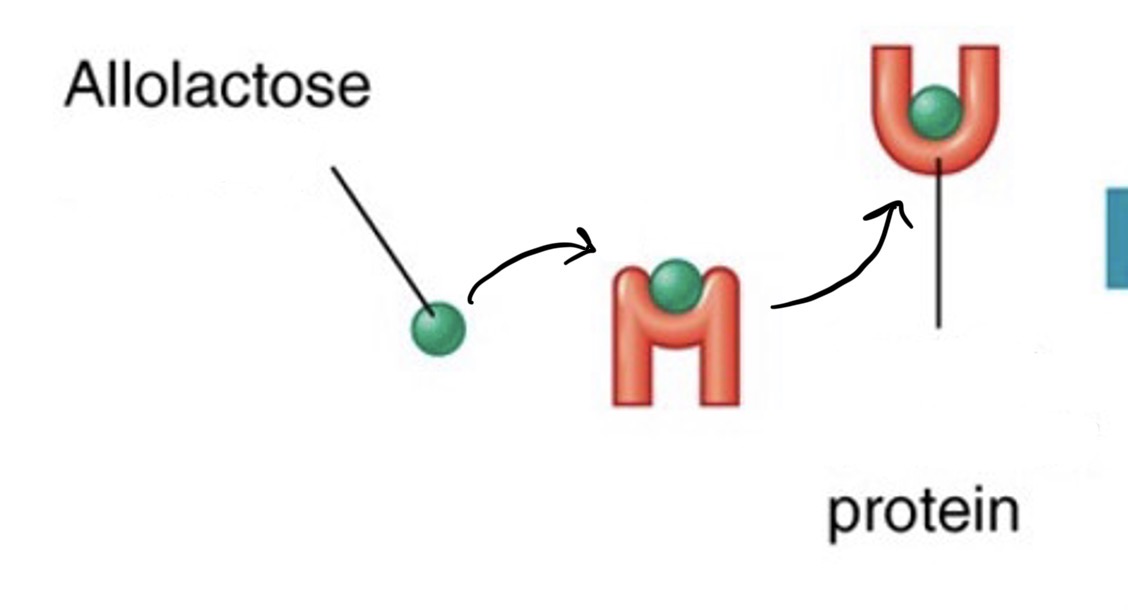
Repressor
An inducer will bind to the - so that it will not bind to the operator
Repressor, inactive
This - has become -
Repressible operons
Structural genes are transcribed until they are turned off
Tryptophan operon
Example of a repressible operon
Repressor
Co-repressors will bind to the - protein to activate it so that it bind to the operon and repress gene expression
Repressor, active
This - has become -
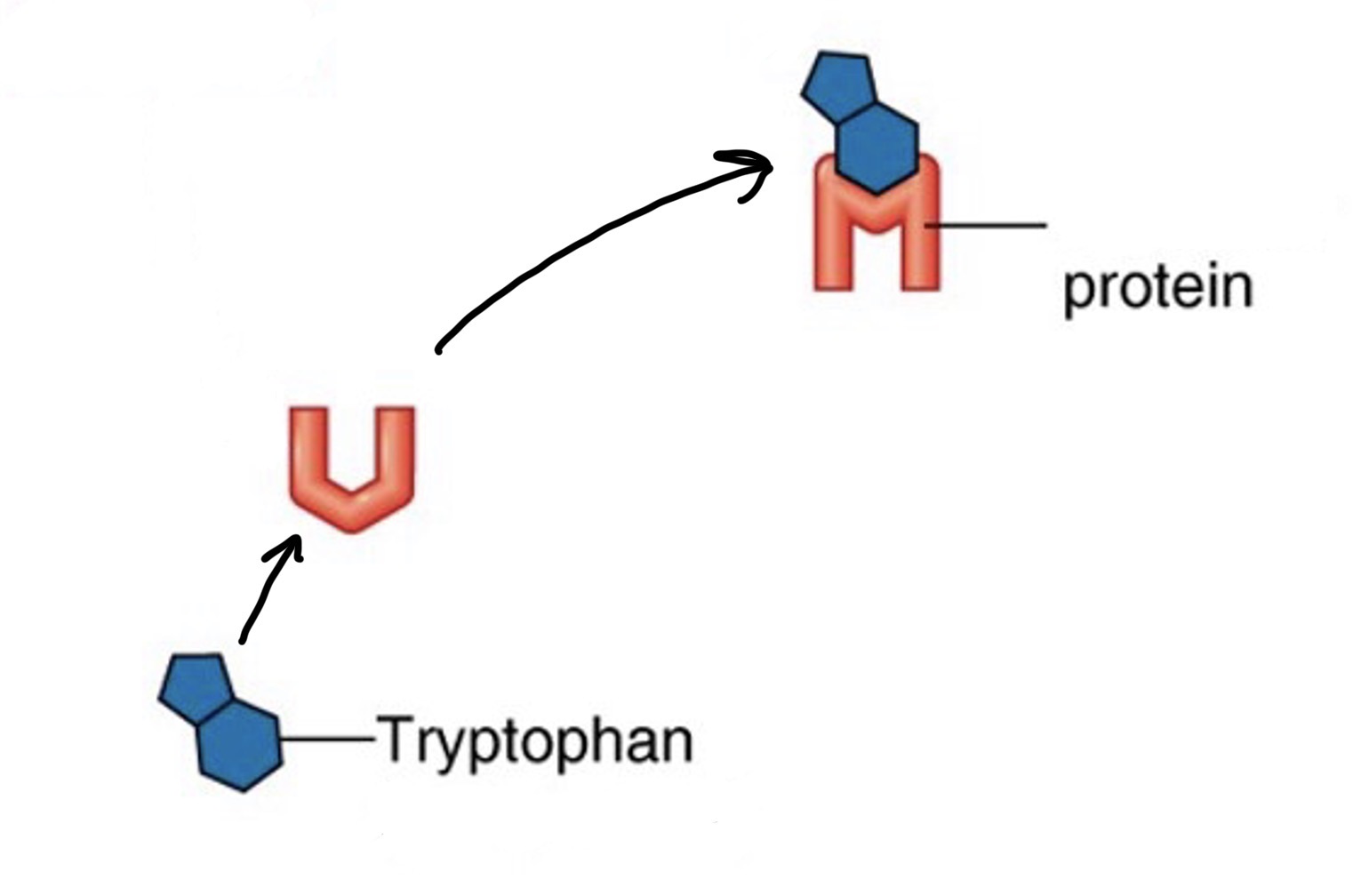
Constitutive genes
Genes that are expressed at a fixed rate, these do not appear to be regulated and are always “on”
Antibiotics
Example of external selection
Spontaneously
Bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics irrespective of antibiotics by occuring -
Mutagens
Agents that cause mutations
Spontaneous mutations
Occurred in an absence of a mutagens. Natural errors the DNA polymerase makes unprovoked.
Silent mutations
Mutations that doesn’t affect activity of the product, may go undetected or when a change in one base still makes the same protein without changing the meaning of the codon.
Base substitution
Change in one base in DNA that will result in mRNA to carry the incorrect base in that position. Incorrect amino acid may be incorporated into the resulting protein.
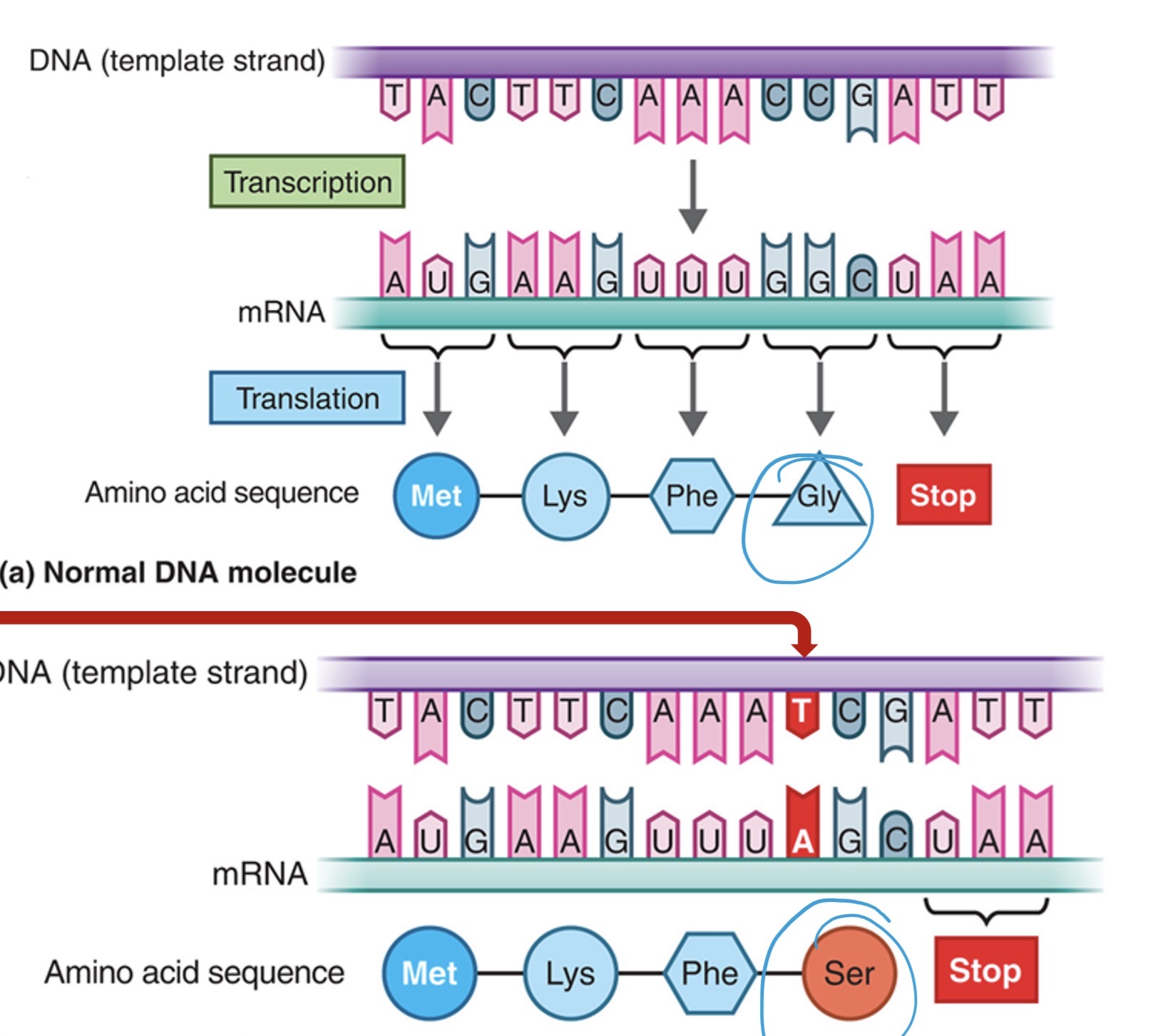
Missense mutation
When a base substitution results in a change in an amino acid
Missense mutation
What mutation happened here
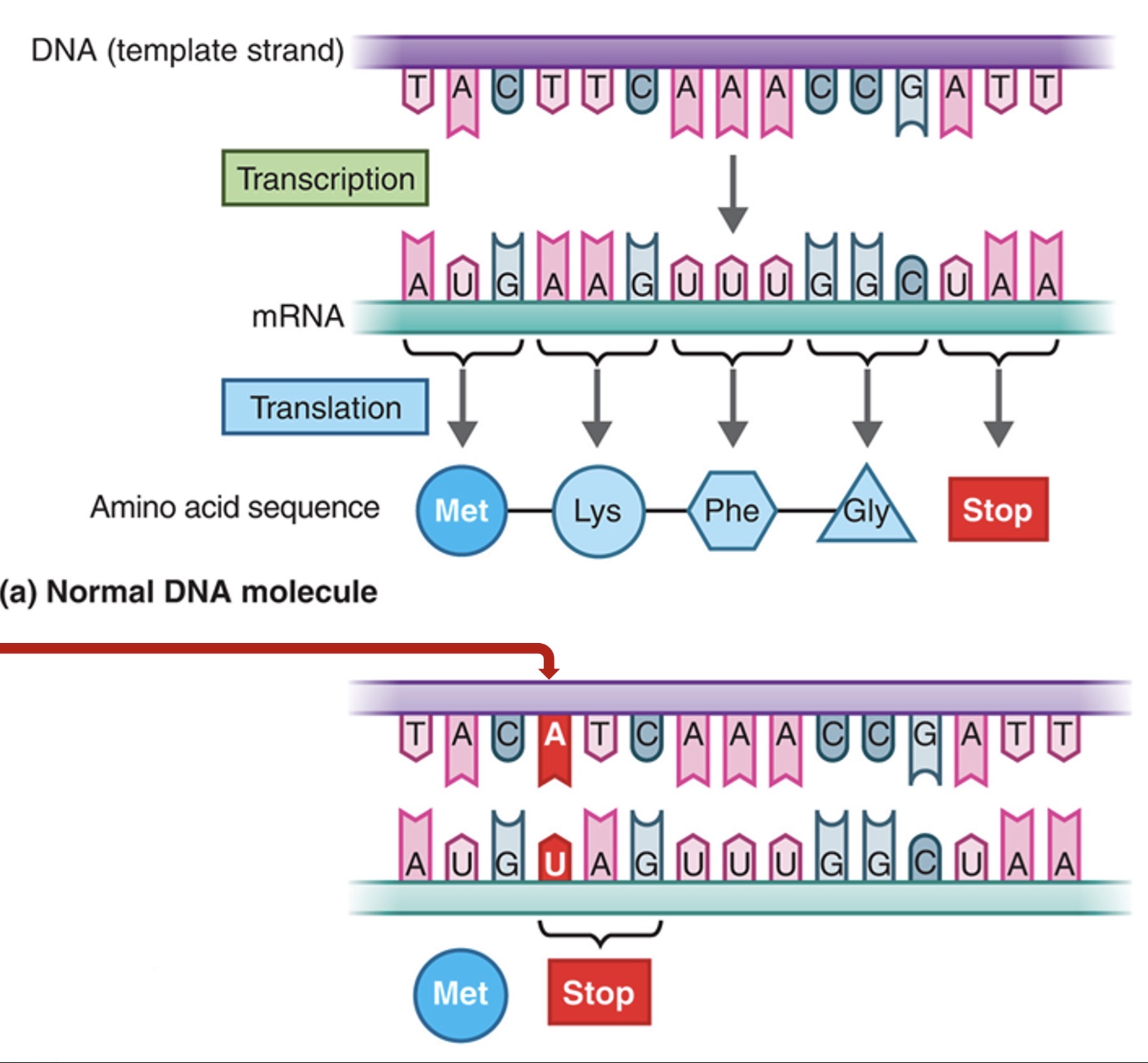
Nonsense mutation
Base substitution that results in a nonsense stop codon. A more serious mutation that results in a premature stop code on in a sequence of amino acid.
Nonsense mutation
What mutation is this?
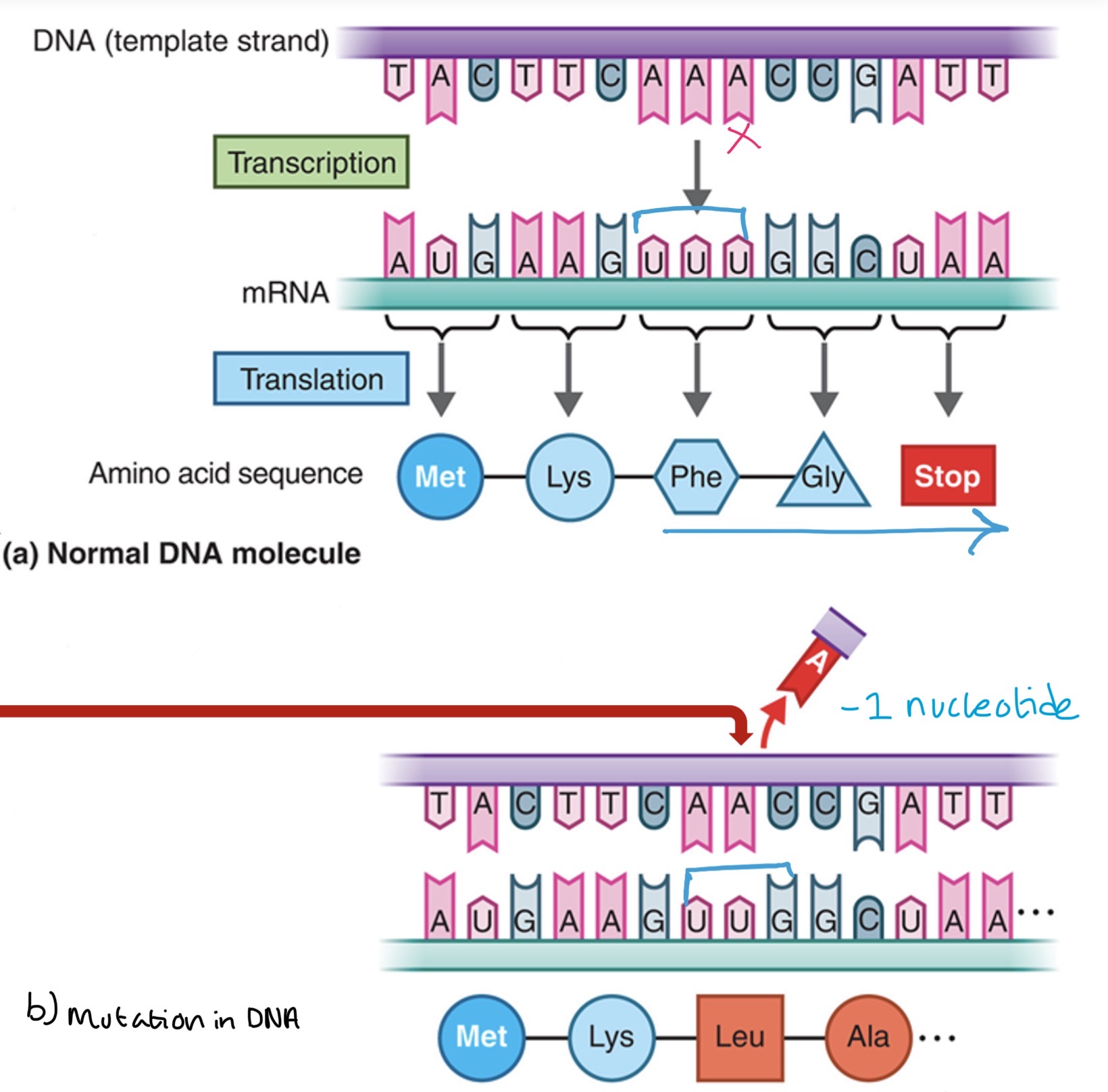
Frameshift mutation
Mutation that results by the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotide pairs.
Causes a shift in the translational reading frame
Every codon of amino acids are altered downstream
Frameshift mutation
What mutation is this?
Chemical mutagents
Chemicals that directly or indirectly cause mutations
Nitrous acid
An example of a chemical mutation that causes adenine to bind with cytosine instead of thymine
Nucleoside analog
Example of a chemical mutation that is structurally similar to normal nitrogenous bases, when incorporated into DNA in place of a normal base will cause mistakes in base pairing
Carcinogens
What is an example of a nucleotide analog?
Frameshift mutagens
An example of a chemical mutagens where chemicals will cause small deletions or insertions, resulting in frame shifts
Aflatoxin
An example of a frameshift mutagen
Ionizing x-ray and gamma rays
A radiation mutagen that causes formation of ions that can oxidize nucleotides and break the deoxyribose phosphate backbone
UV radiation
A radiation mutagen that cause thymine dimmers, which prevent proper replication and transcription of DNA. This can lead to deletion when section affected with thymine dimmers are omitted because of altered shape in the DNA backbone
Photolyases
An enzyme that uses light to separate thymine dimmers and repair UV induced damage in bacteria
Nucleotide excision repair
An enzyme that will cut out incorrect bases and fill in correct bases, and can also repair UV induced damage in bacteria
10^9
What is the mutation rate of spontaneous mutations for replicated base pairs?
10^6
What is the mutation rate of spontaneous mutations for a replicated genes?
10 to 1000 times
By how much can a mutagen increase the mutation rate?
Vertical gene transfer
Genetic transfer of genes from an organism to its offspring
Horizontal gene transfer
Transfer of genes between cells of the same generation
Donor cell, recipient cell
All horizontal transfer mechanisms involve a - that gives some of its DNA to a -
Horizontal gene transfer
Resistance mutations/ genes that can also be acquired from other cells/species via
Plasmids
Self replicating circular pieces of DNA. With an origin of replication that can activate whenever it chooses to
Plasmids
Where could coding for resistance factors and proteins that enhance their pathogenicity of a bacterium take place?
Transposons
Segments of DNA that can move from one region of DNA to another
Insertion sequences
What do transposons have that code for transposase that cut and reseal DNA
Transformation
Genetic exchange where genes are transferred from one bacterium to another as naked DNA
Transformation
This genetic transfer mechanism is what Griffith’s experiment determined how disease-causing genes can be taken up by bacteria
From heat-killed capsulated bacteria
How did non-capsulated bacteria get the genetic information to replicate as capsulated bacteria in Griffith’s experiment
Conjugation
Plasma transferred from one bacterium to another through cell to cell contact. These cells must be opposite mating types, where the donor has a conjugative plasmid and the recipient lacks the conjugative plasmid
Transduction
When DNA is transferred from a donor cell to a recipient via a bacteriophage